One of the evils of paper money is, that it turns the whole country into stock jobbers. The precariousness of its value and the uncertainty of its fate continually operate, night and day, to produce this destructive effect. Having no real value in itself it depends for support upon accident, caprice and party, and as it is the interest of some to depreciate and of others to raise its value, there is a continual invention going on that destroys the morals of the country.—Thomas Paine DISSERTATIONS on government; the affairs of the bank; and paper money
In this issue
Phisix: 2Q GDP Outperforms at 6.4% as Investments Plummets!
-GDP Analytics: The Political Context and the Knowledge Limits
-Household Spending Loses Momentum
-Why the Silence in the “Plunge” of Investments?
-2Q GDP Reveals the Philippine Growth Secret: DEBT DRIVES GROWTH!!!
-Debt Drives Growth at the Industry Level
-The Intensifying Mania
Phisix: 2Q GDP Outperforms at 6.4% as Investments Plummets!
Just a few backs I wrote[1]
The government may for the meantime succeed at the massaging of prices at the financial markets, resort to statistical masquerade or publicity gimmicks. But eventually economic forces will ventilate on the accreted imbalances from all these manipulation of the markets and the economy. It’s just a matter of a not so distant time.
GDP Analytics: The Political Context and the Knowledge Limits
I am not a fan of statistics, especially growth statistics popularly known as Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Such statistics attempts to quantify people’s actions by homogenizing disparate or heterogeneous individuals into aggregates. Think of it, if I value beer and you don’t share my values, then how can such values be “aggregated”. People’s values are in essence subjective therefore non-quantifiable.
And through accounting entries, the simplification process involves the isolation of interrelated variables and the impression to its audiences of the supposed constancy of people’s actions. Importantly GDP has a tacit political spectrum. It frames consumption spending as the “driver” of any economy. Even American producer, John Papola[2] recognizes such inaccuracies, “By definition, GDP is a summary of final sales for new goods and services and not of all economic activity. Raw materials, intermediate goods and labor costs, which comprise the bulk of business spending are not treated in GDP, but are rather rolled up in the final sale price of the “consumer” spending. Only capital equipment, net inventory changes and purchase of newly constructed homes constitute “investment” according to GDP. This framing of the data makes the “consumption drives the economy” a foregone conclusion. But this is circular reasoning.”
Nonetheless the framing to prioritize consumption in the GDP construct has been made to justify government interventions. According to Austrian economist Robert Higgs, such rationalizations exists by supplying “the basic framework for the Keynesian models…from which a key policy conclusion was derived—that the government can vary its spending to offset shortfalls or excesses of private spending and thereby stabilize the economy’s growth while maintaining “full employment”[3]
The GDP’s genesis has been equally politically induced. This has been invented with the motive to calculate war financing. As freelance British economist and author of Princeton University published GDP: A Brief but Affectionate History in a recent interview noted (bold mine)[4]: The origins go back as far as [?] is back to the dawn of capitalist. The [?] history is that in the late 17th century, a person called William Petty started to try to count up national income, the purpose being to help the monarch understand what the tax base, how much taxes he was able to raise despite foreign wars. And it actually proved a great advantage to Britain in its almost constant wars with France in that period to have that information, because they were much more able to raise the funds and raise the troops than their opponents were. The concept changed a lot over time. The interest base[?] became what overseas earnings could a country bring in and how much gold could that bring in. But it wasn't until the 1930s in the Great Depression that anything resembling modern GDP came into existence. And there are two people usually named as being at the forefront of that effort--Simon Kuznets in the United States, and Colin Clark in Great Britain
And the convenience of contemporary politics has likewise impelled for a reconfiguration of the GDP methodology. So aside from the financing of the warfare state, such data has been redrawn to incorporate financing of the welfare-bureaucratic state. Again Ms. Doyle: The decision to include government spending in GDP is mostly recent. It dates back to 1941 and the modern national income accounts. And there was no way at the time that the governments of the United States and United Kingdom were going to produce statistics suggesting that government spending on the military effort was making the country worse off. It just wouldn't have been a good thing to do. And the rationale for it was that for the first time in the post-war era, government started spending, collectively, much more money on behalf of their population through education systems or here in the United Kingdom it was the health system
So if politics has been the underlying force behind the statistical GDP then naturally since GDP have been conducted by governments then the most likely their output may curry in the direction of the political flavor of the moment.
And if one were to simply look solely at statistical GDP as a measure of the real economy one would have the impression that the Union of Socialist Soviet Republic (USSR) or popularly known as the Soviet Union would still be existing. That’s because communist Russia’s GDP, despite a downtrend, has always “grown” (see chart here). That’s even going into her extinction.
And it is this obsession with statistical GDP that has prompted the late Nobel awardee economist Paul Samuelson and coauthor William Nordhaus to predict in 1989 which has been exposed as a glaring error, that the “Soviet economy is proof that, contrary to what many skeptics had earlier believed, a socialist command economy can function and even thrive”. Two years later the USSR dissolved.
The collapse of the Soviet Union essentially validated the prediction of the legendary Austrian economist Ludwig von Mises who warned in 1920 during the “The Socialist Calculation Debate” that an economy would not exist in absence of price mechanism[5]: (bold mine)
Without economic calculation there can be no economy. Hence, in a socialist state wherein the pursuit of economic calculation is impossible, there can be--in our sense of the term--no economy whatsoever. In trivial and secondary matters rational conduct might still be possible, but in general it would be impossible to speak of rational production any more. There would be no means of determining what was rational, and hence it is obvious that production could never be directed by economic considerations.
Mises’s calculation problem was further expounded by his pupil the great Nobel laureate Friedrich von Hayek who also warned that central planning has been structurally inhibited by the Knowledge problem which underpins the economic calculation debate: (bold mine)
The reason for this is that the "data" from which the economic calculus starts are never for the whole society "given" to a single mind which could work out the implications and can never be so given.
The peculiar character of the problem of a rational economic order is determined precisely by the fact that the knowledge of the circumstances of which we must make use never exists in concentrated or integrated form but solely as the dispersed bits of incomplete and frequently contradictory knowledge which all the separate individuals possess. The economic problem of society is thus not merely a problem of how to allocate "given" resources—if "given" is taken to mean given to a single mind which deliberately solves the problem set by these "data." It is rather a problem of how to secure the best use of resources known to any of the members of society, for ends whose relative importance only these individuals know. Or, to put it briefly, it is a problem of the utilization of knowledge which is not given to anyone in its totality.
In short economic calculus is about decentralized knowledge dispersed across individuals expressed through the pricing system.
So the bottom line is that the fundamental problem with GDP analysis is the oversimplification of what truly has been a complex socio-economic-political structure.
As a side note, the Austrian school of economics has encouraged the US Bureau of Analysis BEA to introduce a new economic measure called the “Gross Output” which measures the production side of the economy[6]. While not perfect this would likely be a better substitute than the current politically shrouded methodology.
Household Spending Loses Momentum
This brings us back to the Philippine setting.
The establishment went on another hysteric “pat on the back” binge due to the reported 2Q 2014 growth of 6.4%, which has been hailed as economic growth “back to its higher trajectory” and adulated as “Southeast Asia’s best-performing economy”[7]
The irony of all these is that there has been little mention of the internal contradictions that has backed the data.
Let us see it from first from the household spending perspective.
This quote from the National Statistical Coordination Board (NSCB)[8]: Food and Non-alcoholic beverages expenditures, which accounted for 41.2 percent of the total household spending, grew by 4.0 percent but showed a slowdown from its 5.0 percent growth registered in 2013. Among household expenditure items that boosted the growth were: Alcohol, beverages and tobacco, 11.4 percent from negative 5.7 percent; Clothing and footwear, 6.2 percent from negative 5.0 percent; and Furnishing, household equipment and routine household maintenance, 4.1 percent from negative 5.2 percent. Expansion at double-digit growth of three major household items were registered for Transport, 11.9 percent from 6.6 percent; Health, 10.6 percent from 6.1 percent; and Restaurants and hotels, 10.4 percent from 6.8 percent.
Understand that these figures are obtained from surveys, again from the NSCB[9], “The household sector estimates were calculated using data from two main sources. The parameter used for estimation, the share of education to the total miscellaneous expenditures of households, was calculated based on the results of the Family Income and Expenditure Survey (FIES) of the National Statistics Office (NSO) for the years 1991, 1994 and 1997.” And so with personal consumption expenditures (PCE).
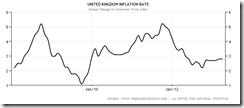
It’s a curiosity to see how so-called household spending on discretionary items continue to post dazzling growth numbers even as consumer price inflation (CPI) has been trekking upwards (April 3.9%, May 4.1% and June 4.5%)
Paradoxically, hasn’t this been the time when soaring domestic food prices has not only hugged headlines but became subject to political attention and inquiries[10]? Hasn’t this period also been when the man on the streets has caviled over rising consumer prices and has talked about shifting consumption towards necessities (substitution and income effects of inflation)[11]? Hasn’t it been likewise a similar timeframe when self-rated poverty also from surveys but conducted by the private sector has become elevated that has led to a decline in chief executive’s popularity ratings[12]? Has it been the days where OFWs in Libya has defied government decrees to return home due to economic “survival” reasons[13]?
Economic data suggests that street level angst has been untrue.
Yet a back of the envelope calculation says that if the average household spends Php 6 pesos on necessities for every Php 10 earned, an inflation rate on these goods and services will imply a reduction of disposable income from Php 4 to Php 3.7. This implies that the only way for disposable income to retain its purchasing power is if income grows faster than the inflation rate.
As a side note, the supply side has been in a race to build inventories based on the latter (expectations of income growth) but ignoring the former (inflation risks). This asymmetrical perspective incited by price disruptions from BSP’s bubble blowing serves as a fundamental force driving current imbalances.
But the key question is WHERE will income growth come from?
The Philippine job market has hardly been buoyant in as much as the economic numbers has shown. Minimum wages has grown only 3.3% this year[14]. Wage level growth has been below par economic growth. In 2012-13, the average wage growth has been a paltry 3.98%. In the 1Q 2014 year-on-year, wages grew by a lower 3.7% than the 2013 average.
So if you add inflation numbers to these figures you’ll have stagnant, if not a decrease in real wages.
And given the environment of zero bound rates, there hardly has been any fixed income growth to depend on in order to boost consumption.
Just to an example, Globe Telecoms reportedly raised Php 10 billion from an Preferred perpetual shares IPO with an initial dividend rate of 5.2006% subject to re-rating. Even at the official inflation rate at 4.9%, add to this the 10% withholding taxes, for those compliant with new BIR rulings involving the submission of the alphabetical list of income payments subject to the withholding taxes, otherwise withholding taxes balloon to 30%, this means subscribers of these shares will receive negative real or inflation adjusted returns. So the second only major telecom provider has essentially benefited from a free lunch provided by the BSP coming at the expense of preferred shareholders who not only finances Globe with essentially free money, but also has assumed risks from Globe’s activities.
Also dividend yields barely helps, dividend yields of publicly listed firms at 2.44% as of May 2014[16] means that real yields have been negative or below the inflation rate!
So given the negative returns, there hardly has been any alternative to earn money from the capital markets except to chase yields, i.e. by bidding up severely overpriced securities as well as to subsidize politically leveraged companies.
Such frenzied reach for yields has led to a torrent of capital raising activities (IPOs, follow-on public offerings, stock rights offerings and private placements) which has soared by 147.2% during the first semester of 2014 from Php 30.8 billion to Php 76.12 billion[17].
And paradoxically, despite the May 2013 ramp to push the index to 7,400, stock market accounts grew by only 11.4% in 2013 to 585,562 from 525,850 in 2012. This has been spearheaded by a surge in online accounts which posted a record of 65.3% growth in 2013[18]. Online accounts at 129,255 now make up 22% share of the total stock market accounts. Additionally retail participants comprised some 96.2% of the total while 3.8% were institutional accounts. In terms of nationality, the shares have been divided into 98.5 % local and 1.5% foreign.
With current population at 98+ million (99.7 million 2Q 2014 says the NSCB) the direct numbers of stock market participants represent a scanty .6% penetration level. So even if we assume that exposure by the retail segment has been expanded indirectly through the institutional funds (UITF, mutual funds) to perhaps 1-2% of population, the point of the above is to show of the LIMITED depth of Philippine capital markets. More importantly, corollary to this has been the CONCENTRATION of the benefits and risks by stock market participants.
And in the face of the 19.71% year to date gains by the Phisix as of Friday’s close, this only means that a small segment in the population can really add to a splurge in consumption from capital markets perspective.
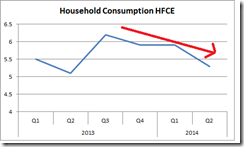
And even if we assume the current data has some accuracy, quarterly growth on a y-o-y basis (2000 constant prices) by household consumption as represented by Household Final Consumption Expenditures (HFCE) has been trending downwards; a trend that has surfaced since the BSP’s unleashed the 30%++ money supply growth rates in July 2013 or in Q3 2013. The 2Q 6.4% growth essentially camouflages this apparent weakening in the growth of consumer demand.
One can also add that growth in some numbers like Food and Non-alcoholic beverages may be representative of price inflation rather than from growth in output. So while the above figures in constant 2000 prices means that the numbers have been adjusted through a deflator, the possible understatement of the deflator, the PCE (denominator), may have boosted “growth” story.
So those numbers supposedly in support of consumption growth can be seen as meaningless as they may represent one-off events or even statistical errors, if not a massaging of statistical data. As one would further note, hardly any of these has been covered by the glorification of mainstream media.
Why the Silence in the “Plunge” of Investments?
If household consumption has underperformed, where has the spectacular rebound been derived from? Investments perhaps?
Unfortunately not.
Let us read this straight from the NSCB (bold original, italics mine): Investment in Fixed Capital Formation plunges Investments in Fixed Capital Formation shrank to 4.0 percent from 13.6 percent in the same period last year. Investments in construction decelerates Total investments in Construction grew by 5.1 percent, a deceleration from the 16.5 percent growth recorded in 2013. Private construction posted a sustained growth of 12.7 percent from 12.8 percent. However, Public construction contracted to 12.9 percent from 26.5 percent in the previous year. Investments in Breeding Stocks and Orchard Development declines Capital formation for combined Breeding Stocks and Orchard Development for the second quarter of 2014 declined by 2.0 percent from negative 1.0 percent. Expenditures for said subsectors contracted during the period. Inventories diminishes Inventories recorded a total of Php 51.3 billion withdrawals in the second quarter of 2014 as compared to the Php 30.5 billion withdrawals in 2013. Establishments and agriculture posted withdrawals in their inventories.
It’s pretty odd for the NSCB to have used the verbs “plunges” and “shrank” rather than to sugarcoat the statement with perhaps “declined less the previous growth rate of”. Shrank and plunges are powerful descriptive verbs.
To make sure of the accuracy of the disclosure, I checked and saw that the NSCB has used this -2.4% in investment in their Power Point presentation. And to further clarify or establish the definition, here is the NSCB based on their glossary (bold original): Gross Domestic Capital Formation - Consists of two major components: -gross fixed capital formation and -change in stocks. Gross fixed capital formation refers to outlays on construction, durable equipment and breeding stocks, orchard development and afforestation. Change in stocks refers to the difference between ending and beginning inventories. Inventories or stocks consists of finished goods, work-in-progress, and raw materials, which have been produced or purchased but not yet sold or consumed as intermediate inputs during the accounting period.
Here is the NSCB’s statement on the plunge in durable equipment: The growth of the Investments in Durable Equipment slowed down by 2.3 percent from 13.2 percent a year ago. Increased investments were registered in ten out of the 20 types of equipment.
Apparently the biggest decline came from Other special Machineries (-11%) and from mining, construction machineries (-32.4%), both comprise 45% of the Machinery Specialized For Particular Industries segment and 13% of Durable equipment. Meanwhile the second biggest component after Road Vehicles which posted a 7.2% growth, Telecommunications & sound recording/ reproducing equip. produced zero growth.
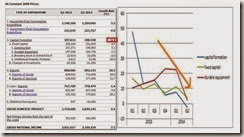
Capital formation has been in a collapse mode since clocking a fantastic 47.7% growth in1Q 2013 (see right window, blue line). The same trend has been reflected on fixed capital (green line). Meanwhile durable equipment has been on an uptrend which peaked during 4Q 2013, plateaued in 1Q 2014 before this quarter’s “plunge” (red line). All three have now converged to the downside (orange line)
Interestingly, the NSCB has been silent on this investment collapse on their Highlight page.
So from the expenditure perspective, 2Q GDP tell us that household growth has been losing momentum, and importantly, investments has been on a decline and has even been accentuated by the “plunge” in durable equipment.
These have been happening outside any weather or external related strains.
The question is has the “plunge” in durable equipment been anomaly or has this been a new trend? Has such been in response to the recent spike in inflation? Perhaps to the BSP’s tightening policies (seemingly not as shown below)? To political quirks, e.g. truck ban? Or to other factors (over indebtedness, slowing demand, etc..)?
Why is this important?
Because investments drive growth. Business spending represents future income, earnings, demand, consumption, jobs, wages, innovation, dividends, capital gains or what we call as growth.
As Austrian economist Robert Higgs explains[19] (bold mine)
Private investment is the most important driver of economic progress. Entrepreneurs need new structures, equipment, and software to produce new products, to produce existing products at lower cost, and to make use of new technology that requires embodiment in machinery, plant layouts, and other aspects of the existing capital stock. When the rate of private investment declines, the rate of growth of real income per capita slackens, and if private investment drops quickly and substantially, a recession or depression occurs.
This also means that if the downturn in investments represents an emergent trend, then current rebound may just be temporary and would hardly account for as resumption to “high trajectory growth”.
And this also means that the reversion to the mean is still in play, as I earlier wrote[20]: if the laws of the regression/reversion to the mean will be followed (even without economic interpolation) then statistical economic growth will most likely surprise the mainstream NEGATIVELY as economic growth are south bound in the coming one or two years, with probable interim bounces.
Moreover, outside households and investments, from the expenditure side of 2Q 2014 growth, the saving grace has been the sector that has previously shunned by the BSP chief who justified aggregate demand policies in order to “boost domestic consumption” by ending the economy’s “dependence on exports”[21].
Exports have been supported by private construction.
Yet export growth remains an X factor given what seem as very challenging if not fragile economic conditions of the Philippines biggest trading partners, particularly Japan, China, ex-Japan and China Asia and Germany.
2Q GDP Reveals the Philippine Growth Secret: DEBT DRIVES GROWTH!!!
But media has framed 2Q data blot on the problem of public construction spending. This report for instance is from a partisan of the establishment[22]: Public construction spending fell, in part due to increased scrutiny of Mr. Aquino's decision in October 2011 to speed up infrastructure spending without congressional approval.
Go back to the NSCB table which shows construction contributing to a boost in statistical growth after posting 5.1% in 2Q. The collapse of the Public sector’s construction by 12.9% which constitutes 24.4% of construction output has been more than offset by the private sector’s gains of 12.7% which holds 75.6% share.
During the first semester of 2014, public sector construction accounted for 22.87% of construction output. Even during the halcyon days of Q1 2012 where public sector posted a staggering 36.6% growth rate combined with another stunning 33.3% growth by the private sector, public sector construction share has been only 17.56%. Quarterly y-o-y growth rates of public, private and overall construction can be seen in the left window.
As one would note, raising the issue of public sector construction has been misleading, not only because this attempts to substitute the burden to the government, but such has been used as media to downplay on the risks from an investment collapse.
Even more, the puffery over the role of government’s contribution has been seen, like the current mania in stocks, as a one way trade.
Yet there is no such thing as a free lunch. Costs are not benefits too.
These people fail to realize that for every ONE peso government spends, it takes the same nominal peso amount away from productive citizens through their income (output) or savings. So why should more of these be desired?
Moreover, government spending benefits the politicians and interest groups more than they benefit the general public as I have explained here[23]. Additionally deficit spending will add pressure on fiscal conditions, as well as increase its risks. If such spending will be financed through debt then raising debt levels means to increase credit risks. If, on the other hand, this will be financed by monetization then currency holders will suffer from a loss of purchasing power. If financed by both debt and monetization then risks facing both actions will apply.
Today’s loss of purchasing power has been from indirect means of providing resources to the government: via asset inflation or boom bust cycle.
While it may be true that the Philippine public debts have been relatively “low”, what has not been seen or appreciated or causally connected has been that private sector debt, that has underpinned the asset inflation, has been exploding!
Government’s seemingly and transiently low debt has been subsidized by zero bound rates and by inflated taxes from the same policies that has encouraged such massive accretion of debt in order to produce statistical output!
Some calls this credit intensity[24] or the amount of borrowing needed to generate a unit of output. I call this the “diminishing returns of debt”.
At the right pane is the 2Q GDP by industry. This is contiguous to the BSP’s bank lending to industries which I associate as “bubble” sectors based on 3 months average growth rates and of the economy.
From the BSP perspective, loans to these bubble sectors have accounted for 50% share of overall loans. From the 2Q GDP perspective, these sectors constitute 40.23% about unchanged from the same period last year.
As one would notice, the Philippine statistical economy has reached a state where instead of debt as a compliment to growth, today DEBT DRIVES GROWTH!
In 2Q 2014, it took an average of 18.53% of credit growth to produce 6.4% economic growth. This implies that for every 1 peso of output required 2.9 peso of borrowed money.
So we have debt growth far far far far exceeding statistical GDP growth. And even at zero bound rates, such rate of credit growth will mean that the economy would one day (soon) drown in an ocean of debt! So how sustainable can this be???
Soaring debt levels in and on itself would pose as hindrance to growth.
The credit to debt ratio reveals that these sectors have been heavily borrowing to produce a peso output.
And debt has been spreading not only to the bubble sectors but likewise to other sectors like manufacturing whose credit to GDP ratio has been previously less than 1.
Debt Drives Growth at the Industry Level
And once this debt to the eyeball bubble sectors reaches their growth speed limits, where will government then generate the amount required to finance her current level of spending? Or as tax revenue falls, which should translate to bigger budget deficits, will these be funded by huge debt issuance or by inflation?
And if we consider the latest BSP data on the banking system’s credit growth last July[25], for the banking system’s loan issuance to zoom by 20.92% to its highest level since 2013 is just an awesome sight (right window)!
Even while construction (38.51%) and hotel (40.56%) loans have partly eased from stratospheric levels, the other major sectors, real estate (16.76%), manufacturing (16.83%), trade (21.41%) and finance (27.81%) has picked up speed. Growth in manufacturing loans last July which rocketed 57.1% compared to June. Growth in July’s financial intermediation loans has likewise sizzled which vaulted by 47.4% relative to June.
Even mining and quarrying loans posted a huge 61.81%! Such has represented a rare jump in the industry’s loan portfolio after mostly stagnant loan growth for 2014. Have these loans been used to reverse the 2Q cascade in mining investments?
Agriculture (51.89%) and fishing (34.95%) has also revealed sharp increases of credit absorption. Agriculture has registered two months of 40+% above of loan increase where loan for most of the year has been mostly 10% and below. Meanwhile, fishing has posted 13 months of above 10% loans or 7 months of 30+% loans. The sad part is that fishing output has been in the red for 3 successive quarters (left window). Where have all the borrowed money gone? Have borrowed money been invested or diverted elsewhere?
And like fishing electricity gas and water supply has been racking up banking loans to the tune of 20% above for the past 13 months. But again all these loans have generated measly growth. Again where have all the borrowed money gone? Have borrowed money been invested or diverted elsewhere?
At least the fabulous loan portfolio by the bubble sectors appears to have lived up to the role as economic boosters over the interim (right window). Real estate has consistently outperformed overall economic growth rates (which implies a boost) while trade and financial has been more or less at par with growth rates and hotel has been in a catch up mode.
Yet the growth trends of financial intermediation loans, see previous chart left window, has essentially mirrored on the Phisix (I used the average monthly close of the Phisix). How much of these loans have been used to bid up prices of publicly listed securities in the Philippine Stock Exchange?
Has this been why the BSP rushed to impose an official rate hike late July[26]? Has this been also related to the BSP Governor’s warning of complacency and of “chasing the market”[27]??
Remember debt hasn’t just been a statistic. Most of borrowed money enters the economic stream through spending, therefore affecting prices, and consequently, economic coordination and production patterns. Borrowed money could also be used to pay down on existing debt which destroys money and reduce the money in circulation.
As for my July prediction[28] of a slump in money supply growth rate, this has been fulfilled at even a deeper pace than I expected. Here is the BSP disclosure which affirms my expectations[29]: Domestic liquidity (M3) grew by 18.3 percent year-on-year in July to reach P7.1 trillion. This increase was slower than the (revised) 23.3-percent expansion recorded in June. On a month-on-month basis, seasonally-adjusted M3 increased by 2.5 percent, following a slight decline of 0.3 percent in the previous month.
For the past two months money supply growth rate seems to be reaccelerating. If this trend continues then the downdraft of money supply growth will ease or even bottom out. Remember a sustained 18% money supply growth rate extrapolates to a risk of an eventual 18% inflation rates. The most recent highly publicized consumer price inflation pressures have already been a manifestation of the earlier 30+ growth rates.
This inflation data will not likely be revealed in the official rates which, like all governments, will suppress its numbers. But the muzzling of numbers will not stop new money from credit creation from impacting prices in the real economy.
Should this happen, then this would be bad news as the second round effects of inflation will gain traction. So no matter how much the recourse to publicity gimmicks, massaging of prices of financial assets plus the statistical skullduggery, economic realities will eventually prevail.
The Intensifying Mania
It’s funny but the establishment brays on “growth” as if they represent some magical pixie dusts that would just emerge out of their wishes. They can hardly see the point where inflationism or debt has naturally been bounded by the laws of scarcity.
And days prior to the GDP disclosure, the deepening manic episode has incited inflation addicts to continue to bid up on outrageously priced Philippine stocks. The consensus never seem to realize that current returns have mostly exceeded this year’s earnings growth rates, and so the constant pushing prices higher would only mean fantastic multiple expansions largely devoid of the hyped up earnings-economic growth story.
Again for two days, the Phisix had to register a higher close through the managing of the index to the upside. I was only able to get one of the two days of a minor “marking the close” which seems to have become regular. (chart from technistock.net)
Another observation is that last week’s weekly volume which soared to Php 16.04 billion has been the third largest since 13th of December and 19th of April 2013. This has been due to Friday’s fantastic cross sales mostly on PLDT. We have yet to see if last week’s volume will rise to 2013 levels when the Phisix touched the 7,400.
Nonetheless record capital raising, grotesque valuations, record daily trades (averaged weekly), record traded issues (averaged weekly), accelerating loans in the financial intermediaries where much loans could have been used to play the stock markets, serial marking the close, widespread misperceptions and the one way trade (or total disregard for risk) have been cumulative signs of the deepening manic episode enveloping the Philippine stock market.
It has also been bizarre that on the day of the growth announcement, I was stunned to see a domestic TV news program which aired a wishy washy warning on a Philippine property bubble by an international think tank. I found this news was also featured in the headline of the business page of the most read broadsheet[30]. Write ups on domestic bubble have usually been on foreign publications such as Forbes.com but has not been published by domestic mainstream media. It’s a curiosity, why the sudden permissiveness?
Once again has this been related to the BSP chief’s sanitized alarm bells of “chasing the market”? Have there been politically influential groups that have come to realize of the Philippines’ unsustainable growth model to actually allow the flow of such news to the mainstream?
It would be misguided to say “risks of bubbles”. For an economy to borrow vastly far more its growth rate for the past few years, means that the economy has been building up unnecessary credit risks. In the case of the Philippines, as shown above, 2.9 pesos of borrowed money for every peso output growth in 2Q 2014, means that the bubble blowing has already been in motion. And symptoms as asset and consumer price inflation and many more as enumerated above reinforce its presence.
And when repeatedly inflated, the next thing to await for, is for the bubble to reach its maximum elasticity point before it pops. It’s not about risks anymore, but about if, then proposition. If one drinks too much alcohol, then hangover should be a natural consequence. This is called the Action Axiom.
Two final thoughts.
Analyst Martin Spring observes that for the Philippines, “just 40 of the country’s richest famillies account for, control and enjoy the benefits of 76 per cent of annual production”, if Mr. Spring’s estimates are anywhere near the truth, then the 2Q 2014 6.4% growth represents “growth” mostly for these elite 40 families. Of course the same 40 families have been the main beneficiaries of the financial asset boom. And if the same elites control the government and mainstream media, then media’s bubble leakage means that a minority in the elite may have growing concerns over sustainability of the phony boom. Will one of them start the selling spree?
More importantly, Could 2Q 2014 of 6.4% have been made to shore up the Philippine President’s eroding popularity and to diminish risks of being impeached?
I will end this note with a quote from author, philosopher and political theorist Thomas Paine from his work published in 1779[31]…
There are a set of men who go about making purchases upon credit, and buying estates they have not wherewithal to pay for; and having done this, their next step is to fill the newspapers with paragraphs of the scarcity of money and the necessity of a paper emission, then to have a legal tender under the pretence of supporting its credit, and when out, to depreciate it as fast as they can, get a deal of it for a little price, and cheat their creditors; and this is the concise history of paper money schemes…
But the evils of paper money have no end. Its uncertain and fluctuating value is continually awakening or creating new schemes of deceit. Every principle of justice is put to the rack, and the bond of society dissolved: the suppression, therefore, of paper money might very properly have been put into the act for preventing vice and immorality.
It seems that there has been little difference between the 18th century and the 21st century.
[9] National Statistical Coordination Board NATIONAL EDUCATION EXPENDITURE ACCOUNTS (NEXA). For PCE: On the other hand, the annual estimates of personal consumption expenditures (PCE) were derived from the National Income Accounts of the National Statistical Coordination Board (NSCB). Personal consumption expenditures consist of the actual and imputed expenditures of households, which subsume the NPISH, for the purpose of acquiring individual consumption goods and services.
[16] Philippine Stock Exchange May Monthly report (subscription required)