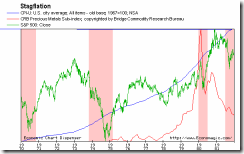
``But on the other hand inflation cannot continue indefinitely. As soon as the public realizes that the government does not intend to stop inflation, that the quantity of money will continue to increase with no end in sight, and that consequently the money prices of all goods and services will continue to soar with no possibility of stopping them, everybody will tend to buy as much as possible and to keep his ready cash at a minimum. The keeping of cash under such conditions involves not only the costs usually called interest, but also considerable losses due to the decrease in the money’s purchasing power. The advantages of holding cash must be bought at sacrifices which appear so high that everybody restricts more and more his ready cash. During the great inflations of World War I, this development was termed “a flight to commodities” and the “crack-up boom.” The monetary system is then bound to collapse; a panic ensues; it ends in a complete devaluation of money Barter is substituted or a new kind of money is resorted to. Examples are the Continental Currency in 1781, the French Assignats in 1796, and the German Mark in 1923.-Ludwig von Mises, Interventionism: An Economic Analysis, Inflation and Credit Expansion
What I think would be the most important driver for the global financial markets over the coming weeks would be the prospective announcement by the US Federal Reserve’s Quantitative Easing version 2.0 on Wednesday.
The Gist of QE 2.0
I do NOT share the view that QE has been FULLY factored IN on the financial markets for the simple reason that estimates of the scale and duration and or terms have been widely fragmented. And there hardly appears to be any consensus on this.
The QE 2.0, in my analysis, is NOT about ‘bolstering employment or exports’, via a weak dollar or the currency valve, from which mainstream insights have been built upon, but about inflating the balance sheets of the US banking system whose survival greatly depends on levitated asset prices.
And all talks about currency wars, global imbalances and others are most likely to be diversionary ‘squid’ tactics to avoid the public from scrutinizing on the Fed’s arbitrary actions.
I see the ongoing QE 2.0 as heavily correlated with the legal issues surrounding the ownership[1] of many mortgage securities that has plagued the industry over the past few weeks.
Of course, it is also possible that Federal Reserve Chairman Ben Bernanke and company maybe pre-empting the results of the midterm elections, which they might think, could upset the current policy directions directed at providing subsidies to the banking system. The possibility of Cong. Ron Paul taking over the banking committee in Congress, they might see as a potential risk that could disrupt the viability of the banking system.
More Evidence Of Inflation
Yet there is hardly any convincing evidence that the US will likely succumb to another recession even without QE 2.0.
Even the credit markets have been saying so as we earlier pointed out[2].

Figure 2: Improvement On US Credit Markets (charts from St. Louis Fed)
For an update (see figure 2): Bank Credit of All Commercial Loans seem to be picking up momentum anew (top window), even Individual loans at ALL commercial which have recently skyrocketed, seem to be in a short pause but still looking vibrant (bottom pane) while Commercial and Industrial Loans of ALL Commercial banks seem to be bottoming out (mid window).

Figure 3: US Monetary Aggregates Points To Inflation (St. Louis Fed)
And even US monetary aggregates[3] appear to be saying the same story: MZM (upper window) and M2 (mid window) have recently been exploding skywards, while the M1 multiplier, a former favourite tool of permabears which tries to measure velocity of money, appears to be emerging fast from a bottom. And this is even prior to the Fed’s supposed renewed engagement with QE.
What all these seem to be pointing out isn’t what the mainstream and the officialdom has been looking at: we seem to be seeing are convergent signs of emergent inflation!
You have seen the actions US credit markets and US monetary aggregates, now the actions of the financial markets.

Figure 3: EM Equities, US Bonds and Commodities In A Chorus
We have argued that the convergence between rallying US bonds and a bullmarket in gold and or commodity markets would seem incompatible, from which the incoherence the markets would eventually resolve.
We seem to be seeing clues of this happening now, of course, going into our direction.
And deflationistas, whom have adamantly argued that bonds will likely benefit from a so-called liquidity trap, and have used the deflation bogeyman as justification for more inflationism, appear to be on the wrong the trade anew.
As one would note in Figure 3, emerging market equities (MSEMF or the MSCI Emerging Market Free Index), the CRB or a major commodity benchmark, a bellwether of Treasury Inflation Protection Securities or TIPS (iShares Barclays TIPS Bond Fund) and 10 year US Treasury Yields appear to be in a chorus.
What all these (credit market, monetary aggregates, financial markets) seem to be indicating isn’t what the mainstream and the officialdom have been looking at. (They’ve been fixated with employment figures).
Instead, what we seem to be seeing is a convergence of surging inflation worldwide!
And this is even prior to the Fed’s coming actions.
Not only that.
Last week, the US government sold $10 billion of 5 year Treasury Inflated Securities (TIPS) at minus .55% or negative interest rates for the first time in US history[4]!
TIPS investors don’t just earn from coupon yields, they earn from the adjustment of the securities’ par value[5] along with that of the consumer price index (CPI) thus giving protection against inflation as measured by CPI (which I think is vastly underreported).
This only means that the aggressive bid up of TIPS, which has led to a milestone of negative interest rates, represents a monumental swing in investor sentiment towards a deepening recognition of our transition to an inflationary environment which over the recent past had only been a fringe idea!
And this, in essence, would validate our 2009 prediction that inflation will be a key theme for 2010[6]!
And this also means that the premises of deflationistas are being demolished or dismantled as inflation expectations emanating from central bank policies deepens.
What To Expect
So how does QE 2.0 translate to the actions in the Financial markets?
If the Fed announcement should fall substantially below market expectations (perhaps $ 1 trillion or less) then we are likely to see some downside volatility which should prove to be our much awaited correction.
Yet any substantial volatility in the financial markets would translate to the Fed likely upping the ante on the QE 2.0. Remember falling asset prices would pressure the balance sheets of the banking system, and thus, would prompt for the Fed to make additional injections.
However, given the penchant of the Fed to resort to shock and awe, I wouldn’t be surprised if the FED would equal or go over the previous $1.75 trillion[7] monetization of treasury and mortgage related securities in 2009.
Of course, the other important aspect would be how other central banks would react to the Fed’s actions. We cannot take the Fed’s action as isolated.
If Bank of Japan and Bank of England would augment the Fed’s QE 2.0 by increasing its exposure on its current programs, then we should expect money flows into emerging markets to expand significantly. And this should go along with commodity prices and commodity currencies.
From the current market actions, we seem to be witnessing the early stages of a crack-up boom.
I remain bullish on equity markets, which I see as protection or serving as insurance against the currency debasement programs being undertaken by central banks to promote covert political agendas.
For Emerging Markets and Philippine stocks, we should remain exposed to commodities, energy and property issues.
[1] See The Possible Implications Of The Next Phase Of US Monetary Easing October 17, 2010
[2] See The Road To Inflation, August 29, 2010
[3] M1: The sum of currency held outside the vaults of depository institutions, Federal Reserve Banks, and the U.S. Treasury; travelers checks; and demand and other checkable deposits issued by financial institutions (except demand deposits due to the Treasury and depository institutions), minus cash items in process of collection and Federal Reserve float.
The M1 multiplier is the ratio of M1 to the St. Louis Adjusted Monetary Base.
MZM (money, zero maturity): M2 minus small-denomination time deposits, plus institutional money market mutual funds (that is, those included in M3 but excluded from M2). The label MZM was coined by William Poole (1991); the aggregate itself was proposed earlier by Motley (1988).
M2: M1 plus savings deposits (including money market deposit accounts) and small-denomination (under $100,000) time deposits issued by financial institutions; and shares in retail money market mutual funds (funds with initial investments under $50,000), net of retirement accounts.
St. Louis Federal Reserve, Notes on Monetary Trends
[4] Financial Times, US Treasury sells negative-rate bonds, October 26, 2010
[5] Investopedia.com Treasury Inflation Protected Securities - TIPS
[6] See Following The Money Trail: Inflation A Key Theme For 2010, November 15, 2009
[7] The Economist, A roadmap for more Fed easing, December 4, 2009