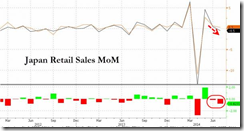
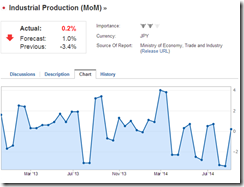
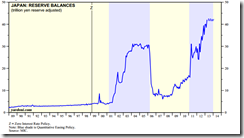
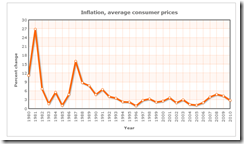
``When governments try to confer an advantage to their exporters through currency depreciation, they risk a war of debasement. In such a race to the bottom, none of the participants can gain a lasting competitive edge. The lasting result is simply weaker and weaker currencies against all goods and services — meaning higher and higher prices. Inflationary policies do not confer lasting advantages but instead make it more difficult to plan for the future. Stop-and-go inflationary policies actually reduce the benefits of using money in the first place.” Robert P. Murphy Currency Wars
For the mainstream, effects are usually confused with the cause to an event. And the misdiagnosis of the symptoms as the source of the disease frequently leads to the misreading of economic or financial picture which subsequently entails wrong policy prescriptions or erroneous predictions.
Yet many mainstream pundits, whom has had a poor batting average in predicting of the markets, have the impudence, premised on either their perceived moral high grounds or their technical knowledge, to prescribe reckless political policies that would have short term beneficial effects at the costs of long term pain with a much larger impact.
Take for instance currency values. Many pundits tend to draw upon “low” currency values as the principal means of attaining prosperity via the “export trade” route. As if low prices mechanically equates to strength in exports. And it is mainly this reason why these so called experts support government interventionism via currency devaluation.
Yet what is largely ignored is that in the real world most of the world’s largest exporters have currencies that are relatively “pricier”, and that most of the “cheap” currency economies tend to be laggards in trade—the latter mostly being closed economies.
In contrast to mainstream thinking, prosperity isn’t about the unwarranted fixation of currency values, but about societies that promotes competitiveness and capital accumulation.
As Ludwig von Mises once wrote[1], (bold emphasis mine)
The start that the peoples of the West have gained over the other peoples consists in the fact that they have long since created the political and institutional conditions required for a smooth and by and large uninterrupted progress of the process of larger-scale saving, capital accumulation, and investment.”
In other words, prosperity emanates from a society which respects the sanctity of property rights premised on the rule of law, which subsequently acts as the cornerstone or foundations of free trade and economic freedom that shapes the state of competitiveness of the economy.
The allure of the polemics of “cheap” currency is no less than “smoke and mirror” chicanery aimed at promoting the interests of a politically privileged class that does little or nothing to advance general welfare.
In short, what is being passed off or masqueraded as an expert economic opinion, is no less than a political propaganda.
Discipline As Basis For Bearishness?
And this applies as well to debt.
Many see the humongous debt load by developed nations as the kernel of the most recent economic crisis. They also use the debt argument as the main basis in projecting the path of economic and financial progress.
Yet debt serves NOT as the principal cause, but as a SYMPTOM of an underlying cause.
It is the collective monetary and administrative policies that have promoted debt financed consumption predicated on the presumed universal validity of AGGREGATE DEMAND that has been responsible for most of the present woes. This has largely been operating for the benefit the government-banking industry-central banking cartel worldwide[2]. Yet such irresponsible policies have spawned endless boom bust cycles and outsized government debts from repeated bailouts and various redistribution schemes which ultimately end in tears. Yet no lesson is enough to restrain these pundits from making nonsensical rationalizations of encouraging a repeat of the same mistakes.
The point is, redistribution has its limits, and we may be reaching the tipping point where the natural laws of economics will undo such false economic premises. And this would represent the grand failure of Keynesian economics from which today’s paper money standard has largely been anchored upon.
For instance the current woes in Ireland, which has not been about the imploding unwieldy social welfare programs yet, but has been about the BLANKET GUARANTEES issued by the Irish government to some of their major ‘too big to fail’ banks, have been used by perma bears to argue for the revival of the ‘deflation’ bogeyman.
While the Ireland debt crisis seem to share a similar characteristic to that of the experience of Iceland[3] in 2008, where the presumed ascendancy or infallibility of government “guarantees” crumbled in the face of economic laws, Ireland’s case is different in the sense that there appears to be political manoeuvring behind the pressure for the latter to comply with the proposed bailout.
Rumors have been rife that the proposed bailout of Ireland have been meant to raise Ireland’s exceptionally low 12.5% corporate tax rates, which has been an object of contention by European policymakers, most especially by the European Central Bank (ECB)
According to the Wall Street Journal[4],
``Brussels has always resented that Ireland transformed its economic fortunes by cutting corporate income taxes and marginal tax rates. At various times, the EU has sued Ireland to raise its rates, accused it of "social dumping" for having a 12.5% corporate income tax, and threatened to cut off European subsidies unless it hiked taxes. None of it worked, but now, with Ireland's banks teetering and its economy in its worse shape in a generation, Europe is moving in for the kill.”
And what better way to compel Ireland to accede to the whims of the bureaucrats in Brussels than to force a crisis from which Ireland would need to accept political conditionalities in exchange for a rescue!
Of course, politicians such as French President Nicolas Sarkozy had been quick to deny the political blackmail[5], saying that “But that’s not a demand or a condition, just an opinion.”
However the important point is that what is being misread by the mainstream as an economic predicament is actually a self inflicted mayhem arising from the political ruse meant at achieving certain political goals.
And unelected politicians have used the markets, largely conditioned to the moral hazard of bailouts and inflationism, to advance their negotiating leverage.
Another point I wish to make is that Euro bears have emphasized that the decision by some Eurozone members to assimilate fiscal austerity has been interpreted as a reason to be bearish on the Euro.
For this camp, the alleged political angst from imposing fiscal discipline would allegedly force the disintegration of the currency union. This is plain AGGREGATE DEMAND based hogwash.
How can it be bearish for individuals or nations (which comprises a community of individuals within defined territorial or geographical boundaries) to act on cleaning up their balance sheets? The excuse is that the lack of AGGREGATE DEMAND will pose as a drag to the economy undergoing the process of “develeraging” from which the government should takeover. What works for the individuals does NOT work for the nation.
Of course the distinction of the paradox can viewed based on time preferences: short term negative and long term positive. People who emphasize on the long term see the positive effects of the structural adjustments even amidst the necessary process of accepting short term pain. Like any therapeutic process, it takes time, regimented diet and regular exercise to recover. There is no short cut, but to observe and diligently work by the process.
On the other hand, there are those who cannot accept any form suffering, or the entitlement mentality. And this mindset characterises the advocates of short term policy fixes.
For politicians who depend on the electoral process to remain in office, any form of suffering represents a taboo as this would signify as loss of votes and consequently the loss of office. Thus, politicians have used short term premised Keynesian economics to justify their actions mostly via the magic of turning bread into stones—printing money.
For unelected bureaucrats the incentives are almost similar, the consequences of any imbalances must be kicked down the road and burden the next officeholder.
For academic or professional supporters, whom are employed in the industries that have privileged ties with the government or whose institutions are funded directly or indirectly by the government, they serve as mouthpieces for these interest groups by embellishing propaganda with expert opinion covered by mathematical models.
The point is this that the AGGREGATE DEMAND paradigm from debt based consumption is not only unsustainable but unrealistic. Yet mainstream experts purposely confuse interpreting the effects as the cause to advance vested interest or for blind belief from dogmatism.
Remaining Bullish On The Euro
And having to confuse effects with the cause is one way to take the wrong side of the markets.
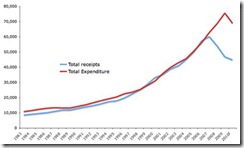
Figure 1: Ireland Government’s Spending Binge
As we pointed out above it is not debt but the incentive by politicians to spend taxpayer money to the point of accruing heavy debt loads that has aggravated the present woes.
As Cato’s Dan Mitchell[6] points out in the case of Ireland,
``When the financial crisis hit a couple of years ago, tax revenues suddenly plummeted. Unfortunately, politicians continued to spend like drunken sailors. It’s only in the last year that they finally stepped on the brakes and began to rein in the burden of government spending. But that may be a case of too little, too late.”
And contrary to the outlook of the Euro bears, the incumbent low corporate taxes seem likely to attract many investors into Ireland.
According to the Economist[7],
IDA Ireland, the agency that targets such investors, says FDI in 2010 will be the best for seven years. A new generation of firms, including computer-gaming outfits like Activision Blizzard and Zynga, are joining the established operations of Intel and Google. Ireland’s workforce is young, skilled and adaptable. Rents are coming down even faster than wages.
So not limited to low taxes, Ireland’s less activist government has resulted to more market based responses in the economy that seems to have also been generating incentives for investors to react positively in spite of the ongoing crisis.
Euro bears are wrong for interpreting discipline and responsible housekeeping as a bearish sign, and equally mistaken for prescribing unsustainable policies that play by the book of mercantilists.
We must be reminded of Professor von Mises’ advise on assessing currency values where ``valuation of a monetary unit depends not on the wealth of a country, but rather on the relationship between the quantity of, and demand for, money”[8]
This means that in terms of relative policies between the US and the Eurozone, the policy of inflationism as administered by the US monetary authorities, seem to tilt the relationship between the quantity (via Euro austerity) and demand, in favour the Euro, whose rally we have rightly predicted[9] in mid of this year.
Alternatively this means that any dip should be considered as a short term countercyclical trend or must be considered a buying window.
Misunderstanding Deflation
Finally, those who continually obsess over the prospects of a deflation environment similar to that of the Great Depression are bound to be incorrigibly wrong.
The Great Depression wasn’t not only a result of contraction of money supply via collapsing banks, but likewise the curtailment of trade from rampant protectionism (Smoot Hawley) and obstructionist policies (regime uncertainty) that inhibited the incentive of the public to invest.
Left to its own devise and unobstructed by government, the marketplace would result to an optimal supply of money. This means for as long as globalization remains operational there won’t be “deflation”.
As another great Austrian Economist, Murray N. Rothbard explained[10],
But money is uniquely different. For money is never used up, in consumption or production, despite the fact that it is indispensable to the production and exchange of goods. Money is simply transferred from one person’s assets to another. Unlike consumer or capital goods, we cannot say that the more money in circulation the better. In fact, since money only performs an exchange function, we can assert with the Ricardians and with Ludwig von Mises that any supply of money will be equally optimal with any other. In short, it doesn’t matter what the money supply may be; every M will be just as good as any other for performing its cash balance exchange function.
If there is any deflation it won’t be from what the mainstream expects, because price deflation would emanate from productivity growth instead of debt deflation, Think mobile phones or computers.
And that’s the reason why perma bears have gotten it miserably wrong, even all the credit indicators previously paraded to argue their case based on the flawed AGGREGATE DEMAND have NOT materialized[11] and worked to their directions.
Now that these indicators either have bottomed out or have manifested signs of improvements, they have NOT been brandished as examples.
So perma bears have been desperately looking for scant real world evidence to support their views.
Bond Markets Reveal Upsurge In Inflation Expectations
IF there would be any ONE thing that would crush the ongoing liquidity party it would be a chain of interest rates increases that eventually would reach levels that would trigger many projects or speculative positions financed by leverage or debt as unprofitable. This would be the credit cycle as narrated by Hyman Minsky.
This means that a bubble fuelled by systemic leverage would be pricked by the proverbial interest rate pin that would unleash a cascade of asset unwinding. This has been a common feature of our paper money system which only shifts from certain asset markets to another.
The motion of rising interest rates would surface from a pick-up in credit demand, which may reflect on policy induced illusory economic growth, broad based consumer inflation as a consequence to sustained monetary inflation or a dearth of capital, which may be prompted for by a surge of protectionism, a collapse in the banking system or snowballing questions over the credit quality on major institutions, if not on claims on sovereign liabilities.
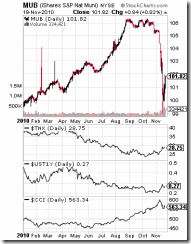
Figure 2: Municipal Bonds by Rising Yields Over The Long End
Despite the recent statistical reports of muted consumer price inflation which marked “the smallest increase since records started in 1957”[12], one must be reminded that consumer price indices represent a basket of goods, services and assets based on the construct of the US government. And these hardly reflect on the accuracy of the real rate of consumer price inflation because they are determined based on the interpretation of government technocrats on what they perceive constitutes as a meaningful measure of “inflation” based on the aggregate assumptions.
So even if food and oil prices have been rising (CCI index in figure 2) it appears that these increases have hardly filtered into the government’s statistical data.
Yet the contradiction appears to have been vented on the bond markets as US treasury yields surge across the long end of the curve as seen in the US 1 year yield (UST1Y) and the 10 year yields (TNX).
As we have been echoing the view of Austrian economists, the inflation which signifies as a political process, would have uneven effects on the economy.
As Professor von Mises wrote, (bold highlights mine)
``Changes in money prices never reach all commodities at the same time, and they do not affect the prices of the various goods to the same extent. Shifts in relationships between the demand for, and the quantity of, money for cash holdings generated by changes in the value of money from the money side do not appear simultaneously and uniformly throughout the entire economy. They must necessarily appear on the market at some definite point, affecting only one group in the economy at first, influencing only their judgments of value in the beginning and, as a result, only the prices of commodities these particular persons are demanding. Only gradually does the change in the purchasing power of the monetary unit make its way throughout the entire economy.
So yes the ‘definite point’ where the symptoms of inflation appear to emerge can be seen in emerging markets, commodities and commodity related industries, with the succession of growing inflation expectations permeating presently into the bond markets.
Remember, recently investors bought into US Treasury Inflation Protected Securities (TIPs) at negative interest rates[13] indicative of mounting expectations of the resurgence of inflation.
So pundits sarcastically questioning “inflation where” are misreading the gradualist dynamics of deepening and spreading inflation. They will instead show you employment data and output gap to argue for “no” inflation regardless of what the bond, stockmarket and commodity markets have been saying.
The other sins of omission by the mainstream has been to read present trends as tomorrow’s dynamics.
Now the tax free US municipal bond markets had likewise been slammed by the surging treasury yields (despite the Fed’s QE 2.0 aimed at keeping interest rates at artificially low levels). As long term US treasury yields have soared, so has these tax free yields.
Other reasons attributed[14] to the recent collapse in muni bond markets have been the expectations of more issuance from many revenue strained states and the potential abbreviation of issuance of Build American Bonds (BABs) given a gridlocked in the US House of Congress, which may have prompted for a deluge of offering in order beat the deadline.
In my view, all these other excuses appear to be secondary to the deepening trend of inflation expectations.
Of course rising interest rates would also put more pressure on the already strained recovery in the US housing markets which I believe has been the object of QE 2.0.
Yet earlier this year we have debunked claims by the government officials and the mainstream pundits supporting the notion of “exit strategies” which I labelled as Poker bluff[15]. (Yes we are once again validated)
And this means that further stress into the housing markets which would translate into balance sheet problems for the US banking system will be perceived by officialdom as requiring more QE’s. So you can expect the Federal Reserve to feed on more QEs as strains on the housing sector remain unresolved.
Another beneficiary of the QE has been the US Federal government. While government spending may be curtailed under the new US Congress, concerns by emerging markets over “currency wars” may lead to less appetite in financing of US debts. This implies that the US will likely resort to the age old ways of financing deficits-debase of the currency. In short, more QEs to come.
So what all these imply for the markets?
It’s still an inflation shindig ahead.
Of course considering the inflation process distorts the market mechanism, we should expect sharp swings in the upside as well as the downside, but with the upside trend becoming more dominant as US monetary authorities resort to more QEs which will be transmitted globally.
Nevertheless, the so-called “crack up boom” or the flight from paper money appears to be taking place worldwide as gold has been fervently rising against all currencies.
With markets expectations over inflation getting more widespread, stay long commodity or commodity related investments.
Lastly, avoid the confusion trap of misreading effects as causes.
[1] Mises, Ludwig von, Period of Production, Waiting Time, and Period of Provision, Chapter 18 Section 4, Human Action
[2] See QE 2.0: It’s All About The US Banking System, November 8, 2010
[3] See Iceland, the Next Zimbabwe? A “Riches To Rags” Tale?, October 14, 2008
[4] Wall Street Journal Editorial Target: Ireland, October 5, 2010
[5] Bloomberg.com Ireland Aid From EU Won’t Require Tax Increase, Sarkozy Says, November 21, 2010
[6] Mitchell, Daniel J. Don’t Blame Ireland’s Mess on Low Corporate Tax Rates, November 18, 2010
[7] The Economist, Saving the euro, November 18, 2010
[8] Mises, Ludwig von Monetary Stabilization And Cyclical Policy (1928) The Causes Of The Economic Crisis, p.18
[9] See Buy The Peso And The Phisix On Prospects Of A Euro Rally June 14, 2010
[10] Rothbard, Murray N. Mystery of Banking, p. 34
[11] See Trick Or Treat: The Federal Reserve’s Expected QE Announcement, October 31, 2010
[12] Reuters.com Dollar hampered by tame U.S. inflation data November 17, 2010
[13] See Trick Or Treat: The Federal Reserve’s Expected QE Announcement, October 31, 2010
[14] Mousseau, John The Spike in Muni Yields - an Opportunity, cumber.com November 16, 2010
[15] See Poker Bluff: The Exit Strategy Theme For 2010, January 11, 2011