``One key attribute that gives money value is scarcity. If something that is used as money becomes too plentiful, it loses value. That is how inflation and hyperinflation happens. Giving a central bank the power to create fiat money out of thin air creates the tremendous risk of eventual hyperinflation. Most of the founding fathers did not want a central bank. Having just experienced the hyperinflation of the Continental dollar, they understood the power and the temptations inherent in that type of system. It gives one entity far too much power to control and destabilize the economy.” Dr. Ron Paul, The Neo-Alchemy of the Federal Reserve
Never has ascertaining the probabilities of the rapidly evolving highly fluid macro environment been as critical today in shaping one’s portfolio or even in anticipation of the how to allocate resources in the coming business environment.
Why? Because future revenue streams, productivity levels, earnings and all other micro metrics, aside from market or business cycles, will all depend on the outcome from the present set of policy choices.
While the investment field shudders at the thought mentioning such ominous phrase; ``it’s different this time”, well, it hard to say it but it does seem different this time.
As we noted in last week’s Stock Market Investing: Will Reading Political Tea Leaves Be A Better Gauge?,
``Even as global governments have been rapidly anteing up on claims to taxpayers’ future income stream by a concoction of “inflationary” actions such as lender of last resort, market maker of last resort, guarantor of last resort, investor of last resort, spender of last resort and ultimately buyer of last resort, a credit driven US economic recovery isn’t likely to happen; not when governments are tightening supervision or regulatory framework, not when banks are hoarding money to recapitalize, not when borrowers are tightening belts and suffering from capital losses on declining assets and certainly not when income is shrinking as unemployment and business bankruptcies rise on falling profits, and most importantly not when the collective psychology has been transitioning from one of overconfidence to one of morbid risk aversion.
``Thus the best case scenario for the credit driven “economic growth” will be a back to basics template-the traditional mechanisms of collateralized backed lending based on borrower’s capacity to pay. But these won’t be enough to reignite the Moneyness of credit. Not even under the US government’s directive.”
We found our assertions pleasantly echoed by the world’s Bond King in his latest outlook; from PIMCO’s Mr. William Gross (who confirms our cognitive biases-emphasis ours)
``My transgenerational stock market outlook is this: stocks are cheap when valued within the context of a financed-based economy once dominated by leverage, cheap financing, and even lower corporate tax rates. That world, however, is in our past not our future. More regulation, lower leverage, higher taxes, and a lack of entrepreneurial testosterone are what we must get used to – that and a government checkbook that allows for healing, but crowds the private sector into an awkward and less productive corner.”
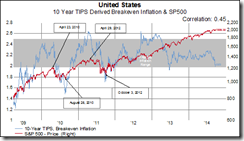
So as global governments take up the shoes from the private sector, the outcomes as reflected by market conditions and on the economic landscape will obviously be different, see Figure 1.
 Figure 1 Gavekal: Portfolio Distribution In Different Environments
Figure 1 Gavekal: Portfolio Distribution In Different EnvironmentsFrom Gavekal’s Brave New World is a simplified template where we see basically four economic environments; from which a long term theme, at the moment, has been struggling to emerge, albeit under a current, possibly temporary, dominant theme which are being battled out by government forces.
But nonetheless, we can identify whence our recent past, posit on the present environment and identify possible outcomes.
From the privilege of hindsight the most obvious is the inflationary boom, which was characterized by a credit inspired boom in almost every asset classes across the world, but in contrast to the template, this includes a boom in government bonds!
Today we are seeing the opposite- a market driven deflationary bust, where the unwinding debt burden has prompted for a reversal of the former order or an across the board selling except for US treasuries and the US dollar. Thus the characteristics as described in the template are presently still being perfected.
Yet, given the observable actions of governments, one may infer that the current deflationary bust phase is being engaged in with a tremendous surge of inflationary forces (bailouts, guarantees, lending, capital provision, etc.) in the hope to restore the former order.
And this has been the source of the fierce debates encapsulating the investment industry; will today’s deflationary bust outrun inflationary forces and transit into a modern day global depression? Will the unintended consequences of the concerted inflationary injections by global central banks result to a US dollar crisis or inflationary bust or hyperinflationary depression? Or will Goldilocks be resurrected with government stilts?
Deflation and Endowment Effects
The basic problem is the house of cards built upon by an unsustainable credit structure from which the world’s economy has been anchored upon, see figure 2.
As we previously noted there are basically two ways to preside over such predicament. One is to allow market forces to reduce debt to levels where the afflicted economy could pay these off. Two, is to reduce the real value of debt via inflation. Of course, there is always the third way: the default option.
But since we believe that the US government and the other debt laden economies are likely to avoid the third option, as their taxpayers have been aggressively absorbing the losses, these relegate us to the first two options.
Deflation proponents (mostly Keynesians) argue that the central bank measures are proving to be impotent when dealing with the tsunami of debt because losses have simply been staggering to drain “capital” than can be replaced and which has similarly devastated the credit system beyond immediate repair. Hence, the global central bank actions are unlikely to rekindle a credit driven (inflationary boom) economic recovery.
In addition, they argue that because of the credit prompted seizure in the banking system its spillover effects to the real economy will lead to a much further decline in aggregate demand which accentuates the overcapacity in the global trade network which will further transmit deflationary forces worldwide.
Moreover, they’ve boisterously indulged in a public blame game in the context of trade balances. They accuse the current account surplus economies, who still seem reluctant to abide by their behest of absorbing declining world aggregate demand via their prescribed policies of increasing domestic consumption, of being ‘beggar thy neighbor’. Some of them have even implied that the continued thrust towards mercantilism in today’s recessionary as “Protectionism In Disguise” (PID).
This of course, according to our self-righteous omnipotent camp will lead to further deflation as excess capacity will forcibly be dumped into the markets and may result to countervailing protectionist actions.
Grim indeed.
The bizarre thing is that Keynesians have been fighting among themselves: the insiders or policymakers believe that eventually their actions will triumph, while the outsiders believe that their sanctimonious wisdoms represent as the much needed elixir to the present predicament.
Yet all of these exhibits nothing more than the cognitive bias of the “endowment effect” or placing a higher value on opinions they own than opinions that they do not.
The rest is speculation.
End Justifies The Means: The Gathering Inflation Storm?
There are two ways one can categorize all these competing analysis.
One, means to an end- (free dictionary) something that you are not interested in but that you do because it will help you to achieve something else; or applied to the recent events, the analysis that “my way has to be followed” regardless of the outcome.
Yes, the US and many European governments have practically followed nearly all Keynesian prescriptions short of outright nationalizations of the affected industries, yet NO definitive progress.
In short, we see many analysis based on the strict adherence to ideological methodologies than the actual pursuit of economic goals.
Of course, this will have to be wrapped with technical gobbledygook, such as liquidity trap, debt trap, and assorted claptraps (possibly even crab traps), to entertain and wow their audience, especially catered to those seeking easy answers or explanations to the performance of today’s market as the trajectory for the future.
Two, end justifies the means- (free dictionary) in order to achieve an important aim, it as acceptable to do something bad or the end result determines the course of action.
As we have earlier said the major alternative recourse to deal with an unsustainable debt structure is to ultimately inflate the real value of debt, which essentially shifts the burden from the debtor to the creditor.
And there have been rising incidences of voices expressing such direction:
This from Atlanta Federal Reserve President Dennis Lockhart (Wall Street Journal) ``A direct path to recovery is unlikely, as we have seen, events arise that knock us off the path to a stable credit environment…the Fed retains a number of options to help the economy.” (highlight ours)
This from former IMF Chief Economist Kenneth Rogoff whom we earlier quoted in Kenneth Rogoff: Inflate Our Debts Away!
``Modern finance has succeeded in creating a default dynamic of such stupefying complexity that it defies standard approaches to debt workouts. Securitisation, structured finance and other innovations have so interwoven the financial system's various players that it is essentially impossible to restructure one financial institution at a time. System-wide solutions are needed….
``Fortunately, creating inflation is not rocket science. All central banks need to do is to keep printing money to buy up government debt. The main risk is that inflation could overshoot, landing at 20% or 30% instead of 5-6%. Indeed, fear of overshooting paralysed the Bank of Japan for a decade. But this problem is easily negotiated. With good communication policy, inflation expectations can be contained, and inflation can be brought down as quickly as necessary.
This from a commentary entitled “Central banks need a helicopter” by Eric Lonergan a macro hedge fund manager at the Financial Times (highlight mine),
``What is lacking is a legal and institutional framework to do this. The helicopter model is right, but we don’t have any helicopters…Central banks, and not the fiscal authorities, are best placed to make these cash transfers. The government should determine a rule for the transfer. It is the government’s remit to decide if transfers should be equal, or skewed to lower income groups….The reasons for granting this authority to the central bank are clear: it requires use of the monetary base. Granting government such powers would be vulnerable to political manipulation and misuse. These are the same reasons for giving central banks independent authority over interest rates.”
Let’s go back to basics, the reason governments are inflating the system away (albeit in rapid phases) is because of the perceived risks of destabilizing debt deflation. Yet you can’t have market driven deflation process without preceding government stimulated inflation. Thereby deflation is a consequence of prior inflation. It is a function of action-reaction, cause and effect and a feedback loop- where government tries to manipulate the market and market eventually unwinds the unsustainable structure.
Our point is simple; if authorities today see the continuing defenselessness of the present economic and market conditions against deflationary forces, ultimately the only way to reduce the monstrous debt levels would be to activate the nuclear option or the Zimbabwe model.
And as repeatedly argued, the Zimbabwe model doesn’t need a functioning credit system because it can bypass the commercial system and print away its liabilities by expanding government bureaucracy explicitly designed to attain such political goal.
As Steve Hanke in the Forbes magazine wrote, ``The cause of the hyperinflation is a government that forces the Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe to print money. The government finances its spending by issuing debt that the RBZ must purchase with new Zimbabwe dollars. The bank also produces jobs, at the expense of every Zimbabwean who uses money. Between 2001 and 2007 its staff grew by 120%, from 618 to 1,360 employees, the largest increase in any central bank in the world. Still, the bank doesn't produce accurate, timely data.”
In other words, the Rogoff solution simply qualifies the ‘end justifying the means’ approach, where the ultimate goal is political -to reduce debt in order for the economy to recover eventually or over the long term for political survival, than an outright economic end. Yet because of the vagueness of such measures, there will likely be huge risks of unintended painful consequences. But nonetheless, if present measures continue to be proven futile, then path of the policy directives could likely to lead to such endgame measures-our Mises moment.
Yet, the Rogoff solution simply cuts through the long chase of the farcical rigmarole advanced by deflation proponents who use their repertoire of technical vernaculars of assorted “traps” to convey a deflation scenario. When worst comes to worst all these technical gibberish will simply evaporate.
Moreover, deflation proponents seem to forget that the Japan’s lost decade or the Great Depression from which Keynesians have modeled their paradigms had one common denominator: “isolationism”.
Japan’s debacle looks significantly political and culturally (pathological savers) induced, while the Smoot Hawley Act in the 1930s erected a firewall among nations which essentially choked off trade and capital flows and deepened the crisis into a Depression.
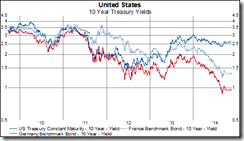
This clearly hasn’t been the case today, YET, see Figure 3.
 Figure 3: US global: Global Central Banks Concertedly Cutting Rates
Figure 3: US global: Global Central Banks Concertedly Cutting RatesThere had been nearly coordinated massive interest rate cuts this week by several key central banks; the Swedish Riksbank slashed its rates by nearly half, cutting 175 bp to 2%, followed by the Bank of England, which slashed rates by 100bp (last month it cut by 150 bp), while the ECB was the most conservative and cut of 75bp. Indonesia followed with 25 bp while New Zealand cut a record 150bp to 5% (guardian.co.uk).
And as we quoted Arthur Middleton Hughes in our Global Market Crash: Accelerating The Mises Moment!, ``the market rate of interest means different things to different segments of the structure of production.”
If the all important tie that binds the world has been forcible selling out of the debt deflation process, then as these phenomenon subsides we can expect these interest rate policies to eventually gain traction.
And it is not merely interest rates, but a panoply of distinct national fiscal and monetary policies targeted at cushioning such transmission.
Remember, even in today’s globalization framework, the integration of economies hasn’t been perfect and that is why we can see select bourses as Tunisia, Ghana, Iraq or Ecuador defying global trends, perhaps due to such leakages.
The point is there is no 100% correlation among markets and economies. And when the forcible selling (capital flow) fades, the transmission linkages will focus on other aspects as trade or remittances which have varying degrees of external connections relative to their national GDP.
Thus, considering the compounded effects of individual economies and their respective national policy actions, market or economic performances should vary significantly.
The idea that global deflation will engulf every nation seems likely a fallacy of composition if not a chimera.
Reviving Smoot-Hawley Version 2008?
Next, there is this camp agitating for a revised form of protectionism.
They accuse nations with huge current account surplus, particularly China, for nurturing trade frictions amidst a recessionary environment-by obstinately opting to sustain the present trade configuration which is heavily modeled after an export led capital intensive investment growth.
The recent surge of the US dollar against the Chinese Yuan and China’s recent policies of providing for higher rebate and removal of bank credit caps have been interpreted to as being implicitly protectionist.
The alleged risks is that given the slackening of aggregate demand, China’s export oriented growth model could pose as furthering the deflationary environment by dumping excess capacity to the world.
Echoing former accusations of currency manipulation, but in a variant form, the adamant refusal by China to reduce its export subsidies (via Currency controls etc.) at the expense of domestic consumption, is seen by critics as tantamount to fostering protectionism and thus, should require equivalent punitive sanctions.
Recessions are, as seen from the mainstream, defined as a broad based decline in economic activity, which covers falling industrial production, payroll employment, real disposable income excluding transfer payments and real business sales.
But recessions or bubble bust cycles are mainly ``a process whereby business errors brought about by past easy monetary policies are revealed and liquidated once the central bank tightens its monetary stance,” as noted by Frank Shostak.
In other words, when China gets implicitly or explicitly blamed for “currency manipulation” or for failing to adopt policies that “OUGHT TO” balance the world trade, it assumes that the US, doesn’t carry the same burden.
But what seems thoroughly missed by such critics is that the extreme ends of the current account or trade imbalances reflect the ramifications of the Paper-US dollar standard system. You can’t have sustained and or even extreme junctures of imbalances under a pure gold standard!
Besides, since the supply or issuance of currencies is solely under the jurisdiction of the monopolistic central banks, which equally manages short term interest rate policies or the amount of bank reserves required, then the entire currency market operating under the Paper money platform accounts for as pseudo-market or a manipulated market.
To quote Mises.org’s Stefan Karlsson, ``Any currency created by a central bank is bound to be manipulated. In fact, manipulating the currency is the task for which central banks were created for. If they didn't manipulate the currency, there would be no reason to have a central bank.” (underscore mine)
In addition, the fact that the US functions as the world’s reserve currency makes it the premier manipulator- for having the unmatched privilege to extend paper IOUs as payment or settlement or in exchange for goods and services.
We don’t absolve the Chinese for their policies, but perhaps, by learning from the harsh experience of its neighbors during the Asian crisis, the Chinese have opted to adopt similar mercantilist nature to protect its interest but on a declining intensity as it globalizes.
The point that Chinese authorities are considering full convertibility of the yuan, as per Finance Asia (emphasis mine), ``The Chinese authorities should raise the profile of the renminbi during the global financial turmoil and get ready for the currency’s full convertibility, according to Wu Xiaoling, deputy director with the finance and economic committee of the National People’s Congress”, or this ``Wu, who was a deputy governor of the People’s Bank of China (PBOC) until earlier this year, told a seminar in Beijing in November that the renminbi should become an international reserve currency in tandem with its full convertibility, reflecting a renewed interest in loosening control of the currency as the country becomes more deeply integrated in the world financial system. She said it was difficult to find an alternative reserve currency but added that the renminbi was ready to become an international currency to replace the dollar,” equally demonstrates the political thrust to gain superiority by becoming more integrated with the world via reducing mercantilist policies and adopting international currency standards.
But, unlike the expectations of our magic wand wielding experts, you don’t expect them to do this overnight.
 Figure 4 Gavekal: China Reserves Outgrow China’s Trade Surplus & FDI
Figure 4 Gavekal: China Reserves Outgrow China’s Trade Surplus & FDIAlso during the past years, China’s currency reserves didn’t account for only trade surpluses or FDI flows, but as figure 4 courtesy of Gavekal Capital shows, a significant part of these reserves could have emanated from portfolio or speculative flows even in a heavily regulated environment.
Thus, the recent surge of US dollar relative to the Yuan may not entirely be a policy choice but also representative of these outflows given the current conditions. The fact that China’s real estate has been decelerating and may have absorbed most of these speculative flows could reflect such dynamics.
Nonetheless Keynesians always focus on the aggregate demand when recessions or a busting cycle also means a contraction of aggregate supply.
Malinvestments as seen in jobs, industries or companies or likewise seen in supply or demand created by the illusory capital or “money from thin air” which would need to be cleared. Or when the excesses in demand and in supply are sufficiently reduced or eliminated, and losses are taken over by new investors funded by fresh capital, then the economy will start to recover.
Again Frank Shostak (highlight mine), ``Contrary to the Keynesian framework, recessions are not about insufficient demand. In fact Austrians maintain that people's demand is unlimited. The key in Austrian thinking is how to fund the demand. We argue that every unit of money must be earned. This in turn means that before a demand could be exercised, something must be produced. Every increase in the demand must be preceded by an increase in the production of real wealth, i.e. goods and services that are on the highest priority list of consumers (we don't believe in indifference curves).”
The point is whatever decline in aggregate demand also translates to a decline in capacity as losses squeezes these excesses out. Today’s falling prices may already reflect such oversupply-declining demand adjustments.
Said differently the calls to maintain or support “demand” by means of more government intervention aimed at propping up of institutions, which are not viable and can’t survive the market process on its own, isn’t a convincing answer. The pain from the adjustments in debt laden Western economies is also felt but to a lesser degree in Asian economies.
Likewise, imposing undue protectionist sanctions to suit the whims of such pious and all knowing experts, will likely have more unintended consequences, foster even more imbalances and or risks further deterioration of the present conditions.
Forcing China to radically reform, without dealing with the structural asymmetries from today’s fractional reserve banking US dollar standard, won’t resolve the recurring boom-bust cycles. This simply deals with the symptoms and not the cause.