Well, if you come up with a lot of wrong ideas and pay a price for it, you’re forced to think about it and to change your ways or else get eliminated. But there is no such test. The only test for most intellectuals is whether other intellectuals go along with them. And if they all have a wrong idea, then it becomes invincible.
The art of economics consists in looking not merely at the immediate hut at the longer effects of any act or policy; it consists in tracing the consequences of that policy not merely for one group but for all groups—Henry Hazlitt
Sunday, May 19, 2013
Quote of the Day: The Intelligencia pay no price for being wrong
Friday, August 31, 2012
Is Financial Knowledge Key to Successful Investing?
The public doesn’t know how to manage their finances, that’s according to a study commissioned by the US SEC.
From the Wall Street Journal Blog,
Good news for those intent on committing fraud. Bad news for most everyone else. American investors apparently don’t know much about anything financial.
According to a review released Thursday of years of surveys of individual investors, they are presumably ripe for the picking by fraudsters because they don’t have much knowledge to counteract any outlandish offerings.
Here’s the key and rather astonishing quote: “These studies have consistently found that American investors do not understand the most basic financial concepts, such as the time value of money, compound interest and inflation. Investors also lack essential knowledge about more sophisticated concepts, such as the meaning of stocks and bonds; the role of interest rates in the pricing of securities; the function of the stock market; and the value of portfolio diversification…”
That is from the Library of Congress, which conducted the review on behalf of the Securities and Exchange Commission. The SEC, for its part, needed to study Americans’ financial literacy and assess what investors wanted to know about investments and advisers and how they wanted to receive the information. The SEC had a mandate for all that from the 2010 Dodd-Frank Act.
This generalized lack of knowledge (there certainly are plenty of exceptions) is particularly worrisome since more and more people are responsible for their own investment decisions as part of defined-contribution retirement plans, usually 401(k)s.
The Library of Congress said: “If employees do not have the requisite knowledge, they will not be prepared to make informed decisions regarding the management of their financial affairs, including investing for a secure retirement.”
The public (not limited to Americans) may not be technically sophisticated in the realm of finances but to claim that they are “not be prepared to make informed decisions regarding the management of their financial affairs” looks outrageously untrue.
This misleading assertion presupposes that government should play a role to compel people to get educated "financially".
In reality, America’s standard of living has been higher than most of the world because of capital accumulation.
As the great Ludwig von Mises wrote,
The average standard of living is in this country higher than in any other country of the world, not because the American statesmen and politicians are superior to the foreign statesmen and politicians, but because the per-head quota of capital invested is in America higher than in other countries. Average output per man-hour is in this country higher than in other countries, whether England or India, because the American plants are equipped with more efficient tools and machines. Capital is more plentiful in America than it is in other countries because up to now the institutions and laws of the United States put fewer obstacles in the way of big-scale capital accumulation than did those foreign countries.
Americans not only knew but appropriately acted to manage their state of affairs through the productive balancing of savings and investments which resulted to such high levels of capital accumulation
Moreover, having financial knowledge does not necessarily translate to having the expertise for “investing for a secure retirement”
In reality, financial knowhow does not make one infallible from loses.
In debunking the idea that financial success comes out of high IQs, I recently wrote,
The landmark bankruptcy by Long Term Capital Management in 1998 had been a company headed by 2 Nobel Prize winners. The company’s failure has substantially been due to flawed trading models.
In 2008, the 5 largest US investment banks vanished. These companies had an army of economists, statisticians and quant modelers, accountants, lawyers and all sort of experts who we assume, because of their stratospheric salaries and perquisites, had high IQs.
When Queen Elizabeth asked why ‘no one foresaw’ the crisis coming, the reply by the London School of Economics (LSE)
"In summary, Your Majesty," they conclude, "the failure to foresee the timing, extent and severity of the crisis and to head it off, while it had many causes, was principally a failure of the collective imagination of many bright people, both in this country and internationally, to understand the risks to the system as a whole."
Imagination had been scarce because the same army of experts heavily relied on mathematical models in dealing with investments. They did not follow the common sense advise by the real experts.
These people had all the supposed “expertise” yet they all burned investor's money.
The failure of pseudo financial mastery explodes the idea that “generalized lack of knowledge” will not enable people “to make informed decisions”.
To add, if one looks at the list of the victims of fraud committed by scam artist Bernie Madoff, they had hardly been about financial ignorance
Again I wrote,
Thus, it is no different when Bernard Madoff bamboozled $50 billion off from the who’s who list which includes top rated financial institutions among them banks, (e.g. BNP Paribas,Banco Santander, Fortis Bank Netherlands, HSBC Holdings, Nomura Holdings, Royal Bank of Scotland and etc.) insurers (CNP Assurances, Clal Insurance, Harel Insurance) and Hedge funds (Tremont Group Holdings, Fairfield Greenwich).
To consider, these institutions account for as supposedly smart money outfits since they are backed by an army of “elite professionals”, e.g. economists, accountants, risk managers, quants etc…). Yet at the end of the day, smart money seemed like everybody else; they got what they deserved because they substituted prudence with fad
In reality, inflationist “bubble” policies, which obscures price signals and whets the speculative or gambling appetite, have been the principal influence to fraud.
As a side note: even the most successful stock market investor Warren Buffett admits of occasional investing mistakes.
In Manias, Panics and Crashes Charles Kindleberger’s insight has been highly relevant, (I quoted from my previous article)
Commercial and financial crisis are intimately bound up with transactions that overstep the confines of law and morality shadowy though these confines be. The propensities to swindle and be swindled run parallel to the propensity to speculate during a boom. Crash and panic, with their motto of sauve qui peut induce still more to cheat in order to save themselves. And the signal for panic is often the revelation of some swindle, theft embezzlement or fraud
Bottom line: having financial knowledge is necessary but not sufficient reason for securing financial success.
Relevant theory backed by quality information from the desire to profit (stakeholder's dilemma) has to be used as framework for such analysis.
Morris Cohen in his 1944 book, A Preface to Logic provides a useful insight (quoted by Professor Don Boudreaux)
There can be no doubt that statistics deals with actuality, and that knowledge of actualities is always empirical, i.e., that we cannot obtain knowledge by purely a priori methods. There is, however, no genuine progress in scientific insight through the Baconian method of accumulating empirical facts without hypotheses or anticipation of nature. Without some guiding idea we do not know what facts to gather. Without something to prove, we cannot determine what is relevant and what is irrelevant.
And this should be complimented by emotional intelligence and self-discipline.
Saturday, August 25, 2012
Video: Peter Schiff takes on Gold Bear Chartist
Peter Schiff here staunchly defends the bullish case of gold based on fundamental long term perspective against a gold (short term) bear chartist. (hat tip: Bob Wenzel)
Charts or trend patterns are usually interpreted based on the underlying bias of the technician.
Moreover, the video wonderfully exhibits the stakeholder's dilemma at work-where the incentives to secure knowledge are driven by the degree of stakeholdings.
Such conspicuous nuances can be seen from the perspective of the institutional "analyst" who lack the meticulousness in her analysis of the gold market (because she don't have exposures on them) and of "equity holders" (as represented by Peter Schiff) who has direct stakeholding on gold.
The contrast of incentives frequently leads to the principal-agent problem or ethical dilemma. It is just in this case, the equity holder has been in command of the situation and is aware of the weakness of the analyst. In usual cases, it is the latter that influences the former.
Monday, June 04, 2012
Will the Phisix Divergence Last?
My source of livelihood has almost entirely been from the local stock market, particularly investing, as I am hardly or rarely a short term trader.
Thus, objective and thorough investigations, assessments and analysis have been IMPERATIVE on me. And as part of my investing philosophy, I try to avoid getting married to a position, in as much as assuming the HIGH RISK role of becoming a stock market CHEERLEADER.
Losing money means my family will starve and this is why I cannot afford to lose money. Therefore such punctilious efforts, on my part, to deal with risks represent what have been known as stakeholder’s problem—where my incentives to attain relevant knowledge are prompted by the degree of my stakes in the financial marketplace. Since I depend on the markets thus I have to know the possible risks attendant to my positions.
And this outlook which I share with you, has not only been based on my battle hardened experience, but also from my candid evaluations of the conditions of the risk environment.
I am not here for an egotistical trip as many have been wont to.
Separating Signals from Noise
I have long been an adherent to the wisdom of the legendary trader Jesse Livermore. I have repeatedly been posting one of my favorite Mr. Livemore’s aphorisms here (bold emphasis mine)
I began to realize that the big money must necessarily be in the big swing. Whatever might seem to give a big swing its initial impulse, the fact is that its continuance is not the result of manipulation by pools or artifice by financiers, but depends on underlying conditions. And no matter who opposes it, the swing must inevitably run as far and as fast and as long as the impelling forces determine.
Simply said, profits are to be made based on underlying conditions which drives the general trend, and importantly, serves as the critical source of big swings.
And this is why I give heavy emphasis at the unfolding events based on the big picture. Unlike most practitioners, I am hardly swayed by vacillations from ticker tape activities.
Yet, ticker tape activities and the big picture frequently represent the noise and signal problem
Nassim Nicolas Taleb in his forthcoming book wonderfully explains the psychological impact from noise and signal[1]
we are not made to understand the point, so we overreact emotionally to noise. The best solution is to only look at very large changes in data or conditions, never small ones.
Just as we are not likely to mistake a bear for a stone (but likely to mistake a stone for a bear), it is almost impossible for someone rational with a clear, uninfected mind, one who is not drowning in data, to mistake a vital signal, one that matters for his survival, for noise. Significant signals have a way to reach you. In the tonsillectomies, the best filter would have been to only consider the children who are very ill, those with periodically recurring throat inflammation.
There was even more noise coming from the media and its glorification of the anecdote. Thanks to it, we are living more and more in virtual reality, separated from the real world, a little bit more every day, while realizing it less and less. Consider that every day, 6,200 persons die in the United States, many of preventable causes. But the media only reports the most anecdotal and sensational cases (hurricanes, freak incidents, small plane crashes) giving us a more and more distorted map of real risks. In an ancestral environment, the anecdote, the “interesting” is information; no longer today. Likewise, by presenting us with explanations and theories the media induces an illusion of understanding the world.
And the understanding of events (and risks) on the part of members of the press is so retrospective that they would put the security checks after the plane ride, or what the ancients call post bellum auxilium, send troops after the battle. Owing to domain dependence, we forget the need to check our map of the world against reality. So we are living in a more and more fragile world, while thinking it is more and more understandable.
The bottom line is that many people get confused when working to separate the proverbial wheat from the chaff or when filtering signal from noise. People with lesser stakeholdings are likely to emphasize on the noise which usually signify as “an illusion of understanding the world” and or embrace steeply biased (but unworkable and highly flawed) theories.
The Dopamine Fetish
I would also add that part of the psychological-neuroscience aspect in dealing with markets has been about dopamine neurons.
People’s dopamine neurons, or brain chemicals, gets fired up when rewards attained are GREATER than expected. In contrast, REGRETS are symptoms of depressed dopamine neurons. Thus short term thinking and short term trading have MOSTLY been about the fetish for dopamine trips.
A study on neuroscience suggests that dopamine flows are pervasive during early stages of a ballooning bubble, reflecting desire for profit. However as the bubble peaks, dopamine flows tend to culminate in a cessation just before the market burst[2]
Monetary policies by central banks also whet or induce dopamine powered speculative behaviors[3].
The lesson here is that we should manage our dopamine flows rather than allowing dopamine neurons to dominate the risk-reward tradeoffs that confront our investing decisions. This is basically about Emotional Intelligence (EI)
Let me further add that the technical construct of the Philippine Stock Exchange has been skewed to inculcate upon the public of the upside bias for issues listed on the markets, as well as, the component index.
The rational for this seems to be part of the political designs to exhibit economic booms.
Take shorting. While shorting has been legalized, rigorous procedural and regulatory compliance requirements have made shorting impractical. So we have a facility that has hardly been used.
And since market participants only earn from an UPSIDE price move, thus logically, the dominant entrenched PSYCHOLOGICAL bias would be for the public to yearn for the stock market to go only in one direction—UP.
Next, complimenting the psychological and physiological aspect, monetary policies have also been rewarding speculative activities at the expense of savings and production.
So intensifying speculative activities extrapolates to the herd effect in motion.
Where the basic function of the stock market has been about the cost of buying future income stream relative to insecurities (risk and uncertainty), such functionality has been negated or substituted by rationalizations for price chasing momentum.
Writes Kevin Dowd, Martin Hutchinson, and Gordon Kerr at Cato Forum for monetary policies[4],
Low interest rate policies not only set off a malinvestment cycle but also generate destabilizing asset price bubbles, a key feature of which is the way the policy rewards the bulls in the market (those who gamble on the boom continuing) at the expense of the sober minded bears who keep focused on the fundamentals, instead of allowing the market to reward the latter for their prudence and punish the former for their recklessness. Such intervention destabilizes markets by encouraging herd behavior and discouraging the contrarianism on which market stability ultimately depends. A case in point is the Fed’s low interest rate policy in the late 1990s: this not only stoked the tech boom but was maintained for so long that it wiped out most of the bears, who were proven right but (thanks to the Fed) too late, and whose continued activities would have softened the subsequent crash. The same is happening now but in many more markets (financials, general stocks, Treasuries, junk bonds, and commodities) and on a much grander scale. Such intervention embodies an arbitrariness that is wrong in principle and injects a huge amount of unnecessary uncertainty into the market.
In essence, the inflationary boom psychology has been distorting economic reasoning.
Add to this the leash effects of bailout policies.
The bottom line is that inflation fueled bull markets have become a religion to many.
And advises to undertake prudent positions—based on appraising the risk environment that may adversely affect one’s portfolio—has been seen as sacrilege.
Short Selling Not Recommendable; Contagion Risks
I also do NOT recommend shorting in the Philippines for the following reasons
-the cost to undertake shorts positions have been enormous relative to prospective gains (if a short position is required the best is to do it from overseas)
-a full blown BEAR market for the Philippines has NOT been yet established, although the RISKS from such scenario seem to be STRENGHTENING.
-global regulators have periodically been intervening. The degree of intervention mostly through bailout policies comes with such INTENSITY such that these can TORCH shorts on short notice. A good example has been Europe’s LTRO which singed Euro shorts at the start of the year[5]
-global regulators have innate biases against short sellers. They have done so lately through direct market interventions, such as drastic imposition of shorting bans which forces short covering to investors at a loss. A great example has been the shorting bans on Europe stock markets in mid-2011[6] in the political belief that speculations, and NOT insolvency, have been the fundamental problem that besets the Eurozone. Yet in spite of the bans, European stock markets continue to bleed PROFUSELY. This represents a vivid example of the “illusion of understanding the world” by political agents who always try to shift what has truly been their mistake to the markets.
Lastly I do NOT wish or DESIRE for a bear market.
Because of the limitations to take on hedge positions, bear markets or even phases of consolidation with a downside bias or volatility translates to income drought for me or most market participants (see the structural bull market bias above)
While I am an optimist who believes that the Phisix will reach 10,000 sometime in the future, I am also a REALIST who understands that external forces have a HUGE influence to actions of the local stock markets and that NO trend goes in a straight line.
In suggesting of the countercyclical trend amidst a secular trend I wrote in March[7],
I am not certain whether we will see a repeat of the discontinuities similar to the 1986-1997 bull market cycle or will suffer more than the past cycle before reaching my goal or if the Phisix will proceed to double. What needs to be monitored are drivers of the current trends and the whereabouts of the present boom cycle based on internal and external dynamics.
In short, the PHISIX, despite the secular trend, is VULNERABLE to a CONTAGION risk.
Could this week’s Phisix Divergence Represent an Anomaly?
The local benchmarket, the Phisix, majestically bucked the global stock market carnage last week.
As one would note, the Phisix has not only outperformed the region, the local benchmark basically defied gravity.
China and Malaysia joined the Phisix, as outliers, with hefty gains amidst a sea of red.
Yet such divergences have given the dopamine to Pollyanna trippers the ammunition to declare “bottom” for the market.
I have yet to be convinced.
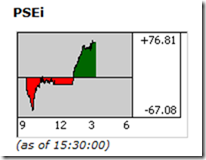
The gist of the weekly gains or 52% of the Phisix came from Thursday’s activities.
Ironically, the sizable gains occurred in the backdrop of staggering US and global markets.
Media and experts has alluded to reports of sturdy domestic economic growth[8], the hints of a possible upgrade[9] by US rating agency Moody’s on the credit standing of the Philippines and the closure of milestone impeachment trial[10] with a conviction of the accused which favors the administration as reasons for this.
I beg to differ.
I raised this concern on this last Thursday[11]. The Phisix went down to as low as 67 points at the early session, dragged by the selloffs in the US and Europe. But suddenly, aggressive and systematic buying of heavyweights (blue chips) throughout the day pushed the Phisix to close at almost at the peak (76.81) at 73 points. The pendulum swing from loss to gain represented an astounding 2.8%!!!
Buyers seem to have, ironically, been resolutely aggressive to push up prices in an environment of MOSTLY falling stock market prices globally, perhaps in the assumption that local stocks will soon experience a strong surge.
Or is it?
The weekly performance of the heavy cap issues reveals that gains of the Phisix were mostly seen through Ayala Corp (AC), JG Summit (JGS), Banco De Oro (BDO), Metrobank (MBT), SM Investments (SM), International Container (ICT), PLDT (TEL) and Bank of the Philippine Islands (BPI).
The logical part for any buyers under such scenario would be to make use of the dour sentiment to take advantage of price declines to bargain hunt. Yet these have not been the case.
Let me lay out my suspicions.
I do not think that these has been due to general market sentiment, although pushing up the PHISIX index succeeded to give a boost to the general market sentiment.
Thursday closed with a mixed showing between advancers and decliners with the latter having a slight edge. On a weekly basis advancers took a slight lead over decliners showing modest improvement in the market breadth or sentiment.
Second my naughty thoughts suggests that Thursday actions was likely executed to create an impression of economic ‘confidence’. I am not so sure why though. Perhaps to squelch demand for signing waivers for top officials.
Buyers suddenly became price insensitive. The likelihood is that non-market entities may have been responsible for aggressively pushing up Big Caps. I would suspect that these may have been government institutions such as the SSS, GSIS or others.
While it is true that Thursday a net foreign buying, the bulk of these buying can be traced to cross trades at DM Consunji.
Besides, net foreign buying data may not reveal of the real extent of activities that took place. Foreign buying can represent overseas based subsidiaries or branches of locally owned corporate vehicles or tycoons, as well as, foreign based politically allied corporations.
Of course I may be wrong and that there may have been special factors driving up the Phisix.
But if my suspicions are valid then such interventions are likely to produce short term effects.
As example the Bank of Japan’s (BoJ) $13.3 billion[12] interventions DID bring down the Yen for about a month. However the Yen has been regaining lost grounds since. This effectively has neutered tax payer financed interventions. In short $13.3 billion down the drain.
Another question that begs to be asked is WHY the PHSIX alone?
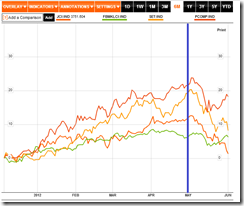
While Malaysia did post hefty weekly gains next to the Phisix, the Malaysia’s benchmark (FBMKLCI:IND, green) has almost missed out the recent bull market. On the other hand, Thailand (SET:IND, orange) and Indonesia (JCI:IND, red) which shared or alternated the lead with the Phisix, since last year, has wilted significantly.
Yet it can be observed that ASEAN’s stock markets have been nearly been moving in nearly synchronous fashion UNTIL the peak in May of this year.
This only means that last week’s gains by the Phisix either represents an ANOMALY or that the Phisix LEADS Asia.
My bet is on the former.
The Decoupling Myth
I have been saying that current environment have been dominated by POLITICAL uncertainty which for the Philippines and ASEAN represents a CONTAGION risk.
If global markets stock markets have been pricing in a bust or the unwinding of malinvestments which is being transmitted to the global economies, then it would dangerous, if not reckless, to presume immunity or “decoupling” where trade and investment linkages of ASEAN economies have been deepening relative to the world.
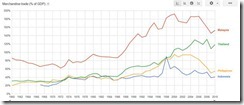
ASEAN economies have largely been exposed to developments abroad through merchandise trade (exports and imports).
The Philippines merchandise trade represents over 50% of GDP, while Malaysia and Thailand are over 100%.
This means any meaningful economic slowdown in the region or in the world will negatively impact economic growth.
Add to this the potential slowdown effect on remittances and supply chain networks.
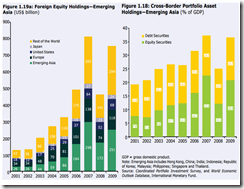
The deepening of financial globalization also means the integration of emerging Asia’s capital markets[13] with the world (left chart) and with intra-region (right pane).
In short, the false notion of DECOUPLING will likely melt in the face of a global recession or when a full blown financial crisis, if such phenomenon transpires.
Let me be clear, the conditional term is an IF, while global economies have indeed been slowing down, a global recession or worldwide contagion from euro’s financial crisis has yet to become evident in Asia.
Of course a decoupling COULD happen if there should be massive inflation or even hyperinflation from any of these major economies. However, under the current circumstances this is unlikely to happen.
This means that for those in the belief that the Philippines can decouple from the world, the following chart should be a helpful reminder…
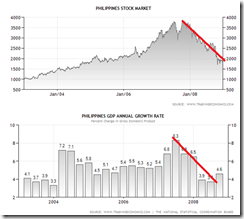
2007-2008 signifies as the contagion based bear market.
Neither has there been an economic recession during the said period nor did earnings fall materially. But the Phisix entered a full blown BEAR Market and lost about 50% peak-to-trough as a result of an exogenously driven financial crisis in 2007-2008.
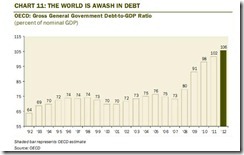
Of course 2008 is different from today. In fact, today has been worst compared to the 2008 crisis. In 2008 the crisis was limited to the banking, property and mortgage industry. Today the crisis dynamics has shifted to envelop banks AND sovereigns. Not to mention that world wide government debts have surged[14] and that US fiscal deficits have skyrocketed (at $1.327 trillion or 8.2 times larger than 2007[15]).
Yet for those who should insist on decoupling, then I wish you the best of luck.
[1] Taleb Nassim Nicolas Noise and Signal — Nassim Taleb Farnam Street, May 29, 2012
[2] ChangingMinds.org The Neuroscience of Financial Bubbles
[3] See How US Federal Reserve Policies Stimulates the Public’s Speculative Behavior, May 8, 2012
[4] Dowd Kevin, Hutchinson Martin, and Kerr Gordon The Coming Fiat Money Cataclysm
[5] Marketwatch.com Euro hits 3-month high on LTRO hopes, February 24, 2012
[6] Wall Street Journal, Europe Short Bans Extended, August 26, 2011
[7] See Phisix: The Journey Of A Thousand Miles Begins With A Single Step, March 12, 2012
[8] ABS-CBNnews.com.ph PH eco grows 6.4% in Q1; highest in ASEAN, May 31, 2012
[9] Businessmirror.com.ph Moody’s raises PHL to ‘positive’ May 29, 2012
[10] See The Lessons and Validity of Public Choice Theory Applied to the Chief Justice’s Corona Impeachment, May 29, 2012
[11] See Phisix: Very Impressive Day or Month End Close for May 2012, May 31, 2012
[12] Bloomberg.com Japan Adopts Stealth Intervention As Yen Gains Threaten Exporter Earnings February 7, 2012
[13] ADB ONLINE Asia Capital Markets Monitor August 2011
[14] Zero Hedge, Presenting Dave Rosenberg's Complete Chartporn, June 1, 2012
[15] Weiss Martin Lehman-Type Megashock Looming, Money and Markets May 21, 2012
Monday, April 30, 2012
“Pump and Dump” Policies Pumps Up Miniature and Grand Bubbles
A friend recently called to say that there have been numerous accounts of “miniature bubbles” in the local markets. Others claim that these have been brought about by unscrupulous people engaged in “pump and dump”.
In reality as I have been pointing out, miniature bubbles are symptoms of the ultimate bubble blower—central bank policies. Central bank policies distort people’s incentives towards money. Savings, investment and consumption patterns will have all been skewered. Where negative real rates punish savers, naturally people whose savings are being diminished through the erosion of purchasing power will seek higher yield, and thus, redeploy their savings into other activities which may include more consumption activities, speculation or high risk investments and or take up more debt to fund these activities. Even private sector Ponzi schemes has been flourishing under today’s environment[1]
In essence policies that tamper with money motivates the public to value short term over the long term.
Thus heightened price volatilities which are deemed as “pump and dump” or as “miniature bubbles” represent as symptoms rather than the cause. People will look for excuses to push up prices or speculate for the simple reason that policies have egged them to do so.
The easy money climate lures the vulnerable public to go for momentum and chase prices using any available tools (charts, corporate fundamentals or even tips[2] and rumors) to do so. And this is why pump and dumps happen.
Large price swings make some people think that stock market operators are culpable for such swing. But this would be mistaking trees for the forests. Absent easy money policies, bubbles and pump and dumps hardly has been a feature. Had there been mini bubbles or pump and dumps during the bear market of 2007-2008? No, because inflated assets were all deflating in response or as contagion to the real estate-banking crisis abroad.
Broken Markets
And as earlier pointed out[3], the US today has not been different, junk bonds or high yielding debt has been booming.
Writes the Buttonwood (Philipp Coggan) of the Economist[4]
Of course, the broader point is that investors are being pushed into these high-yielding assets because of the policy of the Fed (and most developed world central banks) of keeping interest rates close to zero. Similar reasoning drove the enthusiasm for structured products that financed the subprime boom.
Zero bound rates have prompted for yield chasing actions, here or in the US.
The mainstream finally comes to admit what I have been saying all along—that markets have been vastly distorted where one cannot use “fundamentals” in the traditional and conventional sense to evaluate investments.
The excessive price volatility in today’s markets does not match with the fluctuations of conventional metrics of financial ratios. Today’s price volatility has been incongruent with trends of corporate fundamentals. And thus as I earlier pointed out[5], anyone who believed in “fundamentals” would have sold as early as March.
Considering the huge jump in prices from the start of the year, we should be around at near the peak of 2007. So anyone who believes in this stuff ought to be shorting or selling the market. I won’t.
The left window from the chart above as I earlier posted last March has a time series that ended November of 2011. The right chart from DBS represents a more updated one albeit was updated until last March. Considering that the Phisix has now been drifting at over 5,150 which means valuations continues to climb higher away from these charts, the Phisix has become “priciest” stock market in Asia.
Yet leaning on earnings or conventional fundamental metrics, like the Heisenberg uncertainty principle, becomes a permanently moving target which is impossible to pin down, especially punctuated under today’s easy market climate.
Will I sell on the account of earnings/fundamentals? My answer is still no. Not until interest rates climb in response to consumer price inflation, or through heightened demand for credit, or questions over credit quality of government papers or the scarcity of capital becomes apparent[6]. Nominal interest rates are not a one-size-fits-all thing, and there are many measures (like real interest rates, CDS, yield curve et.al.) to gauge if the monetary environment has begun to tighten for one reason or another. This also should come in the condition that the hands of central bankers have also been shackled and would be unable to respond forcefully as they have been doing today.
For now central banks around will continue to find ways and means to push more easing measures in support of the asset markets which was highlighted by last week’s additional stimulus by the Bank of Japan (BoJ)[7]
The following excerpt from the mainstream loudly resonates on what I have been saying.
From the Financial Times[8],
Markets are broken. Accepted investment wisdom has been overturned and the basic tenets of value and diversification no longer work. The financial crisis put the market into a volatile “risk on, risk off” – or Roro – mode for which there is no cure.
For many investors, this has made stockpicking seemingly an impossible task. Markets once responded to their fundamentals. Now, disparate assets have a much greater tendency to move together, individual characteristics lost. Trusted strategies such as relative value and currency carry trades are nearly useless, overwhelmed by daily market-wide volatility.
“Assets now behave as either risky assets or safe havens, and their own fundamentals are secondary,” writes HSBC strategist Stacy Williams in a recent note. “In a world where most asset classes are synchronised, it becomes very difficult to achieve diversification. It also means that since most individual assets are dominated by a common price component, it becomes increasingly futile to invest in them based on their usual fundamentals.”
Though asset classes had been moving in closer correlation since the start of the financial crisis in 2007, the Roro trend became most apparent after the collapse of Lehman Brothers a year later. The uncertainty helped turn investing bimodal, where every price has been contaminated by systemic risk. Everything became a bet on whether we were closer to a global recovery or to deeper crisis.
So what recommendations do they offer for the public to deal with the state of “broken markets? They have three. One is to pick a position from the boom or the bust scenario, second is to chase momentum and third is to hedge positions through index futures.
I would like to emphasize on the second option, not because this is my preferred approach but because of its relevance to the conditions of the local markets, from the same article,
Another option is to seek out an investment strategy that still works. Momentum investing – in effect, buying the winners and selling the losers – is a method that HSBC analysts highlight as having been largely impervious to the risk trade. To chase a trend aims to harvest small but systematic mispricing of assets, and there is no reason to suppose these anomalies would disappear in bimodal markets, the broker argues. (In this context, the growth of high-frequency trading since the start of the crisis is unlikely to be coincidental.)
This simply means that the mainstream will largely be chasing momentum, by targeting frequency over magnitude through “harvest small but systematic mispricing of assets”. So in essence, high risk speculative activities or gambling (a.k.a “miniature bubbles” and “pump and dump”) has been recognized as the common or standardized feature of the current market place. So history will rhyme and a bust will be around the corner.
I would rather “time” the bubble cycle rather than go chasing prices. And this is why it is imperative for any serious investors to understand the bubble process or the boom bust cycle.
Stock Market is about Human Action
Finally financial markets signify a social phenomenon. There is a popular aphorism from former President John F. Kennedy, who said in the aftermath of the failed Bay of Pigs Invasion[9], which seems relevant to the financial markets,
Victory has a thousand fathers; defeat is an orphan.
Winning issues and or market tops tend to attract substantial participants as a function of easy money (get rich quick mentality), keeping up with the Joneses (bandwagon effect) or survivorship bias (focus on survivors or winners at the expense of the others) or social signaling (desire for greater social acceptance, elevated social status and or ego trips).
On the other hand market bottoms results to the opposite: depression, avoidance, isolation and animus behaviour for those caught by the crash.
Most people don’t realize that emotional intelligence or self discipline is key to surviving the market’s volatility, not math models or charts or any Holy Grail or Greek formulas. And this comes from the desire to attain self discipline than from advices of other people.
Yet self discipline is earned and acquired through knowledge and through the whetting of one’s skills based on these accrued knowledge. Alternatively, self discipline cannot be not given or inherited. And that’s why I vehemently opposed the suggestion by a popular religious personality, who had investments on a mutual fund, to get housemaids to invest in the stock market[10].
The incentive to acquire the desired knowledge and skills varies from individual to individual because they are largely driven by the degree of stakeholdings or the stakeholder’s dilemma or stakeholder’s problem[11].
Today’s information age has democratized access to information. What can be given are information relevant to attaining knowledge and skills. What can NOT be given is the knowledge that dovetails to one’s personality for the prudent management of one’s portfolio. Like entrepreneurship this involves a self-discovery process.
And most importantly, what can NOT be given are the attendant actions to fulfill the individual’s objectives.
Stock market investing is about people and their actions. That’s why this is a social phenomenon. No more, no less.
[1] See After 5,000: What’s Next for the Phisix?, March 5, 2012
[2] See New Record Highs for the Philippine Phisix; How to Deal with Tips February 20, 2012
[3] See Self-Discipline and Understanding Market Drivers as Key to Risk Management, April 12, 2012
[4] Buttonwood Hooked on junk, April 27, 2012, The Economist
[5] See Earnings Drive Stock Prices? International Container Terminal and Ayala Land, March 6, 2012
[6] See Global Equity Market’s Inflationary Boom: Divergent Returns On Convergent Actions, February 13, 2002
[7] See Bank of Japan Adds More Stimulus, April 17, 2012
[8] Financial Times ‘Roro’ reduces trading to bets on black or red April 20, 2012
[9] Quotationspage.com Quotation Details John F. Kennedy, "A Thousand Days," by Arthur M. Schlesinger Jr [1965]., p289. Comment made by JFK in the aftermath of the failed Bay of Pigs invasion, 1961.
[10] See Should Your Housemaid Invest In The Stock Market? September 5, 2010
[11] See Knowledge Acquisition: The Importance of Information Sourcing and Quality, March 6, 2011
Sunday, March 06, 2011
Knowledge Acquisition: The Importance of Information Sourcing and Quality
“The Pen Is Mightier Than The Sword”- coined by Edward Bulwer-Lytton English author, (also attributed to Dr. Jose P. Rizal)
Any serious or prudent investors in the financial markets would normally try to look for ways to improve on one’s returns. That’s if one recognizes what is workable and what isn’t. Thus, the main task of prudent investors in the financial markets is to screen information and theories and test them, and apply those that would seem as the most cogent, accordingly.
But again this isn’t true for many as returns might seem as a secondary importance. That’s because these economic agents obstinately adhere to biased or selectively chosen data (selective perception) which they interpret as applying to the whole (fallacy of composition), fixate on what is current (survivalship bias) while ignoring the rest, apply misleading definitions and embrace self contradictory and inconsistent theories.
I am just repeating what I said before. Sometimes it takes a deluge of information before the message sinks in.
Ignorance versus foolishness
Ignorance is one thing, foolishness is another. People who fail based on ignorance could be looked upon with compassion. They perhaps hardly knew of the consequences of their actions, which were most likely guided by wrong quality or sources of information.
But it’s different when people lose despite being informed or forewarned. This may be called as doggedness or practising financial religion.
For instance, when people refuse to heed of the inherent risks of conflict of interests that may arise among interacting agents[1], they are likely to fall into the Agency problem trap. Information embellished with statistics and presented as facts could mislead investors. It’s clearly an intangible or unseen risk, that’s because investors are likely to be unaware of the underlying incentives behind these presentations, which may shape or influence the way we think and how we allocate our resources.
And for non-exclusive reasons, boom-bust cycle happens because of information too. Credit fuels greed which impels people to look for information that would confirm on their preconceived notions. Bias, thereby, seeks information or analysis which performs the way dopamine functions, to serve the pleasure centers. So like drugs, misleading information will always have a market.
Also, in as much as price distortions from government policies affect the way people think, these are likewise exhibited through literatures. That’s because the mainstream usually focuses on the symptoms which are read as the cause and transmitted to the public as valid information or facts. This is also because mainstream information caters to short term orientation. In short, boom bust cycles occur also when people gorge on too much of false information.
Stakeholder’s Problem, If Birds Can Write
Most have been unwittingly seduced to the oversimplification of reading current events into market prices, for the reason that being wrong may have little consequence to them. In short, it’s usually a stakeholder’s dilemma or stakeholder’s problem[2]—where the incentives to secure knowledge are driven by the degree of stakeholdings.
Take for instance, a person who dabbles with the stock market, as sideline or for entertainment, will likely have a lesser intensity of incentives to acquire knowledge relative to an individual who lives by the stock market. The latter’s perceived risk factor is greater than the former who has other lines of revenues.
The varying situational incentives, thus, become crucial factors in determining knowledge acquisition.
Yet luck also plays a crucial role. Because no matter how wrong one’s ideas can be, for as long as such errors are made on the side of the general trend where the market is headed, market trends eventually remedies on such errors. And as a result, false ideas could lead to a self-attribution or self serving bias which according to Wikipedia.org[3], people attribute their successes to internal or personal factors but attribute their failures to situational factors beyond their control.
And this also applies even in academics, where wrong models can be seen as “workable”.
Prodigious author of the bestselling book, the Black Swan, Mr. Nassim Taleb writes of a marvellous example of in his forthcoming book[4],
Think of the following event. A collection of priestly persons from Harvard or some such place lecture birds how to fly. The bird flies. They write books, articles, and reports that in fact the bird has obeyed them, an impeccable causal link. They even believe their own theories. Birds write no such books, conceivably because they are birds, so we never get their side of the story. Meanwhile, the priests broadcast theirs.
Behind Media’s Altruisms And Biased Information
And as stated above, the quality and source of information matters.
The most likely source of information are usually the popular ones, such as mainstream media. They cater too our brain’s desire to get fed with visible, emotional, sensational, shocking or graphic linkages.
Take for instance, in the event of a disaster, media routinely appeals to the public to ask for donations. They appeal to the emotions by advocating charity work for the unfortunate victims. Media outfits create an aura where they are seen as doing purely social work. They become instantaneous heroes especially when celebrities lead them.
But this is only half true, what’s not seen is that by connecting to the public’s emotions and wallets they increase viewership on their medium. And the key to their revenues—advertisement—largely depends on the number of audiences. So media’s missives have almost always been attuned towards winning the public’s viewership. It’s like politics in a private format.
Thus for media, intention can be interpreted two ways, social work to help the community or self interests camouflaged by altruism.
In covering political philosophy, this is the same manner why socialism sells, it appeals to emotional center of the brain but are bereft of how “intentions” parlay into reality.
In terms of investment, it’s also the been same. Most people are continually deceived by information aired or disseminated by the media and their cohorts of experts, which for most instances have little value or are irrelevant.
As Rolf Dobelli writes[5],
Out of the approximately 10,000 news stories you have read in the last 12 months, name one that – because you consumed it – allowed you to make a better decision about a serious matter affecting your life, your career, your business – compared to what you would have known if you hadn’t swallowed that morsel of news.
The point is: the consumption of news is irrelevant to the forces that really matter in your life. At its best, it is entertaining, but it is still irrelevant.
Bottom line: information is vital to one’s decision making process, whether applied to the financial markets or in many other vital aspects of life.
The beauty of today’s technological advances is that information is not restricted or centralized but operates from a free market competitive environment.
And I am just part of the multitude of lowly voices here in the cyberspace trying to speak out what I see as true.
And unknown to most, revolutions begins with ideas.
[1] See Dealing With Financial Market Information, February 27, 2010
[2] See Philippine Elections: Why I Will Vote For President "None Of The Above”, May 5, 2010
[3] Wikipedia.org, Self-serving bias
[4] Taleb, Nassim Nicolas, Birds Do Not Write Books on Birds, Chapter 8, Anti Fragility
[5] Dobelli Rolf Avoid News, Towards a Healthy News Diet Dobelli.com (hat tip Bryan Caplan)