``If it were not for the elasticity of bank credit, which has often been regarded as such a good thing, a boom in security values could not last for any length of time. In the absence of inflationary credit the funds available for lending to the public for security purchases would soon be exhausted, since even a large supply is ultimately limited. The supply of funds derived solely from current new savings and current amortization allowances is fairly inelastic, and optimism about the development of security prices would promptly lead to a "tightening" on the credit market, and the cessation of speculation "for the rise." There would thus be no chains of speculative transactions and the limited amount of credit available would pass into production without delay.”- Fritz Machlup, The Stock Market, Credit and Capital Formation
At this time of the year, many institutions and experts will be issuing their projections. Some, like me[1], have already done so late last year.
Most of the forecasts will be positive as they will likely be anchored on the most recent past performance. And I would belong to this camp but for different reasons.
The Phisix Boom Bust Cycle At A Glance
While the mainstream interpret and analyse events mostly from the lens of economic performance, technical (chart) and corporate financial valuations, as many of you already know, I look at markets based boom bust (business) cycles as a consequence of incumbent government policies (see figure 1).
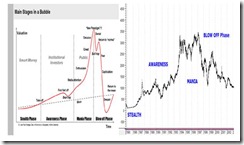
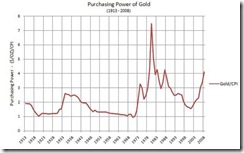
Figure 1: Stages of the Bubble and Phisix Bubble Cycle of 1980-2003
As one would note, the Phisix played out a full bubble cycle over a 23 year period in 1980-2003 (right window). The cycle also shows that in the interregnum, there had been mini-boom bust cycles (1987 and 1989).
A formative bubble cycle appears in the works since 2003, with the 2007-2008 bear market representing a similar mini countercycle similar to the previous period.
The lessons of the previous bubble cycle impart to me the confidence to predict that the Phisix will likely reach 10,000 or even more before the cycle reverses.
Although one can never precisely foretell when or how these stages would evolve, as past performance may not repeat exactly (yes but it may rhyme as Mark Twain would have it), the important point is to be cognizant of the whereabouts of the current phase of the bubble cycle.
And evidence seems to point out that we are in the awareness phase of the bubble cycle as demonstrated by the swelling interest for Philippine assets. The latest success of the $1.25 billion PESO 25-year bond offering[2] and the upgrade of the nation’s credit rating by Moody’s[3] serve as good indications.
In addition, local authorities audaciously and ingeniously tested the global market’s risk appetite for the first time ever with a substantial placement at a long tenor that passed with flying colours. With 160 investor subscriptions mostly from the US and Europe, the Peso bond offering further illustrates the mechanics of cross currency arbitrages or carry trades arising from monetary policy divergences.
Of course for the mainstream, this will be read and construed as signs of confidence. For me, these events highlight the yield chasing phenomenon in response to present policies.
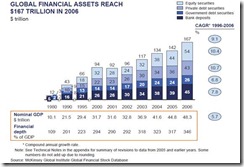
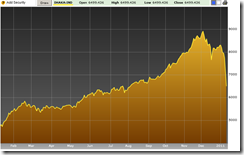
Figure 2: McKinsey.com[4] Global Financial Assets
And considering that the global financial markets have immensely eclipsed economic output as measured by GDP (see figure 2), the yield chasing dynamic will likely be magnified, largely driven by the disparities in money policies and economic performance. Another apt phrase for this would be ‘rampant speculation’.
To reiterate for emphasis, anent the Phisix, we don’t exactly know if there would be another countercyclical phase or if the present bubble cycle will persist unobstructed until it reaches its zenith.
In addition, we can’t identify how the rate of acceleration of the cycle will unfold nor can we ascertain the exact timeframe for each of the stages in succession.
Instead we can measure the bubble cycle by empirical evidences such as conditions of systemic credit, rate of asset or consumer price inflation and mass sentiment.
The Growing Influence Of Negative Real Interest Rates
With interest rates artificially suppressed, which fundamentally distorts the price signals that account for the time preference of the public over money and the economic balance of the credit market, policy influenced interest rates and the interest rate markets that revolve around them will lag the rate of inflation.
In short, real interest rate will be negative for an extended period.
In the milieu where government here and abroad have been working to stimulate ‘aggregate demand’ via the interest rate channel and for developed economies who employ unconventional monetary operations in support of the banking sector and the burgeoning fiscal deficits, the impact on consumer price inflation will likely go beyond the targets of their respective authorities.
As an aside, some governments in the Europe, such as Hungary, Bulgaria, Poland, Ireland and France have begun to “seize” private pensions[5], but applied in diverse degrees, all of which have been aimed at funding unsustainable deficits accrued from welfare programs and the cost of bailouts.
This only serves as evidence that governments are getting to be more desperate and would unflinchingly resort to unorthodox means to keep the status quo.

Figure 3: Global Negative Real Interest Rates[6] and Record Food Prices (courtesy of US Global Funds and Bloomberg)
Real interest rates were at the negative zone for several countries (see figure 3 left window) even as 2010 had largely been benign.
But with the most recent explosion of food prices[7] to record levels on a global scale as measured by the Food and Agriculture Organization Index (FAO- right window), aside from surging energy prices, we should expect consumer price inflation rates to ramp up meaningfully.
Meanwhile, Federal Reserve Chairman Ben Bernanke imputes high oil prices to “strong demand from emerging markets”[8]. This would represent as a half truth as Mr. Bernanke eludes discussing the possibility of the negative ramifications from his policies.
In the Philippines, such broad based price increases in many politically sensitive products or commodities have even triggered alarmism of the local media. Similar to Fed chair Ben Bernanke, local authorities and the media seem to have conspired to sidetrack on the scrutiny of the real origins[9] of such price hikes.
Nonetheless, most governments will, as shown above, try to contain interest rates from advancing, as this would increase the cost of financing of many of their liabilities. But this will only signify a vain effort on their part as politics will never overcome the laws of scarcity.
For the public, the growing recognition of widening negative real interest rates will further spur the dynamics of reservation demand—call it speculation, hoarding or punting, or in the terminology of the Austrian economists the “crack-up boom” or the flight to commodities as the purchasing value of money erodes.
And that those who expect fixed income to deliver positive returns while underestimating on the impact of changes in the rate of inflation will suffer from underperformance.
Yet the same dynamics are likely to incite further “risk taking” episodes (note again: reservation demand and not consumption demand), one of the fundamental source of boom bust or bubble cycles.
As a caveat, I am not an astrologer-seer who will predict day-to-day movements, rather in taking the role of an entrepreneur we should see or parse the business or bubble cycle as an active process that is subject to falsification.
This also means market actions won’t be moving in a linear path.

Figure 4: Markets Drive Policies (source: Danske Bank and economagic.com)
And as earlier stated, policy interest rates trail inflation.
And where market based rates partly reflect on prevailing inflation conditions, one would observe that market rates almost always lead policy rates (see figure 4 right window). Despite the Fed’s QE program aimed at keeping interest rates low, markets have started pricing US treasuries higher. In other words, policy interest rates react to market developments than the other way around.
In a parallel context, the interest rate markets seem to also price aggressively[10] Fed fund rate futures (left window) contradicting the promulgated policy by the US Federal Reserve.
Bottom line: the surging consumer inflation signifies as unforeseen consequences to the current polices.
The Continuing Policy of Bailouts
Of course higher interest rates, at a certain level, will ultimately be detrimental to local or national economies, particularly to those in the hock.
But the risk of a high interest rate environment will depend on the leverage of policymaking. Debt in itself will not be the main source of the risk, prospective policy actions will.
Many government institutions (or even politicians) are aware of the risks of overstretched debt levels.
In the US, the Federal Reserve has its 220 PhDs and many more allied economists in the academia or in financial institutions[11] to apprise of the debt-economic conditions and the available policy options and their possible implications. The problem is that they are math model based and hardly representative of actual state of human affairs.
Besides, most of them are predicated on Keynesian paradigms whose fundamental premises are in itself structurally questionable. Thus, market and economic risks come with the methodology guiding the policy actions that are meant to address present concerns.
For instance, should the problem of debt be resolved by taking on more debt?
Applied to US states whom are in dire financial morass, will the US, through the US Federal Reserve, bail them out?
Ben Bernanke pressed by the Senate recently said no[12], but his statements can’t be relied upon as proverbially carved in the stone. That’s because this would largely depend on the degree of exposure of the banking system’s ownership of paper claims of distressed States on its balance sheets. A ‘no’ today can be a ‘yes’ tomorrow if market volatility worsens and if credit market conditions deteriorates based on the financial conditions of the banking system.
Early last year, Ben Bernanke spoke about ‘exit strategies’[13] when at the end of the year exit strategies transmogrified into QE 2.0 and where talk of QE 3.0[14] has even been floated. Talk about flimflams.
In short, since the banking system is considered as the most strategic economic sector by the present political authorities, enough for them to expose tens of trillions worth of taxpayer money[15], then the path dependence by the Fed would be to intuitively bailout sectors that could weigh on their survival.
The fact that the US has had an indirect hand in the bailout of Europe[16], via the IMF and through the activation of the Fed swap lines hammers the point of Bernanke’s preferred route.
And of course, we shouldn’t be surprised if the Fed collaborated anew with European governments to any new bailout schemes in case of any further escalation in the financial woes of European banks and or governments.
So the US has been in a bailout spree: the US banking system, the Federal government, Europe and the rest of the world (through Fed swaps and through the transmission mechanism of low interest rates), so why stop at US states?
Hence given the policy preference, we should expect a policy of bailouts as likely to continue and should hallmark a Bernanke-led Federal Reserve.
And the policy of bailouts is likely to also continue in developed economies affected by the last crisis.
All these cheap money will have an impact on the relative prices of assets and commodities worldwide.
Thus, we see these internal and external forces affecting the Philippine assets--equities, real estate and corporate bonds.
What Would Stop Bailouts?
The preference for bailout option would only be stymied by natural (market) forces—higher interest rates from heightened inflation expectations (through broad based price signals-we seem to be seeing deepening signs of this)—which reduces the policy tools leverage available to the authorities, the resurrection of bond vigilantes as seen in the deterioration of the credit quality of sovereign papers, or a Ron Paul.
Of course the Ron Paul option, I would see as most unlikely given that a one man maverick is up against very well entrenched institutionalized vested interest groups which have been intensely associated with the government.
As Murray N. Rothbard exposited[17], (bold highlights mine)
But bankers are inherently inclined toward statism. Commercial bankers, engaged as they are in unsound fractional reserve credit, are, in the free market, always teetering on the edge of bankruptcy. Hence they are always reaching for government aid and bailout. Investment bankers do much of their business underwriting government bonds, in the United States and abroad. Therefore, they have a vested interest in promoting deficits and in forcing taxpayers to redeem government debt. Both sets of bankers, then, tend to be tied in with government policy, and try to influence and control government actions in domestic and foreign affairs.
This leaves us with inflation and credit quality which I think are tightly linked underpinned by a feedback mechanism.
A bubble bust elsewhere in the world from high interest rates would drain capital, but if inflation remains high this will reduce authorities leverage to conduct further bailouts. Think the stagflation days of 1970s (the difference is the degree of overindebtedness today and in the 70s).
In addition, high interest rates at a certain point will puncture global governments liquidity bubble which will expose nations propped up by the liquidity mask to deteriorating credit quality.
And at this point, crisis affected governments, including the US, are likely to choose between the diametrically opposed extreme options of continuing to inflate that may lead to hyperinflation or to declare a debt default (Mises Moment).
As a side note, under such scenario, people who argue that the US dollar’s premier status as international reserve won’t be jeopardized would be proven wrong, if, for instance, the policy route would be to inflate.
The health of any currency greatly depends on society’s perception of the store of value function. Once the public recognizes that debasement of the currency has been a deliberate policy and likely a process that would persist overtime, the perception of the store of value function corrodes significantly. And the public will likely look for an alternative.
In finding little option among the available choices, society may choose to revert to a commodity linked currency as default currency, as it always has.
Albeit the worst alternative would be that debasement of the currency or inflationism will lead to totalitarianism.
As Friedrich von Hayek warned[18],
At present the prospects are really only a choice between two alternatives: either continuing an accelerating open inflation, which is, as you all know, absolutely destructive of an economic system or a market order; but I think much more likely is an even worse alternative: government will not cease inflating, but will, as it has been doing, try to suppress the open effects of this inflation; it will be driven by continual inflation into price controls, into increasing direction of the whole economic system. It is therefore now not merely a question of giving us better money, under which the market system will function infinitely better than it has ever done before, but of warding off the gradual decline into a totalitarian, planned system, which will, at least in this country, not come because anybody wants to introduce it, but will come step by step in an effort to suppress the effects of the inflation which is going on.
So the policy tethers will depend on the conditions of several factors such as the rate of commodity and consumer price inflation, real and nominal interest rates, falling bond prices or rising yields, currency volatility and administrative policies choices of protectionism or globalization/economic freedom and capital and price controls vis-a-vis the status quo.
Profiting From Folly: The Inflationary Boom And Cyclical Banking Crisis
For now, the incipient signs of commodity inflation and rising rates have yet to diffuse into alarming levels.
Thus, I perceive that much of the applied inflationism will likely get assimilated into financial assets, thereby projecting an inflationary boom.
So going back to assembling of the pieces of the jigsaw puzzles, the Philippine bubble cycle will merely represent as one of the symptoms of the escalating woes wrought by the paper money system.
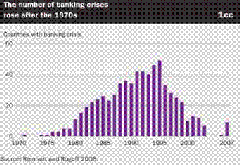
Figure 5: World Bank[19]: Surging Banking Crisis Post 1970s
The Philippine markets like other emerging markets have been the one of the main beneficiaries of the transmission mechanisms of the monetary policies of developed economies aside from the impact from the domestic low interest rate policies.
This favourite chart of mine (see figure 5) reveals of the manifold banking crisis post the Bretton Woods dollar-gold exchange convertibility standard.
While many in the mainstream blame the spate of crisis on capital account liberalization and international capital mobility, this misleads because it is the capacity to inflate (or expansion of circulation credit) rather than capital flows that causes malinvestments. Capital flows merely represent as transmission channels for inflating economies. Like in most account, the mainstream misreads effects as the cause. The repeated banking crisis suggests of a continuing cycle which implies of more crisis to come in the future, despite new regulations introduced meant to curb future crisis.
So while the mainstream will continue to blabber about economic growth, corporate valuations or chart technicals, what truly drives asset prices will be no less than the policies of inflationism here and abroad that leads to cyclical boom and bust in parts of the world including the Philippines.
And that would be the most relevant big picture to behold. Yet relevance seems not a measure of importance for most.
Nevertheless, we’ll heed Warren Buffett’s sage advice,
Look at market fluctuations as your friend rather than your enemy; profit from folly rather than participate in it.
Get it? Our objective then is to profit from folly by playing with the cycle rather than against it.
[1] What To Expect In 2011, December 20, 2010
[2] FinanceAsia.com Philippines and Stats ChipPac usher in new year with style, January 7, 2011
[3] Inquirer.net Moody’s upgrades PH outlook to ‘positive’, January 6, 2011
[4] McKinsey.com Mapping global capital markets: Fourth annual report, January 2008
[5] csmonitor.com European nations begin seizing private pensions, January 2, 2011
[6] US Global Investors Investor Alert, December 31, 2010
[7] Bloomberg.com World Food Prices Jump to Record on Sugar, Oilseeds, January 5, 2011
[8] WSJ Blog, Bernanke on Munis, Oil and Fed’s Mandate, January 7, 2011
[9] The Code of Silence On Philippine Inflation, January 6, 2011
[10] Danske Bank, 2011 off to a good start, Weekly Focus, January 7, 2011
[11] Grim Ryan Priceless: How The Federal Reserve Bought The Economics Profession, Huffington Post, September 7, 2009
[12] Reuters.com Bernanke balks at bailout for states, January 7, 2011
[13] Testimony of Chairman Ben S. Bernanke on the Federal Reserve's exit strategy Before the Committee on Financial Services, U.S. House of Representatives, Washington, D.C. February 10, 2010
[14] QE 3.0: How Does Ben Bernanke Define Change, December 6, 2010
[15] $23.7 Trillion Worth Of Bailouts?, July 29, 2010
[16] Reuters.com U.S. plays 2 roles in European bailout plan, May 11, 2010
[17] Rothbard, Murray N. Wall Street, Banks, and American Foreign Policy, 2005 lewrockwell.com
[18] Hayek, F. A. A Free-Market Monetary System, p. 23
[19] World Bank Data Statistics Worldview 2009 p.9