I’ve been writing about how the internet/web has functioned (and will continue to function) as a critical instrument for the widespread dissemination of the principles of freedom based on what I call the Hayekian Knowledge revolution platform—characterized by a decentralized-horizontal flow of information.
You can read my earlier explanations here or here.
And in realizing that the web has been undermining the current political order, governments around the world has, intuitively, resorted to counterbalancing these evolving spontaneous order by attempting to regulate the internet or by imposing censorship. A good example are reports from wikileaks (such as this and this) that has exposed many covert government activities.
Well my observations seem to be getting substantial validations.
Here is the Economist, (bold emphasis mine)
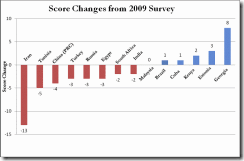
THE number of people with access to the internet has more than doubled in the past five years to over two billion. Many governments have responded with regulation and repression, according to a report published on April 18th by Freedom House, which assigns countries an internet freedom score. Nine of the 15 countries that the Washington-based think-tank assessed in 2009 fared worse this year, among them Iran, Tunisia and China. On the plus side, citizens are growing increasingly adept at sidestepping these threats to their internet freedoms, and the use of social media did much to galvanise political opposition across the Arab world in recent months. Indeed web-users in some countries, such as Georgia and Estonia, have more freedom now than they did two years ago.
Some great charts
The massive growth of Internet Users (Freedom House)
Social media as a widely used application (Internet world stats)
Index of Internet freedom: 37 country score of internet freedom (0 Best, 100 Worst)
A green-colored bar represents a status of “Free,” a yellow-colored one, the status of “Partly Free,” and a purple-colored one, the status of “Not Free” on the Freedom of the Net Index. (Freedom House)
More internet freedom versus less internet freedom (Freedom House)
How Asia has fared.(Freedom House)
Freedom House identifies the typical government’s countermeasures:
(From Freedom House, bold emphasis original)
Key Trends
* Explosion in social-media use met with censorship: In response to the growing popularity of internet-based applications like Facebook, YouTube, and Twitter, many governments have started targeting the new platforms as part of their censorship strategies. In 12 of the 37 countries examined, the authorities consistently or temporarily imposed total bans on these services or their equivalents.
* Bloggers and ordinary users face arrest: Bloggers, online journalists, and human rights activists, as well as ordinary people, increasingly face arrest and imprisonment for their online writings. In 23 of the 37 countries, including several democratic states, at least one blogger or internet user was detained because of online communications.
* Cyberattacks against regime critics intensifying: Governments and their sympathizers are increasingly using technical attacks to disrupt activists’ online networks, eavesdrop on their communications, and cripple their websites. Such attacks were reported in at least 12 of the 37 countries covered.
* Politically motivated censorship and content manipulation growing: A total of 15 of the 37 countries examined were found to engage in substantial online blocking of politically relevant content. In these countries, website blocks are not sporadic, but rather the result of an apparent national policy to restrict users’ access to information, including the websites of independent news outlets and human rights groups.
* Governments exploit centralized internet infrastructure to limit access: Centralized government control over a country’s connection to international internet traffic poses a significant threat to free online expression, particularly at times of political turmoil. In 12 of the 37 countries examined, the authorities used their control over infrastructure to limit widespread access to politically and socially controversial content, and in extreme cases, cut off access to the internet entirely.
The battle rages.





No comments:
Post a Comment