From Zero Hedge (bold emphasis mine)
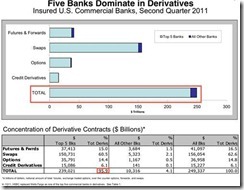
The latest quarterly report from the Office Of the Currency Comptroller is out and as usual it presents in a crisp, clear and very much glaring format the fact that the top 4 banks in the US now account for a massively disproportionate amount of the derivative risk in the financial system. Specifically, of the $250 trillion in gross notional amount of derivative contracts outstanding (consisting of Interest Rate, FX, Equity Contracts, Commodity and CDS) among the Top 25 commercial banks (a number that swells to $333 trillion when looking at the Top 25 Bank Holding Companies), a mere 5 banks (and really 4) account for 95.9% of all derivative exposure (HSBC replaced Wells as the Top 5th bank, which at $3.9 trillion in derivative exposure is a distant place from #4 Goldman with $47.7 trillion). The top 4 banks: JPM with $78.1 trillion in exposure, Citi with $56 trillion, Bank of America with $53 trillion and Goldman with $48 trillion, account for 94.4% of total exposure. As historically has been the case, the bulk of consolidated exposure is in Interest Rate swaps ($204.6 trillion), followed by FX ($26.5TR), CDS ($15.2 trillion), and Equity and Commodity with $1.6 and $1.4 trillion, respectively. And that's your definition of Too Big To Fail right there: the biggest banks are not only getting bigger, but their risk exposure is now at a new all time high and up $5.3 trillion from Q1 as they have to risk ever more in the derivatives market to generate that incremental penny of return.
At this point the economist PhD readers will scream: "this is total BS - after all you have bilateral netting which eliminates net bank exposure almost entirely."
True: that is precisely what the OCC will say too. As the chart below shows, according to the chief regulator of the derivative space in Q2 netting benefits amounted to an almost record 90.8% of gross exposure, so while seemingly massive, those XXX trillion numbers are really quite, quite small... Right?
...Wrong. The problem with bilateral netting is that it is based on one massively flawed assumption, namely that in an orderly collapse all derivative contracts will be honored by the issuing bank (in this case the company that has sold the protection, and which the buyer of protection hopes will offset the protection it in turn has sold). The best example of how the flaw behind bilateral netting almost destroyed the system is AIG: the insurance company was hours away from making trillions of derivative contracts worthless if it were to implode, leaving all those who had bought protection from the firm worthless, a contingency only Goldman hedged by buying protection on AIG. And while the argument can further be extended that in bankruptcy a perfectly netted bankrupt entity would make someone else whole on claims they have written, this is not true, as the bankrupt estate will pursue 100 cent recovery on its claims even under Chapter 11, while claims the estate had written end up as General Unsecured Claims which as Lehman has demonstrated will collect 20 cents on the dollar if they are lucky.
The point of this detour being that if any of these four banks fails, the repercussions would be disastrous. And no, Frank Dodd's bank "resolution" provision would do absolutely nothing to prevent an epic systemic collapse.
...
Lastly, and tangentially on a topic that recently has gotten much prominent attention in the media, we present the exposure by product for the biggest commercial banks. Of particular note is that while virtually every single bank has a preponderance of its derivative exposure in the form of plain vanilla IR swaps (on average accounting for more than 80% of total), Morgan Stanley, and specifically its Utah-based commercial bank Morgan Stanley Bank NA, has almost exclusively all of its exposure tied in with the far riskier FX contracts, or 98.3% of the total $1.793 trillion. For a bank with no deposit buffer, and which has massive exposure to European banks regardless of how hard management and various other banks scramble to defend Morgan Stanley, the fact that it has such an abnormal amount of exposure (but, but, it is "bilaterally netted" we can just hear Dick Bove screaming on Monday) to the ridiculously volatile FX space should perhaps raise some further eyebrows...
Such immense risk exposure by ‘Too Big to Fail’ (TBTF) US banks entail that political actions or policy making will likely be directed towards the prevention of a massive deflationary banking sector collapse from a derivatives meltdown.
And problems at the Eurozone could just be the pin that could ‘pop the bubble’.
This implies greater likelihood of persistent bailout policies which mostly will be coursed through inflationism. It’s an “inflate or die” for politically privileged TBTF banks in the US or in the Eurozone.
Again political leaders appear to be using the financial markets as leverage to negotiate for the passage of such policies.
Proof?
From today’s Bloomberg article, (bold emphasis mine)
U.S. Treasury Secretary Timothy F. Geithner warned at the annual meeting of the IMF failure to combat the Greek-led turmoil threatened “cascading default, bank runs and catastrophic risk.”
German Chancellor Angela Merkel said euro-region leaders must erect a firewall around Greece to avert a cascade of market attacks on other European states that would risk breaking up the currency area.
Expanding the powers of the region’s rescue fund, the European Financial Stability Facility, as agreed by European leaders in July is necessary to avoid Greece’s problems from spilling over to other countries, Merkel said late yesterday on ARD television. The fund’s permanent successor, due to take effect in mid-2013, is needed “so we can in fact let a state go insolvent” if it can’t pay its bills, she said.
Policy makers can make the EFSF more “efficient” by leveraging it without involving the ECB, German Finance Minister Wolfgang Schaeuble said over the weekend. He also raised the prospect of bringing in the permanent backstop before 2013.
Bank of Canada Governor Mark Carney estimated 1 trillion euros ($1.3 trillion) may have to be deployed while U.K. Chancellor of the Exchequer George Osborne said a solution is needed by the time that Group of 20 leaders meet in Cannes, France, on Nov. 3-4.
Policymakers have been intensifying their jawboning or mind conditioning of the public of the exigencies of more bailouts.
They will come. But, perhaps, only after the markets endure more pain.

No comments:
Post a Comment