``Everything you can imagine is real." -Pablo Picasso (1881-1973) Famous Spanish painter and sculptor
The region which holds more than $2.5 trillion in foreign currency reserves has also turned into a substantial holder of sovereign bonds of advanced economies. Aside,
In a recent speech at
``Intra-regional financial integration has lagged. For example, the extent to which investors in
``Data on cross-border banking show that the major foreign lenders in emerging Asia are generally European, Japanese, or
``Local stock markets also have a large international presence, but few foreign players come from the rest of
``Finally, in spite of initiatives underway to promote cross-border holdings, regional integration of bond markets remains underdeveloped by most metrics. According to the Bank for International Settlements, the expanding issuance of foreign-currency-denominated bonds by Asian sovereigns and corporates is for the most part in U.S. dollars--and is marketed outside of
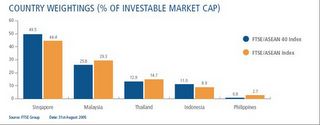
The initiatives to integrate and deepen capital markets could be clearly seen with the establishment of ADB’s Asianbondsonline, an ASEAN+3 initiative funded by the Government of Japan, which provides investors centralized access to information on the region’s 13 bond markets as well as the indexation of select ASEAN publicly listed companies into FTSE/ASEAN 40 and FTSE ASEAN. Both indices are meant for performance benchmarking and to “brand” ASEAN as an asset class. These vehicles would be available for retail and institutional investors via Exchange Traded Funds (ETF) or through derivatives ‘OTC’ contracts.
The share distribution of the participant countries comprising the FTSE/ASEAN portfolio based on free float and liquidity screened considerations according to the FTSE International.
So far, according to BSP data, foreign portfolio flows into the country has mostly been from the Euro zone which accounted for $268 million of the $517 million cumulative outflows in 2004. ASEAN accounted for $137 million with
Further, the region has also embarked on a currency swap agreement via the Chiang Mai Initiative, which aims to reduce foreign currency crisis, support foreign exchange reserves of member countries and provide sufficient liquidity and exchange rate stability within the region. The swap agreement was designed as a contingent support for countries experiencing a foreign exchange crisis to access foreign currency, mostly in US dollar, from another member country to bolster reserves until the crisis has passed.
Lately the
In the continuing efforts to further integrate and strengthen the region’s financial markets, Mr. Kato further noted in his speech that it would require lengthy reforms as to induce the much needed cross border investments, these includes ``enhancing information disclosure and accounting standards, strengthening the role of minority shareholders, supporting effective creditor rights, tightening the prudential supervision of financial firms, and strengthening court processes and the judicial systems.” As well as on the regulatory side ``harmonizing the laws, regulations, tax treatment, and market structures that still prevent investors--from both within and outside Asia--from building pan-regional portfolios.”
Lastly, developing the bond market would also require the marketability of other products such as Municipal and corporate bonds, as well as Mortgage securities and other related instruments. This should provide alternative avenues for fund raising, hedging as well as market based valuations on the underlying securities.
In addition, compared to the previous commodity futures market, particularly the defunct Manila International Futures Exchange (MIFE), which traded foreign and NOT local commodities; in my opinion, a genuine local commodity futures exchange that deals with the country’s major resources or crops should be in place.
Where economics 101 tells us that “markets are usually a good way to organize economic activity”, the establishment of a commodity futures market that allows for pricing, delivery, payment and credit would essentially benefit producers and farmers. Through market based pricing, the farmers or producers would be able to realize the full value of their harvest or produce, eliminate or reduce the role of traders and middlemen and undertake hedging positions for seasonal volatilities in order to reduce risk. 
No comments:
Post a Comment