Many of you may be familiar with the idiom to “fit a square peg to a round hole”. This simply means, according the Free dictionary, “trying to combine two things that do not belong or fit together.”
From Oftwominds.com
I think this expediently characterizes mainstream’s misplaced notion about Japan’s long held predicament: deflation.
Because of the mammoth boom-bust cycle seen in Japan's property and stock markets, which led to Japan’s economic “lost decade”, the image of the Great Depression of the 1930s has frequently been conjured or extrapolated as the modern version for it.
Of course, there is a second major reason for this, and it has been ideologically rooted, i.e. the bubble bust has been used as an opportunity to justify the imposition of theoretical fixes by means of more interventionism.
Has a deflationary depression blighted Japan?
If the deflation is measured in what mainstream sees as changes in the price level of the consumer price index, then the answer is apparently a NO.
As you would notice from the graph from moneyandmarkets.com, deflation isn’t only episodic (or not sustained), but likewise Japan’s intermittent economic growth (blue bars) came amidst the backdrop of negative or almost negative CPI (red line)! In other words, economic growth picked up when prices where in deflation--this translates to real growth.
And if measured in terms of changes in monetary aggregates, then obviously given that the changes in Japan's M2 has been steadily positive, as shown by the chart above from Northern Trust, all throughout the lost decade, then we can rule out a "monetary deflation".
Of course, the next easiest thing for the mainstream to do is to pin the blame on credit growth.
chart from McKinsey Quarterly
While there is some grain of truth to this, this view isn’t complete. It doesn’t show whether the lack of credit growth has been mainly from demand or supply based. It doesn't even reveal why this came about.
We can even say that such generalizations signify as fallacy of division. Why? Because the problem with macro analysis is almost always predicated on heuristics-or the oversimplification of variables involved in the analytic process.
Banks have not been the sole source of Japan’s ‘credit’ market. In fact, there are many as shown below.

``Providing credit to consumers is generally referred to as "consumer credit." This can be classified into two types. The first is providing credit to allow consumers to buy specific goods and services, which is called "sales on financing," and the second is providing credit in cash, which is called "consumer finance." There are many types of financial service companies that offer consumer finance, including banks, but compenies which specialize in providing small loans to consumers are referred to as "consumer finance companies."
Further promise.co.jp describes the function of consumer finance companies as providing credit
``including loans but, unlike banks, do not take deposits are referred to as "non-banks." Leasing companies, installment sales finance enterprises, credit card companies, and consumer finance enterprises belong to the non-bank category.”
So how has Japan’s alternative financing companies performed during the lost decade?
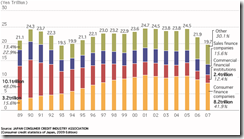
1) During the lost decade or from 1989-2007, the share of consumer financing companies (yellow-orange bar) has exploded from 15.6% to 41.9%!
2) Other forms of credit (apple green bar) also jumped from 13.4% to 30.1% during the same period.
3) The bubble bust has patently shriveled the share of 'traditional bank' based lending or the share of lending from commercial financial institutions collapsed from 48% to 12.4%.
4) The sales financing companies likewise lost some ground from 22.4% to today’s 15.6%.
All these reveals that while it is true that nominal or gross lending has declined, there has been a structural shift in the concentration of lending activities mainly from the banking to consumer financing companies and "other" sources.
And importantly, it disproves the idea that Japanese consumers have “dropped dead” or that the decline in lending has been from the demand side.
Obviously banks were hampered by the losses stemming from the bubble bust. But this wasn’t all, government meddling in terms of bailouts were partly responsible, as we wrote in 2008 Short Lessons from the Fall of Japan
``One, affected companies or industries which seek shelter from the government are likely to underperform simply because like in the Japan experience, productive capital won’t be allowed to flow where it is needed.
``Thus, the unproductive use of capital in shoring up those affected by today's crisis will likely reduce any industry or company’s capacity to hurdle its cost of capital.
``Two, since capital always looks for net positive returns then obviously capital flows are likely to go into sectors that aren't hampered by cost of capital issues from government intervention.
``This probably means a NEW market leadership (sectoral) and or money flows OUTSIDE the US or from markets/economies heavily impacted by the crisis.”
Apparently, our observation was correct, the new leadership had shifted to the financing companies.
But there is more.
Because the banking system had been immobilized, which conspicuously tightened credit access, the explosive growth of the financing companies emerged as result of demand looking for alternative sources of supply.
In addition, financing companies, who saw these opportunities circumvented tight regulations or resorted to regulatory arbitrage, in order to fulfill this role.
According to the Federal Bank of San Franscisco, (bold emphasis mine)
``Prior to the passage of the new legislation, Japan had two laws restricting consumer loan interest rates. The Interest Rate Restriction Law of 1954 set lending rates based on the size of the loan, with a maximum rate of 20 percent. The Investment Deposit Interest Rate Law, last amended in 2000, capped interest rates on consumer loans at 29.2 percent on the condition that any rate exceeding 20 percent requires the written consent of the borrower. Most Japanese CFCs have been operating in this “gray zone” of interest rates, charging rates between 20 and 29.2 percent.
``Non-bank consumer finance companies in Japan comprise a ¥20 trillion industry, averaging 4 percent annual loan growth over the past decade while bank loan growth was negative. Most of the approximately 14,000 registered lenders are small, with the largest seven operators-which include the consumer finance arms of GE Capital and Citigroup- having a 70 percent market share. The significant growth in this industry can be traced directly to the collapse of the asset bubble in the early 1990s when consumers whose collateral had dwindled in value turned to CFCs offering uncollateralized loans. Adding to the success of the industry was the fact that CFCs were more service-oriented than the retail operations of Japanese banks, offering a wider network of loan offices, 24-hour loan ATMs, and faster credit approval.”
In short, banking regulations and policies proved to be an important obstacle to credit access.
Yet, the Japanese government worked to rehabilitate on these legal loop holes. This led to further restrictions to credit access.
According to Yuki Allyson Honjo, Senior Vice President, Fox-Pitt Kelton (Asia), [bold emphasis mine]
``The Supreme Court made a ruling in 2006 to make it easier for individuals to collect repayment of interest in excess of that allowed under the Interest Rate Restriction Law (grey zone interest). The court ruling called into question the legality of the grey zone. This prompted revisiting of the rules governing money lending and forced companies to create grey zone reserves. People were entitled to claim the "extra" interest they paid from their lenders.
``Revisions to the money lending laws were passed, and by June 2010, the maximum lending rate will be unified to rates specified under the Interest Rate Restriction Law, thereby eliminating the grey zone. Loans will be limited to a third of borrowers' annual income. For loans exceeding 1 million yen, moneylenders would be obligated to inquire about the applicant's annual income. Implementation is still ambiguous. Regulators are to have more power, such as the ability to issue business improvement orders.
``The rate decline held various consequences for the industry. Margins were lowered as lenders were forced to lower their lending rates. There was a reduction in volume, with loans to current borrowers no longer being profitable, some customers were deemed too high-risk to borrow at the lower rates. Customers could borrow less due to new legislation restricting total loans as a percentage of income. Also, there has been a rise in write-offs.
``The result of all of this is that the number of registered money lenders has dropped precipitously since regulation began in 1984. The loan market is an oligopoly with 60% of the total loan balance with the Big Four, and 90% percent with the top 25 firms. This oligopoly was created in reaction to regulation.
``Stock prices for money lending companies began to drop steadily in 2006, predating the current economic crisis. The necessity for grey zone reserves has caused problems in money lenders' balance sheets. In March 2007, there are many large negative numbers visible in the balance sheets of Aiful, Takefuji, Acom and Promise. Loans approval rates crashed around 2006, with Aiful only accepting 7% of loans recently, down from over 50% before the 2006 Supreme Court rulings. Every month, 25-30 billion yen is paid out by money lenders to customers in grey zone claims, increasing steadily since 2006. Grey zone refunds have begun to pick up recently as a result of the recent economic crisis.
``The consequences of the court ruling and the re-regulation are that the Big Four companies found direct funding difficult. Credit default swaps have increased dramatically for Takefuji and Aiful, who are now essentially priced to fail. Bond yields also increased and going to market is difficult for these companies.
``From the regulator's perspective, re-regulation has been largely a success, given their aims. The size of the industry and the number of players have been reduced. The government has greater control on the industry and over-borrowing has been reduced. In regard to this last goal, its success is unclear as black market statistics are not reliable. In fact, anecdotes suggest that black market lending demand has increased.”
So aside the aftermath bubble bust, the bailouts of zombie institutions and taxes we discovered that government diktat have been the instrumental cause of supply-side impairments in Japan's credit industry.
Moreover, the other consequences has been to restrain competition by limiting the number of firms which led to the persistence of high unemployment rates, and fostered too-big-to-fail "oligopolies" institutions.
So we can conclude two things:
1. Japan’s economic malaise hasn’t been about deflation but about stagnation from wrong policies.
2. The weakness in Japan’s credit growth essentially has also not been about liquidity preference and the attendant liquidity trap, or the contest between capital and labor, or about subdued aggregate demand, but these has been mostly about the manifestations of the unintended consequences of the Japanese government's excessive interventionism.
As Ludwig von Mises wrote,
``The various measures, by which interventionism tries to direct business, cannot achieve the aims its honest advocates are seeking by their application. Interventionist measures lead to conditions which, from the standpoint of those who recommend them, are actually less desirable than those they are designed to alleviate. They create unemployment, depression, monopoly, distress. They may make a few people richer, but they make all others poorer and less satisfied.”
And it is here that we see how the mainstream can't seem to fit the square peg (deflation) to the round hole (stagnation).




No comments:
Post a Comment