Google engineering director and futurist Ray Kurzweil believes we are close to realizing everlasting life and is dead-set on getting us there.The inventor and noted author believes the key to such a scientific breakthrough is a system of 'bridges' that enable the body to move from strength to strength over time.The youthful 65-year-old currently takes 150 supplements a day, which he argues if the first bridge.The idea is to build enough bridges to ensure the body holds out long enough for life-lengthening technology to come into its own.He has likened the biology of the body to computer software and believes we are all 'out of date'.In an interview with Canadian magazine Maclean's, Kurzweil says he hopes the supplements will keep him healthy enough to reach the 'nanotech revolution'.'I can never say, “I’ve done it, I’ve lived forever,” because it’s never forever,' he said.'We’re really talking about being on a path that will get us to the next point.'Bridge one: Stay as healthy as possible with diet and exercise and current medicine.'The goal is to get to bridge two.'Bridge two (is) the biotechnology revolution, where we can reprogram biology away from disease.'And that is not the end-all either.'Bridge three is to go beyond biology, to the nanotechnology revolution.'At that point we can have little robots, sometimes called nanobots, that augment your immune system.'We can create an immune system that recognizes all disease, and if a new disease emerged, it could be reprogrammed to deal with new pathogens.'Such robots, according to Kurzweil, will help fight diseases, improve health and allow people to remain active for longer.
The art of economics consists in looking not merely at the immediate hut at the longer effects of any act or policy; it consists in tracing the consequences of that policy not merely for one group but for all groups—Henry Hazlitt
Tuesday, October 22, 2013
Ray Kurzweil: Bridge to Bridge System Towards an Everlasting Life
Tuesday, June 26, 2012
Doug Casey: The Human Species will Evolve to Other Species
The visionary Doug Casey believes that people will continue to evolve in line not only with the changes in the environment, but also along with the changes in technology or through adaption to technology
Once humans get established in space, evolution will take over – and take off. Before then, however, and likely even before we leave the planet, I'll bet there's going to be a lot of intentional, as opposed to natural, genetic alteration. It will start with efforts to eliminate undesirable genes that predispose one to heart disease, cancer, or genetic disorders. But while we're at it, why not also select for blue eyes, taller, more muscular frame, greater intelligence, and anything else people might want their children to have? Some people won't want to go that route, preferring to leave things to nature, but their children will be at a disadvantage to those whose parents have selected superior genes. That could lead to speciation along several lines.
Read the rest here.
I encountered this article earlier.
But having been immersed in too many readings, it took Bob Wenzel’s post to remind me to share with you this, what I think is a, significant outlook.
If I am not mistaken, Mr. Casey may have been reading futurist Ray Kurzweil’s Singularity is Near.
Tuesday, April 05, 2011
Remarkable Welfare Gains From The Power of Computing Represent Signs Of Things To Come
Two economists project that the welfare benefits from Personal computers adds up to $1,700 per person annually. And this represents a tremendous growth from the previous years.
The Wall Street Journal Blog reports, (bold emphasis mine)
Despite all the wrenching change the computer age has brought, humanity is probably better off than it would have been if the PC had never been invented. Now, economists have taken a stab at figuring out exactly how much better off we are.
The economists — Karen Kopecky of the Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta and Jeremy Greenwood of the University of Pennsylvania — traced the history of the computer market back to the introduction of the Apple II in 1977 to calculate how much value, or “utility”, American consumers derive from a given amount of computing power. They then looked at how much we actually paid for that computing power, in the form of desktop PCs, laptops, notebooks, software and so on. The difference, known as the “welfare gain”, is the benefit we get from personal computers above and beyond what we pay for them.
Back in the days of magnetic-tape memory, the annual benefit was pretty small — somewhere between zero and about $6 for the average American, adjusted for inflation, depending on the method of calculation. But by 2009, the price of computing power had fallen more than 99.8% and personal computers had become a lot better and more widely used. As a result, the welfare gain rose to somewhere between $1,300 and $2,100 per person, the economists’ estimates suggest. Ballpark average: $1,700.
That’s a massive benefit, adding up to about $500 billion, or 5% of total consumer spending in 2009.
To be sure, the economists’ estimates are based on some assumptions that, while common in the world of economics, are open to debate. For one, they assume that people are extremely rational, and always buy exactly the number of personal computers that maximizes their utility. To the extent that irrational impulses drive people to buy computers, or to the extent that the use of computers entails costs people don’t recognize (say, attention-span deficits or Internet addiction), then the actual benefit could be significantly smaller.
My comments:
First of all, I am flabbergasted that the article would resort to the word “probably” as to ascribe the personal computer’s benefit to mankind, as if such benefits have not been conspicuous.
Second, while I agree that the personal benefits from these computers have been immense, given that the article does not say how or what sort of utility had been measured or rated, I would posit that the figures had been vastly underestimated.
Had the PC been assessed solely from PC sales and turnover? How about time saving gains from added productivity and work process efficiency via diversified applications?
How about savings or value added derived from declining communication costs or from diminishing [Coase’s laws—search costs, contracting and coordination costs or otherwise known as] transaction costs, or the enhancement of business processes or even organizational capital (Garrett Jones)?
And how about the benefits of leisure (e.g. games, etc…) and other intangible gains such as real time connectivity with parents, relatives, friends and associates? Or how about the virtue or non-virtue of self-expression via social networking media?
Three, all these go to show why economists fall for the aggregate trap. They tend to quantify things even if they can’t.
Lastly, nonetheless the above only gives more proof that the world has been transitioning to the age of digitization or the information age, where more and more activities of our lives are becoming decentralized (Third Wave) enabled by technology.
Chart from Ray Kurzweil: Law of Accelerating Returns
I’d add that should the trend of innovations of applications and devices accelerate, this will even deepen and make this transition more widespread.
As Law Professor and author Butler Shaffer writes, “Decentralized technologies are causing us to rethink and redefine what we mean by "society."
The welfare gains of the PC are just signs of things to come.
Friday, February 11, 2011
Will Humans Achieve Immortality By 2045?
So says Ray Kurzweil, chief proponent of Singularity is Near –“an era in which our intelligence will become increasingly nonbiological and trillions of times more powerful than it is today—the dawning of a new civilization that will enable us to transcend our biological limitations and amplify our creativity.”
From Time’s Lev Grossman
Here's what the exponential curves told him. We will successfully reverse-engineer the human brain by the mid-2020s. By the end of that decade, computers will be capable of human-level intelligence. Kurzweil puts the date of the Singularity — never say he's not conservative — at 2045.
Read the rest here
Ray Kurzweil’s betting on the exponential growth of human ingenuity which converts technology into our life preserver.
Tuesday, January 18, 2011
Will Falling Population (Demographic Time Bomb) Lead To A Reversal Of Globalization?
Lately I have encountered several commentaries suggesting that the “demographic time bomb” (falling population) will pose a risk to globalization by creating imbalances that would lead to political upheavals.
Here are two:
From Neil Howe and Richard Jackson in Global Aging And The Crisis Of The 2020's (bold emphasis mine)
“Rising pension and health care costs will place intense pressure on government budgets, potentially crowding out spending on other priorities, including national defense and foreign assistance. Economic performance may suffer as workforces gray and rates of savings and investment decline. As societies and electorates age, growing risk aversion and shorter time horizons may weaken not just the ability of the developed countries to play a major geopolitical role, but also their will.”
From Morgan Stanley’s Spyros Andreopoulos and Manoj Pradhan in ‘Ten for the Teens’(bold emphasis mine)
“The increase in macro instability comes at a time of major demographic transition in most DM and many EM economies. As populations become older, the demand for economic security - stable jobs, pensions - increases. This tension between higher instability and increased demand for security is likely to find its political expression in a backlash against globalisation. So far, the benefits of globalisation - higher income levels for most, i.e., the large middle class - have outweighed its drawbacks - increased competition and job instability. This has kept the globalisation show on the road until now. As this balance tips because the preferences of the middle class shift towards more security/stability, globalisation is likely to stall or reverse.”
There seems to be two separate issues here: unsustainable welfare states and globalization.
However the comments above attempt to make a connection which, for me, looks tenuous and confusingly premised on the fallacious ‘aggregate demand’.
Protectionism Equals Security?
Here is how I understand this: stripped out of the spending capacity due to old age, and with a government hobbled by fiscal straitjacket, the lack of demand (from both the private and the public) means slower economic growth which likewise would extrapolate to a political milieu that shifts from risk appetite (globalization) towards demand for ‘security and stability’ (protectionism), or in short, political stress.
For instance the Morgan Stanley tandem does an incredible turnaround, ``So far, the benefits of globalisation - higher income levels for most, i.e., the large middle class - have outweighed its drawbacks - increased competition and job instability. This has kept the globalisation show on the road until now.”
Are they suggesting that people who benefited from globalization will eventually bite the proverbial hand that feeds them? Are they suggesting too that people will see “security and stability” from lower incomes?
Will protectionism or restricting market activities make goods and services needed by the ageing society abundant and affordable? To the contrary, protectionism will only highlight on the shortages and the exorbitance of these economic goods that should lead to even more instability.
Murray N. Rothbard refuted this age old fallacy, he explained, (bold highlights mine)
It is difficult to see how a decline in population growth can adversely affect investment. Population growth does not provide an independent source of investment opportunity. A fall in the rate of population growth can only affect investment adversely if
-All the wants of existing consumers are completely satisfied. In that case, population growth would be the only additional source of consumer demand. This situation clearly does not exist; there are an infinite number of unsatisfied wants.
-The decline would lead to reduced consumer demand. There is no reason why this should be the case. Will not families use the money that they otherwise would have spent on their children for other types of expenditures?
Thus the problem of declining population can be helped by accepting immigrants or adopting to greater social mobility or the globalization of labor and by even more free trade.
We shouldn’t underestimate how people adjust to the new realities from the current underlying conditions. Importantly, we shouldn’t write off productivity of the senior citizens too (why? see below).
Illusion Or Reality?
Next would be the issue of welfare states. Once society realizes that the welfare state has been unsustainable, will people fight violently to retain the status quo (even if this is recognized as not possible) or will they cope up with the new reality?
The former would fall as part of the entitlement mentality engendered by excessive dependency or the moral hazard from political distribution while the latter will likely result from the realization that there’s no free lunch.
And perhaps in the realization that bellicosity won’t further society’s interests, they may opt for the latter (accepting harsh reality) than the former (live in a charade). And any political tensions from the succeeding reforms would signify as symptoms of ‘resistance to change’ than from a key reversal of political sentiment.
In the context of abrupt political-economic transitions from a crisis, Iceland’s violent riots from her financial crash of 2008 didn’t mechanically translate to close door ‘security’ based policies, as Iceland remains “moderately” economic free (44th), according to Heritage Foundation, even as the crisis did have some negative impact on her economic freedom ratings (due to higher taxes and government spending).
From Heritage Foundation
The point is that the notion that crisis will instigate a radical reversal of people’s sentiment from openness to protectionism seems likely misguided.
Today, Iceland has shown signs economic recovery and has even applied to join the European Union (aimed at achieving more financial and trade openness, aside from social mobility)!
Protectionism likewise did not spread like wildfire in 2008, as earlier discussed.
Ignoring Technology
Another factor would be technology.
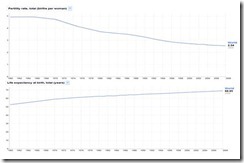
While it may true that fertility rates may be going down (upper window), it is often ignored how the advances in technology has continually enhanced people’s living conditions.
From Google Public Data
Global Life expectancy (lower window) has lengthened from 50 years to 68.95 years over the past 50 years. Japan reportedly has some 41,000 centenarians (over 100 years old)! [But I won’t be lucky to live this long, because of my love affair with beer]
And if futurist Ray Kurzweil is correct, people’s life span may extend to 120 years (by 2030) or even more (180 years) as rate of technology advances accelerates.
Again Murray Rothbard on the importance of technological advancement
“technological progress, is certainly an important one; it is one of the main dynamic features of a free economy. Technological progress, however, is a decidedly favorable factor. It is proceeding now at a faster rate than ever before, with industries spending unprecedented sums on research and development of new techniques. New industries loom on the horizon. Certainly there is every reason to be exuberant rather than gloomy about the possibilities of technological progress.”
In short, should these advances occur then all demographic projections should be thrown to the garbage bin, as they are falsely premised and would be rendered irrelevant.
The basic problem with mainstream insights is that people are treated like unthinking automatons. And because of this they’re most likely wrong.
The ultimate threat to globalization is inflationism and not demographic trends.
Saturday, June 05, 2010
Technology Curve: Terrific Advances In Supercomputers
.bmp)
.bmp)
Thursday, November 13, 2008
The Future According To The Futurists
Since we are in the practice of spotting trends but not limited to financial markets, an interesting article from practicing Futurists (the the study or forecasting of trends or developments in science, technology, political or social structure, etc.-dictionary.com or futurologists) outlines 10 predictions for 2009 and beyond.
The 10 forecasts has been excerpted from the World Future Society (Hat Tip Ray Kurzweil) All highlights mine.
1. Everything you say and do will be recorded by 2030. By the late 2010s, ubiquitous, unseen nanodevices will provide seamless communication and surveillance among all people everywhere. Humans will have nanoimplants, facilitating interaction in an omnipresent network. Everyone will have a unique Internet Protocol (IP) address. Since nano storage capacity is almost limitless, all conversation and activity will be recorded and recoverable. -Gene Stephens, "Cybercrime in the Year 2025," July-Aug 2008, p. 34
2. Bioviolence will become a greater threat as the technology becomes more accessible. Emerging scientific disciplines (notably genomics, nanotechnology, and other microsciences) could pave the way for a bioattack. Bacteria and viruses could be altered to increase their lethality or to evade antibiotic treatment. Another long-term risk comes from nanopollution fallout from warfare. Nanoparticles could potentially cause new diseases with unusual and difficult-to-treat symptoms, and they will inflict damage far beyond the traditional battlefield, even affecting future generations. -Barry Kellman, "Bioviolence: A Growing Threat," May-June 2008, p. 25 et seq.; Antonietta M. Gatti and Stefano Montanari, "Nanopollution: The Invisible Fog of Future Wars," May-June 2008, p. 32
3. The car’s days as king of the road may soon be over. More powerful wireless communication that reduces demand for travel, flying delivery drones to replace trucks, and policies to restrict the number of vehicles owned in each household are among the developments that could thwart the automobile’s historic dominance on the environment and culture. If current trends were to continue, the world would have to make way for a total of 3 billion vehicles on the road by 2025. -Thomas J. Frey, "Disrupting the Automobile’s Future," Sep-Oct 2008, p. 39 et seq.
4. Careers, and the college majors for preparing for them, are becoming more specialized. An increase in unusual college majors may foretell the growth of unique new career specialties. Instead of simply majoring in business, more students are beginning to explore niche majors such as sustainable business, strategic intelligence, and entrepreneurship. Other unusual majors that are capturing students’ imaginations: neuroscience and nanotechnology, computer and digital forensics, and comic book art. Scoff not: The market for comic books and graphic novels in the United States has grown 12% since 2006. -World Trends & Forecasts, Sep-Oct 2008, p. 8
5. There may not be world law in the foreseeable future, but the world’s legal systems will be networked. The Global Legal Information Network (GLIN), a database of local and national laws for more than 50 participating countries, will grow to include more than 100 counties by 2010. The database will lay the groundwork for a more universal understanding of the diversity of laws between nations and will create new opportunities for peace and international partnership. -Joseph N. Pelton, "Toward a Global Rule of Law: A Practical Step Toward World Peace," Nov-Dec 2007, p. 25
6. Professional knowledge will become obsolete almost as quickly as it’s acquired. An individual’s professional knowledge is becoming outdated at a much faster rate than ever before. Most professions will require continuous instruction and retraining. Rapid changes in the job market and work-related technologies will necessitate job education for almost every worker. At any given moment, a substantial portion of the labor force will be in job retraining programs. -Marvin J. Cetron and Owen Davies, "Trends Shaping Tomorrow’s World, Part Two," May-June 2008, p 41
7. The race for biomedical and genetic enhancement will-in the twenty-first century-be what the space race was in the previous century. Humanity is ready to pursue biomedical and genetic enhancement, says UCLA professor Gregory Stock, the money is already being invested, but, he says, "We’ll also fret about these things-because we’re human, and it’s what we do." -Gregory Stock quoted in "Thinking Globally, Acting Locally, Living Personally," Nov-Dec 2007, p. 57
8. Urbanization will hit 60% by 2030. As more of the world’s population lives in cities, rapid development to accommodate them will make existing environmental and socioeconomic problems worse. Epidemics will be more common due to crowded dwelling units and poor sanitation. Global warming may accelerate due to higher carbon dioxide output and loss of carbon-absorbing plants. -Marvin J. Cetron and Owen Davies, "Trends Shaping Tomorrow’s World, Part One," Mar-Apr 2008, p. 52
9. The Middle East will become more secular while religious influence in China will grow. Popular support for religious government is declining in places like Iraq, according to a University of Michigan study. The researchers report that in 2004 only one-fourth of respondents polled believed that Iraq would be a better place if religion and politics were separated. By 2007, that proportion was one-third. Separate reports indicate that religion in China will likely increase as an indirect result of economic activity and globalization. -World Trends & Forecasts, Nov-Dec 2007, p. 10
10. Access to electricity will reach 83% of the world by 2030. Electrification has expanded around the world, from 40% connected in 1970 to 73% in 2000, and may reach 83% of the world’s people by 2030. Electricity is fundamental to raising living standards and access to the world’s products and services. Impoverished areas such as sub-Saharan Africa still have low rates of electrification; for instance, Uganda is just 3.7% electrified. -Andy Hines, "Global Trends in Culture, Infrastructure, and Values," Sep-Oct 2008, p. 20
My comment:
Some of the scenarios mentioned above seems like stuff from the movies, e.g. Sandra Bullock’s "The Net" (Sorry I forgot the titles, if you recall pls suggest).
Although the massive progression, integration and convergence of technology could have both good and bad side effects.
The bad side includes the risks of losing civil liberties, more government intrusion (think national ID), potential conflicts arising from demographic shifts especially in terms of religion and advances in weaponry system which can be exceptionally sophisticated and or even more lethal.
The good side includes longer lifespan due to massive improvement in science, a more advanced and sophisticated lifestyle, alternative means of transports, diversified energy sources and more progressive economies (due to greater division of labor).
Finally, for any of the above scenario to take shape, profitability and investments will be an important underlying concern. This means prospective investment themes.




.bmp)