The essence of the interventionist policy is to take from one group to give to another. It is confiscation and distribution.-Ludwig von Mises
Some say that falling markets won’t account for the imminence of QE 3.0.
That would signify a blatant misread.
For me, falling markets account as one of the two possible conditions for the re-institution of QE
As I previously wrote[1],
Although I expect that this extension won’t come automatically which I see as either tied to the US Congressional vote to raise debt limits or in reaction to growing pessimism in the some of the world’s economic environment due to a cyclical slowdown or to the accrued effects of signaling channels applied by governments or from mainstream’s addiction to inflationism. Besides if the debt ceiling will be raised this gives further excuse for the FED to activate QE 3.0.
Today’s financial markets have essentially been influenced by political forces more than economic developments. All the accounts of bailouts, rescues and assorted market interventions (quantitative easing, currency interventions, credit margin hikes on commodity markets) are part of the many examples. All these have effects on the marketplace[2].
Thereby, the state of the current sluggishness in the Philippine and global markets could likely be symptomatic of more of political design than merely reactions from economic forces.
Markets as Hostage to Politics
This week, we saw a political representative of China and one of the Fed officials jawbone on the possible adverse repercussions[3] from the palpable dabbling of a brief debt default by several Republican lawmakers as the debt ceiling is being deliberated.
This week, reports also say US President Obama pondered on using tax cuts as possible concession to the Republicans to reach a compromise[4].
Earlier both President Obama[5] and Treasury Secretary Tim Geithner[6] warned of a global recession if a settlement on raising the debt limits won’t be reached.
About a month ago a series of studies from the US Federal Reserve came out to state that commodity prices have not been tied with Quantitative Easing. Also during the same period commodity markets were slammed by the repeated increases of credit margins[7] of several commodities.
The point is the markets are seemingly being held hostage by politics. The idea is that markets can indeed go down, for the plain reason that the market is being used as leverage to secure political concessions.
Intervening and manipulating, directly or indirectly in the marketplace has been the du jour trend of today.
And what appears to be the imperative political tenet resonates in the famous statements of President Obama’s former Chief of Staff Rahm Emanuel[8]...
Never let a serious crisis go to waste. What I mean by that is it's an opportunity to do things you couldn't do before.
Don’t you see, the vehement aversion to crises has been the hallmark of today’s politicking?
This runs along with the prevailing economic ideology which guides on the directives of the political orthodoxy, where the prescription to supposed “market failures” would be through interventions channeled mainly through Keynesian concepts of ‘parting with liquidity’ (giving up liquid assets in exchange for employment-creating illiquid assets) ‘euthanizing the rentiers’ (low interest rates), and ‘socializing investment’ (public private partnership)[9].
Even Harvard Professor Carmen Reinhart along with her colleagues observes of the ongoing non-market features of today’s marketplace[10] characterizing an environment which they call as financial repression, (bold emphasis mine)
Undoubtedly, a critical factor explaining the high incidence of negative real interest rates was the aggressively expansive monetary policy (and, more broadly, official central bank intervention) in many advanced and emerging economies during the crisis. This raises the broad question of the extent to which current interest rates reflect the stance of official large players in financial markets rather than market conditions. A large role for nonmarket forces in interest rate determination is a key feature of financial repression.
In short, official players will likely manipulate markets to meet their ends.
Stoking Fear
And part of such tactical operations would probably mean instilling fear to paint an ambiance of urgency.
And speaking of fear, the current stock market declines seem to have twitched Wall Street’s fear measures higher.

Whether seen from original computation of volatility ($VXO), the current VIX ($VIX) and volatility applied to the CBOE S&P 500 3-Month ($VXV) signs of fear have emerged. The rallying US dollar appears to chime with such an environment.
This fear has been evident even seen Google Search trends (chart below).

Lately Google has shown increasing searches by the public for ‘double dip’. Meanwhile news and articles featuring double dip have also grown.
Given that Wall Street has been a politically privileged sector, with more fear comes the greater clamor for interventions.
Wall Street operates in an environment fostered by the moral hazard, which reveals on their sense of entitlement.
Rescues signify political events. Only in the pretext of growing risks of a crisis that would incur pernicious broad market and economy welfare implications will bailout measures be deemed as justifiable by politicians and the bureaucracy.
And along this line, it wouldn’t be farfetched to say today’s actions in the marketplace could be part of the effects of the conventional signaling channel tool used by central banks in preparation for the next set of rescue measures.
That’s why mainstream media seems to have misinterpreted Bernanke’s last comments as having ‘no QE 3.0’ when the fact is Bernanke’s statements prior to November 2010’s QE 2.0 resembled his latest comments[11].
In short, if there is no emergency, then there will be no rescue. Falling markets sow the seeds of alarmism, and thereby, setting in motion the conditions required for prospective rescues.
As previously noted, this has been the routine recourse by political leaders almost everywhere.
A Possible Growth Scare and Not a Crisis

Despite the recent signs of fear, credit markets in the US and in Euro seem to remain calm.
The above chart from Danske Bank[12] shows marginal signs of impact from the current equity-commodity downdraft on US bond markets and on interbank loans as represented by the LIBOR OIS spread.
But this has not been powerful enough to stir the proverbial hornet’s nest.

And the cyclical downturn of major economies following a vigorous upside could also be part of the story.
As the Danske Research writes[13],
Global leading indicators have suffered a setback recently, pointing to slower growth. The US ISM dropped considerably in May and European PMIs also fell faster than expected. China, on the other hand, seems to have stabilised, as the PMI dropped slightly in May and order-inventory bottomed.
The current declines could represent more of a growth scare instead of imminent risks of crisis or recession as presented by politicians.
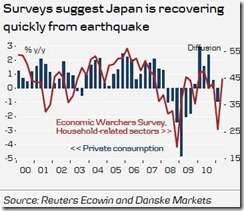
Also, Danske Research[14] thinks that the dislocation from Japan’s recent disaster has partly been the culprit of the downturn of economies. But signs according to them are that Japan has been recovering fast.
The above evidences seem to show that the essence of fear being manifested by reports which highlights ‘double dip’ concerns may seem unwarranted.
A growth scare and not a crisis could be taking place.
Yet it is quite obvious that politics have been dominating feature of the marketplace.
[1] See ASEAN’s Equity Divergence, Foreign Fund Flows and Politically Driven Markets, June 5, 2011
[2] See Poker Bluff: No Quantitative Easing 3.0?, June 5, 2011
[3] See China Warns US on Debt Default as ‘Playing with Fire’, June 9, 2011
[4] See US President Obama Mulls Tax Cuts as Compromise for Raising Debt Limits June 9, 2011
[5] Huffington Post, Obama Debt Ceiling Warning: Raise Limit Or Risk Global Recession, April 15, 2011
[6] Wall Street Journal Geithner Issues Warning on Debt Ceiling, May 15, 2011
[7] See War on Commodities: Intervention Phase Worsens and Spreads With More Credit Margin Hikes! , May 14, 2011
[8] Wall Street Journal A 40-Year Wish List, January 28, 2009
[9] what-when-how.com SOCIALIZATION OF INVESTMENT
[10] Reinhart Carmen M., Kirkegaard Jacob F., Sbrancia M. Belen Financial Repression Redux, June 2011, IMF FINANCE & DEVELOPMENT
[11] See Bernanke’s Comments Mirror Those of Pre-QE 2.0 in 2010, June 8, 2011
[12] Danske Bank, Bad macro indicators and Greece weigh on market sentiment, Weekly Credit Market, June 10, 2011
[13] Danske Bank, Global: Business Cycle Monitor, June 6, 2011
[14] Danske Bank, ECB confirms July rate hike, Weekly Focus June 10, 2012






