The art of economics consists in looking not merely at the immediate hut at the longer effects of any act or policy; it consists in tracing the consequences of that policy not merely for one group but for all groups—Henry Hazlitt
Thursday, June 20, 2013
Chart of the Day: Bernanke’s 2014 Taper
Monday, June 10, 2013
Phisix Meltdown: A Reality Check on the Bullish Dogma
"Carry works as long as things don't change, and what really changed in our mind a few weeks ago was the message from the Fed," Rajiv Setia, the head of US rates research at Barclays in New York, said in a May 30 phone interview. "Once you start worrying about hikes, all these trades start to fail massively."
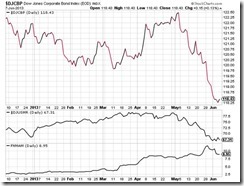
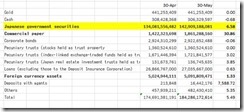
The Japanese government’s tax revenues have been estimated by the Ministry of Finance at ¥ 43.1 trillion for 2013. National debt service accounts for ¥ 22.241 trillion which accounts for 24% of the general account budget or 51.4% of tax and stamp revenues. This may have been computed using perhaps less than 1%, if based on the yields of 10 year bonds. Thus a spike of interest rates to 2% will most likely wipe out the Japanese government’s ability and capacity to pay her obligations.
Thursday, June 06, 2013
Phisix and the SET: Why Talking Up the Embattled Stock Markets Won’t Work
Stock exchanges in the Philippines and Thailand have moved to soothe investors after speculation the U.S. Federal Reserve may scale back bond purchases prompted selloffs by overseas investors.Stock Exchange of Thailand President Charamporn Jotikasthira today urged investors not to panic, saying economic and corporate earnings growth in Southeast Asia’s second-biggest economy remains strong. The benchmark SET Index dropped to two-month low. Philippine Stock Exchange President Hans Sicat described the selloff as an “extreme overreaction.”The Philippines benchmark index has slumped 11 percent and the Thai gauge 8.4 percent since May 22, when Fed Chairman Ben S. Bernanke said policy makers could consider reducing the pace of monetary stimulus if the nation’s labor market improves. Overseas investors have sold a net $414 million of Thai stocks and $147 million of Philippine shares this month.“Foreign net selling is an extreme overreaction to Bernanke’s” outlook on possible stimulus cuts, Sicat said in a televised interview with ABS-CBN News today. “Technical corrections tend to be buying opportunities for others who are more conservative.”
A reduction of stimulus, and not a cessation, simply means of a partial tightening of monetary environment. This could be suggestive of the advent of high interest rate regime.
Sept. 1929: "There is no cause to worry. The high tide of prosperity will continue." Andrew W. Mellon, Secretary of the TreasuryOct. 14, 1929: "Secretary Lamont and officials of the Commerce Department today denied rumors that a severe depression in business and industrial activity was impending, which had been based on a mistaken interpretation of a review of industrial and credit conditions issued earlier in the day by the Federal Reserve Board". New York TimesJanuary 21, 1930: "Definite signs that business and industry have turned the corner from the temporary period of emergency that followed deflation of the speculative market were seen today by President Hoover. The President said that reports to the Cabinet showed the tide of employment had changed in the right direction." News dispatch from WashingtonMay 1, 1930: "While the crash only took place six months ago, I am convinced we have now passed the worst and with continued unity of effort we shall rapidly recover. There is one certainty of the future of a people of the resources, intelligence and character of the people of the United States-that is prosperity." President HooverJune 29, 1930: "The worst is over without a doubt." James J. Davis Secretary of Labor.Sept. 12, 1930: "We have hit bottom and are on the upswing" James J. Davis Secretary of Labor.
Saturday, September 15, 2012
Video: Former Fed Governor on Bernanke’s QE: Unproven Experiment , Risks of Exit have to be Higher
Here are some key points:
Ben Bernanke is a “modest man” with “an immodest move”
Yesterdays move was an “aggressive move”…which means that “They are really worried with the state of the economy”….part of it could be that “They must be dealing with some of the Tail Risk Europe is in an early innings of a recession” while Asia has been “weakening too”
For Mr. Warsh “Exit is a four letter world” where “exiting from a monetary policy is technically difficult”. He sees the benefits from QE as “incontestably small and that the risks are unknown”…He further notes that “This is an unproven experiment so risks of exit have to be higher”
So the FED’s hands are essentially tied and risks are magnified rather than suppressed.
Mr. Warsh also talks about the moral hazard risks by open ended QE on Washington where
“The risk in Washington is real too. I don’t mean political risks. What I mean is if the Federal Reserve is now in a business of private pullout, “rabbit out of hat” everytime the economy loses control, then the rest of Washington can say there is not much we can do or need to do because Bernanke has got my back. I do not think that is his intent”.The implied incentive provided by QE to Washington is to rely on more inflationism.
Mr. Warsh adds that in reality the US state of the economy has been struggling “We’re not in a panic we are in a lousy recovery”
Short term oriented “informercial” policies have also been amplifying risks, yet this has been the framework guiding Fed and Washington policies
“For 4-5 years…Washington has been in the business of solving the next quarter, solving for the next election $5 trillion trying to turbocharge the economy we’ve been running stimulus program after stimulus program and GDP can look a little better next quarter but we’ve been running this program like it’s an infomercial…this time of short term policy has not served as well. I don’t they served the politicians well. We need to fundamentally change what our time horizon is”Real recovery must come through improving competitiveness
“The private sector has much better at asset allocation than the government”And that central planning has been hobbled by the knowledge problem
“There is lots of talent there, but they do not know which direction capital should go”Mr. Warsh delineates what central banks can and cannot do
“Central banks are in the business of buying time…until the economy gets into the groove. But what we heard yesterday was that we will be buying time for a very long time”He also notes that
“Policy makers should be humble”Most importantly Mr. Warsh sees the market as I see it
“If you continue to look at the markets right now, where asset prices continue to melt up where asset prices are driven less by fundamentals in particular companies and more by speeches and policies come out of Washington you are taking this risks. Risk are highest in the economy when measures of risk ARE lowest, when I look at the VIX at this level and you compare that to the headlines you guys read every morning they certainly do not seem in sync that’s when shocks happen”Shocks happen because inflationism has obscured the market price signals.
Sunday, August 15, 2010
Why Deflationists Are Most Likely Wrong Again
“After the crisis arrives and the depression begins, various secondary developments often occur. In particular, for reasons that will be discussed further below, the crisis is often marked not only by a halt to credit expansion, but by an actual deflation — a contraction in the supply of money. The deflation causes a further decline in prices. Any increase in the demand for money will speed up adjustment to the lower prices. Furthermore, when deflation takes place first on the loan market, i.e., as credit contraction by the banks — and this is almost always the case — this will have the beneficial effect of speeding up the depression-adjustment process.” Murray N. Rothbard
I find it bizarre for many mainstream experts, if not nearly all, would try to interpret government’s policy actions as means to support the economy (read: property markets) and NOT the politics (read: the banking system).
And these are the same set of people who appear to impassionedly invoke the reprehensible deities of deflation in order for the government to apply more inflationism.
Figure 1: Mark Perry[1]: Relative Bank Failures/St. Louis Fred: M2 annual change
It doesn’t really matter whether the US government put in line an estimated $23.7 billion in bailouts[2], and the countless alphabet soup of stop-gap measures or programs in terms guarantees, swaps, and the various functionality of last resorts, all of which had been applied to ensure the untrammelled flow of liquidity into the financial system.
What seem to only matter to them is that “deleveraging” and the attendant alleged price contraction on every level will be due to loss of “aggregate demand” which ensures a deflationary outcome. As if these “deleveraging” is straightforwardly corollary with “price decline” regardless of the validity and strength of causation linkages.
Yet it’s been nearly two years since deflationists have brandished charts similar to the M2 in figure 1 (right window) to call for the unsustainability of the current economic recovery, and now, since the deflationary spiral hasn’t still happen, they invoke new references such as low interest rates to try to argue their case based on a preconceived bias.
Equally, they now junk this piece of evidence since it has now gone against their argument. So selective perception dominate the mainstream’s reasoning to argue for their rabid fear of deflation.
It doesn’t really matter too, that today’s banking failure hardly matches EVEN the savings and loans meltdown during the 90s and remains a fraction to the domino effect of bank collapses during the GREAT Depression of the 1930s (left window). Yes this includes the 110th bank in Illinois[3], which failed August 13th.
Gustave Le Bon appear to be correct[4] anew when dealing with crowd perception, “A crowd thinks in images, and the image itself immediately calls up a series of other images, having no logical connection with the first.”
These people fail to acknowledge that the deflation mess of 1930s wasn’t only due to banking collapses which paved way for the monetary contraction but importantly had also been due to the massive waves of regulations imposed that inhibited trade (Smoot-Hawley Act) and the necessary adjustments in the price levels within the system (New Deal Programs)[5].
Blindness Stems From Political and Economic Religion
The difference why many pundits can’t seem to see is because the monetary contraction they’ve hoped for, out of their predetermined bias, had been offset by an expansion of free trade worldwide.
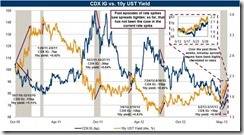
Thus whatever contraction in US based credit from the banking system had clearly been offset by a surge in globalization[6]and the attendant boom of credit elsewhere. And this is why despite the incremental improvement in the traditional credit system, there has been a boom ongoing in US corporate bonds[7].
Some have argued that corporate bond market are meant to fall, due to the possibility of a double dip, but which is chicken and which is the egg? Given their logic, bonds markets should have never rebounded on the first place.
Besides, there is also the uneven impact from convergent rescue policies applied by respective governments. Given the idiosyncratic nature of each economy, the impact has clearly been asymmetric. And German’s stunning 2nd quarter outperformance in economic growth seems to be an example[8].
So far, this has been what the Fed has accomplished: By preventing the collapse in the US banking system, which incidentally still remains as the de facto reserve currency of the world, it has managed to keep afloat the payments and settlements function that has allowed the trade mechanism to flourish in spite of signs of credit contraction at home.
This represents as Pyrrhic ‘battle’ (meaning short term) victory at astounding cost to the US taxpayers to sustain the her stature as the world’s currency reserve standard, with the big possibility of a huge unintended payback in the future. That payback, from our perspective will be in the form of higher inflation, bear market in US treasuries or an overall stagflationary environment.
The point is by preventing a collapse in the banking system the Fed has effectively staved off deflation in the 1930 context.
In addition, I don’t see Japan’s lost decade[9] as the path for America in the way the mainstream bears paints her to be. So it’s hardly a paradigm for adequate comparison.
The second and most important point is, the reason why monetary contraction hasn’t impacted the US the way mainstream foresees it is because they ignore that trade by itself, is first and foremost the liquidity provider.
How?
As Murray N. Rothbard explained[10],
“We come to the startling truth that it doesn’t matter what the supply of money is. Any supply will do as well as any other supply. The free market will simply adjust by changing the purchasing power, or effectiveness of the gold-unit. There is no need to tamper with the market in order to alter the money supply that it determines.” (italics original)
Since money’s purchasing power will naturally adjust to the level of existing stock, then there won’t be any required money level in a free market regime. Thus, the persistence of trade is enough to assure the continuity of liquidity and the avoidance of deflation. This applies even if the Fed would remain non-activist.
Even the popular Harvard duo Carmen Reinhart and Kenneth Rogoff whom has made extensive reviews of the historical relationship of debt, inflation and economic growth during every banking and property crisis worldwide, can’t pinpoint out the definite critical offsetting threshold on how debt and economic growth balance.
Figure 2: VoxEu.org: Reinhart-Rogoff: 90% Debt As Threshold?
This comes with the exception when debt levels have reached or exceeded 90% of GDP (see figure 1), they write, “relationship between government debt and real GDP growth is weak for debt/GDP ratios below 90% of GDP” and “no apparent contemporaneous link between inflation and public debt levels for the advanced countries as a group (some countries, such as the US, have experienced higher inflation when debt/GDP is high)”.
It’s truly difficult to try and compare with past episodes because there is simply NO two similar situations, one can only make estimates and hope that the performances will fall within the ambit of models. However, their implicit point is, this addiction to debt has got to stop. And this is what truly plagues the mainstream mindset.
The third important point is that we have been validated anew.
US authorities on fear of a slowdown that may transform into a double-dip at a time nearing national elections, where the ruling incumbents seem at the risks of being politically dethroned, has called on our poker bluff.
Here is what I wrote at the start of the year[11],
``Many have used the strong showing of 2009 to advert that 2010 would be the year of “exits”. I don't buy it.
``As in the game of poker, I’d call this equivalent to a policymaker’s Poker bluff.”
The FOMC has changed tunes about adapting an exit strategy and will maintain their bloated balance sheets.
Here is the Danske Research team[12], (emphasis added)
``The FOMC revised downward the near-term growth outlook and decided to reinvest the principal payments from the Fed’s portfolio of Agency and MBS holdings in longer-term Treasuries. This implies that the balance sheet will be held constant and effectively puts the exit strategy on hold. While the amount of treasuries to be bought is insignificant, the decision sends a strong signal to markets. It provides a clear indication that rate hikes remain in the indefinite future and that the central bank is prepared for another round of quantitative easing if necessary.”
In short, the Fed’s action is a direct communication to the market that the policy spigot towards Quantitative Easing 2 is being recalibrated as insurance for any material economic growth slowdown.
So there you go—path dependency, economic ideology and the morbid fear emanating from wrong perspectives and analytics will drive the Fed to pump the next wave of liquidity into the system.
For the mainstream, anything that goes down is DEFLATION. There never seems to be within the context of their vocabulary the terms as moderation, slowdown and reprieve. Everything has got to go like Superman, up up up and away!
I’m quite sure, even if statistics would prove to be a false alarm the Fed, would be quick-handed to initiate the trigger.
Let me guess, politics will dictate such action. The Democrats don’t want go without a fight and the Fed will supposedly provide the backdrop for a benign outlook with the slowdown as pretext. It has never really been about economics but the politics of control. Yet the mainstream obstinately refuses to see this.
Of course, there are many other aspects that could debunk the deflation outlook, such actions in commodities markets, the yield curve, exploding emerging bonds and some EM equity markets.
But it really doesn’t matter, because for the mainstream these markets are out of the ambit of “aggregates”. Unfortunately, as F. A. Hayek[13], “aggregates conceal the most fundamental mechanisms of change”.
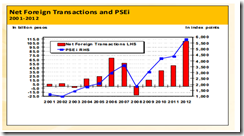
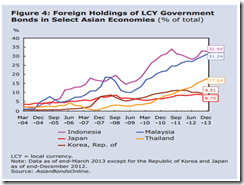
Phisix: No Decoupling, Only Outperformance
Also this is just a reminder to our Filipino colleagues and audiences where today’s market action is seen or interpreted by some as in some semblance of decoupling.
I’m glad that the ASEAN markets have been showing a steady outperformance, but the case for a decoupling hasn’t clearly been established (see figure 3).
Thus, it would be a darned big mistake to be presumptive of a “decoupling” in the event of another turbulent episode such as US recession which I don’t think will leave the Philippines or ASEAN markets unscathed.
One must be reminded that decoupling and outperformance are two different dynamics.
Figure 3: Tradingeconomics.com[14]: US and Philippine GDP
What ASEAN markets seem to imply is that the US isn’t headed for a double dip as the US mainstream bears suggests.
By the way, the definition of a Double dip recession[15] is a backslide to a recession (negative growth) following one or two quarters of positive growth. Based on semantics, the window for a double dip is fast closing—the end of third quarter of 2010 as per definition (if January of 2010 is the starting point of the recovery based on chart).
For me, if there would any immediate real risk worth monitoring this would possibly emanate from China[16] (yes she is slowing down).
That’s because she has engaged in massive credit expansion to immunize herself from a global growth slowdown in 2008 and many of these loans have channelled via shell companies[17] and lent to government projects that likewise got involved in real estate speculation which is hardly part of their core businesses. And such expansion usually creates alot of malinvestments and would likely result to capital consumption, when the imbalances are forced by the natural laws of economics to reveal themselves.
One thing going for China is that she is replete still with savings. There is as much as 9.3 trillion yuan ($1.4 trillion) of hidden assets or undeclared assets according to Yahoo News[18].
Nevertheless, I think signs are pointing to a soft landing more than a hard landing.
The problem anew for the bears is that following a slowdown and prospective stabilization, a renewed reacceleration will likely spur another episode of serious lift-off for ASEAN and many emerging markets, whom depend on China for trade and investments. And this should also help boost the US and the Eurozone too.
And another thing, for as long as the US won’t fall into a recession, the expressed policy by the Fed to indefinitely postpone the ‘exit strategy’, and reemergent possibility to engage in QE version 2 is also likely to serve as another tremendous boost for Asia.
For instance, Hong Kong is already having a difficult time fighting her internal bubbles recently having to impose a “60% limit on the loan to value for property purchases worth more than $1.55 million”[19], given her peg to the US dollar which basically makes her import Fed policies. The transmission mechanism will just get magnified by the ensuing policy divergences.
So bears will continue to fumble from one mistake after another, until the broken clock finally strikes twice a day and claim victory. How bizarre.
[1] Perry, Mark 106 Bank Failures in Perspective, Enterprise Blog
[2] See $23.7 Trillion Worth Of Bailouts?
[3] Thestreet.com Another Illinois Bank Fail, August 14, 2010
[4] Le Bon Gustave, ibid p. 23
[5] See Financial Reform Bill And Regime Uncertainty
[6] See How Free Trade Saved The World From Depression
[7] See US and Global Economy: Pieces Of The Jigsaw Puzzles All Falling In Place
[8] Marketwatch.com German GDP grows 2.2% in second quarter, August 13, 2010
[9] See Japan’s Lost Decade Wasn’t Due To Deflation But Stagnation From Massive Interventionis
[10] Rothbard Murray N. What Government Has Done To Our Money p.29
[11] See Poker Bluff: The Exit Strategy Theme For 2010
[12] Danske Weekly, Fear of a slump August 13, 2010
[13] Hayek, Friedrich August von Reflections on the Pure Theory of Money of Mr. J.M. Keynes, Mises.org
[15] Investopedia.com, Double-dip recession
[16] See China’s State Driven Bubble
[17] FinanceAsia.com, China's endless moral hazard, May 6, 2010
[18] Yahoonews.com Hidden trillions widen China's wealth gap: study, August 11, 2010
[19] Wall Street Journal Blog, Hong Kong Forced to Fight Fed Again, August 13, 2010











![clip_image002[4] clip_image002[4]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjaf0-rWedvo0tl5TWomhDWRByQzjmtWLpm4tCgFCAWgr853Hy3AO1PJfb-FUY8qWJXIOm0eRN7HGvtoQPNLAYlLJwy2agAur4C8vj-0RWR-bXYikOCQOhbemA6_Z56QJooswIa/?imgmax=800)

