The art of economics consists in looking not merely at the immediate hut at the longer effects of any act or policy; it consists in tracing the consequences of that policy not merely for one group but for all groups—Henry Hazlitt
Friday, June 27, 2014
Graphic of the Day: Inflation as seen by consumers and economists
Tuesday, May 28, 2013
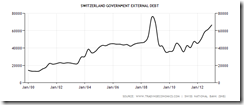
The Religion Called Central Banking: Swiss National Bank Edition
The Swiss National Bank (SNBN) has shielded the economy from the effects of the slump in the euro region with its currency ceiling of 1.20 francs per euro. Such a policy has helped ensure Switzerland suffered only one quarter of contraction since the cap was imposed in September 2011, and an unemployment rate about a quarter of that in the 17-nation bloc.
Tuesday, May 14, 2013
UN’s FAO on World Hunger: Let them eat insects
Eating more insects could help fight world hunger, according to a new UN report.The report by the UN Food and Agriculture Organization says that eating insects could help boost nutrition and reduce pollution.It notes than over 2 billion people worldwide already supplement their diet with insects.However it admits that "consumer disgust" remains a large barrier in many Western countries.Wasps, beetles and other insects are currently "underutilised" as food for people and livestock, the report says. Insect farming is "one of the many ways to address food and feed security".
Tuesday, April 30, 2013
IMF to Asia: Put a Brake on Credit Bubbles!
Asian policy makers must be ready to respond “early and decisively” to overheating risks in their economies stemming from rapid credit growth and rising asset prices, the International Monetary Fund said.Growth is set to pick up gradually during the year and inflation is expected to stay within central banks’ comfort zones, the Washington-based lender said in a report today. Greater exchange-rate flexibility in the region would play a “useful role” in curbing overheating pressures and coping with speculative capital inflows.Asian economic growth that the IMF estimates will be almost five times faster than advanced nations this year, and increasing investor appetite for risk have spurred capital inflows into the region. The Bank of Japan this month joined counterparts in the U.S. and Europe in unleashing monetary stimulus, which may fuel further currency gains in developing markets such as the Philippines, where policy makers have stepped up efforts to cool appreciation.
Financial imbalances and rising asset prices, fueled by strong credit growth and easy financing conditions, are building in several Asian economies,” the IMF said. “Policy makers in the region face a delicate balancing act in the near term: guarding against the potential buildup of financial imbalances while delivering appropriate support for growth.
Thursday, April 25, 2013
This Time is Different: Central Bankers as Superheroes
In other ages, we have called on shamans or saints in times of crisis when the usual remedies have not worked.In the stagnant world economy today, we have designated central bankers as our superheroes, and we are relying on their magical monetary powers to restart global growth.As the European Central Bank president, Mario Draghi, whom some have nicknamed Super Mario, said this month: "There was a time, not too long ago, when central banking was considered to be a rather boring and unexciting occupation."Not anymore. No one embodies this new glamour more than Mark Carney, the 48-year-old governor of the Bank of Canada, who has been tapped to lead the Bank of England, making him the first foreign governor in the institution's 319-year history.The bar for Carney could not be higher. A cartoon in the British papers made the point. It showed a Bethlehem inn with Joseph leading Mary on a donkey. The caption above the innkeeper's head declares: "Unless you're Mark Carney, you'll have to make do with the stable."
The Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas has been chosen as the 2013 Best Macroeconomic Regulator in the Asia Pacific Region by The Asian Banker, one of Asia’s leading financial services consultancies. The award was given during The Asian Banker Leadership Achievement Awards in Jakarta, Indonesia on 23 April 2013.
The man of system, on the contrary, is apt to be very wise in his own conceit; and is often so enamoured with the supposed beauty of his own ideal plan of government, that he cannot suffer the smallest deviation from any part of it. He goes on to establish it completely and in all its parts, without any regard either to the great interests, or to the strong prejudices which may oppose it. He seems to imagine that he can arrange the different members of a great society with as much ease as the hand arranges the different pieces upon a chess-board. He does not consider that the pieces upon the chess-board have no other principle of motion besides that which the hand impresses upon them; but that, in the great chess-board of human society, every single piece has a principle of motion of its own, altogether different from that which the legislature might chuse to impress upon it. If those two principles coincide and act in the same direction, the game of human society will go on easily and harmoniously, and is very likely to be happy and successful. If they are opposite or different, the game will go on miserably, and the society must be at all times in the highest degree of disorder.
Tuesday, November 13, 2012
Sovereign Life Cycles and the Bubble Psychology
Via Bridgewater:Throughout history, Dalio advises these two influences have changed countries’ competitiveness and indebtedness which have caused changes in their relative wealth and power. He goes on to add that since different experiences lead to different psychological biases that lead to different experiences, etc., certain common cause-effect linkages drive the typical cycle of a nation's growth, power and influence.To summarize, we believe that countries typically evolve through five stages of the cycle:1) In the first stage countries are poor and think that they are poor.In this stage they have very low incomes and most people have subsistence lifestyles, they don’t waste money because they value it a lot and they don’t have any debt to speak of because savings are short and nobody wants to lend to them. They are undeveloped.2) In the second stage countries are getting rich quickly but still think they are poor.At this stage they behave pretty much the same as they did when they were in the prior stage but, because they have more money and still want to save, the amount of this saving and investment rises rapidly. Because they are typically the same people who experienced the more deprived conditions in the first stage, and because people who grew up with financial insecurity typically don’t lose their financial cautiousness, they still a) work hard, b) have export-led economies, c) have pegged exchange rates, d) save a lot, and e) invest efficiently in their means of production, in real assets like gold and apartments, and in bonds of the reserve countries.3) In the third stage countries are rich and think of themselves as rich.At this stage, their per capita incomes approach the highest in the world as their prior investments in infrastructure, capital goods and R&D are paying off by producing productivity gains. At the same time, the prevailing psychology changes from a) putting the emphasis on working and saving to protect oneself from the bad times to b) easing up in order to savor the fruits of life. This change in the prevailing psychology occurs primarily because a new generation of people who did not experience the bad times replaces those who lived through them. Signs of this change in mindset are reflected in statistics that show reduced work hours (e.g., typically there is a reduction in the average workweek from six days to five) and big increases in expenditures on leisure and luxury goods relative to necessities.4) In the fourth stage countries become poorer and still think of themselves as rich.This is the leveraging up phase – i.e., debts rise relative to incomes until they can’t any more. The psychological shift behind this leveraging up occurs because the people who lived through the first two stages have died off or become irrelevant and those whose behavior matters most are used to living well and not worrying about the pain of not having enough money. Because the people in these countries earn and spend a lot, they become expensive, and because they are expensive they experience slower real income growth rates. Since they are reluctant to constrain their spending in line with their reduced income growth rate, they lower their savings rates, increase their debts and cut corners. Because their spending continues to be strong, they continue to appear rich, even though their balance sheets deteriorate. The reduced level of efficient investments in infrastructure, capital goods and R&D slow their productivity gains. Their cities and infrastructures become older and less efficient than those in the two earlier stages. Their balance of payments positions deteriorate, reflecting their reduced competitiveness. They increasingly rely on their reputations rather than on their competitiveness to fund their deficits. They typically spend a lot of money on the military at this stage, sometimes very large amounts because of wars, in order to protect their global interests. Often, though not always, at the advanced stages of this phase, countries run “twin deficits” – i.e., both balance of payments and government deficits.5) In the last stage of the cycle they typically go through deleveraging and relative decline, which they are slow to accept.After bubbles burst and when deleveragings occur, private debt growth, private sector spending, asset values and net worths decline in a self-reinforcing negative cycle. To compensate, government debt growth, government deficits and central bank “printing” of money typically increase. In this way, their central banks and central governments cut real interest rates and increase nominal GDP growth so that it is comfortably above nominal interest rates in order to ease debt burdens. As a result of these low real interest rates, weak currencies and poor economic conditions, their debt and equity assets are poor performing and increasingly these countries have to compete with less expensive countries that are in the earlier stages of development. Their currencies depreciate and they like it. As an extension of these economic and financial trends, countries in this stage see their power in the world decline.
As caveat, history rhymes but events which led to them have been markedly different.
Sunday, July 15, 2012
Phisix: Why the Contagion Risk Must Not be Discounted
Here is what I wrote last week[1]
after 3 successive weeks of advances which racked up 8.53% in returns, it would be normal to see some profit taking.
So apparently correction of the Phisix materialized.
In line with the activities of the region’s bourses, the Phisix fell 2.76% this week.
For our ASEAN peers, the outcome had been mixed. Thailand and Malaysia was modestly higher while Indonesia joined the Phisix in a correction mode but had been down moderately.
The BRICs or Brazil, Russia, India and China continue to suffer from hefty losses.
Whatever bounce we have seen lately have mostly signified as deadcat’s bounce for the BRICs. So far only India (BSE) has shown a little bit of strength compared to her contemporaries; China (SSEC), Brazil (BVSP) and Russia (RTSI)
If you have noticed, events have become sooo incredibly short term oriented, exceedingly volatile, and at worst, complacency seems to have become a dominant feature, especially in the Philippine setting, where the current environment has largely been seen as hunky dory.
And part of my concern stems from idea that BAD news has been interpreted as GOOD news where many have come to believe that either local and regional markets have become immune to the external developments or that interventions has been seen as a sure thing and will always be successful.
And as I have pointed out during the past few weeks, my other concern is that perhaps the Philippine market may have been “jockeyed” to project political goals.
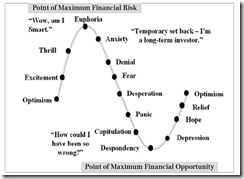
Bubble Cycles: This Time Will NOT be Different
“This time is different” are four words that I fret most. For the late investment legend Sir John Templeton these are the four most dangerous words in investing[2].
Such statement is symptomatic of overconfidence, a deeply ingrained euphoric sentiment or an embedded belief that a new paradigm has somewhat reconfigured how life would play out.
A classic example is when the late distinguished monetary economist Irving Fisher infamously declared that the US stock market, at the climax of the bullmarket in 1929, had reached “a permanently high plateau.”[3] What followed in the coming months were the gruesome Wall Street Crash and the Great Depression.
So when I stumble upon news which avers that “Southeast Asia is looking more a safe haven than a risky bet, with foreign investors souring on China and India and pouring money into markets proving resilient to the global gloom”[4] such assumptions gives me a creepy feeling.
That’s because such sentiment evokes of the memories of the excruciating Asian crisis which once was heralded as the “Asian Economic Miracle”[5] in 1994 and which ultimately turned out into a grand cataclysmic bubble bust in 1997.
Yet it took 3 years for the bust to occur.
But euphoria does seep through public’s consciousness even when bubble cycles have not been homemade.
Exactly during the pinnacle of the last boom phase of the Philippine stock market, a local news outfit featured the ‘basura queen’ in June of 2007[6]. Basura is a local term for garbage and a stock market colloquial or slang for high risk issues.
The ‘Basura’ Queen swaggered about her making millions out of ‘basura’ issues, or the penny stock equivalent of Wall Street.
Overconfidence and the increasingly desperate search for returns seem to be revving up the public’s appetite for gambling.
But the seeds of a homegrown bubble are also being sown.
The Fitch Rating, a US credit rating agency recently, seems to have echoed on what I have been repeatedly warning about: that the Philippines may be on the ‘brink’ of a domestic credit boom[7]. Not just on the brink, we are already having a domestic credit boom[8].
Of course, local officials will hardly do anything about this, since the credit boom will spruce up the economy over the short term and would thereby provide an image booster or political advertisement to the incumbent administration as their “major accomplishment”.
The boom will be seen as a feat, but the bust will be passed on like a hot potato. In politics, who cares about the future?
Besides, officials have limited knowledge of the unseen or undefined “equilibrium” levels from where or which point to put the policy brakes on.
In addition, since the Philippine political economy have been mostly state driven, chieftains of the industries involved in the boom, who are most likely allies of the administration, will exert their political capital to influence on the direction of policymaking thereby extending the boom to unsustainable levels.
Finally since policymakers have innate Keynesian leanings, who try to promote consumption as the main policy thrust, the policy of negative real rates will drive
1. consumer spending through acquisition of more debt via mortgages, credit cards, and other consumer loans,
2. encourage more government spending which will be financed by low interest rates from the private sector, particularly channelled through banks and other financial institutions, which again would add to systemic debt, and importantly leads to consumption at the expense of production, and lastly,
3. fuel capital intensive speculation which will likely be directed to real estate projects, manufacturing and mining, and which again leads to more systemic debt accrual. Such misdirection of allocations of resources eventually leads to the consumption of capital. A great bust.
Again all inflation is political, designed to push the interests of a few at the expense of the society
And I am talking here of a locally fuelled bubble which is aside from today’s present risk: contagion.
Europe’s Capital Flight Paradigm
In case of a full blown global recession, there has hardly been convincing evidence that ASEAN bourses will entirely decouple.
As I predicted Japanese foreign direct investments capital flows into ASEAN has currently been intensifying[9].
Since Japan’s capital flows into ASEAN have still been couched on the term ‘investments’ based on ‘growth’, this has yet to translate into a full capital flight dynamic where Japanese investors frantically stampede into ASEAN assets regardless of risk conditions.
Once Japan’s debt crisis reaches a ‘tipping point’[10], where in the face of the dearth of access to private capital and from external financing, and where the Bank of Japan (BoJ) will substitute as the buyer or financier of last resort of local sovereign papers in order to save the banking system, then this ‘growth’ dynamic will likely be substituted for ‘flight to safety’[11].
Such dynamic appears as partially being played out in the Eurozone: government debts of Germany, Finland and Netherlands[12] (as well as Denmark[13]) have become lightning rods against the concerns of the Eurozone’s dismemberment and this dynamic has also began to diffuse into Belgium and France.
Yes, it is panic time in the Eurozone as expressed by the bond markets…
…but not in the equity markets
I think that the difference is that the European Central Bank (ECB) has yet to aggressively step up as the buyer and financier of the last resort which is why most of the capital flows have been absorbed into government bonds.
Nevertheless some of these safehaven flows may have already been rechanneled to the equity markets of Germany (DAX), Denmark (KFX), Netherland (AEX) and Belgium (BEDOW).
Meanwhile the Finnish and French bellwether has yet to ventilate similar ‘capital flight’ dynamics.
Remember if the risk conditions in the Eurozone stabilize, then these capital flight dynamics will likely be reversed as money flows back to their sources, and the current boom may turn out to another bust, which ironically may again fuel more destabilization.
Some bullish background, eh?
Contagion Risk Must Not be Discounted
We shouldn’t forget that the Asian Crisis proved that contagion risk was a real risk that spread throughout the region.
As the Reserve Bank of Australia noted[14],
One can then locate the onset of crisis in Korea, Indonesia, Malaysia, and the Philippines in a process of contagion: a flip to the bad equilibrium to which the economies were vulnerable, in response to the ‘wake-up call’ (i.e. signal) from Thailand that this was a possible outcome.
This was likewise true with the 2007-2008 meltdown of the US property and mortgage bubble.
Remember that the real effects of an external transmission of contagion were hardly felt since the Philippine economy escaped a recession and that the ensuing global slowdown hardly left an imprint to local corporate earnings, yet the Phisix lost over half of its value from peak to trough[15]!
So while it may be true that those years had different conditions from today, despite some of the real relatively positive changes on ASEAN economies, we must be reminded that globalization and dependence on the US dollar through international currency reserve accumulation via the global banking system has been the umbilical cord for global asset markets.
Merchandise trade as % of GDP remains as a significant factor to ASEAN economies particularly to the Malaysia and Thailand.
But the Philippines also depends on foreign remittances (10.73% of GDP 2010[16]) as well, and to the lesser extent Indonesia (>1% of GDP 2010[17])
While the Philippines and Indonesia may be less exposed, the question will be internal dynamics.
Dependence on government spending only provides temporary relief (benefits the cronies) at the expense of the future (higher taxes, higher debt levels, and higher inflation)[18].
Has the political, legal, tax and regulatory environment eased to incentivize entrepreneurs to take on more productive ventures?
Philippine economic growth has recently been powered by exports[19], most likely due to global restocking. But with a ongoing recession in the Eurozone, as well as, a pronounced slowdown China and other major emerging market economies, and importantly the US, expectations of robust “double digit” growth signifies as wishful thinking…unless major central banks come up with more aggressive short term palliatives.
And a slowdown in global merchandise trade has been prompting for a contraction on trade surpluses (perhaps partly due to increasing domestic demand) and a reduction of foreign currency reserves, as some emerging market central banks have attempted to stabilize exchange rate values with use of these surpluses and thus results to monetary tightening conditions that may not be conducive for equities[20].
In addition, the banking crisis at the Eurozone will prompt for major balance sheet adjustments in order to raise capital mostly through shrinkage, particularly banks are slated to reduce balance sheets by €2 trillion by dumping 7% of these assets by the end of 2013. This also means that supply of credit to the economy will contract.
Of course the real problem isn’t due to credit contraction which affects mostly the government and their protégé the banking system but of the failure to undertake real reforms focused on competitiveness and productivity[21].
Yet under the worse policy scenario arrived by IMF estimates according to DBS Research[22], a dramatic slowdown in the economy compounded by bank deleveraging (bursting bubble) will affect even the US and emerging markets will not be spared (most especially in Eastern Europe).
So we can hope for the best and prepare for the worst.
So underneath the headlines, ASEAN+3 (China Japan and South Korea) have doubled their Chiang Mai Initiative Multilateralism (CMIM) currency swap buffer to USD 240 billion which was a third funded by total foreign reserves accumulated by ASEAN 5 (US 765 billion as of April)[23][24].
So while Asian central bankers have been adding insurance against the risk of the aggravation of Europe’s banking crisis, domestic investors have been in a buying binge.
Yet the ongoing Euro-Brazil, Russia, India, China slowdown compounded by deleveraging within their respective economies has already affected Singapore whose economy suffered a contraction last quarter[25]
Yes China’s economy managed to post 7.6% growth last quarter, but many questioned on the validity of the statistics used to arrive at this output which for some have been overstated for political reasons[26]
And yet US and European markets rallied fiercely last Friday, which according to news drew on the conclusion that the recent conditions of China’s economy will lead to more monetary accommodation by policymakers[27]. Bad news again seen as good news.
I think that such knee jerk response represents more of a melt-up from “crowded short positions” rather than a major inflection point.
As Prudent Bear analyst Doug Noland rightly points out[28],
But the downside of the Credit cycle radically alters rules of the game. Over time, reality sinks in that the previous prosperity was in fact an unsustainable boom-time phenomenon. The downside of the Credit cycle ensures faltering asset prices, deflating household net worth and financial sector deficiencies, along with the revelation of problematic economic imbalances and maladjustment. It’s not long into the bust before many see themselves as losers – and to have lost unjustly at the hands of an unfair system. The growing ranks of losers become an increasingly powerful political force.
Nevertheless I expect Friday’s huge jump to filter into Asian markets including the Phisix at the start of the week.
My conclusion remains: for as long as political gridlock over policies persists (in the US, China and Eurozone) and central bankers of major economies remain rudderless, markets will remain subject to extreme volatility from the collision of hope (expectations of decoupling, deeply embedded Pavlovian expectations of major central bankers coming to the rescue and of the narcotic effects of inflationism) and reality (ramifications from deflating bubbles: economic slowdown and deleveraging). Not to discount of the possibility of major policy errors from too much focus on the short term fixes.
While I remain bullish over the Phisix over the long term, the short term horizon has been filled to the brim with uncertainties coming from almost every direction. This for me magnifies the tail event risks.
[1] see Why Current Market Conditions Warrants a Defensive Stance July 9, 2012
[2] SirJohnTempleton.org Consider these 'words of wisdom' about investing September 20, 2006
[3] Wikipedia.org Irving Fisher
[4] Reuters.com Southeast is Asia safe haven as China, India stumble, July 14, 2012
[5] Wikipedia.org 1997 Asian financial crisis
[6] See Philippine Stock Exchange: The PUBLIC’s MILKING Cow???!!!, June 17, 2012
[7] Inquirer.net Philippines on the brink of a credit boom, must be wary of dangers—Fitch Rating, July 6, 2012
[8] See Why has the Phisix Shined? July 2, 2012
[9] See Japan’s Capital Flows to ASEAN Accelerates July 4, 2012
[10] See The Coming Global Debt Default Binge: Japan’s Government Under Financial Strains July 9, 2012
[11] See Will Japan’s Investments Drive the Phisix to the 10,000 levels? March 14, 2012
[12] Bloomberg.com AAA Yields At Zero Drive Investors To Belgian Debt: Euro Credit July 13, 2012
[13] See Denmark Cuts Interest Rates to Negative July 6, 2012
[14] Corbett Jenny, Irwin Gregor and Vines David From Asian Miracle to Asian Crisis: Why Vulnerability, Why Collapse? 1999 Reserve Bank of Australia
[15] See Dealing With Financial Market Information February 27, 2011
[16] Tradingeconomics.com Workers' remittances and compensation of employees; received (% of GDP) in Philippines
[17] Tradingeconomics.com Workers' Remittances And Compensation Of Employees; Received (% Of GDP) In Indonesia
[18] See S&P’s Philippine Upgrade: There's More than Meets the Eye July 3, 2012
[19] ABS-CBNNews.com May exports growth at 17-month high, July 10, 2012
[20] See Emerging Market “Liquidity” Conditions Deteriorate July 5, 2012
[21] See What to Expect from a Greece Moment June 17, 2012
[22] DBS Vickers Economics Markets Strategy 3Q 2012 June 14, 2012
[23] Ibid
[24] Wikipedia.org Chiang Mai Initiative
[25] See Contagion Risk: Singapore Economy Contracts, July 13, 2012
[26] See China’s Economic Growth Slows Anew, Economic Data Questioned July 13, 2012
[27] Bloomberg.com S&P 500 Erases Weekly Loss On JPMorgan Rally, China, July 13, 2012
[28] Noland Doug Game Theory And Crowded Trades Credit Bubble Bulletin, Prudent Bear.com July 13, 2012
Monday, June 04, 2012
Will the Phisix Divergence Last?
My source of livelihood has almost entirely been from the local stock market, particularly investing, as I am hardly or rarely a short term trader.
Thus, objective and thorough investigations, assessments and analysis have been IMPERATIVE on me. And as part of my investing philosophy, I try to avoid getting married to a position, in as much as assuming the HIGH RISK role of becoming a stock market CHEERLEADER.
Losing money means my family will starve and this is why I cannot afford to lose money. Therefore such punctilious efforts, on my part, to deal with risks represent what have been known as stakeholder’s problem—where my incentives to attain relevant knowledge are prompted by the degree of my stakes in the financial marketplace. Since I depend on the markets thus I have to know the possible risks attendant to my positions.
And this outlook which I share with you, has not only been based on my battle hardened experience, but also from my candid evaluations of the conditions of the risk environment.
I am not here for an egotistical trip as many have been wont to.
Separating Signals from Noise
I have long been an adherent to the wisdom of the legendary trader Jesse Livermore. I have repeatedly been posting one of my favorite Mr. Livemore’s aphorisms here (bold emphasis mine)
I began to realize that the big money must necessarily be in the big swing. Whatever might seem to give a big swing its initial impulse, the fact is that its continuance is not the result of manipulation by pools or artifice by financiers, but depends on underlying conditions. And no matter who opposes it, the swing must inevitably run as far and as fast and as long as the impelling forces determine.
Simply said, profits are to be made based on underlying conditions which drives the general trend, and importantly, serves as the critical source of big swings.
And this is why I give heavy emphasis at the unfolding events based on the big picture. Unlike most practitioners, I am hardly swayed by vacillations from ticker tape activities.
Yet, ticker tape activities and the big picture frequently represent the noise and signal problem
Nassim Nicolas Taleb in his forthcoming book wonderfully explains the psychological impact from noise and signal[1]
we are not made to understand the point, so we overreact emotionally to noise. The best solution is to only look at very large changes in data or conditions, never small ones.
Just as we are not likely to mistake a bear for a stone (but likely to mistake a stone for a bear), it is almost impossible for someone rational with a clear, uninfected mind, one who is not drowning in data, to mistake a vital signal, one that matters for his survival, for noise. Significant signals have a way to reach you. In the tonsillectomies, the best filter would have been to only consider the children who are very ill, those with periodically recurring throat inflammation.
There was even more noise coming from the media and its glorification of the anecdote. Thanks to it, we are living more and more in virtual reality, separated from the real world, a little bit more every day, while realizing it less and less. Consider that every day, 6,200 persons die in the United States, many of preventable causes. But the media only reports the most anecdotal and sensational cases (hurricanes, freak incidents, small plane crashes) giving us a more and more distorted map of real risks. In an ancestral environment, the anecdote, the “interesting” is information; no longer today. Likewise, by presenting us with explanations and theories the media induces an illusion of understanding the world.
And the understanding of events (and risks) on the part of members of the press is so retrospective that they would put the security checks after the plane ride, or what the ancients call post bellum auxilium, send troops after the battle. Owing to domain dependence, we forget the need to check our map of the world against reality. So we are living in a more and more fragile world, while thinking it is more and more understandable.
The bottom line is that many people get confused when working to separate the proverbial wheat from the chaff or when filtering signal from noise. People with lesser stakeholdings are likely to emphasize on the noise which usually signify as “an illusion of understanding the world” and or embrace steeply biased (but unworkable and highly flawed) theories.
The Dopamine Fetish
I would also add that part of the psychological-neuroscience aspect in dealing with markets has been about dopamine neurons.
People’s dopamine neurons, or brain chemicals, gets fired up when rewards attained are GREATER than expected. In contrast, REGRETS are symptoms of depressed dopamine neurons. Thus short term thinking and short term trading have MOSTLY been about the fetish for dopamine trips.
A study on neuroscience suggests that dopamine flows are pervasive during early stages of a ballooning bubble, reflecting desire for profit. However as the bubble peaks, dopamine flows tend to culminate in a cessation just before the market burst[2]
Monetary policies by central banks also whet or induce dopamine powered speculative behaviors[3].
The lesson here is that we should manage our dopamine flows rather than allowing dopamine neurons to dominate the risk-reward tradeoffs that confront our investing decisions. This is basically about Emotional Intelligence (EI)
Let me further add that the technical construct of the Philippine Stock Exchange has been skewed to inculcate upon the public of the upside bias for issues listed on the markets, as well as, the component index.
The rational for this seems to be part of the political designs to exhibit economic booms.
Take shorting. While shorting has been legalized, rigorous procedural and regulatory compliance requirements have made shorting impractical. So we have a facility that has hardly been used.
And since market participants only earn from an UPSIDE price move, thus logically, the dominant entrenched PSYCHOLOGICAL bias would be for the public to yearn for the stock market to go only in one direction—UP.
Next, complimenting the psychological and physiological aspect, monetary policies have also been rewarding speculative activities at the expense of savings and production.
So intensifying speculative activities extrapolates to the herd effect in motion.
Where the basic function of the stock market has been about the cost of buying future income stream relative to insecurities (risk and uncertainty), such functionality has been negated or substituted by rationalizations for price chasing momentum.
Writes Kevin Dowd, Martin Hutchinson, and Gordon Kerr at Cato Forum for monetary policies[4],
Low interest rate policies not only set off a malinvestment cycle but also generate destabilizing asset price bubbles, a key feature of which is the way the policy rewards the bulls in the market (those who gamble on the boom continuing) at the expense of the sober minded bears who keep focused on the fundamentals, instead of allowing the market to reward the latter for their prudence and punish the former for their recklessness. Such intervention destabilizes markets by encouraging herd behavior and discouraging the contrarianism on which market stability ultimately depends. A case in point is the Fed’s low interest rate policy in the late 1990s: this not only stoked the tech boom but was maintained for so long that it wiped out most of the bears, who were proven right but (thanks to the Fed) too late, and whose continued activities would have softened the subsequent crash. The same is happening now but in many more markets (financials, general stocks, Treasuries, junk bonds, and commodities) and on a much grander scale. Such intervention embodies an arbitrariness that is wrong in principle and injects a huge amount of unnecessary uncertainty into the market.
In essence, the inflationary boom psychology has been distorting economic reasoning.
Add to this the leash effects of bailout policies.
The bottom line is that inflation fueled bull markets have become a religion to many.
And advises to undertake prudent positions—based on appraising the risk environment that may adversely affect one’s portfolio—has been seen as sacrilege.
Short Selling Not Recommendable; Contagion Risks
I also do NOT recommend shorting in the Philippines for the following reasons
-the cost to undertake shorts positions have been enormous relative to prospective gains (if a short position is required the best is to do it from overseas)
-a full blown BEAR market for the Philippines has NOT been yet established, although the RISKS from such scenario seem to be STRENGHTENING.
-global regulators have periodically been intervening. The degree of intervention mostly through bailout policies comes with such INTENSITY such that these can TORCH shorts on short notice. A good example has been Europe’s LTRO which singed Euro shorts at the start of the year[5]
-global regulators have innate biases against short sellers. They have done so lately through direct market interventions, such as drastic imposition of shorting bans which forces short covering to investors at a loss. A great example has been the shorting bans on Europe stock markets in mid-2011[6] in the political belief that speculations, and NOT insolvency, have been the fundamental problem that besets the Eurozone. Yet in spite of the bans, European stock markets continue to bleed PROFUSELY. This represents a vivid example of the “illusion of understanding the world” by political agents who always try to shift what has truly been their mistake to the markets.
Lastly I do NOT wish or DESIRE for a bear market.
Because of the limitations to take on hedge positions, bear markets or even phases of consolidation with a downside bias or volatility translates to income drought for me or most market participants (see the structural bull market bias above)
While I am an optimist who believes that the Phisix will reach 10,000 sometime in the future, I am also a REALIST who understands that external forces have a HUGE influence to actions of the local stock markets and that NO trend goes in a straight line.
In suggesting of the countercyclical trend amidst a secular trend I wrote in March[7],
I am not certain whether we will see a repeat of the discontinuities similar to the 1986-1997 bull market cycle or will suffer more than the past cycle before reaching my goal or if the Phisix will proceed to double. What needs to be monitored are drivers of the current trends and the whereabouts of the present boom cycle based on internal and external dynamics.
In short, the PHISIX, despite the secular trend, is VULNERABLE to a CONTAGION risk.
Could this week’s Phisix Divergence Represent an Anomaly?
The local benchmarket, the Phisix, majestically bucked the global stock market carnage last week.
As one would note, the Phisix has not only outperformed the region, the local benchmark basically defied gravity.
China and Malaysia joined the Phisix, as outliers, with hefty gains amidst a sea of red.
Yet such divergences have given the dopamine to Pollyanna trippers the ammunition to declare “bottom” for the market.
I have yet to be convinced.
The gist of the weekly gains or 52% of the Phisix came from Thursday’s activities.
Ironically, the sizable gains occurred in the backdrop of staggering US and global markets.
Media and experts has alluded to reports of sturdy domestic economic growth[8], the hints of a possible upgrade[9] by US rating agency Moody’s on the credit standing of the Philippines and the closure of milestone impeachment trial[10] with a conviction of the accused which favors the administration as reasons for this.
I beg to differ.
I raised this concern on this last Thursday[11]. The Phisix went down to as low as 67 points at the early session, dragged by the selloffs in the US and Europe. But suddenly, aggressive and systematic buying of heavyweights (blue chips) throughout the day pushed the Phisix to close at almost at the peak (76.81) at 73 points. The pendulum swing from loss to gain represented an astounding 2.8%!!!
Buyers seem to have, ironically, been resolutely aggressive to push up prices in an environment of MOSTLY falling stock market prices globally, perhaps in the assumption that local stocks will soon experience a strong surge.
Or is it?
The weekly performance of the heavy cap issues reveals that gains of the Phisix were mostly seen through Ayala Corp (AC), JG Summit (JGS), Banco De Oro (BDO), Metrobank (MBT), SM Investments (SM), International Container (ICT), PLDT (TEL) and Bank of the Philippine Islands (BPI).
The logical part for any buyers under such scenario would be to make use of the dour sentiment to take advantage of price declines to bargain hunt. Yet these have not been the case.
Let me lay out my suspicions.
I do not think that these has been due to general market sentiment, although pushing up the PHISIX index succeeded to give a boost to the general market sentiment.
Thursday closed with a mixed showing between advancers and decliners with the latter having a slight edge. On a weekly basis advancers took a slight lead over decliners showing modest improvement in the market breadth or sentiment.
Second my naughty thoughts suggests that Thursday actions was likely executed to create an impression of economic ‘confidence’. I am not so sure why though. Perhaps to squelch demand for signing waivers for top officials.
Buyers suddenly became price insensitive. The likelihood is that non-market entities may have been responsible for aggressively pushing up Big Caps. I would suspect that these may have been government institutions such as the SSS, GSIS or others.
While it is true that Thursday a net foreign buying, the bulk of these buying can be traced to cross trades at DM Consunji.
Besides, net foreign buying data may not reveal of the real extent of activities that took place. Foreign buying can represent overseas based subsidiaries or branches of locally owned corporate vehicles or tycoons, as well as, foreign based politically allied corporations.
Of course I may be wrong and that there may have been special factors driving up the Phisix.
But if my suspicions are valid then such interventions are likely to produce short term effects.
As example the Bank of Japan’s (BoJ) $13.3 billion[12] interventions DID bring down the Yen for about a month. However the Yen has been regaining lost grounds since. This effectively has neutered tax payer financed interventions. In short $13.3 billion down the drain.
Another question that begs to be asked is WHY the PHSIX alone?
While Malaysia did post hefty weekly gains next to the Phisix, the Malaysia’s benchmark (FBMKLCI:IND, green) has almost missed out the recent bull market. On the other hand, Thailand (SET:IND, orange) and Indonesia (JCI:IND, red) which shared or alternated the lead with the Phisix, since last year, has wilted significantly.
Yet it can be observed that ASEAN’s stock markets have been nearly been moving in nearly synchronous fashion UNTIL the peak in May of this year.
This only means that last week’s gains by the Phisix either represents an ANOMALY or that the Phisix LEADS Asia.
My bet is on the former.
The Decoupling Myth
I have been saying that current environment have been dominated by POLITICAL uncertainty which for the Philippines and ASEAN represents a CONTAGION risk.
If global markets stock markets have been pricing in a bust or the unwinding of malinvestments which is being transmitted to the global economies, then it would dangerous, if not reckless, to presume immunity or “decoupling” where trade and investment linkages of ASEAN economies have been deepening relative to the world.
ASEAN economies have largely been exposed to developments abroad through merchandise trade (exports and imports).
The Philippines merchandise trade represents over 50% of GDP, while Malaysia and Thailand are over 100%.
This means any meaningful economic slowdown in the region or in the world will negatively impact economic growth.
Add to this the potential slowdown effect on remittances and supply chain networks.
The deepening of financial globalization also means the integration of emerging Asia’s capital markets[13] with the world (left chart) and with intra-region (right pane).
In short, the false notion of DECOUPLING will likely melt in the face of a global recession or when a full blown financial crisis, if such phenomenon transpires.
Let me be clear, the conditional term is an IF, while global economies have indeed been slowing down, a global recession or worldwide contagion from euro’s financial crisis has yet to become evident in Asia.
Of course a decoupling COULD happen if there should be massive inflation or even hyperinflation from any of these major economies. However, under the current circumstances this is unlikely to happen.
This means that for those in the belief that the Philippines can decouple from the world, the following chart should be a helpful reminder…
2007-2008 signifies as the contagion based bear market.
Neither has there been an economic recession during the said period nor did earnings fall materially. But the Phisix entered a full blown BEAR Market and lost about 50% peak-to-trough as a result of an exogenously driven financial crisis in 2007-2008.
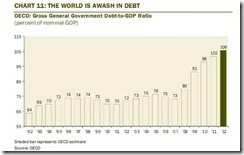
Of course 2008 is different from today. In fact, today has been worst compared to the 2008 crisis. In 2008 the crisis was limited to the banking, property and mortgage industry. Today the crisis dynamics has shifted to envelop banks AND sovereigns. Not to mention that world wide government debts have surged[14] and that US fiscal deficits have skyrocketed (at $1.327 trillion or 8.2 times larger than 2007[15]).
Yet for those who should insist on decoupling, then I wish you the best of luck.
[1] Taleb Nassim Nicolas Noise and Signal — Nassim Taleb Farnam Street, May 29, 2012
[2] ChangingMinds.org The Neuroscience of Financial Bubbles
[3] See How US Federal Reserve Policies Stimulates the Public’s Speculative Behavior, May 8, 2012
[4] Dowd Kevin, Hutchinson Martin, and Kerr Gordon The Coming Fiat Money Cataclysm
[5] Marketwatch.com Euro hits 3-month high on LTRO hopes, February 24, 2012
[6] Wall Street Journal, Europe Short Bans Extended, August 26, 2011
[7] See Phisix: The Journey Of A Thousand Miles Begins With A Single Step, March 12, 2012
[8] ABS-CBNnews.com.ph PH eco grows 6.4% in Q1; highest in ASEAN, May 31, 2012
[9] Businessmirror.com.ph Moody’s raises PHL to ‘positive’ May 29, 2012
[10] See The Lessons and Validity of Public Choice Theory Applied to the Chief Justice’s Corona Impeachment, May 29, 2012
[11] See Phisix: Very Impressive Day or Month End Close for May 2012, May 31, 2012
[12] Bloomberg.com Japan Adopts Stealth Intervention As Yen Gains Threaten Exporter Earnings February 7, 2012
[13] ADB ONLINE Asia Capital Markets Monitor August 2011
[14] Zero Hedge, Presenting Dave Rosenberg's Complete Chartporn, June 1, 2012
[15] Weiss Martin Lehman-Type Megashock Looming, Money and Markets May 21, 2012