Thus elections, quite apart from who won them, performed a powerful cultural function for the elites. To the degree that -everyone had a right to vote, elections fostered the illusion of equality. Voting provided a mass ritual of reassurance, conveying to the people the idea that choices were being made systematically, with machine-like regularity, and hence, by, implication, rationally. Elections symbolically assured citizens that they were still in command—that they could, in theory at least, deselect as well as elect leaders. In both capitalist and socialist countries, these ritual reassurances often proved more important than the actual outcomes of many elections. Alvin Toffler, The Third Wave chapter 75
It’s the eve of the much awaited 2012 US national elections.
On November 6th Tuesday many Americans will flock to their respective precincts to exercise their suffrage. The national elections will cover the executive (President-Vice President) and the legislative branches (Senate and House of Representatives) as well as some positions at the state level[1].
The Follies of Pattern Seeking Behavior
We are told that certain outcomes from the coming election may lead to specific results on the financial markets.
For instance, a Barclay’s survey on professional investors[2] proposed that a Romney victory would be good for stocks while Obama’s re-election will favor the bond markets.
Others suggested that the elected President’s political party matters. The median return for the S&P 500 favors a Democrat President over a four year period, as against a Republican President who may spur a short term rally. All these are based on statistics derived from historical data[3].
For me, surveys are hardly reliable measures of the tradeoffs between profits and risks.
What people say and what they actually do may be different. Many people talk to signal Social Desirability Bias or to say things in a matter that they will be viewed favorably[4].
People are also highly sensitive to changes in preferences due to many factors as new information, social pressures, and more. Besides, surveys can also yield distortive results based on the influence from how questions are framed by the pollster.
Further, candidness of the survey participants also account for as another important variable to be leery on.
On the other hand, statistical constructs based on historical events signify as veneer to people’s desire to seek patterns in order to deal with uncertainty or to simply tell stories again for social signaling purposes.
Yet historical events are complex phenomena that had been arrived at through multifarious causes. They cannot simply be oversimplified or seen or interpreted as homogenous replication of the current environment. Even Wall Street acknowledges this dynamic through the axiom: Past performance does not guarantee future results.
Thus assignment of numerical probabilities on partially similar episodes, are not only irrelevant in forecasting the future, but such accounts for a form of entertainment to its practitioners.
As I previously wrote[5],
numerical probabilities serve to gratify one’s cognitive biases which in essence is a form of self-entertainment rather than a dependable methodology for risk analysis
Pattern seeking behavior can also be representative of the gambler’s fallacy or the Monte Carlo fallacy, which Investopedia.com defines as[6]:
When an individual erroneously believes that the onset of a certain random event is less likely to happen following an event or a series of events. This line of thinking is incorrect because past events do not change the probability that certain events will occur in the future.
Yet there has been no precedent in terms of the scale of policymaking for any meaningful comparison to be made with past US national elections.
Such distinction even holds true in terms of other social phenomenon such as technological advances or innovation and of the diffusion of voluntary exchanges expressed as globalization
Yet social policies, which shape people’s incentives to save, invest, produce and consume, implemented and enforced through the political spectrum, have reached extraordinary proportions.
Regulatory growth has morphed into a large scale bureaucratic quagmire. Notes Mises Institute President Douglas French[7],
The Federal Register, a publication with all the country’s (federal, nonclassified) rules is now over 81,000 pages long. President Obama’s Affordable Care Act is 906 pages. The Dodd-Frank Act totals 849 pages. Once upon a time, in 1913, the Federal Reserve was created with only 31 pages. The U.S. Constitution required only six pages.
It would account for as a glaring mistake to construe neutral effects from these new-fangled edicts or rules or decrees on people’s economic and social activities.
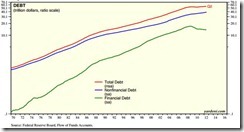
Moreover, systemic debt has been ascending to unsustainable levels.
Chart from Dr. Ed Yardeni’s Flow of Funds[8]
Financial analyst and fund manager Doug Noland recently observed of the political imperative to keep the system afloat[9]
After beginning 1990 at $12.8 TN, Total System Marketable Debt ended June 2012 at $55.0 TN. And Washington politicians and central bankers are now doing everything they can to sustain the Credit boom and avert the downside of an historic Credit cycle. Similar efforts are afoot globally.
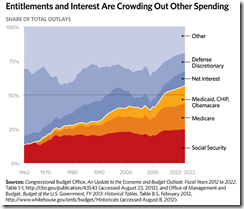
The accelerating erosion of America’s productive dimensions has been due to the escalating welfare state, ballooning bureaucracy and other state based expenditures which transfers scarce and valuable resources to non-productive political based spending and entitlements, which has also been crowding out the private sector. Chart from Heritage Foundation[10]
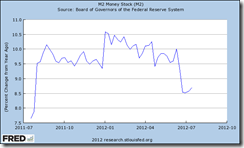
America’s social policies have also led to the unparalleled deployment of the US Federal Reserve as chief provider of funds for the US government.
In 2011, more than half or 61% of US debts had been monetized by the US Federal Reserve. US Federal holding of US treasury debts of all maturities has surpassed $1.8 trillion (lower window).
This represents the highly fluid debt economics of the US government, where the Fed has stepped up the plate relative on the declining interests from the private sector, as well as, foreign public and private investors (upper window).
As Mr. Lawrence Goodman, president of the Center for Financial Stability wrote at the Wall Street Journal early this year
The Fed is in effect subsidizing U.S. government spending and borrowing via expansion of its balance sheet and massive purchases of Treasury bonds. This keeps Treasury interest rates abnormally low, camouflaging the true size of the budget deficit. Similarly, the Fed is providing preferential credit to the U.S. government and covering a rapidly widening gap between Treasury's need to borrow and a more limited willingness among market participants to supply Treasury with credit.
The failure by officials to normalize conditions in the U.S. Treasury market and curtail ballooning deficits puts the U.S. economy and markets at risk for a sharp correction.
The point being: The current state of imbalances borne out of America’s political dynamics has been unmatched in scale and depth. This only means that America’s future will depend on the actions of political authorities which will either deepen systemic fragility or take remedial but highly painful measures.
Risk Reward analysis, thus, requires a focus on the actions of policymakers.
Campaign Promises Hardly Are Reliable Measures of Projecting Future Policies
It would be conceivably naïve to rely on political rhetoric of competing candidates as basis for examining and projecting prospective policies.
Politicians usually appeal to the views the median voter to ensnare votes. In other words, politicians, who are running for office, are predisposed to say what the public wants or expects to hear.
On the obverse end, people hardly vote for policies but for symbolisms which these candidates represent. Thus aspiring politicians work hard to project themselves as symbols to reinforce people’s biases.
And this is why politicians usually end up with unfulfilled promises or have usually gone against their rhetorical assurances made during the campaign sorties.
Voters become useful only to politicians when election season arrives.
Take for instance, the Reason Magazine enumerates[11] some of the unmet campaign pledges by presidential candidate Barack Obama in 2008:
1. Creating five million green jobs.
Unfortunately President Obama’s green energy industry has been suffering from a string of high profile bankruptcies[12], which includes the controversial Solyndra scandal.
The highly influential think tank Council of Foreign Relations recently noted that Obama’s creation of green jobs from the green energy sector have penalized taxpayers heavily relative to the other non-renewable energy industries[13]
2. Balance the budget
As of Monday October 29th, the US is on path to reach its debt limits before 2013. According to the Reuters[14], the U.S. Treasury was $235 billion below the $16.4 trillion statutory ceiling on the amount it can borrow.
3. Refusing to raise taxes on the Middle class
4. Reforming Immigration
The Reason.com says that the Obama administration has been deporting illegal immigrants like crazy, leaving Hispanic Caucus Democrats in the awkward position of changing the subject to health care, and otherwise blaming Republicans.
5. Restoring America’s moral standing in the world
President Obama has been expanding the theatre of warfare to include Pakistan, Yemen and Libya and from the backdoor, Syria[15].
So whether Obama or Romney, there will unlikely be any radical changes in the political structure to headoff the looming debt crisis.
This goes to show that elections have mainly been used to justify policies which benefit many entrenched power blocs operating behind the scenes.
Given the above conditions, the pricing dynamics of the markets will, thus, represent expectations from the feedback loop mechanism between policies and market responses to them.
The late illustrious French American mathematician Benoit Mandelbrot in his book The Misbehavior of Markets[16] dealt with the difference of economics with natural science.
Finance is a black box covered by a veil. Not only are the inner workings hidden, but the inputs are also obscured, by bad economic data, conflicting news report or outright deception…And then there is the most confounding factor of all, anticipation. A stock price rises not because of good news from the company, but because the brightening outlook for the stock means investors anticipate it will rise further, and so they buy. Anticipation is a feature unique to economics. It is psychology individual and the mass—even harder to fathom than the paradoxes of quantum mechanics. Anticipation is the stuff of dreams and vapors.
Anticipation is part of human action. People’s divergent expectations, anticipations, and responses are what differentiate economics from natural sciences.
Yet anticipation of the prospective polices, the actual policies, and of its attendant effects on the marketplace will most likely anchor on market dynamics post-election season.
Unlikely Change of Direction for Fed Policies in case of a Change of Administration
A good test of these will be to assess the scenario of a Romney victory (Although I have big doubts of a Romney win. In a close battle, the incumbent have the edge. This is because they hold the political machinery which can be used to their advantage through whatever means).
Yet under a Romney victory, would the new President discharge on his vows to replace the incumbent chairman US Federal Chairman Ben Bernanke at the expiry of the latter’s term? Will Mr. Romney spearhead through his appointee a massive overhaul to the US Federal Reserve’s current policies? I don’t think so.
Given the reality or the fact that the US government’s huge budget deficits heavily depend on the US Federal Reserve for financing, it is unlikely that the Romney appointee to rock on the establishment’s boat.
I have predicted in the past[17] and have been validated that Fed Chairman Ben Bernanke would work to ensure Obama’s re-election through “stock market friendly” policies. This places an ethical issue of the agency problem or conflict of interests between Mr. Bernanke and his policies which affects the average Americans on the political table.
To downplay the political bias from his recent action, Ben Bernanke has floated to media the possibility of his retirement even if Obama wins[18]. Of course, the re-elected President Obama can always “persuade” Mr. Bernanke to change his mind.
Mr. Bernanke seems to be applying the same communications signaling strategy to the public for his personal affairs. This leaves a bad taste on the mouth for Bernanke apologists.
As an aside, all the blarney about “QE forever” designed as monetary policy to supposedly aid the economy through the spending transmission channels of the wealth effect, has really been a diversion, if not a subordinated priority, to the real or primary objective: the FED as contingent financier to the US government’s intractable US budget deficit as expressed through surging debt levels.
Yet candidates floated by the mainstream[19], particularly Glenn Hubbard, Greg Mankiw and John Taylor, to replace Mr. Bernanke have mostly been “dovish” or in favor of the Fed’s contemporary policies (This is with the exception of John Taylor, of the Taylor rule fame, whom I don’t think stands a chance).
In addition, the composition of voting members of the FOMC has been, and will be, most likely leaning towards the “doves” or conformists.
Such would include the previously vacant seats which were recently filled (Jeremy Stein and Jerome Powers), aside from the replacement of the 4 voting regional Federal Reserve Presidents, as part of the customary rotational process, which again favors the “doves”[20]
At the end of the day, regardless of whoever wins, US policies will remain embedded to the interests of the political economic establishment. Changing personalities who runs the same show hardly accounts for a change in the system.
And as such policies will likely remain accommodative primarily to shield the US government from interest rate and credit risks, which should for the meantime, benefit the financial markets, particularly stocks, bonds and commodities (yes despite last Friday’s shakeout) whom have been the secondary beneficiaries.
After all, the main risks I believe will emanate from the market’s ventilation of the unsustainable imbalances from the welfare-consumption-debt based political system, which eventually will render politicians utterly helpless in the face of market-economic chaos. But it is unclear if the day of reckoning is sooner or will surface later.
For the highly interconnected and interrelated global stock markets, including the Philippines, the actions of the US Federal Reserve will have very important transmission implications, and this will be backed by the actions of other major central banks, as well as, from the auxiliary effects of domestic policies. As far as the Philippine BSP is concerned they have aligned their policies to ease along with the US and with most of the major central banks.