Prices are relative: high prices may go higher, while low prices may go lower.
The accretion of price actions is what constitutes a trend. Trends can be seen in a time variant lens: intraday, day, weekly, monthly, yearly or decades.
A bullmarket is when the dominant or major trend is up, while the opposite, a bearmarket is when the major trend is down. A market in consolidation means neither the bulls nor the bears get the dominance.
Yet price trends can be seen in many ways depending on reference points. Having said so, people can make biased and deceptive claims by the manipulating the frame of the trend’s reference points to uphold their perspective.
Meanwhile inflection points extrapolate to a reversal of trends which may allude to major or minor trends.
The actions over the past two weeks may yet be seen as normal correction. That is what I hope it is. But I can’t vouch for this.
We Have Met The Enemy And He Is Us
Yet relying on hope can be a very dangerous proposition. As a popular Wall Street maxim goes, bear markets descends on a ladder of hope. While I am not saying we are in a bear market, it pays to understand that quintessentially “hope” represents the basic shortcoming of vulnerable market participants.
Managing emotional intelligence or having a street smart-commonsensical approach, or prudence is a better a part of valor is my preferred option in dealing with today’s torturous bubble plagued markets[1]. There are times that require valiance, however, I don’t see this as applicable today yet.
As an aside, in testy times as these, market participants should learn how to control their emotions or temperaments so as to prevent blaming somebody else for one’s mistakes, and learn how to take responsibility for their own actions. Self-discipline should be the elementary trait for any investors[2].
Regrets should be set aside for real actions. This means that we can opt to buy, sell or hold, depending on our risk tolerance, time orientation and perception of the conditions of the markets. People forget that holding is in itself an action, because this represents a choice—a means to an end.
And because the average person are mostly afflicted by the heuristic of loss aversion[3] or the tendency to strongly prefer avoiding losses to acquiring gain, in reality since a loss taken signifies an acknowledgement of mistakes, the pain from such admission leads to one to take on more risks that leads to more losses, than to avoiding losses.
As American financial historian, economist, author and educator Peter Bernstein wrote[4],
When the choice involves losses, we are risk-seekers, not risk averse.
Egos, hence, play a big role in shaping our trading, investing or speculative positions.
To borrow comic strip cartoon character Pogo most famous line[5]
We have met the enemy and he is us
The Essence of Risk ON Risk OFF Moments
Nevertheless current developments continue to reinforce my perspective of the markets.
1. Despite all the recent hype about local developments driving the local market, external factors has remained as the prime mover or influence in establishing Phisix price trend. This has been true since 2003. Remember, the Philippine President even piggybacked on this[6]
The good thing about market selloffs is that this has been unmasking of the delusions of greatness and its corollary, the deflation of many puffed up egos.
This also shows that there has been no decoupling
2. Global financial markets have moved in on a Risk On or Risk Off fashion.
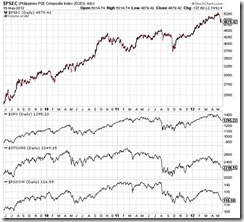
While the degree of performances may differ, actions in the global financial markets today have shown increasingly tight correlations. The general trend direction and even the undulations of the Phisix, the US S&P 500, the European Stox 50 and the Dow Jones Asia Pacific index over past 3 years have shown increased degree of conformity.
Risk ON moments are mostly characterized by greater appetite for speculative actions as seen in the correlated upside movements of prices of corporate bonds, equities, commodities, and ex-US dollar currencies.
On the other hand, Risk OFF episodes or risk-averse moments like today, have accounted for “across the board selloffs” a flight to safety shift to the US dollar and US treasuries.
There has been little variance in price trends that merits so-called portfolio diversification. As pointed out before these have been signs of “broken”[7] or highly distorted financial markets.
Observe that whether the actions WITHIN the Philippine Stock Exchange, or among major developed and emerging market bellwethers or the other asset markets, current market trends produces the same Risk ON-Risk OFF patterns.
A dramatic upside move during the first four months only to be substantially reduced this month exhibits little evidence of conventional wisdom at work. Neither earnings can adequately explain the excessive gyrations in market fluctuations nor has contemporary economics.
Risk ON and Risk OFF, are in reality mainstream’s euphemism for boom bust cycles, which have been caused by inflationism and various forms of interventions—that has engendered outsized volatility in price actions.
Knightean Uncertainty: Greece Exit, China Slowdown and Fed’s End Program Volatility
As pointed out last week, there have been three major forces that have been instrumental in contributing to the recent distress being endured by global financial markets, particularly, the SEEN factor: Greece and the Euro crisis, the UNSEEN factors—China’s slowdown (or an ongoing bust???) and anxieties over US monetary policies.
Since risks implies of measured probability of future events while uncertainty refers to the incalculable probability of future events[8], current events suggests of GREATER uncertainty than of the average risk environment.
For the third time in 6 months, the People’s Bank of China (PBoC) last week cut reserve requirements[9], yet the Shanghai index ignored the credit easing measures and posted a significant weekly loss.
Moreover, the economic slowdown in China has hardly abated.
China’s four biggest banks reported almost zero growth of net lending over the past two weeks[10].
In addition, according to a study by made by a think tank affiliated with PRC’s state council, the estimated the debt-to-asset ratio[11] of Chinese state and private companies, as well as individuals, has reached about 105.4 percent, the highest among 20 countries.
These represent the increasing likelihood of the unwinding of China’s unsustainable bubble. For the moment China’s authorities seems to be in a quandary as they have implemented half-hearted measures which her domestic markets appear to have taken in blase.
Yet if the economy does sharply deteriorate, I would expect more forceful policies to be put in place. So far this has not been the case.
It has been no different in the Euroland where politics have posed as an obstacle to further interventions from the European Central Bank (ECB)
The risks of a Greece exit from the Eurozone seem to have been intensifying. This has been evidenced by the open acknowledgement by Mario Draghi, European Central Bank president, that Greece could leave the Euro. The ECB has even halted to provide loans to four Greek banks[12].
Lending to banks in Greece, which has been experiencing slow-mo bank runs but seem to be escalating over the last week on fears of massive devaluation from the return to the drachma[13], are presently being funded by the national central bank of Greece[14] via the Emergency Lending Assistance.
While there have been estimates as to the degree of exposures by major banks of several nations on Greece, particularly €155 billion for Germany and France[15], no one can really assess on the psychological impact that would translate to financial losses that may occur once official ties have been disconnected. Even Singapore has reportedly been exposed with “a stunning 60%-plus of GDP tied up in European bank claims” according to Zero Hedge[16].
Add to this undeclared the derivatives exposure on Greek securities at an estimated $90 billion[17], the losses from a full blown contagion can reach trillions to the global banking system.
Thus, the probability looms large that that major central banks would use this as an excuse to justify massive inflationism to protect their respective banking systems.
Again the problem that prevents the ECB from further inflating today has been the uncertain status from the politics of Greece. Since nobody in Greece seems to be in charge, the ECB doesn’t know whom to strike a deal with yet. And perhaps in an attempt to influence Greek politics, as stated above, the ECB has partially cut off funding to some Greece banks.
So this should be another evidence of the interruptions of the money spigots.
But the issue here will be the scale of interventions once the process of the Greece exit is set on motion. This will practically be a race between the market and central bank interventions.
And this is why I believe the markets could be exposed to excessively huge volatility during this May to June window, mostly likely with volatility going in both directions, but having more of a downside bias, until the forcefulness of interventions would be enough to temporarily provide patches to malinvestments from becoming evident.
And perhaps in the realization of the risks from financial isolation and the benefits of conditional redistribution from their German hosts, the good news is that the pro-austerity or the pro-bailout camp appears to be gaining ground.
Recent polls seem to suggest that pro-bailouts as having a slight edge[18] or are in dead heat[19] with former favorites, the anti-austerity camp.
The term austerity has been deliberately contorted by the neoliberals. In reality there has been NO real[20] austerity[21] in the Eurozone as government spending (whether nominal, real or debt to gdp) has hardly been reduced. What has been happening has been more of tax increases with little reforms on the labor market or on the regulatory front to make these economies competitive[22][23].
Finally, compounded by external developments, US markets are likewise being buffeted by the uncertainty towards the Fed’s monetary policies where each time the FED ended their easing measures, downside volatility follows.
This was the case for QE 1 and QE 2, and apparently with the closing of OPERATION TWIST this June, US markets have become volatile again.
And as the US markets has recently sagged, the Federal Market Open Committee (FOMC) once again has signaled that they are open to more credit easing measures using the Euro crisis and the US government budget and or debt-ceiling issues[24] as pretext.
The so-called Bush Tax cuts which is set to expire at the end of the year, will translate to a broad increase in tax rates for all[25], will also be a part of the economic issue. Tax increases in a fragile economy heightens a risk of a downturn, and this will likely be met with more easing policies.
Bottomline: The major issues driving the markets has been about the feedback loop between the markets and inflationism (bubble cycles).
Lethargic prices of financial assets have accounted for as symptoms of the artificiality of price levels set by the governments and major central banks through credit easing programs and zero bound interest rates meant to protect the banking system that has been integral to the current political structures which includes the welfare-warfare state and central banking.
In short, falling markets are simply signs of pricked bubbles.
Outside additional support from central banks, asset prices have been weakening, supported by some episodes of debt liquidations, particularly in the Eurozone and in China.
Currently the PBoC, ECB or the FED appear to be constrained or reluctant to pursue with further aggressive interventions for one reason or another. As previously noted, the BoE has officially put to a halt their QE[26].
It could be that they may be waiting for more downside volatility, which should provide them political cover for such action. Also the unresolved political problems of Greece have been an impediment.
So yes, today’s markets have still principally been driven by the ON and OFF steroids or inflationism from central bankers and will continue to do so until markets or politics forces them to cease.
[1] See Applying Emotional Intelligence to the Boom Bust Cycle, August 21, 2011
[2] See Self-Discipline and Understanding Market Drivers as Key to Risk Management, April 2, 2012
[3] Wikipedia.org Loss aversion
[4] Bernstein Peter Against The Gods, The Remarkable Story of Risks, p. 273 John Wiley & Sons
[5] Wikipedia.org "We have met the enemy and he is us." Pogo (comic strip)
[6] See The Message Behind the Phisix Record High May 7, 2012
[7] See “Pump and Dump” Policies Pumps Up Miniature and Grand Bubbles April 30, 2012
[8] See The Fallacies of Inflating Away Debt August 9, 2009
[9] See China Cuts Reserve Requirement May 14, 2012
[10] Businessweek.com/Bloomberg.com Loan Growth Stalled at China’s Biggest Banks, News Says May 15, 2012
[11] Bloomberg.com Chinese Company Debt Is At ‘Alarming Levels,’ Xinhua Says May 17, 2012
[12] See Hot: ECB Holds Loans to Select Greek Banks, ECB’s Draghi Talks Greece Exit May 17, 2012
[13] MSNBC.com Greeks withdraw $894 million in a day: Is this beginning of a run on banks?, May 16, 2012
[14] Brussel’s Blog The slow-motion run on Greece’s banks Financial Times, May 17, 2012
[15] See Greece Exit Estimated Price Tag: €155bn for Germany and France, Possible Trillions for Contagion May 17, 2012
[16] Zero Hedge Why Stability Stalwart Singapore Should Be Seriously Scared If The Feta Is Truly Accompli, May 18, 2012
[17] Zero Hedge, Alasdair Macleod: All Roads In Europe Lead To Gold, May 19, 2012
[18] See Are Greeks turning Pro-Austerity? May 19, 2012
[19] Reuters India Greek election race tightens into dead heat May 20, 2012
[20] See More on the Phony Fiscal Austerity, May 16, 2012
[21] See In Pictures: The Eurozone’s “Austerity” Programs, May 8, 2012
[22] See Choking Labor Regulations: French Edition, May 14, 2012
[23] See Greeks Mount Civil Disobedience, Scorn Taxes, May 16, 2012
[24] Bloomberg.com Several on FOMC Said Easing May Be Needed on Faltering, May 17, 2012
[25] See What to Expect when the Bush Tax Cuts Expire May 19, 2012
[26] See Bank of England Halts QE for Now, May 10, 2012