The current political status quo, however, is built around protecting investors—rather than the taxpayers who ultimately pay all the bills—from risk. This method of turning debt into inflation is attractive to governments and their Wall Street enablers because it shifts the burden of runaway spending to ordinary savers and consumers who pay the real price of de facto inflationary default through price inflation, unaffordable homes, stagflation, and falling real wages—Ryan McMaken
In this issue
June CPI’s Decline Reflects Demand-Side Slowdown: Will the BSP Join Global Peers in Easing Policies, and Will the Government Pursue 'Marcos-nomics Stimulus'?
I. Global Central Banks Predominantly on an Easing Trajectory
II. The BSP’s Programming of the Inflation Narrative via the Confirmation Bias
III. Widening Inequality: Headline CPI vs. Bottom 30% CPI Hits 22-Year High!
IV. June’s Demand Side Disinflation: Non-Performing Loans Surge in May
V. Escalating Deficit Spending as a Floor on the CPI; Will Belated Rate Cuts Sow the Seed of the Next Wave of Inflation?
June CPI’s Decline Reflects Demand-Side Slowdown: Will the BSP Join Global Peers in Easing Policies, and Will the Government Pursue 'Marcos-nomics Stimulus'?
The decline in June CPI was broad-based and signifies primarily a demand-side factor. And with global central banks on an easing spree, will this and deficit spending anchor the "Marcos-nomics stimulus"?
I. Global Central Banks Predominantly on an Easing Trajectory
Figure 1Easy money policies have made a dramatic comeback, and charts reveal that global central banks have been reinforcing the market's propensity for leveraged speculative activities.
For the first time since October 2020, the Bank of America (BofA) reports that there were zero rate hikes from central banks last June. (Figure 1, topmost and middle charts)
Ironically, even as inflation has yet to be fully contained or subdued, this aggregate easing trajectory reinforces the path dependency of authorities, primarily in support of the swelling of government control of the economy channeled through the rapid expansion in deficit spending (partly via the war economy), boosting asset prices which serve as collateral, and the backstopping of systemic leveraging (debt expansion).
In the same vein, the uptrend in US government deficit spending should serve as a template for the world. (Figure 1, lowest image)
In the Asian region, governments like Thailand (USD 13.5 billion for household debt relief), South Korea (USD 18 billion for Micro Businesses), and Indonesia (USD 28 billion-Free Meal for schools) have been rolling out various forms of politically targeted subsidies in "support of the economy."
II. The BSP’s Programming of the Inflation Narrative via the Confirmation Bias
The Philippine June CPI data illustrates such conditions from the lens of the Philippine political economy.
Business Times/ Reuters July 5, 2024: PHILIPPINE annual inflation was at 3.7 per cent in June, easing from the previous month on a slower increase in utility costs, the statistics agency said on Friday. The rate, which was below the 3.9 per cent forecast in a Reuters poll, brought the average reading in the six months to June to 3.5 per cent, within the central bank’s 2 to 4 per cent target range. The Philippine central bank said inflation was expected to have settled between the 3.4 to 4.2 per cent range in June.
This outlook represents an update of our June 10th post, predicting the temporary peak of the recent bounce in inflation.
Firstly, the Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP) exercises significant control over the inflation narrative.
Before releasing the Consumer Price Index (CPI) data, the BSP projects a path that serves as the basis for consensus estimates, representing the survey's "normal distribution."
While media outlets focus on the BSP's annual targets when reporting CPI numbers, the public often overlooks the deviation of the consensus median estimate from the actual outcome. It also discounts their flawed predictive track record.
The selective attention from the "pin the tail on the donkey" approach perpetuates "confirmation bias," reinforcing the public's preconceived notion that authorities have complete control over the economy.
III. Widening Inequality: Headline CPI vs. Bottom 30% CPI Hits 22-Year High!
Next, authorities bask in the glow of reported slowdown in inflation, they quickly claim credit or take a victory lap.
Inquirer.net, July 5, 2024: The lower inflation rate registered in June — at 3.7 percent — is proof that the administration’s economic policies have been effective, House of Representatives Speaker Ferdinand Martin Romualdez said on Friday.
However, few notice that data from the Philippine Statistics Authority (PSA) reveals a different story—this includes officials.
In fact, it shows that inflation has had an adverse impact on households at the bottom 30%, leading to a widening inequality gap.
Figure 2
The gap between the national CPI and the CPI of households in the bottom 30% has surged to its highest level since the post-Asian crisis in 2002! (Figure 2, topmost graph)
While the bottom 30% buys goods at the same prices from the same stores as everyone else, their higher inflation rate highlights the disproportionate loss of purchasing power against goods and services.
The slowdown in the statistical inflation rate has barely alleviated conditions, affecting not only the lowest-income households but also average households, while elites benefit from direct access to the formal banking system and capital markets to safeguard their assets.
Evidence?
Including government external borrowings, FX deposits in Philippine banks have soared to Php 3.324 trillion in May 2024, marking the third-highest level recorded, in tandem with the surging US dollar-Philippine peso pair. (Figure 2, top and middle windows)
Given the low penetration levels of formal finance and financial literacy, this surge in FX deposits could be interpreted as FX "speculation" by elites and upper echelons of households within the BSP’s jurisdiction.
Amazing, right?
IV. June’s Demand Side Disinflation: Non-Performing Loans Surge in May
Authorities may view the slowing inflation rate as an accomplishment, but the easing of the CPI is likely to slow further for several politically unpalatable reasons:
Figure 3One. The PSA's CPI month-on-month rate continues to decline, in contrast to its strengthening which had backed the previous uptrend in the CPI. (Figure 3, upper chart)
Two. Outside of food CPI, there has been a sustained moderation of the Core (non-food and non-energy inflation) which posted a steady 3.1% in June. Importantly, prices have been falling across the board. Paradoxically, food inflation has been moderating globally. (Figure 3, lower diagram)
Figure 4
Three. Philippine treasury traders have bet against inflation. T-bill rates have been coming off their recent highs, and the narrowing of the treasury curve or a "bullish flattening" has highlighted weaker inflation and slower GDP growth, supporting the BSP's desired rate cuts. (Figure 4, top and bottom charts)
Four. While the slowing inflation rate has been perennially sold to the public as a supply-side phenomenon, the real story is that this represents a demand-side downturn.
For instance, in June, we pointed out the surge in consumer credit card and salary loan non-performing loans (NPLs) in Q1 2024. These NPLs have now surfaced to the "core" from the "fringes."
Businessworld, July 5, 2024: THE BANKING INDUSTRY’S nonperforming loan (NPL) ratio soared to a near two-year high in May, data from the Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP) showed. The Philippine banking industry’s gross NPL ratio rose to 3.57% in May from 3.45% in April and 3.46% a year ago. This matched the 3.57% ratio in July 2022. It was also the highest in 23 months or since 3.6% in June 2022.
The BSP data on the banking system’s selected performance indicators confirm our view that the accelerating accounts of consumer borrowings (and businesses) have been used to roll over or refinance existing record debt rather than for consumption.
Therefore, refinancing has been used by the banking system to conceal the mounting liquidity and solvency issues that are plaguing it.
We are oblivious to the actual numbers of "zombie" institutions, which survive by constantly rolling over debt and remaining afloat solely through the accumulation of debt.
Aside from relief measures and regulatory subsidies, the banking system continues to accumulate imbalances, exacerbated by the BSP's pseudo "tightening" policies, which are actually easy money policies.
In reality, the BSP cannot afford to "tighten" as it did in 2018, as it would risk triggering a domino effect or contagion due to the growing liquidity and solvency issues.
The Philippine economy and financial system have been gradually devolving into a Ponzi finance-economy. (Prudent Investor, 2024)
Figure 5Aside from the historic high of held-to-maturity (HTM) assets, rising non-performing loans (NPLs) could exacerbate liquidity tightening in the banking system and exert pressure on banks' accounting profits. (Figure 5, topmost chart)
Loan growth in the banking system has declined in similar fashion to 2018-19, with NPLs on the rise following rate hikes from the increase in the CPI. (Figure 5, middle and lowest graphs)
Rising NPLs would not only slow loan growth but also negatively impact banks' investment portfolios, increase credit risks, and deteriorate asset quality, ultimately affecting capital conditions.
While the BSP has employed various regulatory and liquidity measures to disguise the decaying conditions in the banking system, eventually, the chickens come home to roost or these measures will eventually prove ineffective.
Figure 6
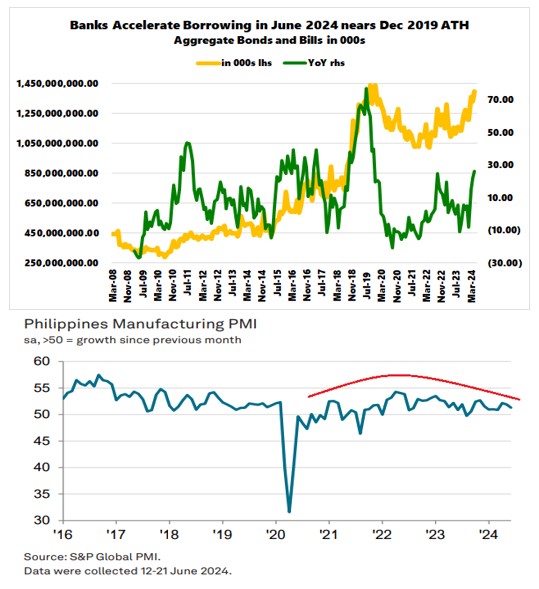
Haven’t you noticed? Banks have been increasing their borrowings from the public. While they market these as 'green' or 'sustainable' bonds to piggyback on politically favored themes, they are essentially debt.
At Php 1.398 trillion, the banking system's outstanding bills and bonds have nearly reached Php 1.44 trillion—levels similar to those seen in 2019 (pre-pandemic). (Figure 6, upper diagram)
Of course, everyone calls this "sound banking"…until it isn’t.
The government will release labor data tomorrow, on July 8th.
Other economic sensitive data, such as external trade and manufacturing, have yet to be released.
Nonetheless, the S&P Global PMI reported a softening of the manufacturing conditions last June. (bold added)
The first half of 2024 ended with a further improvement in operating conditions across the Filipino manufacturing sector, as per the latest PMI® data by S&P Global. Output and purchasing activity rose at accelerated rates. However, June marked a notable slowdown in new orders growth. Moreover, manufacturing companies in the Philippines continued to reduce their backlogs, and further trimmed back their staffing levels. Turning to prices, despite a fresh rise in cost burdens, the rate of input price inflation remained weaker than that seen historically. Meanwhile, charges were raised at a softer pace in June. The headline S&P Global Philippines Manufacturing PMI – a composite single-figure indicator of manufacturing performance – fell to a three-month low of 51.3 in June, from 51.9 in May. (S&P Global, July 2024)
The Philippine PMI seems to have been plagued by a "rounding top." (Figure 6, lower image)
A slowdown in credit usage by businesses and households will likely exert downward pressure on inflation and GDP.
V. Escalating Deficit Spending as a Floor on the CPI; Will Belated Rate Cuts Sow the Seed of the Next Wave of Inflation?
On the other hand, inflation could find a floor from the ramping up of deficit spending.
May's expenditure was historic as it almost reached the three-year streak of record-breaking December levels.
For instance, the Philippine government proposes to import costly fighter jets, which, if pursued, would swell trade deficits and increase the need for external borrowings, potentially further weakening the Philippine peso. Instead of pursuing this path, it might be more effective to focus on resolving territorial disputes via negotiations.
It's as if these jets would make a significant difference in deterrence and actual combat.
Figure 7
Nevertheless, helped by May's expenditure-driven budget deficit, May’s public debt soared by 8.9% YoY and 2.2% MoM to a record Php 15.35 trillion in May.
The all-time high in public debt was primarily fueled by a surge in foreign debt (up 8.8% YoY and 4.2% MoM) that spiked its share of the total from 31.4% to 32%. (Figure 7, topmost graph)
It is no surprise that public debt dynamics are correlated with the USD/Philippine peso exchange rate, as well as with the CPI. (Figure 7, middle image)
Alongside the transformation of the banking system's business model towards consumer spending, the trickle-down "spending one’s way to prosperity" economic development paradigm focuses on centralizing the economy via the credit-financed record savings-investment gap, channeled through the "twin deficits." This translates to an increasing reliance on foreign savings.
Subsequently, the deepening reliance on credit increases the incentives for the BSP to ease its monetary policies.
This also implies that the USDPHP rate is driven nearly entirely by the policy path, as confirmed by data, rather than monetary policy differences between the Fed and BSP.
With global central banks easing, the BSP can justify its shift to an accommodative stance.
And as noted earlier, the BSP easing and increased public spending in support of GDP growth could signify the "Marcos-nomics stimulus."
In light of this, the Philippines would most likely join the ranks of its neighbors in throwing down the gauntlet of stimulus.
It wasn't until a single 100-basis-point rate cut that the CPI began to rise, accelerate, and sow the seeds of the present 9-year CPI trend. (Figure 7, lowest chart)
Are we witnessing a repetition of the inflation cycle?
___
References
Ryan McMaken, Three Lies They’re Telling You about the Debt Ceiling May 23, 2023, Mises.org
Prudent Investor, Has the May 3.9% CPI Peaked? Are Filipinos Really Spending More On Non-Essentials? Credit Card and Salary Loan NPLs Surged in Q1 2024! June 10, 2024
S&P Global, Production growth sustained, although underlying demand trends soften S&P Global Philippines Manufacturing PMI July 01, 2024 PMI.SPGLOBAL.com