``Information is the currency of the Internet. As a medium, the Internet is brilliantly efficient at shifting information from the hands of those who have it into the hands of those who do not...The Internet has accomplished what even the most fervent consumer advocate usually cannot; it has vastly shrunk the gap between the experts and the public. The Internet has proven particularly fruitful for situations in which a face-to-face encounter with an expert might actually exacerbate the problem of asymmetrical information-situations in which an expert uses his informational advantage to make us feel stupid or rushed or cheap or ignoble.”-Steven Levitt and Stephen Dubner in Freakonomics
Prior to the Christmas break, I was asked if Unit Investment Trusts (UIT) would be a good way to go, for the coming year. To my understanding, UITs operate like mutual funds in the sense that it holds a portfolio of securities. But unlike mutual funds they have been designed for a specific length of time and structured as a fixed portfolio. I was particularly asked, which among the bank’s locally offered portfolio namely, the Peso denominated fixed income, equity or combination of (balance fund), I would recommend, considering the bank’s bullish outlook for the coming year.
To the surprise of the client, my response was to buy US dollars (relative to the Peso) or US dollar short term fixed income instruments and Precious Metals or its proxy (mines) instead.
It is not that I seek to purposely become a contrarian, but my interest considering today’s ambiguous investing climate, is to preserve capital or minimize losses and optimize profits, yet much of today’s optimism comes in the light of a global downshifting of economic growth or a heightened risk environment.
It’s all about Incentives
During the holiday, I came about a very insightful book of which I am in halfway, by Steven Levitt and Stephen Dubner, called “Freakonomics” which essentially deals with how people respond to incentives; to both negative and positive stimulus, something like getting penalized for committing mistakes or receiving awards for a job well done.
Similar to the Austrian School of Economics “Praxeology” which basically deals with the study of human conduct, Mr. Levitt and Dubner wrote (emphasis mine), ``An incentive is simply a means of urging people to do more of a good thing and less of a bad thing. But most incentives don’t come about organically. Someone-an economist or a politician or a parent-has to invent them.”
For instance, in the environment where a country’s currency is rising, mainstream economists would demand for government intervention in support of the export industry, or politicians in response to a public’s outrage would act to impose restrictions or regulations such as the recent “Anti-billboard law”, or a parent would ground their child based on current misbehavior.
And in many instances, as Freakonomics team cites, an individual or the public or society responds to such incentives in manners which have not been anticipated, wherein, as the Freakonomics team says “the conventional wisdom is often wrong”.
Let me cite possible analogies in the local arena; while Economics 101 tell us that rising currencies are essentially bad for exports, why are there “substantially” numerous if not greatly significant cases of Asian, European and Latin American countries with rising currencies YET accompanied by years of rapidly GROWING exports?
Or the Freakonomics team quotes risk communication expert Peter Sandman in New York Times (emphasis mine),``The basic reality is the risks that scare people and the risks that kill people are very different...When hazard is high and outrage is low, people underreact, and when hazard is low and outrage is high, they overreact.” An example would be the dread of death from terrorism than from heart attack.
In the Philippine setting, could the recent Anti-Billboard law as a consequence of a once-in-10 year event, i.e. Typhoon Milenyo’s direct hit to Manila, reflect an overreaction to a low-hazard-high-outrage circumstance?
Since there are three basic forms incentives, moral (how the people would like the world to function), social and economic (“how it actually does work”-Freakonomics), I would relate to the latter with respect to this field of endeavor.
In such light, the economic incentives for brokers, bankers, fund managers and investors are divergent. Brokers earn by commissions, thereby our incentive is to encourage market participants to trade more. Bankers, on the other hand, earn by fees, whereby to entice the public for more placements opportunities by offering more products, while fund managers earn by a combination of fees and profit-sharing scheme, where the purported incentive is to earn from more placements and investing profitably (return based).
While the investing public seeks to grow their money through the incentives of “rate of returns”, it is incumbent upon them to understand the incentives of the intermediary they deal or transact with. Simply because the investing public’s incentives more often than not varies and could, in fact, be in conflict with their intermediary’s interest.
So it would be natural for bankers or fund managers or brokers to promote their product line or services regardless of the return outlook because it is their “economic incentive” to do so.
The Wisdom of Conventional Thinking
Now relative to the “wisdom of conventional thinking”, today’s investor sentiments emanating from the recent buoyancy in global equity markets could be depicted through this newspaper heading...
Figure 1: SCMP: December 30 Headline: “20,000” Roaring Through
The headline above from South China Morning Post reveals of the conspicuously bullish overtones by Hong Kong’s Hang Seng Index (+34.2% year-to-date) which recently carved fresh record highs, like almost any other benchmark indices all over the world.
For money managers, these are known as the “Magazine Cover or Newspaper Headline” indicators, a contrarian signal. Since the “incentive” of the press is to “sell its media to the public”, it usually does so by conveying recent developments backed by a STRONG consensus view. In other words, they vend information which caters to mostly what the public wants to hear about.
This reminds me vividly of the yearend 2004 where several magazines as the Economist declared the “Death” of the US dollar following two successive years of rout. In 2005, the US dollar simply proved the consensus wrong by rebounding mightily across the board.
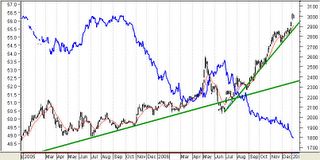
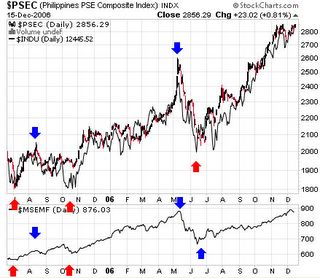
Figure 2: Phisix At 3,000 level backed by Strong Peso on Massive Foreign InflowsAt the start of the year, I forecasted that the conditions of the Peso and the region would reflect on the Phisix see January 2 to 6 edition, (2006: Global Liquidity and the US Dollar to Drive the Phisix), ``It is apropos to view the recent strengths in Asian bourses as well as in the Phisix to the incipient signs of the US dollar strength reversal. This essentially serves as the bullish case for the Phisix.”
As shown in Figure 2, the Phisix ended the year up 42.29% for its best performance in over a decade, with gains of almost the same intensity as the inception of the bull run in 2003 (+41.63%) and for its fourth consecutive year of advance in synchronicity with global equity markets.
Figure 3: Asianbondsonline.com: Declining Yield Spreads of on Major USD Philippine issues
Apparently, the massive inflows from foreign money came at the heels when I became alot cautious calling for extra vigilance in the latter half of the year from the same outlook, ``On the later semester of the year I would be extra vigilant/cautious for any possible signs of weaknesses that may arise in the US or from China.”
Yes, while it is true that weakness in the US did materialize, the subsequent effect to the financial markets was instead a “melt-up” on the account of expectations of a “Goldilocks” outcome backed by a more extra loose money environment.
The Peso gained 7.69% in 2006 to Php 49.03 per US dollar supported at the margins by these massive portfolio investments into the Phisix, the Philippine debt instruments in both local and dollar denominated issues as shown in Figure 3 and other asset classes. Of course, remittances have been a factor, yet as we argued before, it is the unseen working at the margins that have shifted in favor of the Peso.
As evidence to this, remarkably, the spread of the 10-year Peso Philippine denominated Treasuries and the 10 year US dollar denominated Philippine Treasuries has narrowed to only 34.9 basis points as Friday (Jan 05), from 278.4 basis points at the end of 2005 (Dec 29th).
The thinning of the spreads astonishingly reflects on the enormous money flows into Philippine assets mostly on the grounds of a global low risk premia and low volatility aside from the moving out of the risk spectrum in the stretch for yields mentality.
Of course, local analysts and experts will construe these as mostly reform based since they hardly comprehend the dynamics of the macro cycle which the local media would unsparingly carry up. To quote again Mr. Levitt and Mr. Dubner, ``Journalists need experts as badly as experts need journalists. Every day there are newspaper pages and television newscasts to be filled, an expert who can deliver a jarring piece of wisdom is always welcome. Working together, journalists and experts are the architects of much of conventional wisdom.”
Increased Portfolio Risks Plus Unfavorable Cost-Return Analysis
Figure 4: IMF: Sub-Saharan Africa: Trading Volumes
Arguing incessantly that today’s highly globalized financial landscape have been a manifestation of the above du jour thematic investing psych, figure 4 from IMF shows that money flows towards “exotic” themes, such as the Sub-Saharan region, have been dramatically expanding, as fund managers with a torrential “leap of faith” towards a protracted placidly rated risk environs; go for every “nook and cranny” with regards to any asset classes in the mission to seek above average returns.
Since I believe that today’s directional path of money flows are inexorably moored towards the fate of the US dollar [US dollar index -9.01% in 2006], we might as well consider the recent actions which may be as well be indicative of the directions of the Phisix and related Philippine assets.
I have argued in November 27 to December 1 (see Falling US Dollar Fuels Rising Oil Prices) outlook that aside from “demand-and-supply” factors the prices of oil or other commodities could be determined by the gyrations of the currencies where they are predominantly traded in, i.e. US dollar. For instance as oil prices recently swooned, media outlets took the quick-and-easy version of a warmer weather attributed to its actions. Nevertheless, oil’s decline came about as the US dollar massively rallied.
Which brings us to the unseen, could the inverse relationship of commodities and the US dollar signal a demand contraction and a rise in risk aversion similar to the case last May?

Figure 5: IMF US Housing Indicators
In the US, as shown in Figure 5 from IMF, Housing Stats continue to manifest steep deterioration. The OFHEO Price Index (blue line), Housing Starts (red line) and Total Existing sales (green line) appears to have “peaked out” (green blocked arrow) during the latter portion of 2005.
Warns the IMF (emphasis mine), ``The shift in recent years toward more risky mortgages may make segments of the mortgage credit markets more vulnerable to the deceleration in housing prices. Innovations in the origination of mortgages have allowed a widening range of borrowers to finance more expensive homes at a given income level. These include mortgages for subprime borrowers, mortgages with high degrees of leverage, and mortgages that feature sharply rising monthly payments, resulting in “payment shock” (Figure 10). More than half of mortgages originated in 2005 and 2006 are estimated to contain provisions that will eventually lead to a sharp rise in payments, even if the level of market interest rates does not change.
``Furthermore, as shorter-term interest rates have increased in recent years, rising payments on conventional adjustable rate mortgages will add to payment shock. Although the overall level of home equity remains high, a recent study suggested there may be significant pockets of home purchasers with low or negative equity; that is, mortgage debt in excess of the value of their homes. This may owe to several factors, including falling home prices in some regions, mortgages that initially allow for a buildup of debt over time, and the fact that some homeowners may have overpaid for their homes at the speculative height of the market, facilitated by overly liberal underwriting. Thus, homeowners with small or no equity cushions in their homes may find the payment shock difficult to manage.”
The good news is that so far the housing recession has been contained to within the industry premises. However, as the IMF warns, adjustments to subprime mortgages, which could have a significant impact and may translate to more tightening of belts by the US consumers, which has been the single most important engine of growth on the demand side for the global trade structure.

Figure 6 Stockcharts.com: Commodities take a DrubbingMeanwhile, commodities appear to take a drubbing as shown in figure 6. We can observe that both oil and copper, commodities widely used in the economy, which have coincidentally peaked in May of 2006, as with the benchmark CRB, trailed the peak of the US Housing industry by about 3 quarters. Noticeably, a broad spectrum of commodities went into a sharp and accelerated decline last week.
Lest be accused of the logical fallacy of “Cum Hoc, Ergo Propter Hoc” [With this, therefore because of this], we are curious to know if the inflection point seen above are correlated, since they broke down almost simultaneously? And if this could be reflective of the lagged effects of the above stated US housing recession? Or does this effectively represent a diffusion of the weakening of the US economy into the global economy?
Writing prior to the recent rally of the US dollar Chief Economist Paul Kasriel of Northern Trust last December to give us a clue, ``This weakening in copper prices corroborates the slowdown in the pace of U.S. manufacturing activity – it appears as though manufacturing output peaked in August 2006 – and the recession in housing. The decline in the dollar price of copper is all the more indicative of faltering goods-producing activity in the U.S. inasmuch it has occurred at the same time that the foreign exchange value of the dollar has been falling. All else the same, the dollar price of an internationally-traded generic commodity would be expected to rise as the foreign-exchange value of the dollar fell. The fact that the dollar price of copper has declined along with the fall in the dollar implies that the price of copper has declined in terms of other currencies, not just the dollar. This could suggest that manufacturing activity globally is slowing.”
So as Mr. Kasriel asserts a possible candidate could be a US-led global manufacturing activity slowdown, which is not a good news at all.
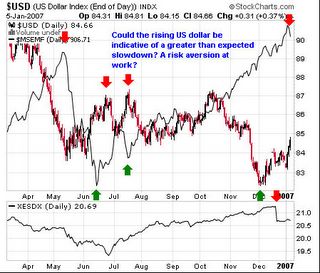
Figure 7: Stockcharts.com: Inverse Relationship between the US dollar and Emerging MarketsIn addition, the IMF in its unusually cautious “Global Financial Stability” tone admonishes (emphasis mine)``A transition from the current state of low volatility to one in which volatility returns to historically more normal levels would likely not be straightforward. The task has been made more difficult by the rapid growth of some innovative instruments and the build-up of leverage in parts of the financial system. Carry trades have grown and the unwinding of those trades has potential to cause perturbations in markets. A “volatility shock”—perhaps caused by a downward shift in growth expectations or by renewed inflationary pressures—could precipitate portfolio adjustments and raise underlying volatility.”
A benign decline of the US economy is more likely to lead to an incremental decrease of the US dollar index. However, a greater-than-expected incidence of the housing industry and auto manufacturing recession, which may spread to the general economy or the sudden emergence of adverse developments, such as “volatility shocks”, unwinding of carry trades, hedge fund collapse, geopolitical uncertainties-as possible catalysts, emanating from elsewhere could lead to a rush into “safehaven” instruments as the US dollar.
Thus likely, as shown in Figure 7, the inverse correlation between the US dollar and emerging market equities have been quite strong over the past year. To wit, as the US dollar rallies emerging market equity indices tend to decline, while emerging market bourses rally when the US dollar index is on a downshift.
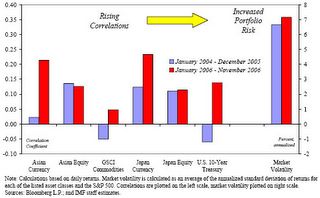
Figure 8: IMF: Correlation of Asset Classes with S & P 500 and Broader Market Volatility
Moreover, the IMF Chart in Figure 8 shows that various asset classes have been in a trend towards increased correlation. Increased correlation suggests that the objective of diversification, which is “to reduce risk by spreading portfolio holdings”, effectively diminishes.
To quote the IMF, ``If these positive correlations were to persist, or even to rise, in a sell-off, the traditional diversification benefits of investing in a wide variety of asset classes might be less than investors expect. The possibility that the correlations may persist underscores that investors may eventually demand higher risk premiums.”
What this implies is that going forward considering the hefty advances of the Global Equity Indices (“priced for perfection”), as well as the Phisix, considering the record low volatility, tight credit spreads, extreme optimism (newspaper cover), the diminution of seasonal strength, the non-confirmation of Dow Theory (see December 4 to 8 Dow Theory: The Emergence of a Divergence?), technically overbought conditions, mean reverting cyclicality and tendencies of the financial markets, rising correlation among diverse asset classes, conflicting messages by the bond and equity markets, the recent massive decline of broad based commodities, a rallying US dollar, an inverted yield curve, rising potentials for “volatility” shocks (while the Euro is down lately, the Yen is up- further increases in the Yen could unnerve the widely utilized Carry Trade) and uncertainties towards the ripple effect of the present slowdown in the US suggests of Increased Portfolio Risks. Of course, aside from our oft mentioned “Fat Tail” or Sigma risks.
This coupled with the rising cost of our capital over potentials returns on our invested capital makes the investing in the local UITs a less palatable proposition today. Sometime in the middle of 2007 could be a good entry point.