Here is what I wrote last week[1],
Also the Phisix is likely to surf on the global ‘EU Summit honeymoon’ sentiment, as well as on the momentum from an imminent RECORD breakout.
Whether this breakaway run will be sustainable remains unclear as global markets will remain volatile on both directions.

Indeed the jubilation from the EU Summit combined with momentum powered the major local equity benchmark, the Phisix, to a fresh record high.
Of course this breakaway run will be subject to the question of sustainability given the recent developments abroad.
Nevertheless after 3 successive weeks of advances which racked up 8.53% in returns, it would be normal to see some profit taking.
Nonetheless today’s exemplary standings have more stories to tell.
The ASEAN Standout

From my radar screen of 70+ international equity benchmarks, the Phisix only ranks fourth among the best performers based on a year-to-date returns.
But the Phisix is the ONLY bellwether among the elite contenders that has been trading at record highs.
Except for Venezuela which has been drifting close to the recently etched milestone highs established last May, it is only Thailand that comes close to having a superb feat.
All the rest are still way off from their apogees set during the last 3-5 years
I do not count Venezuela’s stock market as a real contender for the simple reason that the outperformance of the Venezuelan stock market could be a reaction to the amplified risks of hyperinflation.
Due to a combination of price controls and massive imports by the government, Venezuela’s inflation rate has been down reportedly to 21.3% last June[2]. But this is likely to be temporary and designed for the reelection of President Chavez this October
Combined with falling oil prices and massively expanding government expenditures, the Venezuelan government will likely run out of hard currency or of foreign exchange which may force them to ramp up on the printing presses for financing.
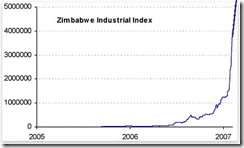
Stock markets have been functioned as safehaven during episodes of hyperinflation as people jettison currency for real assets. A good example is the recent bout of horrific hyperinflation[3] endured by Zimbabwe which culminated in 2008[4].
Surging stocks amidst hyperinflation has barely been about real (investment) returns but about people trying to preserve savings through acquisition of claims on real assets (insurance against monetary disorder).

And going back to the top 11, Thailand’s stock market as measured by the major bellwether the Stock Exchange of Thailand (SET) is second only to the Phisix to demonstrate remarkable gains.
While the SET is at a milestone multi-year high, the Thai bellwether is still about 30% off from the 1994 pre-Asian crisis record.
Yet the best annual performers masks or are framed to exclude the position of the others. This shows why the use of statistics can tricky and can be tailored to fit a predetermined conclusion.
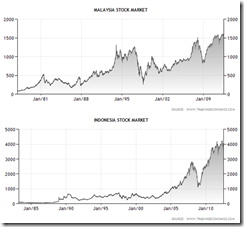
Indonesia and Malaysia may have posted moderate year-to-date returns relative to the Phisix, up only 6.1% and 5.87% respectively, but Malaysia, like Philippines, trades at record HIGHs.
Meanwhile Indonesia trades a few percentages or (3.5%) off the recent record.
So ALL four major ASEAN bourses are AT or NEAR landmark highs but so far the Phisix leads the pack.
Outside the region, I have not encountered any national stock markets that have come close to beating their 3-5 year highs.
Growing Detachment between Stock Markets and Real Events
It is obvious that any economic or financial gains would be used as political advertisement.
For instance the recent S&P upgrade of the Philippine credit rating have been painted as a puffery of good governance. The fact is that whatever gains seen in the Philippines has been a regional dynamic. They are in reality symptoms of the boom phase of the business cycle that has mainly been driven by the domestic monetary policies through the negative real rate regime and supplemented by external monetary policies which has induced a search for yield dynamic from foreign investors in response to international easing policies. This ‘search-for-yield’ can also be interpreted as capital flight.
The current market conditions of the Phisix fit the inflationary boom scenario described by the late Austrian economist Fritz Machlup[5]
If, however, we inquire into the causes of the inflow of speculative capital from abroad which is so much objected to, we shall often find that it was the boom tendencies that were already present on the stock exchange which attracted the foreign funds. La hausse amene la hausse. The beginnings of the speculative boom originated in a flow of money from domestic sources. And as it is extremely difficult domestic to conceive of a sudden epidemic of saving, we are once again driven back to credit expansion by the banks. It is the "domestic" creation of credit which usually produces that sentiment on the stock exchange and that movement of stock prices, which act as an by foreign invitation to foreign funds.
The occasions when the short-term foreign funds flowing onto the stock exchange are to be regarded with real mistrust are when these funds owe their boom is existence to a credit inflation abroad. In this case foreign they bring the foreign “business cycle germ” into the home country
Yet the much ballyhooed upgrade has been based on superficial measures. They have most likely been influenced by surging prices in the asset markets (reflexivity theory), by political Public Relations campaign, particularly the phony war against corruption (where corruption is misleadingly portrayed as a function of ethical virtuosity rather than from real cause: arbitrary statutes and regulations[6]) and could even possibly be related to dwindling stock of “safe assets” for the global banking system than from real changes or market based economic reforms as I explained earlier[7]
What the credit upgrade does is to give license to the Philippine government to lavish on public expenditures. This would only promote crony capitalism, (yes guess which parties will be awarded with the proposed $16 billion of public work spending?) and that rewarding debt would work to the detriment of the economy over the long run through the adverse effects of the crowding out phenomenon[8], higher taxes and the serial blowing of the bubble cycles.
Grandiose skyscrapers (or the Skyscraper Index) have exhibited uncanny accuracy as harbingers of the bust phase of financial bubbles.
And believe it or not, 9 of the 10 of the world’s tallest building will rise in Asia and have been slated for completion from 2015 onwards—with China having four, South Korea three and one apiece for Indonesia (3rd largest) and Malaysia[9].
So if the skyscraper index remains a functional indicator of financial excesses then we could or we may see a regional financial crisis anytime during the time window of 2015-2017.
Yet given the extreme fluidity of current conditions, such bubble conditions may be delayed or hastened depending on the direction of external and domestic social policies mostly channeled through monetary policies, particularly the complicit war by central bankers against interest rates (or the euthanasia of the rentier).
From the prescient admonitions of the great Ludwig von Mises[10]
Public opinion is prone to see in interest nothing but a merely institutional obstacle to the expansion of production. It does not realize that the discount of future goods as against present goods is a necessary and eternal category of human action and cannot be abolished by bank manipulation. In the eyes of cranks and demagogues, interest is a product of the sinister machinations of rugged exploiters. The age-old disapprobation of interest has been fully revived by modern interventionism. It clings to the dogma that it is one of the foremost duties of good government to lower the rate of interest as far as possible or to abolish it altogether. All present-day governments are fanatically committed to an easy money policy.
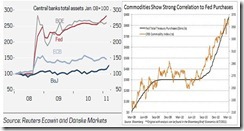
Of course, I see the soaring Phisix as effects of the bubbles parlayed as symptoms of Panglossian complacency (based on the belief that the Phisix or the region will decouple) or if not Pavlov’s classic mental conditioning (of the strongly held belief that central bankers will successfully bailout financial markets) or as effects of “jockeyed” markets.
As for the latter, aggressive buying in a landscape where global political authorities have been exhibiting anxieties over global economic conditions simply does not match with the current state of exuberance.
To give some examples.
The Bloomberg quotes IMF’s Christine Lagarde’s diagnosis of the world economy[11]
“Over the past few months, the outlook has regrettably become more worrisome,” Lagarde said. “Many indicators of economic activity -- investment, employment, manufacturing -- have deteriorated. And not just in Europe or the United States.”
Or how about the “45-minute salvo” fired by 3 central banks last Thursday as acts of desperation?
From another Bloomberg article[12]
Global central banks went on the offensive against the faltering world economy, cutting interest rates and increasing bond buying as a round of international stimulus gathers pace.
In a 45-minute span, the European Central Bank and People’s Bank of China cut their benchmark borrowing costs, while the Bank of England raised the size of its asset-purchase program. Two weeks ago, the Federal Reserve expanded a program lengthening the maturity of bonds it holds and Chairman Ben S. Bernanke indicated more measures will be taken if needed.
Many major global equity markets sagged following the news of the 45 minute interval coordinated easing from 3 major central banks.

The most curious response I saw came from China.
The Shanghai index remained wobbly and even traded on the negative for almost two thirds of Friday’s session which appeared to have discounted the interest rate cuts. The above chart from Bloomberg shows of the intraday actions. It took the last minute for the Shanghai index to surge, which according to news reports had been led by the property sector[13].
That last minute adrenalin shot may not persist as China’s Premier Wen Jiabao immediately shot down the notion of the lifting property controls in a comment today[14].
This is yet another example of the confounding stance by China’s political authorities.
The weaknesses in global markets following the reported near simultaneous interventions in the bourses of major economies could be deemed as “buy the rumor, sell on news” or of reality check relative to hope based expectations.
As I wrote a few weeks back[15],
One, if central bankers FAIL to deliver in accordance to market’s expectations, then we will likely see another huge bout of downside volatility in global equity markets….
On the other hand, if markets may be temporarily satisfied with REAL actions of central banks (e.g. $1 trillion bailout) then we should see a minor or a slight “sell on news”. But this should be seen as opportunities to RE-ENTER the markets incrementally.
Considering that the Phisix has soared since, I don’t see today as a providing a buying window, unless global central bankers would bring on their vaunted bazookas or until there will be meaningful improvements in the global economic arena
When financial markets flows into the opposite direction from the economy sans support from central bankers then the risks of a crash becomes a factor to reckon with.
One thing that could be justify divergences or decoupling is the possibility of intensified capital flight. While there are little signs of these affecting ASEAN markets yet, as explained last week, Denmark’s case seems like a relevant model.
Denmark’s bond markets which earlier have exhibited negative yields have now been reinforced by Denmark’s central bank policy of negative interest rates. Capital flight from the Eurozone to Denmark has prompted for an outperformance of Denmark’s equity markets[16] and has been on my top 11 list.
However the same capital flight phenomenon has not boosted the Switzerland’s Swiss Market’s Index in the same degree as Denmark. So we need to observe this further.
Outside More Central Bank Intervention, Expect Downside Pressures
Current conditions could be ripe for a significant retrenchment for global equity markets based on ‘fundamentals’.

Nearly 80% of the world’s industrial activities have been contracting[17].
Compared to 2007-2008 which had the US property bust as the epicenter, today’s slowdown has been coming from different directions, particularly, the Euro area and the BRICs.

Even in the US, both the industrial activities[18] and non-industrial activities[19] have been exhibiting considerable signs of weakening.
These may not signal yet the imminence of recession, but the risk of recession grows if both domestic and international conditions deteriorate further.
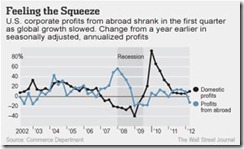
And the global economic slowdown has shown incipient signs of filtering into US corporate profits[20].
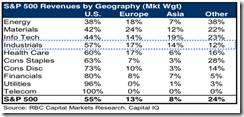
While the distribution of revenues from S&P 500 member companies has marginally been tilted towards US, nonetheless revenues from abroad still accounts for a substantial 45% share[21].
This means that slowing global economic growth will pose as material drag to current “fundamentals”.
So in the absence of further interventions by central banks or when steroid dependent markets have been left to their own devices, broad based downturns on the world economy would hurt profits and will get reflected on the stock prices.
The alternative view is that since global weakness has been coming from different directions interventions will require global coordination similar to the 45 minutes salvo.
In addition, “liquidity” conditions in emerging markets have reportedly been faltering.
This essentially reflects on the ongoing monetary tightening or increasing manifestations of bubble bust conditions in major economies as the Eurozone and the BRICs to Emerging Markets.
The transmission mechanism of which can be seen through the deterioration in trade balances which has been exacerbated by falling commodity prices, declining foreign reserve accumulation as some EM authorities have used excess reserves to support their domestic currency and a slowdown in capital inflows (which even may risk a reversal, if current conditions worsen)[22].
I would further point out that easing through interest rate policies will have miniscule effects to economies laden with debt.
Demand for credit will be limited as hock to the eyeball indebted individuals, households or corporations will be working to pay off existing liabilities. Further, impaired credit ratings diminish access to debt. Also supply of credit will be limited as institutions whose balance sheets have been compromised by problematic assets will work on building up capital reserves. Also, slowing of economic conditions will also hamper debt activities.
This means that unless global central banks pull out another rabbit out of a hat trick of aggressive ‘delaying the day of reckoning’ interventions through money printing, money conditions will tighten, as the malinvestments from previously inflated activities will have to undergo price adjustments that would need re-coordination in the transfer of resources from non-productive to productive activities.
So debt acquired during the bubble heydays will have to be dealt with eventually through the laws of economics.
Aside from the ECB, all eyes will be on the US Federal Reserve FOMC’s meeting on July 31 to August 1, 2012[23]
It would be interesting to see how the Phisix and ASEAN bourses will react in the face of a more pronounced slowdown in the US
Stay Defensive

The principal reason why the Philippines and her ASEAN neighbors have been more receptive towards negative real rates policies is that these economies has been excised of leverage as a result of the Asian crisis as shown in the above chart[24].
But this does not mean that the Philippine and ASEAN economies will be immune from a global economic slowdown. Again the exceptionalism and resiliency of ASEAN markets will be tested with a US economic slowdown.
Again since negative real rates rewards debt and speculation, today’s low debt era may easily transform low debt ASEAN economies into speculative and consumption activities based on debt similar to conditions which plagues developed economies today.
That’s the nature of bubble cycles.
For now, unless the US Federal Reserve (and or the European Central Bank) brings out the BAZOOKA soon, expect the Phisix, ASEAN and global markets to retrench.
At record and near record highs for the Phisix and ASEAN markets, retracements should be seen as normal countercyclical process.
But since events have been so fluid, we cannot discount the risks of a global recession emanating from continuing political stalemate, dithering over monetary policies and from policy errors. Recessions can turn bullmarkets into bear markets.
Oppositely, powerful responses from central bankers may alter the risk scenario for the benefit of the bulls for another short period.
And this is why excessive volatility in both directions will continue to characterize the financial marketplace.
Yet if the Phisix continues to soar, alone or along with ASEAN, despite all the mounting risks, and without support by the FED and or by the ECB, and if they are not driven by capital flight, the tail risks of downside volatility may become magnified.
The current conditions of financial markets can be analogized to navigating in treacherous waters where one’s survival depends on skillful handling of the steep ebbs and flows of the tides, and of course guided too by lady luck. Yet chance according to Louis Pasteur favors the prepared mind.
So still, I would advise that prudence will remain a better part of valor in terms of portfolio management
[1] See Why has the Phisix Shined? July 2, 2012
[2] Businessweek/Bloomberg Venezuela Inflation Slows for Seventh Month on Import Surge, July 3, 2012
[3] See Zimbabwe's Hyperinflation February 25, 2009
[4] See Zimbabwe In The Aftermath Of Hyperinflation: Free Markets November 16, 2009
[5] Machlup Fritz A Digression On International Speculation Chapter 10, The Stock Market, Credit And Capital Formation William Hodge And Company, Limited p.163 Mises.org
[6] See Doug Casey On Corruption: Laws Create Corruption And Corruption Engenders Laws February 10, 2011
[7] See S&P’s Philippine Upgrade: There's More than Meets the Eye July 5, 2012
[8] Wikipedia.org Crowding out (economics)
[9] See Does the Skyscrapers Curse Signal a coming Asian Crisis?, July 6, 2012
[10] Mises Ludwig von 8. The Monetary or Circulation Credit Theory of the Trade Cycle XX. INTEREST, CREDIT EXPANSION, AND THE TRADE CYCLE Human Action Mises.org
[11] Bloomberg.com Lagarde Says IMF To Cut Growth Outlook As Global Economy Weakens, July 5, 2011
[12] Bloomberg.com, Central Banks Deliver 45-Minute Salvo As Growth Weakens, July 5, 2012
[13] Reuters.com China bank shares pull down Hong Kong HSI, property lifts Shanghai, July 6, 2012
[14] See China’s Property Controls: Mistaking Forest for Trees July 8, 2012
[15] See Dealing with Today’s Uncertainty: Patience is the Better Part of Valor June 17, 2012
[16] See Denmark Cuts Interest Rates to Negative, July 4, 2012
[17] Zero Hedge 80% Of The World's Industrial Activity Is Now Contracting July 5, 2012
[18] Yardeni.com US Manufacturing Purchasing Managers Index July 3, 2012
[19] Wall Street Journal Blog Vital Signs: Slowing in Nonmanufacturing, July 6, 2012
[20] Wall Street Journal Blog, Number of the Week: Rest of World Pulls Down U.S. Profits June30, 2012
[21] Businessinsider.com CHART: A Breakdown Of Where S&P 500 Companies Get Overseas Business, June 27, 2012
[22] See Emerging Market “Liquidity” Conditions Deteriorate July 5, 2012
[23] US Federal Reserve Meeting calendars, statements, and minutes (2007-2013)
[24] Zero Hedge, Asia's Downside Risk And The Three Big Hopes June 21, 2012