Saudi riyal forwards hit their highest level in almost two decades as oil plummeted: twelve-month forward contracts for the riyal climbed 260 points, and set for the steepest close since December 1996 on growing speculation the world’s biggest oil exporter may allow its currency to slide against the dollar for the first time since 1986 (incidentally, Bank of America's "Number One Black Swan Event For The Global Oil Market In 2016").
The art of economics consists in looking not merely at the immediate hut at the longer effects of any act or policy; it consists in tracing the consequences of that policy not merely for one group but for all groups—Henry Hazlitt
Friday, January 08, 2016
Charts: Saudi Riyal, Dow Jones Industrials, OPEC Basket, Baltic Dry and Commodity Returns
Monday, August 23, 2010
The Importance of Peripheral Vision
``Entrepreneurial profit and loss emanate from the dedication of factors of production to definite projects. Stock exchange speculation and analogous transactions outside the securities market determine on whom the incidence of these profits and losses shall fall. A tendency prevails to make a sharp distinction between such purely speculative ventures and genuinely sound investment. The distinction is one of degree only. There is no such thing as a nonspeculative investment. In a changing economy action always involves speculation. Investments may be good or bad, but they are always speculative. A radical change in conditions may render bad even investments commonly considered perfectly safe.”-Ludwig von Mises
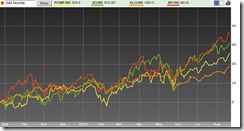
ASEAN Markets Ablaze!
Here is an update of the seemingly majestic performances of ASEAN bourses (see Figure 1).
Figure 1: Bloomberg: ASEAN Bourses On Fire!
Of course, the reason why we should take the BIG PICTURE into perspective is primarily to avoid getting mired with the FALSE impression that domestic politics has been the DRIVER of these dynamics.
As one would note from the above, despite the tremendous showing of the Philippine Phisix (yellow trend line), which has been up over 17% on a year-to-date basis (as of Friday’s close), the fact is the local benchmark TRAILS the fiery actions of Thailand’s SETI (red line) and the Indonesia’s JCI (green line), up nearly 22% and 23% over the same period respectively.
Incidentally, the turbocharged Thailand’s SETI has already caught up and surpassed Indonesia’s JCI based on a one year basis and has been closing in fast even based on the year-to-date as reference point.
Now Asia markets have been uneven in terms of performances. What I am saying is that the inflationary milieu hasn’t lifted all boats similarly, and this simply validates the theory that inflationism has relative effects on almost everything, whether applied to financial assets, commodities to consumer goods or services. This also disproves the fictitious Keynesian construct of neutrality of money and of the obsessive fixation on aggregatism.
Yet the ASEAN bourses, while stirring hot, would seem only a shadow to the spitfire actions of South Asian bourses, particularly, Sri Lanka and Bangladesh up 64% and 49% respectively. Outside South Asia, Mongolia seems to be another bourse ablaze and has been likewise up 65% as of Friday’s close.
In other words, the trajectory of impact from global inflationism has been conspicuous in the markets (financial and non-financial) of the periphery nations. And I also would infer that these effects have been amplified by globalization.
The China Influence
Although China has been getting most of the news, such as having to successfully overtake Japan as the second largest economy in the world[1], the kernel of important actions again are in the peripheral markets but somewhat related to China.
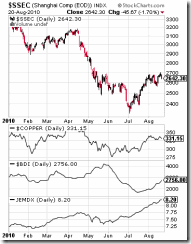
Despite an up week, both of China’s bourses have been significantly down on a year to date basis (see figure 2).
Figure 2: stockcharts.com: China, Emerging Market Bonds and the Baltic Dry Index
One must NOT forget that the actions in China’s stock markets have been repeatedly tampered by with government interventions since late last year. This has been aimed at preventing a homegrown policy induced bubble from inflating into an unwieldy monster, and thus the material underperformance of China’s stock market indices.
And most of financial markets of developed Asia seem to either track the actions of China (e.g. Australia) or the market motions of the West (e.g. Singapore, Hong Kong and Japan).
Nevertheless following a steep decline last quarter, the Shanghai index (SSEC) seems to be manifesting of a rebound.
We can’t say if the momentum will persist until she successfully breaks out of the 2,700 level. A successful breach would possibly suggest that the Shanghai index will attempt for the threshold level of 3,000-3,150.
And China’s stock market actions appear to synchronize with the actions of the copper market (COPPER-the window below the Shanghai Index).
While we are NOT suggesting that China’s stock market has influences on the copper market, what both of these markets seem to say is that they could be responding to the current crop of policies being effected by the Chinese government.
The ongoing slowdown in China’s economy appears to reduce China’s government’s interest to tighten the monetary landscape, and thus, the prospects of lesser government intervention could be giving China’s stockmarkets a boost, especially in the light of the still generally loose credit environment.
Whereas the rebound in the copper market, while possibly partially influenced by these developments, could also be exhibiting signs of “inflationary pressures”. Monetary easing for China could extrapolate to more “speculative” flows from, or “reservation demand”[2] for, commodity buyers. As previously pointed out[3], the commodity price inflation appears to be rotating or diffusing into the “soft” or agriculture based commodities.
Debunking Selective Perception
Another thing that I’d like to point out, which the bears have been pounding on in the recent past, has been the Baltic Dry Index (BDI).
The recent collapse of BDI had been used to prognosticate a market collapse from what we see as fictitious “deflation” in a world of fiat money and central banking. And like US monetary aggregates, such as the M2 which we earlier discussed[4], these indicators have now tilted against them hence the apparent reticence or the deliberate omission of this indicator in current “deflation” discussions.
The selective use of the perma bears of these indicators to prove their case has gradually and repeatedly been falsified. Now to turn the tables, we use these indicators to disprove them.
They never seem to run out of materials to throw in, after the earlier “death cross” and the ERCI leading indicator, whose effects remain to be seen, now they point to the Hindenburg Omen[5] as a reason to take flight.
While September-October tend to be the seasonally weakest month for the stockmarket—where most crashes tend to occur—the dynamics for a crash doesn’t seem to be in place.
Not with the Federal Reserve already embarking on to replace the maturing mortgage bonds with fresh Treasury purchases[6] and certainly not with interest rates at zero bound for an extended period for key developed OECD economies.
Selective use of data for interpretation apparently disregards other things that matter more. For instance, the underlying ‘mixed’ actions (albeit mostly bullilsh) for emerging markets stocks doesn’t seem to be congruent with the actions in emerging bonds which has been exploding (JEMDX)!
Moreover we’d like to add that the steep yield curve has definitely had diversified or distinctive impact on the asset markets (see Figure 3) as we have repeatedly been pointing out[7].

We can still say that the US and Europe has very steep yield curves (as of August 13-green bar) despite recent signs of flattening.
Moreover, outside these crisis affected economies, where the effects of the yield curve could be muted due to balance sheet constrains on the respective domestic banking system, in crisis free Asia, the Philippines still has the steepest yield curve.
What this seem to imply is that Philippine banks will likely take advantage of the maturity transformation[9] (converting short term liabilities to long term assets) in a system which has relatively higher savings, less systemic leverage and unimpaired banking system. In short, credit growth is likely to explode here.
And I would discern that many of the new credit issued could be finding its way into the domestic asset markets including the domestic stock market.
And I would also suspect the same dynamics in operation in other ASEAN economies which has fuelled her recent outperformance.
And one can’t ignore the influences of the divergences of monetary policies between developed economies and emerging markets, where the expectations in the changes of policies seem to induce international capital in favour of emerging markets.
For many, the temptation to get into the bandwagon would seem irresistible. And as the region’s stock market continues to flourish, short term momentum trades would be appear to very lucrative.
In addition, these shifts appear to hallmark the seeds of the bubble.
[1] See The Power of Slow Change: The China-Emerging Market Story
[2] See Financialization of Commodities: Boon Or Bane?, May 31, 2010
[3] See Breakfast Inflation, August 5, 2010
[4] See Why Deflationists Are Most Likely Wrong Again, August 15, 2010
[5] Kahn Michael, Taking Stock of a Scary Market Signal, Barrons, August 18, 2010
[6] Bloomberg.com Fed Buys $3.609 Billion of Notes to Keep Yields Low, August, 19, 2010
[7] See What Has Pavlov’s Dogs And Posttraumatic Stress Got To Do With The Current Market Weakness?, February 1, 2010
[8] Asian Bonds Online, Weekly Debt Highlights, August 16 2010
[9] Wikipedia.org, Financial intermediary
Tuesday, September 01, 2009
Failed Correlation Trade Suggest China's Slump Could Be A Pause
The SSEC could probably be haunted by the September-October seasonal stock market weakness.
In addition, many have used the Baltic Dry Index (BDI) as a "rational" for a major inflection point on China's stock market aside from the purported policy induced slowdown in credit flows.
 Do we share the view that China's stocks will continue to collapse? No.
Do we share the view that China's stocks will continue to collapse? No.In contrast to the past where a decline in China's market had prompted for a rise in the US dollar index (for example see April) or our correlation trade, the recent slump have ironically been opposite-the US dollar Index fell!
Our correlation trade extrapolates to falling global stock markets and commodities along with a rising US dollar index (flight to safety) where a higher US dollar index would have signaled 'tightening liquidity'.
But this doesn't seem so. Hence the continued buoyancy in most stock markets.
The US stock markets ended lower last night but hardly reflected on SSEC's crash.
So if the US dollar index persist on weakening amidst sagging global markets, they are likely to signify an "interim pause" and not a major reason for a collapse.
And this should also apply to commodities.
 As we see from the Russian experience, where the RTSI earlier fell by 30%, the Russian benchmark have managed to recover most of its loses and now trades above the 50-day moving averages.
As we see from the Russian experience, where the RTSI earlier fell by 30%, the Russian benchmark have managed to recover most of its loses and now trades above the 50-day moving averages.This looks likely the paradigm for the SSEC than for a major meltdown.
Sunday, August 16, 2009
Will China’s Stock Market Correction Spread Globally?
``We have seen that according to popular thinking, an asset bubble is a large increase in asset prices. A price is the amount of dollars paid for a given thing. We may just as well say, then, that a bubble is a large increase in the payment of dollars for various assets. As a rule, in order for this to occur there must be an increase in the pool of dollars, or the pool of money. So, if one accepts the popular definition of what a bubble is, one must also concede that without an expansion in the pool of money, bubbles cannot emerge. If the pool of money is not expanding, then people — irrespective of their psychological disposition — simply do not have the ability to generate bubbles in various markets.” Frank Shostak, How Can the Fed Prevent Asset Bubbles?
It looks likely that we may have reached a turning point for this cycle.
I’m not suggesting that we are at the end of the secular bull market phase, but given the truism that no trend moves in a straight line, a reprieve should be warranted.
To consider, September and October has been the weakest months of the annual seasonal cycle, where most of the stock market “shocks” have occurred. The culmination of last year’s meltdown in October should be a fresh example.
Although, this is not to imply that we are about to be envisaged by another crisis this year (another larger bust looms 2-4 years from now), the point is, overstretched markets could likely utilize seasonal variables as fulcrum for a pause-or a window of opportunity for accumulation.
A China Led Countercyclical Trend
My case for an ephemeral inflection point is primarily focused on China.
Since China’s stockmarket bellwether, the Shanghai Index (SSEC), defied “gravity” during the predominant bleakness following last year’s crash, and most importantly, served as the inspirational leader for global bourses, its action would likely have a telling impact on the directions of global stock markets.
In short, my premise is that global markets are likely to follow China.
True, the SSEC had a two week correction, which have accounted for nearly 11% decline (as seen in Figure 1) but this has, so far, been largely ignored by global bourses.
Nevertheless, the action in China’s market appears to weigh more on commodities on the interim. This should impact the actions in many commodity exporting emerging markets.
The Baltic Dry Index (BDI) which tracks international shipping prices of various dry bulk cargoes of commodities as coal, iron ore or grain has been on a descent since June.
This has equally been manifested in prices Crude oil (WTIC) which appears to have carved out a “double top” formation.
In short, there seems to be a semblance of distribution evolving in the China-commodity markets.
The possible implication is perhaps China’s leash effect on global stock markets will lag.
From a technical perspective, using the last major (Feb-Mar) correction as reference, a 20% decline would bring the SSEC to a 50% Fibonacci retracement, while a 25% fall would translate to 61.8% retracement.
And any decline that exceeds the last level may suggest for a major inflection point, albeit technical indicators are never foolproof.
Moreover, from a perspective of double top formation in oil; if a breakdown of the $60 support occurs then $49-50 could be the next target level.
As a reminder, for us, technicals serve only as guidepost and not as major decision factors. The reason I brought up the failure in the S&P 500 head and shoulder pattern last July [see Example Of Chart Pattern Failure] was to demonstrate the folly of extreme dependence on charts.
As prolific trader analyst Dennis Gartman suggests in his 22 Trading rules, ``To trade successfully, think like a fundamentalist; trade like a technician. It is imperative that we understand the fundamentals driving a trade, but also that we understand the market's technicals. When we do, then, and only then, can we or should we, trade.”
In short, understanding market sponsorship or identifying forces that have been responsible for the actions in the marketplace are more important than simple pattern recognition. Together they become a potent weapon.
So despite the recent 11% decline of the SSEC, on a year date basis it remains up by a staggering 67%.
Politicization Of The Financial Markets
Some experts have suggested that when global stock markets would correct, such would transpire under the environment of a rising US dollar index, since this would signal a liquidity tightening.
I am not sure that this would be the case, although the market actions may work in such direction where the causality would appear reflexive.
Unless the implication is that the impact from the inflationary policies has reached its pinnacle or would extrapolate to a manifestation of the eroding effects of such policies, where forces from misallocated resources would be reasserting themselves, such reasoning overlooks prospective policy responses.
The US dollar index (USD) has recently broken down but has been drifting above the breached support levels (see above chart).
It could rally in the backdrop of declining stock markets and commodity prices, although it is likely to reflect on a correlation trade than a cause and effect dynamic.
By correlation trade, I mean that since the markets have been accustomed or inured to the inverse relationship of the US dollar and commodities, any signs of weaknesses in the commodities sphere would likely spur an intuitive rotation back into the US dollar.
Some may call it “flight to safety”. But I would resist the notion that the US dollar would represent anywhere near safehaven status given the present policy directions.
However, if the US dollar fails to rally while global stocks weaken, then any correction, thus, will likely be mild and short.
So yes, the movement of the US dollar index is an important factor in gauging the movements of the global stock markets.
But one must be reminded that last year’s ferocious rally in the US dollar index was triggered by a dysfunctional global banking system when the US experienced a near collapse prompted by electronic “institutional” bank run.
This isn’t likely to be the case today.
So far, aside from the seeming “normalization” of credit flows seen in the credit markets, our longstanding premise has been that global authorities, operating on the mental and theoretical framework of mainstream economics, will refrain from exhausting present gains from which have been viewed as policy triumph.
Hence our bet is that they will likely pursue the more of the same tact in order to sustain the winning streak. The latest US FOMC transcript to maintain current policies could be interpreted as one.
Why take the party punch bowl away when the financial elite are having their bacchanalian orgy?
As we noted in last week’s Crack-Up Boom Spreads To Asia And The Philippines, ``Where financial markets once functioned as signals for economic transitions, it would now appear that financial markets have become the essence of global economies, where the real economy have been subordinated to paper shuffling activities.”
Where policymakers inherently sees rising financial assets as signals of economic growth, the reality is that most of the current pricing stickiness has been fueled by excessive money printing that has prompted for intensive speculations more than real economic growth.
For instance, Floyd Norris of the New York Times has a great chart depicting the year on year changes of global trade based on dollar volume of exports.
While there has indeed been some improvements coming off the synchronized collapse last year, the growth rates haven’t been all that impressive.
In short, rapidly inflating markets and a tepid growth in the global economy manifest signs of disconnect!
Yet global policymakers won’t risk the impression that economic growth will falter as signaled by falling financial asset prices. Hence, they are likely to further boost the “animal spirits” by adopting policies that will directly support financial assets and hope that any improvements will have a spillover effect to the real economy via the “aggregate demand” transmission mechanism.
Alternatively, one may interpret this as the politicization of the financial markets.
To give you an example, bank lending in China has materially slowed in July see figure 3. This could have accounted for the recent correction in the SSEC.
According to US Global Investors ``China’s new lending data for July may be a blessing in disguise, as the slowdown can partly be attributed to a sharp month-over-month decrease in bill financing. Excluding bills, July’s new loans to companies and households were comparable to May and higher than April. With more higher-yielding, long-term loans replacing lower interest-bearing bill financing, margins at Chinese banks should improve as long as corporate funding demand remains strong and overall loan quality stays healthy.”
While this could be seen as the optimistic aspect, the fact is that aside from the overheated and overextended stock markets, property markets have likewise been benefiting from the monetary shindig- property sales up 60% for the first seven months and where residential investments “rose 11.6 percent, up from 9.9 percent in the six months to June 30” “powered by $1.1 trillion of lending in the first six months” (Bloomberg)
True, some of these have filtered over to the real economy as China’s power generation expanded by 4.8% in July (Finfacts) while domestic car sales soared by 63% (caijing) both on a year to year basis.
So in the account of a persistent weak external demand, Chinese policymakers have opted to gamble with fiscal and policies targeted at domestic investments…particularly on property and infrastructure.
Remember, the US consumers, which had been China’s largest market, has remained on the defensive since they’ve been suffering from the adjustments of over indebtedness which would take years (if not decades) to resolve (see figure 4).
 Figure 4: Danske Research: US Consumers In Doldrums
Figure 4: Danske Research: US Consumers In Doldrums
And since investments accounts for as the biggest share in China’s economy, as we discussed in last November’s China’s Bailout Package; Shanghai Index At Possible Bottom?, ``the largest chunk of China’s GDP has been in investments which is estimated at 40% (the Economist) or 30% (Dragonomics-GaveKal) of the economy where over half of these are into infrastructure [30.8% of total construction investments (source: Dragonomics-Gavekal)] and property [24% of total construction investments]”, the object of policy based thrust to support domestic bubbles seem quite enchanting to policymakers.
Besides, if the objective is about control, in a still largely command and control type of governance, then Chinese policymakers can do little to support US consumers than to inflate local bubbles.
Aside, as we discussed in last week’s The Fallacies of Inflating Away Debt, “conflict-of –interests” issues on policymaking always poses a risk, since authorities are likely to seek short term gains for political ends or goals.
From last week ``policymakers are likely to take actions that are designed for generating short term “visible” benefits at the cost of deferring the “unseen” cumulative long term risks, which are usually are aligned with the office tenure (let the next guy handle the mess) or if they happen to be politically influenced by the incumbent administration (generates impacts that can win votes)”
In China, political incentive issues could be another important variable at work in support of bubble policies.
Michael Kurtz, a Shanghai-based strategist and head of China research for Macquarie Securities Michael Kurtz, in an article at the Wall Street Journal apparently validates our general observation.
From Mr. Kurtz (bold highlights mine),
``…far from being an accidental consequence of loose monetary policy, stand out as the purpose of that policy. The fact that housing construction must carry so much of the growth burden means policy makers likely prefer to err well on the side of too much inflation rather than risk choking off growth too early by mistiming tightening.
``Meanwhile, China's political cycle may exacerbate risks of an asset bubble. President and Communist Party Chairman Hu Jintao and other senior leaders are expected to step down at the party's five-year congress in October 2012. Much of the jockeying for appointments to top jobs is already under way, especially for key slots in the Politburo. Mr. Hu will want to secure seats for five of his allies on that body's nine-member standing committee, ensuring his continued influence from the sidelines and allowing him to protect his political legacy.
``This requires that Mr. Hu deliver headline GDP growth at or above the 8% level that China's conventional wisdom associates with robust job creation, lest he leave himself open to criticism from ambitious rivals. The related political need to avoid ruffling too many feathers in China's establishment also may incline leaders toward lower-conflict approaches to growth, rather than deep structural reforms that would help rebalance demand toward sustainable private consumption. Easy money is less politically costly than rural land reform or state-enterprise dividend restructuring. This is especially the case given that much of the hangover of a Chinese asset bubble would fall not on the current leadership, but on the next.”
So the “window dressing” of the Chinese economy for election purposes fits our conflict of interest description to a tee!
Overall, it would seem like a mistake to interpret any signs of a prospective rally in the US dollar on “tightening” simply because policymakers (in China, the US, the Philippines or elsewhere) are likely to engage in more inflationary actions for political ends (policy triumph, elections, et. al.).
Hence, any signs of market weakness will likely prompt for more actions to support the asset prices.
Wednesday, June 17, 2009
Has World Trade Been Picking Up?
This from Businessweek's Joe Weber,
``In yet another sign that some key players are acting as if recession is on the run, more offshore manufacturers are shipping goods into the consumer-driven U.S. market, global-trade tracker Panjiva reports. The May trade data mark the third consecutive monthly rise in the number of shippers moving such goods, the first such Trifecta since the firm began following this metric in July 2007.
``“Increasingly, it feels that the worst is behind us,” says Josh Green, chief executive officer of the trade-tracking firm. Waxing cautious, however, he adds “Still, we have a long way to get back to the pre-crisis level of global trade.”
``Nonetheless, the data, released June 16, suggest that global trade has hit bottom and is taking the first steps toward recovery. Some 131,688 suppliers were active in May, up 2% from the number in April. The rises in shipper tallies give the Panjiva analysts heart, since such totals have been sliding since at least July 2007, when they counted 161,905 shippers moving goods into the U.S.
``The analysts point to other barometers of improvement, too. The percentage of significant manufacturers on a watch list – those in danger of going out of business – dropped a percentage point to 30% in May, for instance. This marked the first such decline since Panjiva started tracking this metric last September."
Read the rest here. (Hat tip: Mark Perry)
The recent rise in the Baltic Dry Index, commodities (CRB) and oil could be partly be due to this.
Nevertheless, our take has been that the collapse in global trade was mainly a consequence of the seizure "shock" in the US banking system which virtually shackled global trade flows by constricting access to financing.
Although the paradigm which underpinned the past boom won't be revived, present signs of recovery could have been due to the replenishment of inventory destocking.
As for how sustainable this would be remains to be seen.
Sunday, February 01, 2009
What Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) Have To Do With Today’s Financial Crisis
``The most popular method of deprecating capitalism is to make it responsible for every condition which is considered unsatisfactory. Tuberculosis and, until a few years ago, syphilis, were called diseases of capitalism. The destitution of scores of millions in countries like India, which did not adopt capitalism, is blamed on capitalism. It is a sad fact that people become debilitated in old age and finally die. But this happens not only to salesmen but also to employers, and it was no less tragic in the precapitalistic ages than it is under capitalism. Prostitution, dipsomania, and drug addiction are all called capitalist vices. Ludwig von Mises Economic Teaching at the Universities
Lessons from Nassim Taleb
There are two important things I’ve learned from my favorite iconoclast Nassim Taleb, the chief proponent of the Black Swan Theory.
One is that he cautions the public to indulge in the study of markets or economies centered upon highly flawed but popular econometric models which are nothing but algorithms designed to operate on sterilized environments similar to classroom or laboratory conditions.
Since these computer models unrealistically operate on the assumption that every factor can be anticipated, examined and evaluated, risks are therefore assumed to be under control. Yet, the complex nature of our world can lead to manifold variables which can’t be read, evaluated or anticipated. The impact of which is known as randomness or the BLACK SWAN, a low probability but HIGH impact event, and is the nemesis of these ‘quant’ models. For instance the humongous losses in today’s financial crisis have been be partially blamed on the failure of quant models to anticipate risks from statistical fat tails.
Second, the other lesson taught by our unorthodox savant is to avoid getting trapped with cognitive biases such as projecting past connections and outcomes into the future.
The Sanctity of Delusion
Today we are told that the world is going to the sewer.
That is because the US, which has functioned as the only major ‘aggregate demand’ of the world, can’t live up to its role as it is undergoing a deep recession. In corollary, these experts further assert that the world won’t be able won’t replace the US as the provider of demand because of its sheer size. In other words, past performance guarantees tomorrow’s outcome.
Based on their economic premise, where supply exists only as a function of demand, then with today’s imploding private sector credit bubble, which has deeply dented the demand equation, must be replaced and absorbed by the government. Therefore, the government’s role MUST be to create artificial demand by printing up as much money in order to sustain the bursting bubble structure.
Tersely said, from the private sector, the credit bubble now is being reconfigured to one known as a government credit bubble. And this seems to be what we are seeing all around the world. From nationalization, “bad bank” or other means of government interventions, the idea is to transfer the leverage and the attendant losses to the government.
The same logic says that if Bernard Madoff was a fraud, and had operated on an unsustainable platform which didn’t last, the government’s insistence of operating on the same an unsustainable platform, but charged to the taxpayers and meant for the “good of the citizenry”, MUST SUCCEED. The difference was that Madoff was a felon, while governments sustaining bubbles for chimerical prosperity, are deemed as legitimate and for a good cause.
Unfortunately for Madoff, he was an individual and not privileged to conduct the same scheme which is equally being thrown to the public by governments. But the underlying principle of both Madoff and the governments is the same: to get something from nothing!
In other words, you resolve the problem of drug addiction by providing more drugs. If you are Madoff you get charged with drug pushing. But if you are the government, you receive plaudits for a fighting for a good cause.
In a reality check, unsustainable trends which can’t last, won’t! NO amount of the printing press nostrums will make illusions a reality.
Reality has finally landed in Zimbabwe. The Mugabe-Gono government finally capitulated to the marketplace realities by allowing the depressed African economy to trade in foreign currencies which in effect jettisoned the local currency, the Zimbabwe dollar. This also means the Mugabe-Gono government will fall soon. And in the same vein, all nationalizations or government guarantees are only as good as the real capital standing behind these.
Does the words of Karl Marx in Das Kapita in 1867…``Owners of capital will stimulate the working class to buy more and more of expensive goods, houses and technology, pushing them to take more and more expensive credits, until their debt becomes unbearable. The unpaid debt will lead to bankruptcy of banks, which will have to be nationalized, and the State will have to take the road which will eventually lead to communism"…ring a bell?
Fairy Tales Cures and Self Righteousness
Yet popular opinion believes in fairytale cures.
To call for market forces to rectify the situation, one risks being labeled as insane, inhuman or bloodless.
Nevertheless just look at level of desperation policymakers are into so as to consider ridiculous ideas to restore an unsustainable structure of economic growth:
-In déjà vu to the hog reduction program of the Great Depression of the 1930s, US policy makers are considering to boosts car sales via a program known as "cash for clunkers". (CNNmoney) Yes, the US government plans to buy and junk old cars so as to motivate its populace to buy new ones. If the policy gets enacted, this is going to be a waste of productive resources.
-Moreover, they are considering “to renegotiate mortgages it owns that might otherwise enter foreclosure” (Washington Post) or allow “bankruptcy judges to modify the mortgages of troubled homeowners” (Washington Post) all at the expense of the property rights of American people.
To add, not content with plans to impose tons of regulations on the national level, the statists have been contemplating on to expand impositions abroad. Signs of protectionism, which had greatly contributed to the Great Depression of the 1929, are surfacing in the political arena. At the confirmation hearing, Treasury Secretary Tim Geither unleashed what he “believes that China is manipulating its currency” (Wall Street Journal). In addition, the stimulus bill which was recently passed by Congress contained a “Buy America” rider (Washington Post).
All these actions seem to agitate for a mutually devastating global trade war.
And why would authorities engage in such potentially calamitous actions? We understand 3 possible things: economic ignorance, messianic complexity or plain political rhetoric.
Realities say that the US doesn’t produce enough, that’s why it incurs trade deficit. And a trade war would mean massive catastrophic shortages. Think oil. The US imports 60% of its oil requirements (CNNmoney). If world trade shuts, the economic implication would be a collapse in the US economy with a geopolitical implication of a possible World War 3.
And also considering that the US is the largest debtor nation in the world, it wouldn’t be far where a trade war would also extrapolate to an equally internecine debt default. And what’s to stop these interventionists fools from inciting a war economy or the misguided belief that only war, after everything else fails, can stimulate the economy?
Now we turn the tables and wonder who is insane, inhuman or bloodless? Does provoking a trade war which has dire consequences similar or worst in scale than the Great Depression a humane and charitable option? How altruistic is it, if the world goes into war out of the desire to stimulate the economy? How does hyperinflation as in the case of Zimbabwe lead to progress? How charitable can it be to live a world of self delusion?
Does the 2008 Global Trade and Production Collapse Signify Posttraumatic Stress Disorder?
If a bubble structure can be characterized by unrestrained credit creation, speculative excess seen in asset inflation and unparalleled concentration of financial wealth and power, then in as much as the massive wage or income disparities or “Shameful bonuses” in Wall Street relative to the average Americans had been a function of a bubble structure, the world’s production-supply chain structure have also been partly been built around the same bubble environment.
And today’s bursting bubble which has prompted for “demand destruction” has been met by more “supply destruction”.
Yet what seems to be remarkable has been the sharp collapse in global production and trade.
 Figure 3: IMF World Economic Outlook: Collapse of Global Industrial Production and Merchandise Trade
Figure 3: IMF World Economic Outlook: Collapse of Global Industrial Production and Merchandise TradeThe chart IMF’s World Economic Outlook demonstrates the seeming peculiarity of the last quarter’s world trade and production activities.
If you are to compare with the dot.com days or the previous bubble bust and its ensuing recession, you’d notice that the same trends went into a steady decline over a period of time (years). But this hasn’t been the case last year. The outright collapse in just ONE MONTH by both economic variables suggests that world suddenly stopped doing anything and merely watched in shock and awe!
And why would the world do that? The obvious answer is the shock emanating from the near meltdown of the US banking system subsequent to the Lehman debacle. This has been prompted for by the institutional bank run in the US banking system as discussed in last October’s Has The Global Banking Stress Been a Manifestation of Declining Confidence In The Paper Money System?
So contrary to mainstream views which ANCHORS upon this collapse as their basis for prediction, we suggest instead that this could be a function of a Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) where according to Wikipedia.org, ``is an anxiety disorder that can develop after exposure to one or more terrifying events that threatened or caused grave physical harm.”
As an example, the 9/11 terrorist attack on the World Trade Center was graphically captured in living color by media. The repeated airing of the deplorable terrorist event heightened the fear of air travel which thereby caused a shift or substitution in some of the public’s traveling patterns.
And the shift emanating from the fear, resulted to more casualties from the higher risk land transportation.
According to a study The Impact of 9/11 on Driving Fatalities: The Other Lives Lost to Terrorism by Garrick Blalock, Vrinda Kadiyali, Daniel H. Simon, ``We find that driving fatalities increased significantly following the terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001, an event which prompted many travelers to substitute less-safe surface transportation for safer air transportation. After controlling for time trends, weather, road conditions, and other factors, we attribute an increase of 242 driving fatalities per month to additional road travel undertaken in response to 9/11. In total, our results suggest that about 1,200 driving deaths are attributable to the effect of 9/11. We also provide evidence that is consistent with the 9/11 effect on driving fatalities weakening over time as drivers return to flying. Our results show that the public response to terrorist threats can create unintended consequences that rival the attacks themselves in severity.”
Why is this so? According to Trevor Butterworth, ``Because fear strengthens memory, catastrophes such as earthquakes, plane crashes, and terrorist incidents completely capture our attention. As a result, we overestimate the odds of dreadful but infrequent events and underestimate how risky ordinary events are. The drama and excitement of improbable events make them appear to be more common.”
So given Mr. Butterworth’s tread, could we be “overestimating the odds of dreadful but infrequent events and underestimating how risky ordinary events are”?
Evidences of PTSD
Some evidences show we are.
One, global barter trade has been picking up. [see Does Growing World Barter Trade Suggests Of Bigger Cracks In Today's Monetary Order?]
According to the Financial Times, ``Officials estimated that they ranged from $5m for smaller contracts to more than $500m for the biggest.” It could be more. There have been accounts of barter since this episode has unraveled.
And the reported cause? ``Failure to secure trade financing as bank lending has dried up.”
The fact that governments have traded OUTSIDE the financial system, means demand and supply seems intact for basic necessities for them to conduct trade. The fundamental problem lies within the traditional means of facilitating payment and settlement via the banking system.
Two possible reasons why governments have been undertaking barter, which is a primitive method of trade:
One, the banking system remains dysfunctional despite the heavy interventions by global governments and
Two, there is a growing distrust for the present medium of exchange. The second finds a voice in Russian Prime Minister Vladimir Putin’s speech in Davos, ``Excessive dependence on a single reserve currency is dangerous for the global economy. Consequently, it would be sensible to encourage the objective process of creating several strong reserve currencies in the future. It is high time we launched a detailed discussion of methods to facilitate a smooth and irreversible switchover to the new model.”
The next evidence could be seen via the surging Baltic Dry Index see figure 4.
The Baltic Dry index according to the wikipedia.org is ``a number issued daily by the London-based Baltic Exchange. The index provides "an assessment of the price of moving the major raw materials by sea. Taking in 26 shipping routes measured on a timecharter and voyage basis, the index covers Handymax, Panamax, and Capesize dry bulk carriers carrying a range of commodities including coal, iron ore and grain.”
Plainly put, the Baltic Index is the cost of freight to move raw materials or basic commodities. It could be seen as a leading indicator.
So far the Baltic Index has risen by 60%, whereas oil and copper appears to be consolidating or “bottoming” even as the US dollar index has been going up. To recall, during the October-November collapse, the US dollar has inversely accompanied the rapid declines of the Baltic index as with the oil and copper.
The seeming divergence could be added signs of the diminishing influences of debt deflation.
Furthermore, even in the US, there are signs that production and inventory or supply destruction have been catching up with its counterpart demand destruction see figure 5.
These observations from the Danske Team (bold emphasis mine),
``First, prior to the recession the US manufacturing industry ran very lean inventories. Second, the liquidity squeeze from the credit crisis has led to an unusually fast alignment of production to demand fundamentals.
``Consequently, the pace of production is now undershooting the slowdown in demand. Hence, it will merely take stabilisation in demand growth to spark an industrial recovery.
The Danske team suggests that the first signs of recovery will be manifested over the ISM index which may stabilize and recover over the coming 3-6 months. In addition, a recovery in the ISM index will most likely add pressure to long US bond yields and signal stabilization in corporate earnings.
While I don’t necessarily share the optimism of the Danske team, the point is that the recent collapse have meaningfully adjusted both the demand and supply equation possibly enough to generate some market based (and not government instituted) revival.
So from growing world barter activities, buttressed by the rising Baltic Dry index, and a potential run down of inventories and similar downside adjustments in the supply side production could mean a semblance of restoration of global trade.
And if indeed the Danske Team is right about their forecast about the manufacturing recovery in the US, then this could signal a potential trough or nearing close of the US recession.
But then again, as a reminder, the cardinal sins in policymaking that could lead to prolonged bear markets: protectionism (nationalism, high tariffs, capital controls), regulatory overkill (high cost from added bureaucracy), monetary policy mistakes (bubble forming policies as negative real rates), excess taxation or war (political instability). Except for the last threat, the 4 seems likely a clear and present danger.
Will An Easing PTSD Lead To A Resurgent Asia?
Nonetheless, if the US supply side has adjusted to counterbalance the sharp fall in demand, then it is likely that the spate of sharp declines in the economic activities in most of Asia can be construed as the same degree of supply/production side adjustments.
Like in 2001, Asia’s heavy exposure to the technology sector hit exporters. Today, the sharp decline in US consumer spending has equally affected Asia’s exports as much as it also affected production. However, the sharp drop late last year could likely be explained by the Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) emanating from the distress in the banking system.
But unlike in 2001, which saw Asia as floundering from the nasty side effects of the Asian Crisis, where there essentially had been no domestic demand, this isn’t the case today. Asia has simply grown bigger and more dynamic and with ample shield from its high savings enough to potentially generate its own demand.
The recent DBS bank outlook says it best, ``Asia now generates almost as much new demand every year as the US- and it is that fresh demand that’s the very definition of global growth. The US is still a key driver and will remain so for a long time. But it is not the driver it used to be.” (bold emphasis mine)
And the Economist seems to agree, ``The question is, might domestic demand now take up some of the slack? There are reasons to think so. Falling commodity prices are boosting consumers’ purchasing power, just as they squeezed it last year. More important is the impact of monetary and fiscal expansion…(bold emphasis mine)
And the Economist sings to be singing a tune similar to ours, ``Asia has never before deployed its monetary and fiscal weapons with such force. Every country across the region has cut interest rates and announced a fiscal stimulus. In previous downturns, Asian governments were often constrained by dire public finances or the need to support currencies. But most countries entered this downturn with small budget deficits or even surpluses. All the main Asian emerging economies apart from India have relatively low ratios of public debt to GDP.” (bold emphasis mine)
In our Will “Divergences” Be A Theme for 2009?, we brought up the Austrian economics explanation that ``market rate of interest means different things to different segments of the structure of production.”
In essence we believe that convergent actions by global central banks will ultimately lead to divergent responses based on the capital and production structure of every economy.
Where the same amount of rain is applied to a desert land, forest land or grass land, the output will obviously be different. And to complement the DBS and Economist outlook, we recently said ``this crisis should serve as Asia’s window of opportunity to amass economic, financial and geopolitical clout amidst its staggering competitors. But this will probably come gradually and develop overtime and possibly be manifested initially in the activities of the marketplace.”
So to refrain from overestimating the odds of dreadful but infrequent events and underestimate how risky ordinary events are, we revert to the study of Garrick Blalock, Vrinda Kadiyali, Daniel H. Simon who concludes, ``Although we are unable to identify precisely reasons for either the 9/11 effect or its weakening, the existence of the effect is consistent with theoretical models in behavioral economics and psychology of inaccurate assessment of risks by consumers and exaggerated adjustments to risk assessments. The fortunate weakening of the 9/11 effect may be attributable to consumer learning over time in response to environmental changes. For example, the perceived risk of flying may have declined with the absence of any further terrorist incidents since 9/11, or travelers may have become accustomed to the increased inconvenience of flying.”
No we don’t just read past data and project them to the future like most of the experts. Instead, we try to understand that human action, to quote Ludwig von Mises, is a purposeful behavior!