``But the administration does not want to stop inflation. It does not want to endanger its popularity with the voters by collecting, through taxation, all it wants to spend. It prefers to mislead the people by resorting to the seemingly non-onerous method of increasing the supply of money and credit. Yet, whatever system of financing may be adopted, whether taxation, borrowing, or inflation, the full incidence of the government's expenditures must fall upon the public.” Ludwig von Mises
It’s time for a little gloating.
Last week we noted how global financial markets would likely respond to two major events that just took place in the US this week.
Globalization Versus Inflationism
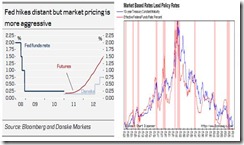
We noted that while the outcome of the US elections would matter, it would be subordinate to the US Federal Reserve’s formal announcement of the second phase of the Quantitative Easing or QE 2.0.
Nevertheless we mentioned that in terms of the US Midterm Elections, still the odds greatly favoured a rebalancing of power from a lopsided stranglehold by left leaning Democrats towards the conservative-libertarian right that could result to what mainstream calls as “political gridlock”.
Such stalemate would thereby reduce the chances of government interventionism, which should have positive implications for both the markets and the US economy[1].
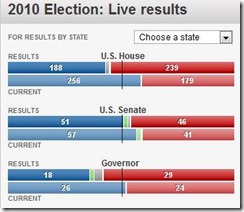
Figure 1: The Drubbing Of Keynesian Policies (USA Today[2])
Of course, what the surveys earlier conveyed had been merely translated into actual votes-Americans largely repudiated the highhanded Keynesian spend and tax policies adapted by the Obama administration. This also signifies as a decisive defeat for President Obama’s illusory “Change we can believe in”.
Except for the Senate which had only 37 seats, out of the 100, contested, Republicans swept the House (239-188) and the Governorship position (29-18). Yet, even in the Senate, the chasm in the balance of power held by the Democrats had been significantly narrowed (from 57-41 to 51-46).
To rub salt into the wound, even President Obama’s former seat at Illinois was won by a GOP candidate[3], Mark Kirk.
The burgeoning revolt against interventionist Keynesian policies has likewise been an ongoing development in Europe[4].
And as we have repeatedly been pointing out, two major forces have been in a collision course: technology buttressed globalization (represented by dispersion of knowledge and the deepening specialization expressed through free trade) and inflationism (concentration of political power).
The rising tide against Keynesianism, which translates to a backlash from these two grinding forces, can be equally construed as a manifestation of an evolving institutional crisis or strains from traditional socio-political structures adjusting to a new reality.
As Alvin and Heidi Toffler presciently wrote[5],
``Bureaucracy, clogged courts, legislative myopia, regulatory gridlock and pathological incrementalism cannot but take their toll. Something, it would appear will have to give...
``All across the board –at the level of families firms industries national economies and the global system itself—we are now making the most sweeping transformation ever in the links between wealth creation and the deep fundamental of time itself. (italics mine)
For now, the forces of globalization appear to be the more influential trend.
Validated Anew: QE 2.0 Is About Asset Price Support
However, as we also noted, Keynesianism hasn’t entirely been vanquished[6]. They remain deeply embedded in most of the political institutions represented as unelected officials in the bureaucratic world. Importantly, they are personified as stewards of our monetary system.
Here is what I wrote last week[7],
``The QE 2.0, in my analysis, is NOT about ‘bolstering employment or exports’, via a weak dollar or the currency valve, from which mainstream insights have been built upon, but about inflating the balance sheets of the US banking system whose survival greatly depends on levitated asset prices.
Straight from the horse’s mouth, in a recent Op-Ed column[8] Federal Reserve Chair Bernanke justifies the Fed’s QE 2.0,
``This approach eased financial conditions in the past and, so far, looks to be effective again. Stock prices rose and long-term interest rates fell when investors began to anticipate the most recent action. Easier financial conditions will promote economic growth. For example, lower mortgage rates will make housing more affordable and allow more homeowners to refinance. Lower corporate bond rates will encourage investment. And higher stock prices will boost consumer wealth and help increase confidence, which can also spur spending. Increased spending will lead to higher incomes and profits that, in a virtuous circle, will further support economic expansion. (bold highlights mine)
Once again I have been validated.
The path dependency of Ben Bernanke’s policies has NOT been different[9] from his perspective as a professor at Princeton University in 2000 when he wrote along the same theme.
``There’s no denying that a collapse in stock prices today would pose serious macroeconomic challenges for the United States. Consumer spending would slow, and the U.S. economy would become less of a magnet for foreign investors. Economic growth, which in any case has recently been at unsustainable levels, would decline somewhat. History proves, however, that a smart central bank can protect the economy and the financial sector from the nastier side effects of a stock market collapse. (bold emphasis mine)
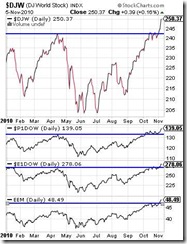
Figure 2: stockcharts.com: Global Equity Markets Explode!
The net effect of QE 2.0 has been almost surreal.
Global equity markets (DJW), as expected, skyrocketed to the upside from the higher than expected $600 billion or $75 billion a month (for 8 months) of US treasury long term security purchases that the Federal Reserve will be conducting with new digital dollars. Markets reportedly estimated the QE program at $500 billion[10].
And the Federal Reserve made sure in their announcement that $600 billion will not be a limiting condition. The FOMC said that they “will adjust the program as needed to best foster maximum employment and price stability”[11].
It’s simply amazing how the Fed’s QE 2.0 transmission mechanism has been worldwide. Whether in Asia (P1DOW-Dow Jones Asia), Europe (E1DOW-Dow Jones Europe) or Emerging markets (EEM-iShares MSCI Emerging Markets Index), the story has all been the same—markets breaking out to the upside.
I’d like to add that such bubble blowing policies has NOT been limited to the Federal Reserve.
Immediately after the Fed’s announcement, the Bank of Japan voted unanimously to support the domestic stock market by engaging on their own version of QE that would include “exchange-trade funds linked to the Topix index and Nikkei Stock Average, and Japanese real-estate investment trusts rated at least AA, the bank said. It said it would begin buying Japanese government bonds under its new program next week.[12]” (bold emphasis mine)
Add to these the inflation of global central banks international reserve position to the tune of $ 1.5 trillion over the past 12 months[13].
Hence the consequences of massive inflationism are likely to be fully felt yet in the markets.
The False Premise: Aggregate Demand Story
The substantiation of our analysis isn’t limited to Bernanke’s statements alone. Markets have likewise bidded up the major beneficiaries of the QE 2.0 program—the banks and the financial industry (see figure 3).

Figure 3: Financial Industry: From Laggards to Leaders (charts from US global Investors and stockcharts.com)
The mainstream wisdom goes this way: Money printing does not create inflation. With low inflation, printing money is, therefore, needed to generate demand that would spur inflation. This form of circular reasoning[14], which characterizes Keynesian economics, is what is sold to public as rationalization for the current policy. The mainstream sees it as an aggregate demand problem that can only be addressed by money printing.
The mainstream fails to see that there is NO such thing as a free lunch or that prosperity cannot be conjured or summoned by the magic wand of the printing presses.
All these so-called technocratic experts refuse to learn from history or deliberately distort its lessons, where debasing money has always been meant to accommodate for the political goals or interests of the ruling class.
Yet monetary inflation eventually crumbles to nature’s laws of scarcity for the simple reason that it is unsustainable. Printing of money does NOT equate anywhere to the same degree as producing goods and services. Printing of money can be limitless, while production of goods and services are limited to the available scarce resources.
Unknown to many, printing of money is subject to the law of diminishing returns (getting less for every extra output or a law affirming that to continue after a certain level of performance has been reached will result in a decline in effectiveness[15]) and law of diminishing marginal utility (general decrease in the utility of a product, as more units of it are consumed[16]).
And it is why repeated experiments with paper money throughout the ages of human affairs have repeatedly failed[17]. And I don’t see why the grand US dollar standard experiment today as likely to succeed either. The QE programs fundamentally reflect on the same symptoms of any degenerating or festering de facto money regime. We should expect more QE programs to happen.
Yet the aggregate demand story is basically premised on debt. To promote aggregate demand is to promote debt. Debts either incurred by the private sector or by governments in lieu of the private sector. While productive debt and consumption debt are hardly distinguished, consumption debt is promoted. Savings are disparaged as economically harmful. And the promotion of debt is the essential or critical element to fostering bubbles.

Figure 4: World Bank: Banking Crisis Since the 1970s
Hasn’t it been a wonder that since the closing of the Bretton Woods gold-dollar window in 1971, bubbles became a permanent fixture worldwide?
Yet, the public hardly can see through who the major beneficiaries from the debt based aggregate demand story. Obviously, it is the banking and the financial industry as they represent as the major funding intermediaries or financiers to both the private sector and importantly to the government.
And the banking system had been structurally incented to hold (or buy or finance) government debts into their balance sheets as they have been classified as less risky assets and thus requires less capital in accordance to the Basel Accord[18].
During the last crisis the unholy alliance of the central banking-banking industry cartel had been exposed as seen by the trillions worth of bailouts by the US Federal Reserve[19].
Yet the politicized nature of central banking (everywhere) obviously leads to cartel structured relationships, as survivability depends not on profitability based on market forces, but from the privileged conditions bestowed upon by the political strata.
And the QE 2.0, which I argued as having been unmoored from the prospects of the US or global economy, but rather aimed at safeguarding the balance sheets of the banking system has successfully boosted the prices of financial equity benchmarks, such as S&P Bank Index (BIX), the Dow Jones Mortgage Finance Index (DJUSMF), the S&P Insurance (IUX) and the Dow Jones US General Financial Index (DJUSGF), all along the lines of Bernanke’s design.
The industry that had miserably lagged[20] the recent stock market recovery in the US has in one week suddenly outclassed the rest.
Of course people who argue about the success or failure of policies frequently look at the effects depending on the time frame that support their bias.
For instance, policies that induce bubbles will benefit some participants, during its heydays. Hence, policy supporters will claim of its ‘success’ seen on a temporary basis as the bubble inflates. Yet overtime, an implosion of such bubbles would result to a net loss to the economy and to the markets. The overall picture is ignored.
And the same aspects would also apply to those arguing that the Fed’s rescue of the banking system has been worthwhile. They’re not. The benefits of a temporary reprieve from the recent crisis envisages greater risks of a monumental systemic blowup. If Fed policies had been successful, then why the need for QE 2.0?
So for biased people, the measure of success is seen from current activities than from the intertemporal tradeoffs between the short term and long term consequences of policies.
In other words, yes, the QE 2.0, which constitutes the continuing bailout of the US banking industry, seems to successfully inflate bubbles, mostly overseas. But at the end of the day, these bubbles will result to net capital consumption, if not the destruction of the concurrent monetary regime.
The next time a major bubble implodes there won’t likely be free lunch rescues as these will be limited by today’s massive debt overhang.
The Effects of QE 2.0: Promotes Poverty And A Shift To A New Monetary Order
Of course while the equity price performance of the US financial industry stole the limelight the next best performers have been the Energy and the Materials Index.
In other words, as I have long been predicting, the accelerating traction of the inflation transmission channels are presently being manifested in surging prices of commodities and commodity related equity assets aside from global equity markets.
While this should benefit equity owners and producers of commodity related enterprises, aside from the financial sector, those who claim that inflationism is justifiable and a moral policy response to the current conditions are just plain wrong. Such redistributive policies to the benefit of the banking sector come at the expense of the underprivileged.
What is hardly apparent or seen is that the current government structured inflation indices have been vastly underreporting inflation.
Yet surging agricultural and food prices would not only harm a significant percentage of financially underprivileged by reducing their money’s purchasing power but also promote poverty in the US and elsewhere.

Figure 5: Food Expenditures By Income Level
Tyler Durden of Zero Hedge quotes a JP Morgan study[21], (bold emphasis mine)
When the Fed considers the possible consequences of a falling dollar resulting from QE2, it should perhaps focus on food and energy prices as much as on traditionally computed core inflation. First, the food/energy exposures of the lower 2 income quintiles are quite high (see chart). Second, the core CPI has a massive weight to “owner’s equivalent rent”, which suggests that the imputed cost of home occupancy has gone down. Unfortunately, this is not true for families living in homes that are underwater, and cannot move to take advantage of it (unless they choose to default and bear the consequences of doing so). Due to the housing mess, there has perhaps never been a time when traditionally computed core inflation as a way of measuring changes in the cost of things means less than it does right now.

Figure 6: ADB[22] Asia’s Share of Food Expenditure to Total Expenditure
And as said above the effects are likely to hurt the underprivileged of the emerging markets more than the US.
So inflationism or QE 2.0 poses as a major risk to global poverty alleviation and prosperity, a blame that should be laid squarely on these policymakers and their supporters.
Of course as the ramifications of inflationary policies worsen, the subsequent scenario would be for political trends to shift towards holding the private sector responsible for elevated prices and for ‘greed’ in order to institute more government control and inflationism.
As the great Ludwig von Mises once wrote[23],
``They put the responsibility for the rising cost of living on business. This is a classical case of the thief crying "catch the thief." The government, which produced the inflation by multiplying the supply of money, incriminates the manufacturers and merchants and glories in the role of being a champion of low prices. While the [the government] is busy annoying sellers as well as consumers by a flood of decrees and regulations, the only effect of which is scarcity, the Treasury [and the Fed] go on with inflation”
Here free trade will likely give way to protectionism; that is if public remains ignorant of true causes of inflation and if the world would stubbornly stick by the US dollar as preferred global medium of exchange.
Of course Asian nations were hardly receptive to the unilateral actions by the Federal Reserve. The conventional recourse in dealing with QE 2.0 has been via currency appreciation, tightening of domestic liquidity by raising bank reserves or increase policy rates or lastly ‘temporary’ capital controls. So far some countries as South Korea have threatened to impose some variation of capital controls.
Yet we should expect the world to shift out of the US dollar regime once inflationism becomes rampant enough to pose as a meaningful hurdle to national economic development and global trade. The Bloomberg quotes China’s Central Bank adviser Xia Bin[24],
``China should counter the U.S. through regional currency alliances, speeding international use of the yuan and seeking stability in exchange rates through the Group of 20, which holds a summit next week”
A currency from a political economy that engages in significantly less inflationism, has deep and developed sophisticated markets, has a convertible currency and hefty geopolitical exposure is likely to challenge the US dollar hegemony, whether this would be the yuan (which for the moment is unlikely) or the Euro, only time will tell.
Of course, we can’t discount gold’s role in possibly being integrated anew in the reform of the monetary architectural system.

Figure 7: Virtual Metals[25]: Central Bank Gold Holdings and Sales
Global Central banks appears to be rediscovering gold as possibly reclaiming its role as money in a new monetary order. A new monetary order is not question about an if, but a when.
Once as net sellers, central banks seem to be transitioning into potential net buyers.
So again, our peripheral insight seems being validated with the ongoing process of shifting expectations by authorities on the functions of gold.
As I pointed out last year[26], gold is presently seen by an ECB official as a form of economic security, risk diversification, a confidence factor and an insurance against tail risks. Once these factors become well entrenched, a store of value role would likely be the next step. And more QE’s would only serve to push gold towards such a path.
Those who obstinately relish the bias that gold is nothing but a barbaric relic will likewise suffer from taking on the wrong positions. But they eventually will succumb to the shifting expectations as with many monetary authorities today. The reflexive process of having prices influence fundamentals has clearly been taking shape.
With gold prices at $1,390 mainstream economists like celebrity Nouriel Roubini[27], who last year debated savvy investor Jim Rogers and declared “Maybe it will reach $1,100 or so but $1,500 or $2,000 is nonsense”, must be squirming on his seat for the likelihood to be proven wrong once again.
[1] See US Midterm Elections: Rebalancing Political Power And Possible Implications To The Financial Markets, October 31, 2010
[2] USA Today, 2010 Elections: Live Results
[3] Politico.com Roland Burris will serve in November, November 5, 2010
[4] See An Overextended Phisix, Keynesians On Retreat And Interest Rate Sensitive Bubbles, October 25, 2010
[5] Toffler, Alvin and Toffler, Heidi Revolutionary Wealth Random House p.40
[6] See Trick Or Treat: The Federal Reserve’s Expected QE Announcement, October 31, 2010
[7] Ibid
[8] Bernanke, Ben What the Fed did and why: supporting the recovery and sustaining price stability, Washington Post, November 4, 2010
[9] Bernanke, Ben A Crash Course for Central Bankers, Foreign Policy.com or wikiquote Ben Bernanke
[10] Macau Daily Times Asian markets rise, dollar falls, November 5, 2011
[11] Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, November 3, 2010 Press Release
[12] Marketwatch.com Bank of Japan holds steady, details asset plans, November 4, 2010
[13] Noland, Doug QE2 Credit Bubble Bulletin, Prudent Bear.com
[14] See Thought Of The Day: The Keynesian Circular Thought Process, June 22, 2010
[15] Wordnetweb.princeton.edu law of diminishing returns
[16] Wiktionary.org law of diminishing marginal utility
[17] See Surging Gold Prices Reveals Strain In The US Dollar Standard-Paper Money System, November 1, 2010
[18] See The Myth Of Risk Free Government Bonds, June 9, 2010
[19] See $23.7 Trillion Worth Of Bailouts?, July 29 2010
[20] See The Possible Implications Of The Next Phase Of US Monetary Easing, October 17, 2010
[21] Durden Tyler, How Ben Bernanke Sentenced The Poorest 20% Of The Population To A Cold, Hungry Winter, Zerohedge.com November 5, 2010
[22] Asian Development Bank: Food Prices and Inflation in Developing Asia: Is Poverty Reduction Coming to an End? April 2008
[23] Mises, Ludwig von The Truth About Inflation
[24] Bloomberg.com Asians Gird for Bubble Threat, Criticize Fed Move November 4, 2010
[25] Virtualmetals.co.uk The Yellow Book September 2010
[26] See Is Gold In A Bubble? November 22, 2009
[27] See Jim Rogers Versus Nouriel Roubini On Gold, Commodities And Emerging Market Bubble, November 5, 2009