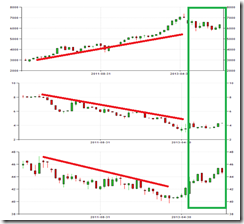
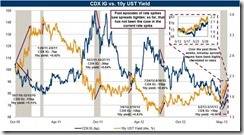
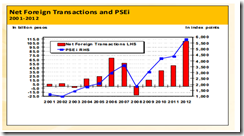
The following charts are illustrative of the evolving dynamics of Philippine financial markets
As shown by the red trend lines, the boom in the Philippine Phisix (top pane) sailed on the tailwinds of easy money environment. Such stock market boom has been accompanied by falling bond yields (10 year peso denominated treasuries) and the strengthening of the peso or falling US Dollar (lowest pane). In other words, the previous stock market boom highlights an outsized demand for Philippine assets that also included the currency, the peso, and bonds.
On the other hand, the green rectangle, which underpins today’s conditions, has been indicative of a significant transitional shift: sharply volatile stocks, falling peso (rising US dollar) and a reversal in the yields of the domestic bond markets represented by a bottoming or incipient signs of rising yields.
This shows that rallying stocks have hardly been in consonance with the actions in the peso and Philippine treasuries. In short, the Phisix faces headwinds from what seems as a structural changeover in the financial sphere, particularly from easy money to tight money conditions.
The sharply volatile stocks, particularly seen via the violence in the degree of denial rallies, has been a symptom of the massive “resistance to change” by the bulls who attempts at reestablishing the old setting.
They have justified such actions by relying on statistical financial or economic data that has been shaped by the erstwhile easy money days.
They have essentially ignored how the current transformations will reconfigure ‘fundamentals’ amidst unfolding changes in the global and domestic financial environment; a makeover that is being brought about by the global bond vigilantes, whose transmission mechanism is being ventilated via the “yield spread” adjustments that has been disorderly in emerging markets, including the Philippines[1], relative to the developed economies, in particular the US. In short, tomorrow’s fundamentals will materially be distinct from that of the yesterdays.
And the attendant transfiguration has been exposing on the fragile conditions that have emerged from the excesses committed by various parties, both public and private, on the heels of social policies imposed, specifically easy money policies that have accommodated debt based frenzied asset market speculations and vast debt financed fiscal actions.
So not only has the former order spurred a colossal buildup of foreign debt in Emerging Markets acquired through bonds and off shore banks to the tune of $2 trillion via interest rate based carry trade[2], the immense accumulation of debt also has a large domestic dimension.
BIS: US Interest Rates have major implications in the financial stability of Emerging Markets
In a working paper by the central bank of central banks, the Bank of International Settlement, economist Philip Turner virtually reinforces my view of how yields of US treasuries affected Emerging Market policies which Mr. Turner notes has been channelled via the “compression” of US treasury term premium (Excess of the yields to maturity on long-term bonds over those of short-term bonds) that has significantly lowered interest rates has sparked a debt acquisition spree through a “much larger” local government bonds and “stimulated off shore dollar credit” (mostly through bonds).
Writes Mr. Turner[3],
Whatever the causes of this extraordinary and quite long-standing shift, the impact on long-term local currency government bond yields in EMEs has been remarkable. The average nominal long-term yield for major EM countries (that is, those countries with floating exchange rates and genuine long-term debt markets included in Graph 3 on page 13) fell from about 8% at the beginning of 2005 to around 5% by May 2013. Using the year-on-year change in consumer prices, this amounted to a real long-term interest rate of just 1%.
Emerging market local currency debt based on World Bank estimates has almost doubled to $ 9.1 trillion by the end of 2012, compared with $4.9 trillion at the end of 2008. This should be a lot larger or must be about double today.
Foreign holdings of EM local currency bonds have also swelled, where from World Bank estimates, as noted by the BIS, non-residents now hold 26.6% or more of local currency bonds, compared with 12.7% in 2008.
Mr. Turner brings about the boom day transformation from the UST yield compression in noting that “There is clear statistical evidence that, since 2005, EM local currency bond yields have moved closely with US yields – which was not the case earlier”
The BIS affirms US dollar or offshore borrowing has expanded by about $990 billion on international bond markets from 2010 until the first half of 2013, where non banks accounted for accounted for more than $700 billion or about 78% of US dollar based borrowing.
The BIS notes of three channels where a possible “stop” may occur:
Local banks. External borrowing has eased credit conditions much “more than the expansion in total domestic bank credit aggregates suggest”. This implies that a reversal of external easing conditions may cause more domestic tightening “even if total domestic bank credit continues to rise”
Wholesale funding markets. External borrowing has increased wholesale deposits with local banks. And if external conditions tighten not only are these deposits “flighty” (meaning prone to runs) these will translate to more difficulties “for domestic banks to fund themselves at home”.
Lastly hedging of their forex or maturity exposures, often via derivative contracts with local banks. This implies of counterparty risks such that even when “local banks hedge their forex exposures with banks overseas, they still face the risk that local corporations will not be able to meet their side of the contract. The upshot is that the domestic bank that thinks it has managed its risks, will find itself, if its corporate clients fail, with unhedged exposures vis-à-vis foreign banks”
In finale, the lesson from the BIS study is that “movements in US long-term interest rates, which is the global benchmark, can have major implications for both monetary policy and financial stability in EME” and as such policy shift unfolds as expressed by movements in the UST yields “uncertainty about the policy path could unsettle global bond market”.
I believe the same movements which has been emblematic of unfolding transformation is not only affecting the Philippine assets, these are presently being vented on the substantial depreciation of the Chinese yuan. I will deal with the latter later.
The Rate of Money Supply Growth Will Influence Tomorrow’s Fundamentals
And when I talk about “tomorrow’s fundamentals will materially be distinct from that of the yesterdays” one can just note of the adamant insistence by the Bangko Sentral Governor Amando Tetangco Jr. who keeps arguing for a supposed deceleration (to 12-14%) of the fantastic growth in money supply which he says as “temporary” and “is not expected to translate to significant inflationary pressures or asset price misalignment”[4].
The problem with such a statement is that even his underlings have impliedly contended otherwise. Contra the BSP chief’s expectations, money supply growth soared even higher in January 2014 to a jaw dropping 38.6%!!!
Here is the BSP’s official declaration[5]: (bold mine)
Domestic liquidity (M3) increased by 38.6 percent year-on-year at end-January 2014 to reach P6.9 trillion. This increase was faster than the 32.7-percent expansion recorded in December 2013. Month-on-month, seasonally-adjusted M3 rose by 5.5 percent, following the 1.5-percent contraction in the previous month. Money supply continued to expand due to higher demand for credit in the domestic economy. Domestic claims rose by 16.2 percent in January from 11.6 percent in December 2013 as bank lending accelerated, with the bulk going to manufacturing, utilities, wholesale and retail trade, as well as financial and business services. These sectors provide large multiplier effects to the real sector.
Can you now spot where the BSP chief’s contradictory and evasive argument has been premised from? The BSP announcement says that money supply growth has been caused by demand for credit. Domestic claims on the private sector and financial sector practically accounts for 67.5% of M3 in January 2014.
The BSP chief practically eludes the “money supply-demand for credit” causality issue by seemingly evoking a King Canute—ordering money supply to shrink even when zero bound rates continue to stoke intensive demand for credit. In the world of politics, economics has been supplanted by wishful thinking.
As I keep repeating, it is natural for BSP officials to function as salesmen for the administration. It’s their job. For in doing otherwise, this would translate to self-incrimination on their imposed policies, as well as, a potential loss of tenure, since they will no longer serve in confidence of their political leaders.
But it is for us to see whether we are being told of the reality or of a possible contortion.
The BSP data shows that banking loans continues with its relentless climb in January[6] which essentially reinforces the money supply growth.
While real estate lending has softened (17.3% y-o-y) from the 20% levels, growth in construction loans continues to sizzle at a whopping 51.67% rate. Such the fabulous rate of growth of construction loans has been seen through 2013 as shown above.
Moreover, loans to hotel and restaurant industry has amazingly spiked to 48.44%, which appears as fast approaching the rate of growth in the construction sector.
The real estate-construction-hotel credit binge has been virtually inflated a frenzied property bubble which is now being ventilated on the stock market.
Yet for 2013 the dramatic growth rates by these sectors have hardly shown any productive growth at all. As I noted[7],
Yet what appear as quite disturbing have been in the growth figures of the construction, real estate and hotel industries. For every 1.9 pesos of loans acquired by the real estate sector generated only 1 peso of additional growth. More staggering has been the proportionality of each peso growth for the construction and the hotel industry that has been financed by borrowings of 3.25 pesos and 2.7 pesos respectively.
The 2013 credit boom-economic output link is a clear sign of a burgeoning unsustainable growth in malinvestments or capital consumption
Meanwhile, loans in trade also edged higher to 16.31%
And if you have seen a bounce in securities listed in the Philippine Stock Exchange (PSE), this may have been most likely financed by a resurgence of loans to the financial intermediation sector which jumped by 10.9% last January.
All the above implies that when individuals (personal or through various legal entities) borrow money, they usually spend the proceeds either for productive or non-productive activities. This means that such spending activities will affect money prices of goods and services. This also means that changes in relative prices will reflect on the evolving balance of demand for specific goods and services, as well as, the balance of available and prospective specific supply of goods and services.
So the increases in the rate of borrowing unbacked by savings that has been encouraged by zero bound rates and enabled by “money from thin air” means that we should expect volatile changes in relative prices or relative price inflation in economic goods as well as assets, and we should also expect the deepening of distortions or imbalances in the production structure of the economy (economic bubbles) where more capital and labor will be drawn to the capital consuming traphole.
Money supply, thus, represents a measure of the circulation of money mostly from credit inflation in the economic system. Therefore to argue that that a fantastic rise money supply growth has little effect on inflation or on asset prices sees money as operating in a black hole or in fantasyland. Such is predicated not as an economic argument but a political bromide.
This is a wonderful example of how economist Thomas Sowell distinguishes the role played by politics with that of economics[8].
The first lesson of economics is scarcity: There is never enough of anything to fully satisfy all those who want it.The first lesson of politics is to disregard the first lesson of economics.
When money is said to be delinked from prices, then this implies the omission of scarcity, thus splendidly expressed “the first lesson of politics is to disregard the first lesson of economics”.
Yet soaring unemployment rates and deterioration of the general public’s sentiment over life quality standards in 2013 have already been indicating of the deepening of the stagflationary process.
And as I previously noted[9], (bold original)
the recent decline of forex reserves serve as evidence that in the impossible trinity, where government can only use two of the three factors: free movement of capital, exchange rate and domestic policy targets, the BSP intends to keep the credit boom alive in the hope that EM storm will breeze over. I hope they are right because the alternative would be worse.This also means that M2 will remain elevated and sometime in the future. This means that unless these are restrained, the Philippines will likely suffer from a serious inflation problem ahead (10% or more??).
And money supply will remain elevated for as long as the BSP intends to keep the credit boom alive at the cost of advancing stagflation
The same BIS study above avers that exchange rate and long term interest rates expectations are often “jointly determined” where “expectations of currency depreciation, for instance, may also drive down the prices of local currency bonds”. This would seem as a natural outcome as expectations for currency depreciation usually redound to higher inflationary expectations thus should get revealed in falling bonds (higher yields and eventual interest rates). But the bad news is that this increases the risks of “financial shocks”
Thus the continuing credit boom will mean a weaker peso and significantly higher interest rates than the consensus expectations. Tomorrow’s fundamentals will materially be distinct from that of the yesterdays. Mull over how all these will impact earnings, economic growth, credit conditions and more. And be cautious of reading and interpreting pre-June data with current data.
So while stocks may rise amidst a meltdown in a currency as with the current cases of Venezuela (see how Venezuela’s hyperinflation induced food shortages extrapolates to snaking food lines), Argentina, Egypt[10], Kazakhstan[11] or even Ukraine, rising stocks amidst a currency meltdown are signs of runaway inflation more than a booming economy.
As a side note, amidst the intensifying standoff between Russia, whom reportedly launched a tacit invasion of parts of Russian dominated ethnic groups in Crimea[12], and the US[13], Ukraine’s equity benchmark, the PFTS skyrocketed by 25% this week! Would you believe that Ukraine had 2 credit fuelled stock market bubbles in a span of 5 years 2007-2012 that imploded and led to the current political mess??!! Unfortunate developments in Ukraine signify an example of the devastating effects of inflationism on society[14].
Deepening Mania Points to Interim Profit Taking
Since I have made my case where “tomorrow’s fundamentals will materially be distinct from that of the yesterdays”, the vehement reaction against perceived changes or the “resistance to change” outlook has been to inspire violent denial rallies not only in Philippine but likewise in other ASEAN equity markets, including Singapore.
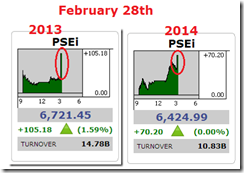
One recent sign of reinvigoration of the mania phase has been for us to witness another incredible episode of what seems as “marking the close”.
For two successive years, the sessions ending February 28th in 2013 and 2014 saw a similar intense closing bell push. But the difference between the two similar episodes has been in the scale, the volume and breadth of the actions.
In 2013 the thrust had been broad based (all sectors), thus the bigger degree in gains (1.59%) backed by a substantial volume (14.8 billion pesos)[15]. The 2014 version has been concentrated mostly in two issues, Ayala Land [ALI] and Jollibee Foods Corporation [JFC], thus a significantly lesser volume (10.83 billion pesos) and reduced degree of gains (1.1%) compared to 2013.
Nevertheless, the difference between two seemingly parallel actions highlights on the divergence of the underlying sentiments that reinforces my perception of last week “bullish sentiment based on the above facts reveal of a largely uncommitted stance”[16]. Why so? Because today’s fundamentals (see above) have been ‘materially distinct’ from 2013, where the current rebound is not being shared by the bond markets and the peso.
I also noted last week “how fragile the current rally has been” as four market breadth indicators (flow) peso volume and foreign money flux and (trade) daily trades and advance-decline spread seem to be headed to an interim peak. This week’s rally buttresses the signal for a major correction ahead.
Again that’s if past will resonate.
In terms of flow, the degree of foreign inflows appear to have turned the corner (right window). This comes as the peso volume (averaged weekly) have regained some of the strenght seen from the previous denial rallies (left window).
In terms of trade sentiment, the number of daily trades averaged weekly (upper left pane) has almost reached levels where serious corrections occurred. This is a sign that retail participants have stepped on the gas pedal, based on the belief that the salad days have returned.
And further signs of reinforcement of drastically increased trades from retail participants have been the issues traded averaged weekly (bottom). Retail participants have been bidding up the broader market to include third tier securities. Last week’s market actions have practically eclipsed all the previous denial rallies.
So while advance-decline spread seem to have also turned the corner, retail participants seem to have rotated to issues with lesser liquidity.
In sum, the degree of foreign participation seems to be slowing and this seems as being shared by a narrowing of the advance decline spread. If such momentum gains, then this will be revealed through a correction.
On the other hand, while peso volume trade has risen to capture some proportion of the lost volume relative to previous denial rallies, retail participants seem to have pounced on illiquid issues and have become more wildly bullish as evidenced by sharp increases in issues traded and the number of daily trades. So there appears to be an ongoing shift from big investors to retail trades.
What this seems to point at is that a serious correction may be at hand soon. If current market actions will be a replica of February 2013, then a 5% decline may be ahead.
Again the reasons for the similarities are that the consensus sees or interprets the past as the present (resistance to change), so they enforce such beliefs via trading actions as shown by the recent dramatic momentum based rally.
But again currency and bond market traders appear to be seeing a different view from stock market players.
No Asset Price Misalignment or the Greater Fool Momentum?
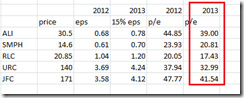
Even if the BSP Governor denies of “asset price misalignment”, the Price Earnings ratio by the industries, particularly the property and industrial sector, that has driven the current rally has shown massive “asset price misalignment” or outrageous mispricing.
The above stocks are the dominant representatives or the leaders of the property and of the industrial sectors.
When has PE ratios’ of 44.85 (ALI), 37.94 (URC) or 47.79 (JFC) been considered as inexpensive? If the PE ratio indicated above are annualized based, then this means buyers of these stocks are buying 44, 38 and 48 years of earnings today, respectively.
Based on the above PSE data, if I were to assume that the 2012 PE ratios to get into the 15 level, then implied growth would be for ALI 299%, SMPH 160%, RLC 133.67% URC 252.93% and JFC 319%. How probable or even possible is this even if we consider a span of 2-3 years?
And if I were to use an assumed compounded rate 30% growth, these companies will need for 2-4 years to attain such levels. 30% growth extrapolates to 4.2x the economic growth. While this may be possible for a finite time[17], this is unlikely to become a long term phenomenon[18] especially since the above companies are mature companies.
Now if I use the stated 2012 PE ratio to estimate on earnings growth at a more realistic 15% for 2013 for the abovestated firms, then current PE ratio still registers at ALI 39, SMPH 20.81, RLC 17.43, URC 33 and JFC 41.54. That’s still stunningly excessive mispricing.
In the US we see ridiculous valuations on many smaller “growth” stocks but hardly the same levels as the Philippines in terms of blue chips.
The incredulous valuations of domestic blue chips exhibit that participants, whether local or foreign, are hardly paying for discounted stream of future cash flows, but rather anchoring on the illusions of the sustainability of the current statistical high growth credit driven boom to power earnings, or to put more bluntly, today’s buyers of excessively valued securities have been hoping that many greater fools will emerge to buy into the same securities at even more extremely overvalued price levels.
And this is why some studies like those from Credit Suisse sees buy distress and sell growth as a trading strategy[19].
The former value investor and current political entrepreneur Warren Buffett, in a recent Op-Ed offers an unsolicited advice for yield chasers[20]. (bold mine)
If you instead focus on the prospective price change of a contemplated purchase, you are speculating. There is nothing improper about that. I know, however, that I am unable to speculate successfully, and I am skeptical of those who claim sustained success at doing so. Half of all coin-flippers will win their first toss; none of those winners has an expectation of profit if he continues to play the game. And the fact that a given asset has appreciated in the recent past is never a reason to buy it.With my two small investments, I thought only of what the properties would produce and cared not at all about their daily valuations. Games are won by players who focus on the playing field -- not by those whose eyes are glued to the scoreboard. If you can enjoy Saturdays and Sundays without looking at stock prices, give it a try on weekdays.
The point is that when people irresponsibly chase on yields in the hope of finding a greater fool, the likely result will be “a fool and his money are soon parted”
And again think of the implications of the 30+% money supply on future earnings.
Property Boom: The Incredible Embrace of Delusions
So what are the bulls buying into?
In the property sector, it seems that record profits for some companies in 2013 has impelled for even more “aggressive” expansion plans for this year.
For 2014, Ayala Land proposes a 70 billion[21] pesos capex, SM Prime 36 billion[22] pesos, SMDC 15-18 billion[23], Robinsons Land 16 billion[24], Vista Land 25 billion[25], Century Properties 17 billion[26], Filinvest Development 27 billion[27] (33 billion minus 6 billion for energy), Empire East 5 billion[28] (25 billion over 5 years), Rockwell Land 2 billion[29] (for Cebu only), Puregold 3 billion[30], Roxas & Co 1.5-2 billion over 2 years[31] or .75 -1 billion and Aboitiz Equity 4 billion for property out of the 88 billion[32]
Megaworld proposes a 112,000 sqm office space without disclosing the amount involved[33].
For the above companies, proposed capex tabulates to 221 billion pesos. And this doesn’t include publicly listed companies that have not disclosed their capex plans yet, such as Lucio Tan Group via ETON, Shangri-la properties, Phil Realty and more, as well as non listed major developers such as Metrobank’s Federal Land and many other regional or local developers.
So a proposed 250 billion pesos (US $5.62 billion at 44.5 exchange rate) spending would be an easily accomplishable target for the property and allied sectors. My guess is that this could reach 300-350 billion.
So how big is 250 billion pesos? In statistical GDP terms, based on the type of expenditure at current prices of 1,236,436 million pesos for construction in 2013, 250 billion pesos will translate to a growth of 20% for 2014.
Based on industrial origin, where construction accounts for 715,634 million at current prices in the category of industry, perhaps I can add to this the service category of the Real Estate, Renting & Business Activity which amounts to 1,382,686 million pesos at current prices, proposed capex will amount to 12% growth.
Of course, not all such spending will extrapolate to growth. As indicated above, the property sector borrowed 2-3 pesos more to generate one peso growth in 2013.
Now if we look at final demand via Household Final Consumption Expenditure (HIFE) we find that at current prices, demand grew by only 7.9% in 2013 down from 9.9% in 2012.
As you can see, there remains a wide gap between demand side (7.9%) and the supply side (whether 12% or 20%). The obvious result from such discrepancy will be oversupply.
Oversupply won’t be a problem if funded by savings, as losses will be contained on the investor. But a credit driven oversupply will have a leash effect on the banking sector and to the other creditors (bond holders) as well as the many enterprises that grew out of their attachment to such unsustainable bubble.
Take a look further at what the public hasn’t seen.
Aside from outgrowth from the supply side, the massive expansion will mean severe competition by developers to acquire land for development. This means property price inflation.
As I long noted, property inflation will not only reduce consumer affordability and disposable income, it will also reduce profit opportunities for small and medium scale enterprises thereby posing a deterrent or an obstacle to real economic growth[34].
Property bubbles will hurt both productive sectors and the consumers. Property bubbles increases input costs which reduces profits thereby rendering losses to marginal players but simultaneously rewarding the big players, thus property bubbles discourage small and medium scale entrepreneurship. Property bubbles can be seen as an insidious form of protectionism in favor of the politically privileged elites.Property bubbles also reduces the disposable income of marginal fixed income earners who will have to pay more for rent and likewise reduces the affordability of housing for the general populace.
And this also means price inflation on sectors piggybacking or ancillary sectors supporting the property bubble. Eventually the diffusion of price inflation will flow into most segments of society and get reflected on the inaccurate official CPI data.
Notice too that most of the proposed capex financing in 2014 will be raised via debt (bonds) rather than equity.
This adds to another unseen variable for the mainstream, what if for some reason or another, a black swan event occurs from anywhere from around the world, which like in 2008 will have a contagion effect? The Philippines was hardly exposed to dangerous debt levels in 2008. Although the US crisis had an impact, this wasn’t enough rattle the economy hardly tainted by debt.
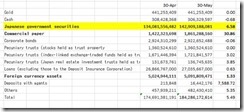
But it has been a different story today as shown above whether seen in nominal peso or in %. Like almost every emerging market economy, the Philippines have immersed herself in debt. The above graphics based on BSP data only covers banking loans. It excludes local currency and foreign currency denominated bonds, as well as, offshore bank dollar or foreign currency based borrowing.
Will the Philippine property boom be immune to any contagion for the shindig to continue? The last time a selloff occurred in June 2013, it appears that hardly any major emerging market or even developed markets has been spared. Yet the aftereffect from the June 2013 tremors still lingers via a weak peso and higher bond yields.
Also I find it bizarre (or even disturbing) how some companies trumpet ‘reservation sales’ as part of their sales feat. As a former licensed real estate practitioner, where the previous boom of the pre-Asian crisis days allowed me to play golf 3-4x a week, reservation sales like goodwill money hardly became basis for our commissions. Commissions come from downpayment that had been covered by sales contracts. Since many buyers may back out, and where reservation fees may be forfeitable in favor of the developers, income from reservation fees from discontinued sales will hardly be enough to finance their debt based expansion binge.
As a side note, then I thought I was good, instead the Asian crisis revealed to me that I had been lucky from perseverance more than my initial impression of being an expert. I learned from a very expensive experience which is why I preach prudence.
Finally there are some who propose that rising property stocks could be due to rumors of full liberalization of ownership to foreigners. If true then this should be a very welcome development. But such won’t mean a foreign stampede into the property sector.
There are many factors that drive foreign demand for local properties. They could be for housing use (e.g. retirement[35]), they could be for used for business operations, they could be for rental yields and they could be for flipping or for other unstated reasons.
For instance if foreigners are considering property for business operations, where property represent a means to an end, viz. business operations, then liberalization of property will not be enough. It requires liberalization of the obstacles to business operations backed by liberalization of ownership for a foreigner to be enticed to buy property and to invest.
For business operations, speculation and for rental yield, this would also require a material loosening up of capital controls, something which this or previous administrations have been very reluctant to act on. Loosening of capital controls would mean easing of financial repression. With a government looking to tax anything, easing of financial repression will unlikely signify as an option.
The point being liberalization of property ownership isn’t an elixir.
And more, I seriously doubt that this government who has been raising nationalist sentiment to generate popular appeal will ever resort to liberalization whether in business or property ownership.
Nationalism which dictionary.com defines as “the policy or doctrine of asserting the interests of one’s own nation viewed as separate from the interests of other nations or the common interests of all nations”—is simply contradictory or incompatible to economic freedom since this based on the premise of "us against them".
And even if I may be wrong and the government does open the doors of ownership to foreigners, such is not a free pass to bubble blowing. When the bubble pops, those inflows will easily morph into outflows. And one can expect bubble bursting episodes as an excuse for the government to expand political power through various forms of interventionism. So any opening will be reversed when economic slowdown becomes a political issue.
Going back to the above, do all of such arguments justify 30 to 40 PE ratios?
I am simply awed by the incredible embrace of delusions.
At the current rate of all these bubble worship, the “this time is different” mentality backed by 30+++% money growth on a perceived endless nirvana, will not only lead to a full bear market but likewise increase the risks of a financial/economic crisis.
Again let me quote again and again and again the fateful ingredients behind all the crises during the past eight centuries. From Harvard Professors Carmen Reinhart and Kenneth Rogoff[36] (bold mine)
The essence of the this-time-is-different syndrome is simple. It is rooted in the firmly held belief that financial crisis is something that happens to other people in other countries at other times; crises do not happen here and now to us. We are doing things better, we are smarter, we have learned from past mistakes. The old rules of valuation no longer apply. The current boom, unlike the many previous booms that preceded catastrophic collapses (even in our country), is built on sound fundamentals, structural reforms, technological innovation, and good policy. Or so the story goes …
[1] See Emerging Markets: Why Adjustments For Relative Yield Spreads has been Disorderly February 17, 2014
[2] See Emerging Market $2 trillion Carry Trade: The Pig in the Python February 24, 2014
[3] Philip Turner BIS Working Papers No 441 The global long-term interest rate, financial risks and policy choices in EMEs February 2014 Bank of International Settlements
[4] GMANetwork.com Money supply growth to decelerate further —Tetangco February 18,2014
[5] Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas Domestic Liquidity Growth Rises in January February 28, 2014
[6] Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas Bank Lending Sustains Growth in January February 28, 2014
[7] See Phisix: Global Financial Volatility Intensifies February 10, 2014
[8] Thomas Sowell Is Reality Optional? — And Other Essays Clancycross.com
[9] see Phisix: Stagflation is here, Expect a Weaker Peso February 17, 2014
[10] See Egypt’s Booming Stocks are Symptoms of Runaway Inflation February 26, 2014
[11] See Lessons from Kazakhstan’s currency Meltdown February 17, 2014
[12] Time.com Many Ukrainians Want Russia To Invade March 1, 2014
[13] BBC.com Ukraine crisis: Obama warns Russia against intervention March 1, 2014
[14] See Consequences of Inflationism: Caracas (Venezuela) and Kiev (Ukraine) Burns February 21, 2014
[15] See Phisix: Another Marking the Close Day? February 28, 2013
[16] see Phisix: Scrutinizing the Property Inspired Rally February 24, 2014
[17] Arnold Kling Stocks and the Economy, Again July 8, 2011 Econolog
[18] Wikipedia.org Earnings growth Relationship with GDP growth
[19] See Why Strong Economic Growth Hardly Equals Outsized Equity Returns February 24, 2014
[20] Warren Buffett Buffett's annual letter: What you can learn from my real estate investments February 24, 2014 Fortune.cnn.com
[21] Rappler.com Ayala Land allots P70B for 2014 projects February 17, 2014
[22] Manila Standard SM Prime investing P36b for expansion January 29, 2014
[23] Interaksyon.com SMDC to spend as much as P18-billion for new condo projects in 2014 December 12, 2013
[24] Manila Standard Robinsons set to sell P15-b bonds February 28, 2014
[25] Philstar.com Vista Land eyes P25-B new projects February 7, 2014
[26] Philstar.com Century Properties opens P1-B Century City Mall February 17, 2014
[27] Philstar.com Filinvest allots higher capex for 2014 December 15, 2013
[28] Philstar.com Empire East to launch 5 new projects December 9, 2013
[29] Philstar.com Rockwell invests P2B in Cebu February 6, 2014 (2 billion Cebu)
[30] Philstar.com Puregold to put up 25 new stores January 9, 2014 (3 billion)
[31] Interaksyon.com Roxas & Co to raise funds for expansion of property business February 26, 2014
[32] BusinessMirror AEV allocates P88-billion capex for 2014 January 29, 2014
[33] Interaksyon.com Megaworld sees 112,000 sqm of office space ready by yearend February 5, 2014
[34] See Cracks in the Philippine Property Bubble? October 7, 2013
[35] See Southeast Asia as Retirement Haven February 12, 2014
[36] Carmen Reinhart and Kenneth Rogoff From Financial Crash to Debt Crisis Harvard University