This should be another slap on the face for inflationistas or people who myopically advocate inflation as economic elixir.
From Reuters,
Argentine banks have seen a third of their U.S. dollar deposits withdrawn since November as savers chase greenbacks in response to stiffening foreign exchange restrictions, local banking sources said on Friday.
Depositors withdrew a total of about $100 million per day over the last month in a safe-haven bid fueled by uncertainty over policies that might be adopted as pressure grows to keep U.S. currency in the country.
The chase for dollars is motivated by fear that the government may further toughen its clamp down on access to the U.S. currency as high inflation and lack of faith in government policy erode the local peso.
"Deposits keep going down," said one foreign exchange broker who asked not to be named. "There is a disparity among banks, but in total it's about $80 million to $120 million per day."
U.S. dollar deposits of Argentine banks fell 11.2 percent in the preceding three weeks to $11.5 billion, according to central bank data released on Friday. The run on the greenback has waxed and waned since November, after President Cristina Fernandez won a second term on promises of deepening the state's role in the economy.
From May 11 until Friday, data compiled by Reuters from private banks showed $1.9 billion in U.S. currency had been withdrawn, or about 15 percent of all greenbacks deposited in the country.
Feisty populist leader Fernandez was re-elected in October vowing to "deepen the model" of the interventionist policies associated with her predecessor, Nestor Kirchner, who is also her late husband.
Since then she has limited imports, imposed capital controls and seized a majority stake in top energy company YPF.
Earlier, Argentina’s central bank President Mercedes Marcó del Pont even mocked at the laws of economics and haughtily declared that printing money does NOT lead to inflation.
Like in the Eurozone, what governments and their minions say and what people do always clash: The prospects of intensifying devaluation worsened by concerns over capital controls and other forms interventionism have been prompting people to turn to black markets, take refuge on foreign currencies and flee the Argentine banking system altogether
Joel Bowman at the Daily Reckoning has a nice take on this…
The Argentinean government’s policy of theft via inflation has created a demand for the relative safety of US dollars. Obviously, a massive flight from pesos would create considerable headaches for the Argentine State and its efforts to control “its” people…and their taxable income. And so, even though there is no official rule preventing the purchase of US dollars (or any other foreign currency), Argentina’s equivalent to the IRS, AFIP, has made it virtually impossible to do so through regulated channels (i.e., banks).
Therefore, the informal exchange houses do a roaring trade responding to a very real and honest demand for US dollars. And there’s still enough business left over to maintain a vibrant market for the “green rate.” This exchange rate is even less official than the unofficial “blue rate.”
The “green rate” is offered by los arbolitos — i.e. “little trees” — who stand along Florida Street waving their arms (like little trees) and offering their exchange services. That rate, currently at 6.20 pesos to the dollar, is quite literally the “street price” for dollars.
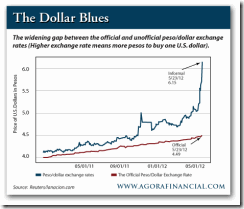
The nearby chart shows the wide — and rapidly widening — gap between the official exchange rate and the blue rate, the most often quoted parallel dollar rate.
Exactly as you would expect, the more money the government prints, and the tighter the capital controls they impose, the greater the urgency to swap pesos into dollars…and the higher the unofficial exchange rates soar.
Clearly, this is a trend that cannot continue indefinitely.
The Argentine State is scrambling to outlaw the consequences of its own recklessness. For years now, Argentina’s Central Bank (BCRA) has brought forth freshly inked fiat notes by the billions to pay for unaffordable election promises. Our North American readers will recognize this crafty monetary prestidigitation as “money printing.”
The practice is nothing new, of course — neither here nor in any country where the tyranny of the mobjority — democracy — enjoys the power to decide the cost to be levied on the minority.
What seems peculiar about Argentina’s case is the government’s Herculean effort to ignore the immutable laws of economics in their pursuit of grand larceny. The country has seen five currencies in just the past century, averaging a collapse every twenty years or so. In 1970, the peso ley replaced the peso moneda nacional at a rate of 100 to 1. The peso ley was in turn replaced by the peso Argentino in 1983 at a rate of 10,000 to 1. That lasted a couple of years, and was then replaced by the Austral, again at a rate of 1,000 to 1. To nobody’s surprise, the Austral was itself replaced by the peso convertible at a rate of 10,000 to 1 in 1992. During the past four decades, when all was said and done, after the various changes of currency and slicing of zeroes, one peso convertible was equivalent to 10,000,000,000,000 (1013) pesos moneda nacional.
Obviously Argentinians haven’t learned, yet they are adversely responding to such policies via capital flight. Nevertheless sustained capital flight should help starve the beast.
While stock markets have functioned as to flight to safety against governments going into a maximum inflation overdrive, apparently Argentina’s worsening capital controls has been sending their benchmark index the Merval into a steady downhill as Argentinians seem fearful that their savings could be seized anew like in 2001.
Inflationism constitutes part of, or a mixture of the many other repressive measures from an increasingly despotic government such as higher taxes, price controls, capital controls, nationalization, protectionism and other forms of anti-market interventions. So whatever interim gains will be offset by lower real economic growth.
Argentina seems likely headed for for another sordid chapter of hyperinflation.
The other hyperinflation candidates are neighboring Venezuela, communist North Korea or any European crisis affected nations who will severe ties with the EU.

No comments:
Post a Comment