In this issue:
How Philippine Capital Markets Will Benefit From Free Trade
-Will Lady Luck Probably Smile On The Aquino Regime?
-Explaining Free Trade
-Anti-Free Trade: Political Dynasties and The Maguindanao Massacre
-The Invisible Hand
-How Free Trade Should Benefit The Philippine Capital Markets
At a recent speaking engagement, I was asked of what I thought of the new Aquino administration and his economic policies. My reply, first that I was apolitical, and second, that there are major forces such as globalization, regionalization and the technological revolution that has been and will be driving global policymaking and this includes the Philippines.
Obviously far from being a populist answer, such reply would seem stoic since it didn’t whet the sensationalist craving of the audience.
Will Lady Luck Probably Smile On The Aquino Regime?
As any regular reader would know, in my opinion, the new administration is NO more than representative of the status quo[1], which for me would seem better, compared to activist ‘messianic’ left-leaning leaders, such as Venezuela’s Chavez or even the US president Obama.
And yes, most signs have been validating my perspective, be it on the pronounced policies on jueteng[2], cabinet appointments[3] packed with representatives from big business and even to populist sound bite (or what Mark Twain would refer to as "a minimum of sound to a maximum of sense" or simply “attention generating”) policies such as the “Wang Wang”[4] or the recent administrative action: the censure of PAG-ASA[5] (government weather forecasting) personnel in the wake of the recent widespread brownouts caused by typhoon Basyang.
And based on my analysis I predict that the administration’s performance (success or failure) will likely be aligned with the patterns of “global” if not regional political economic trends.
As previously stated[6], ``the direction of political winds in the Philippines is likely to get influenced more by our deepening interactions with external forces-particularly, the new free trade zone (with ASEAN and China), China's growing role as a major political force as regionalism deepens, a deeper impact from globalization buttressed by technology and OFWs (or migration flows) and deepening financial globalization which includes transmission effects of inflationism, steep yield curves, bubble policies and etc.”
In short, luck or the lack of it, will dominate the Aquino regime.
Well it didn’t take long for more signs to surface which would seem to validate my prognosis.
This from yesterday’s article from the Inquirer.net[7], (all bold emphasis mine)
``In a speech before members of the Philippine Chamber of Commerce and Industry Wednesday evening, Trade Secretary Gregory Domingo said it was now common practice among economies to participate in multilateral trade pacts.
“You have to be part of every trade agreement because to be excluded is a disadvantage for you. We’re not yet part of [the TPP], but at some point, I think it is our desire to join as well,” he said.”
It is unfortunate enough for the Aquino administration’s trade secretary to seem to have little appreciation of the essence of free trade agreements. For Mr. Domingo, and if this should represent the insights of the administration, free trade agreements are simply a fad, take note of “common practice”.
So while I applaud the Aquino administration for supposedly espousing free trade, the essence of the administration’s policymaking, as stated before, is because “everybody else is doing it”. It’s definitely not out of principle, but out of the socio-economic signalling known as “Keeping up with the Joneses”.
This again lends credence to our projection of: one—popularity based policies (in this case globalization) and two—the deepening influence of global political trends which has been influencing local policymaking.
Let me add that while the practice of free trade seem to get more ingrained globally, this remains a virtually unpopular or severely misunderstood concept in the eyes of the domestic populace.
Take for example, this free trade agreement definition from the media; from the same article
``The aim of the free trade agreement is to bring all tariffs down to zero by 2015. The coverage of the deal spans trade in goods and services, rules of origin, trade remedies, sanitary and phytosanitary measures, technical barriers, intellectual property, government procurement and competition policy.”
True, these are mostly technically “legal” definitions, but this hardly dwells on the kernel or the cost-benefits tradeoffs from the said policy.
And in evincing more proof of miscomprehension of free trade, but this time from the officialdom; the same article quotes the incumbent trade secretary anew, (bold highlights mine)
“We will be very vigilant in joining various trade agreements. We’ll try to join as many trade agreements as possible, but still keeping in mind that our interest is really to protect the interest of Philippine businesses and Philippine consumers,” Domingo said.”
But free trade is of the interest of the Filipino consumers and businesses!
Free trade is VOLUNTARY exchange! It allows people to conduct exchanges to satisfy personal and commercial needs.
When we go to a store to ‘freely’ purchase things or services which we deem to need, don’t we achieve immediate satisfaction from the activity?
If people, on their unfettered disposition, buy from me, do I not use the proceeds from the exchange to subsequently also buy from the marketplace, either to fulfil my consumption goals or expand or replenish my business needs or even make contribution to social projects for the betterment of our community/society? Because producers are themselves consumers, then trade is a benefit to all parties involved.
Hence, the fundamental role of the marketplace is to satisfy our sundry needs by means of voluntary, and NOT coercive, exchange. So why does Mr. Domingo express scepticism with “protect the interest of Philippine businesses and Philippine consumers”?
Explaining Free Trade
There are two way to acquire wealth. German sociologist Franz Oppenheimer[8] once said that there is the ‘economic means’ via work and exchange and there is the ‘political means’ by forcible exploitative means either by plunder or by redistribution.
Acquiring wealth through work and exchange is NET beneficial to the society since it fosters the creation of value added products or services.

Figure 1: World Bank[9]: Explosion In Global Mobile Subscribers (left window) and Internet Use (right window)
Think the internet and the mobile phones. Twenty years ago these were non-existent. Yet competition in the marketplace cultivated a sweeping technological innovation, which the introduction of these highly efficient revolutionary tools exponentially expanded access to communication and greatly reduced transaction costs.
Today, I can talk with my mom in Hong Kong everyday at the minimal cost of the bandwith, compared with costly occasional long distance phone calls 20 years back.
Of course there will always be losers anywhere. Creative destruction from free market innovation led to the phasing out or the obsolescence of the pager and the telegraph, the reduced usage of the fax machine, postal mail and even a decline in the newspaper industry[10]. However the gains from innovation have virtually eclipsed the selective losers. In short, by large, society benefited from the new technology.
Moreover, because of the immensely lowered transaction cost, global trade blossomed.
Meanwhile, the obverse side of acquiring wealth from economic means is the political means.
‘Political means’ essentially is parasitic which lives off the work of others. This involves taxation and forcible redistribution, war and corruption. The benefits only accrue to the parties involved in conducting such affairs, primarily government. And such actions signify a ZERO SUM game- where one benefits, as the others losses, which in general do NOT add wealth to the society—since resources is just taken away from someone else.
Furthermore, by allowing people to exchange voluntarily, this furthers the division of labor that creates jobs, and importantly, accumulates capital or wealth.
And increased global trade or globalization, as noted above, has definitely been the prime engine of wealth accumulation (see figure 2).

Figure 2: Google: Deepening Free Trade And Exploding Global Wealth
The correlation of the growth of global merchandise trade relative to the explosion of global per capita income may not be perfect, but it has been strong and rigorously supported by theory and empirical micro evidences as the rapid diffusion of the mobile phone and the web around the world.
Anti-Free Trade: Political Dynasties and The Maguindanao Massacre
In addition, free trade greatly reduces pressures from political redistribution which frequently leads to internecine political conflicts.
Take for instance the Maguindanao massacre[11]. The fundamental reason why such atrocious and barbaric act had been committed was allegedly due to the political insecurity by the incumbent local leadership over the preservation of his regime.
The horrid Maguindanao incident appears to be symptomatic of the latent inherent defects of the Philippine political ‘democratic’ framework, which has cultivated a brood of political dynasties (estimated at about 250) that has used politics to arrogate upon themselves economic opportunities and thus the imperative to remain in power at nearly all cost.
Even this New York Times article of 2007[12] presciently noted of the violent nature from this political arrangement, ``For generations, political dynasties have dominated elections and governments in the Philippines...As these clans protect their reign, they often resort to violence to frustrate any attempt by rivals to unseat them.”
And how do you sustain political dynasties? By systematic redistribution. The above board taxes generated from the local economy are used to pay off voters indirectly by virtue of massive welfare programs [e.g. free movies, free health care, senior citizens discount and etc...] or directly (vote buying) during elections. For instance, local authorities discreetly allow people to squat on empty government and private lands and are given protection from doing so in exchange for votes.
Yet this form of squatting has been provided with a legal cover in the face of the Lina Law (RA 7279)[13], where relocation is required for squatters evicted from their domicile. In short, the law rewards the violation of property rights.
Of course there is also the issue of the undeclared tax payments, which usually ends up in the pockets of the politicians.
Hence, the violence in Maguindanao has been representative of the state of economic deprivation from the operative highly skewed political-legal environment.
According to the Focus on the Global South, Maguindanao remains as one of the poorest provinces in the country. With a population of more than 1 million in 2006, six out of ten people are considered poor in the province, which is almost three times higher than the national average. Maguindanao is also a “mainstay” in the list of ten provinces with the biggest income gap, poverty gap, and severity of poverty[14]
In other words, where politics has been substituted for trade, we get violence as a result of the exploitative grab for resources by the use of political means, as Franz Oppenheimer has postulated.
And this also validates the great Frédéric Bastiat who once said that, “When goods do not cross borders, soldiers will.”
Apparently, in Maguindanao, the order of private armies determined past economic fortunes which had largely been held and distributed by the entrenched political class and which appears as modern day vestiges of a medieval age political structure known as feudalism.
Likewise, history has revealed that the same political means to attain wealth in favour of vested interest groups had been responsible for the mass slaughter of humanity seen in the two horrendous world wars of the 20th century, where the casualties as estimated by the Wikipedia.org[15] for World War I is anywhere in the range of 10-64 million people while World War II at 40-72 million people.
As historian Michael A. Heilperin poignantly observed[16], Economic nationalism was the real victor of World War I, just as collectivism was to be the real victor of World War II.
So why does the new trade secretary remain fearful of free trade?
The answer is simply because the entrenched political and economic class are concerned and apprehensive that their current economic privileges, which on the other hand signify as economic inefficiencies, brought about by protective walls of legal and political barriers, might not cope with the onslaught of market based competition.
In short, free trade means putting to risks inefficient and uncompetitive firms which has operated on the premises of political concessions such as monopolies, cartels, subsidies, liberal access to state financing, tax shields, various licensing or other state based privileges which has been an enduring trait for Southeast Asian economies, as journalist and author Joe Studwell rightly notes[17], “The lesson of the past decade has been that the relationship between political and economic elites in Southeast Asia is more enduring than almost anyone imagined.”
Thus, by reading in between the lines, the trade secretary appear to signal the administration’s possible intent to enforce gradual change on a regime that thrives on the status quo.
The Invisible Hand
It is likewise foolhardy and mendacious to assert that free trade works to harm consumers as free trade primarily benefits consumers through manifold choices.
Free trade allows consumers to benefit from the various offerings from the producers or service providers, all in competition to satisfy their needs. And the thrust to market products to satisfy consumers comes in many facets such as pricing, quality, utility, aesthetics, self-esteem and etc...
In short, for the consumers, the essence of free trade is choice, the more the array of choices, the greater the value of the exchange.
On the other hand, for the producers, the essence of trade is profits,
As Ludwig von Mises wrote[18],
Profits are the driving force of the market economy. The greater the profits, the better the needs of the consumers are supplied. For profits can only be reaped by removing discrepancies between the demands of the consumers and the previous state of production activities. He who serves the public best, makes the highest profits. In fighting profits governments deliberately sabotage the operation of the market economy.
Thus in connecting the two, free trade gives the consumers the best possible alternative while for producers, the profit incentive from doing so. In short, free trade signifies as the best possible arrangement for achieving satisfaction and profits.
Yet sometimes media gives the illusion that consumers are too dumb that they can’t distinguish between what’s good enough for them and what’s not, and thus require the nanny state via various regulatory interdictions.
Ironically, the same media would pontificate on the virtues of democracy where people get to vote on political leaders, as if people have been bequeathed with intelligence only when they vote for leaders and the lack of it when they spend their own money.
In reality, it works the opposite way.
When people spend for goods and services they expect to get direct benefits from an exchange and thus always exercise the option to choose based on perceived order of needs and of the accompanying value from the available choices.
Isn’t it commonsensical for consumers not to further patronize on what they feel as inferior, inadequate, substandard, or a product or service that is perceived as worth less than the price which they had earlier paid for?
By the pattern of spending, consumers, thus, impose market discipline on producers without the need for state intervention.
The father of modern economics, Adam Smith called this as the Invisible Hand.
In contrast, in elections when people vote for political leaders, what you vote for isn’t what you exactly get. Whether it is Philippine President Joseph Estrada of 1998, Japanese PM Yukio Hatoyama[19] or US President Obama, the point is—populist politics usually ends up with the opposite expectations from which they had been ushered into office.
Of course in any field, one can’t discount that there will always be unscrupulous agents. But such devious entities are likely to fool people ONCE and will be refused further patronage. Thus, any gains will be temporary and by deceiving consumers, they will be penalized by the virtue of monetary and reputational losses, if not lawsuits.
Yet, in the case where physical harm that should emanate from the use of their products or services, then this should also be subjected to legal remediation.
How Free Trade Should Benefit The Philippine Capital Markets
So if the Aquino regime will truly usher the Philippines more as an active participant in free trade engagements this should augur very well for the Philippine economy.
Of course, the Philippines has been a signatory of many free trade[20] accord, even prior to the Aquino regime, which includes including the Asean Trade in Goods Agreement, Asean-Australia-New Zealand Free Trade Agreement, and the Japan Philippines Economic Partnership Agreement, but sustaining and more importantly (and hopefully) expanding the ‘gradualist’ momentum will be a very crucial dynamic.
However, given the administration’s faddish perception of globalization, the consistency of this policy is yet unclear.
Theoretically, increased free trade and/or economic freedom should bode well for the local capital markets, since more investments should translate to the increased access to domestic and global savings which should get intermediated via the banking system or through the capital markets.

Figure 3: McKinsey Global Institute[21]: Share of Financial Assets By Region 2008
In developed economies, except for Japan, bank deposits make up a smaller share of the capital markets as shown by figure 3. The greater part of the distribution of financial assets has been into the private sector debt securities and in the equity markets.
Thus while there are cultural and domestic regulatory dynamics that could also shape the divergences in the distribution of financial assets, we should expect a larger share of private bond and equity markets for mature market economies. This implies Emerging Asia could likely be headed on that path.
Considering that the Philippines, whose primary line of financing has been channelled through the banking sector, where banking penetration level is only 35% of the population, according to McKinsey Quarterly[22] estimates, this means there is a huge amount of unaccounted capital afloat in the system.
And this squares with the estimated 40% share of the informal economy[23] and with 4 of the top 11 largest malls[24] in the world, according to the Forbes Magazine, housed in the Philippines.
In other words, free trade and or economic freedom will compel enterprises and institutions to deal with this enormous untapped savings which should translate to a huge boom for the domestic capital markets.
Part of the early move on this has been the advent of mobile banking.
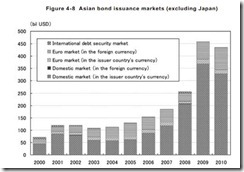
In terms of bond markets the Philippines accounts for one of the smallest in Asia (see figure 4)
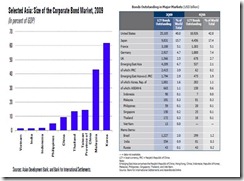
Figure 4: IMF[25]-Size of Corporate Bond Market, ADB[26]-Local Currency Bonds Outstanding
Aside from the untapped savings, which is most likely sourced from the informal economy, the existing bank deposit base is likely to tap into both the bonds and the equity markets.
The factors that are likely to drive these would be amplified relative returns, reforms that would enable the lowering of transaction costs, introduction of derivatives and other more sophisticated financial instruments that allows the public to hedge. Incidentally, if I’m not mistaken only the Philippines among the ASEAN-4 have yet to introduce derivatives in the stock exchanges.
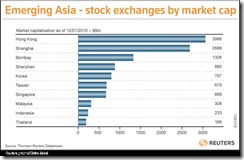
Figure 5: Reuters[27]: Market Capitalization of Emerging Asia
I’d also like to further point out that the Philippine Phisix accounts for as one of the smallest bourse in Asia (not included in Figure 5).
As of Thursday’s close the Phisix free float market cap is estimated at US $66.5 billion (exchange rate of Php 46.5 to a US dollar) compared to $188 billion of Thailand last January 12th or possibly at $212 billion today adjusted for the 12.7% advance from the aforementioned period.
And it is of no surprise to us that the ASEAN-4, which comprises as the smallest bourses of the region, has accounted for the biggest gains.
The trend of the ASEAN-4 towards freer markets, aided by technological revolution, is just one of the major positive structural long-term factors at play.
Nevertheless, the other major and more influential medium term dynamic is the risks of blowing asset bubbles originating from the current concerted global central banks’ bubble policies, which is likely responsible for today’s buoyant asset markets.
Since the risk for Asia and the ASEAN seem to be a brewing boom-bust cycle, where a boom is a positive and bust is a negative, the larger net effect of a bust which constitutes as capital consumption signifies as a NET NEGATIVE. So we have major two forces counteracting on each other.
But this is a story we have long been talking about.
Anyway, in closing, speaking of bubbles, this news report is just too compelling for me to exclude from this week’s report.
From Bloomberg[28],
``South Korea will ‘soon’ announce plans to stimulate the nation’s property market, Yonhap News reported… The nation’s land ministry is drawing up measures to boost real-estate prices, and the ruling Grand National Party may begin discussions on easing debt-to-income restrictions on homeowners…”
People never seem to learn.
[1] See Philippine Election Aftermath: Goodbye Illusion, Welcome Reality!
[2] See Plus Ca Change: President Aquino's Policy On Jueteng
[3] See President Aquino’s Cabinet Appointments: The More Things Change, The More They Remain The Same
[4] See Why The Sell-Offs In Global Markets Are Unlikely Signs Of A Double Dip Recession
[5] See Privatize Pag-Asa or Open Weather Forecasting To Competition
[6] See Philippine Election Myth: New President Will Determine Direction of Economy And Markets
[7] Inquirer.net, RP eyes participation in free trade deal, July 23, 2010
[8] Oppenheimer Franz, The State
[9] World Bank, States and Markets, World Development Index 2009
[10] See Is The Newspaper Industry Dead? Probably Not If It Is For Free
[11] Wikipedia.org, Maguindanao massacre
[12] SFGate.com, Philippine political dynasties stifle democracy, nurture violence / Powerful clans have a stranglehold on system, experts say, New York Times, March 13, 2007
[13] Answers.com, What is the Lina Law?
[14] Manahan, Mary Ann Maguindanao in Focus Focusweb.org
[15] Wikipedia.org, List of wars and disasters by death toll
[16] Heilperin, Michael A. Heilperin Economic Nationalism: From Mercantilism to World War II
[17] Studwell, Joe, Ties That Bind, July 22, 2007
[18] Mises, Ludwig von Confiscatory Taxation, Chapter 32, Section 3
[19] See How Populist Leadership Goes Kaput: Japan Edition
[20] Inquirer.net, loc. cit.
[21] McKinsey Global Institute Global capital markets: Entering a new era, September 2009
[22] See How Free Markets In The Telecom Industry Aids Economic Development
[23] See Does The Government Deserve Credit Over Philippine Economic Growth?
[24] See A Nation Of Shoppers??!!
[25] IMF Regional Economic Outlook Leading the Global Recovery Rebalancing for the Medium Term
[26] Asian Bond Monitor, Asian Development Bank, March 2010
[27] Reuters ANALYSIS-For Singapore bourse, IPOs remain the Achilles heel, January 13, 2010
[28] Prudentbear.com, Trichet Challenges Inflationism, Bloomberg July 19, 2010