Nowhere does history indulge in repetitions so often or so uniformly as in Wall Street. When you read contemporary accounts of booms or panics the one thing that strikes you most forcibly is how little either stock speculation or stock speculators today differ from yesterday. The game does not change and neither does human nature.- Edwin Lefevre, Reminiscences of a Stock Operator
Yet there has been much reluctance for profit taking to occur.
That’s what I wrote last week[1] when I conveyed my suspicions over the supposed miniscule correction phase which barely even happened.
The bulls in the Philippine Stock Exchange took almost every instance of perceived weakness as opportunities to charge with inexorable ferocity.
The Phisix closed with a stupendous 2.88% returns over the week, the best weekly advance for 2013. This year’s bullish winning streak now runs 9 of 10 weeks with the other week’s .34 decline signifying a deviation.
The Phisix posted a whopping month-on-month 7.4% (nominal domestic currency) gain in January, and this was further magnified by another gigantic 7.7% advance for February. If the 7% m-o-m pace of returns will be sustained, then the Phisix at 10,000 will be reached by the end of August 2013.
So far, two weeks into March, accrued returns have been at 1.7%; this is 5.3% shy of the 7% level. Will the Phisix deliver over the next two weeks?
Again, let me be clear: I am NOT saying that Phisix 10,000 in August of 2013 will definitely happen, I am saying that given the rate of how the manic phase has been progressing, then we cannot discount that Phisix 10,000 will be reached within the year. This may or may not necessarily occur in August. Current trajectory suggests that 10,000 is a likely target anytime 2013-2014.
Yet such watershed event will essentially depend on how markets will respond to the prospective actions of the domestic and international central bankers.
Populist Elixirs with Nasty Consequences
And it’s really not just the Philippines.
Except for China, whose Shanghai Composite Index slumped 3.78% for this week, almost every major global equity benchmarks has been ablaze.
Along with Denmark, the US stock markets led by the Dow Jones Industrials have set fresh record highs[2], ending the decade long consolidation.
The broadening bullishness of US financial assets has not been limited to equities. Such events emerged as both US Federal Reserve Chair Ben Bernanke and Vice Chair Janet Yellen chimed to say the Fed’s $85 billion monthly asset purchases should be sustained[3].
The reality is that much of current optimism has been underpinned by strengthening rate of credit expansion. Growth in non-Financial debt has recorded the strongest gain since 2008 primarily from the corporate sector and from the Federal government. (chart from Yardeni.com)
As Credit Bubble Bulletin analyst Doug Noland observed[4],
For Q4 2012, Total Non-Financial Credit expanded at a 6.4% rate, the strongest expansion since Q3 2008 (7.0%). Total Household Borrowings expanded 2.4% annualized, the briskest pace going back to Q1 2008 (3.6%). Household Mortgage Credit contracted 0.8% annualized, the smallest pace of decline since Q1 2009 (positive 0.2%). Corporate borrowings grew at a blistering 10.7% pace, the quickest since Q4 2007 (11.5%). Federal debt expanded at an 11.2% rate during the quarter. In nominal dollar terms - seasonally-adjusted and annualized (SAAR) - Q4 Total Non-Financial Credit expanded $2.536 TN. Looking at the main categories, Total Household debt increased SAAR $312bn, Total Business SAAR $1.076 TN, and Federal Government SAAR $1.259 TN. Credit expansion has become increasingly broad-based.

Yet record highs can be deceiving. In spite of the current cheerleading by Wall Street, the Dow Jones Industrials has severely been underperforming bananas and gasoline[5], which exposes the inflation adjusted returns of the key US benchmark.
On the other hand, Japan’s Nikkei have been on a sustained bullish blitz with a 5.84% week-on-week spike.
Former Asian Development Bank President Haruhiko Kuroda, who has been officially been nominated as the next Bank of Japan chief has echoed ECB’s Mario Draghi’s stance of pledging to do “whatever it takes to save the euro[6]” or from Mr. Kuroda’s version: “whatever is needed to end 15 years of deflation[7]”. Mr. Kuroda is seen as technocratic ally in support of Japan’s Prime Minister Shinzo Abe’s aggressive inflationism or “Abenomics”.
On a year to date basis and from nominal currency terms, the Nikkei’s 18.17% return is just a head length away from the Phisix. But again nominal can be misleading, considering 9.6% decline relative to the US dollar as of Friday, a foreign investor would net less than half of the nominal returns.
Japan recently posted a paltry statistical economic growth of .2%[8] as her current account continues to deteriorate significantly, despite yen’s dramatic devaluation.
While devaluation typically provides short term steroids, Japan’s aggressive easing policies appear to be worsening her economic conditions even in the short term[9].
Whatever supposed gains aimed at the political façade of attaining economic “competitiveness” appears as being neutralized by factors such as higher import costs and reduced consumption.
Worst, a sustained deterioration of current accounts means that Japan will increasingly rely on foreign capital and or draw down from the her pool of savings which has been estimated at $19 trillion and which could also extrapolate to a reduction of assets held overseas or $4 trillion net foreign investment position[10].
And given the deliberate debasement of the yen, I am not inclined to see a reduction of foreign assets by Japanese households. Instead, Japan’s private sector will likely increase their exposure overseas couched under euphemism of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) or portfolio flows when in reality they account for as “capital flight”[11].
So “Abenomics” will mean that Japan will transition from a net savings-net creditor nation to eventually a net debtor country overtime or a sordid tale of from riches to rags, if such policies continue.
And adding to the devaluation-offsetting factor, the stock market bullrun prompted for by Japan’s devaluation-inflationism will hardly translate to any material benefits from the “wealth effect”.
The equity share of total financial assets held by Japanese households, accounts for only 5.8% as of September 2012, compared to 32.9% in the US (as of September 2012) and 14.3% in the Euro area (as of June 2012), according to the Bank of Japan[12].
This implies that the major beneficiaries of the collective easing policies by political authorities of Japan, the EU and the US, as seen through the current stock market boom, have hardly been about interests of the consumer via households, but of those politically privileged sectors covering non-private financials and the financials.
The worst ramification from the current set of policies has been one of increasing the geopolitical strains that has emerged out of financial protectionism coursed through inflationism or devaluation policies.
Recently China’s sovereign-wealth fund president Gao Xiqing warned of Japan’s domestic policy as inflammatory to the already current fractious state of bilateral relations stating that, according to the International Business Times[13],
Treating the neighbors as your garbage bin and starting a currency war would not only be dangerous for others but eventually be bad for yourself
In short, devaluation which represents one step towards the slippery slope of protectionism serves as tinderbox to wars.
Only the mentally challenged will see war as morally, politically and economically justified.
Such are populist elixirs with nasty consequences.
China’s Politically Induced Volatile Markets as Paradigm
And speaking of the volatility, the material 3.78% weekly decline of China’s Shanghai index seem as in response to the prospects of potential tightening by Chinese authorities in the face of the sustained ballooning of her property bubble. The Shanghai index now stands with a paltry 2.18% year-to-date gains.
Inflation rates have surprisingly spiked to 3.2%[14] which is just a few percentage away from the inflation ceiling target of 3.5% set by Chinese authorities.
Price inflation signify as symptoms of credit expansion or bubble polices
This even comes after State Council or China’s cabinet, put pressure on the Chinese central bank, the People’s Bank of China (PBOC) to increase downpayment and mortgage rates for “second-home buyers and ordered stricter enforcement of home-sale taxes”, as well as for property sellers to pay 20% sales tax.
As I have been saying, rising inflation rates will put pressure on interest rates that will likely send the latter higher.
And a path of higher rates will negatively impact marginal projects erected from a low interest environment, whom will be forced to bankruptcies. And as interest rates go higher to reflect on price inflation, in a debt laden economy, increasing incidences of insolvencies from marginal projects spreads from the periphery to the core.
So far China’s high savings rate has kept her economy from a tailspin.
Yet China’s markets seem to have been speculating that political authorities may tighten by increasing interest rates for the first time since 2011.
Interestingly a senior researcher affiliated with the country’s top planning agency admits that there are some “structural bubbles” in her real estate market and sees two ways to address such problem. Mr. Chen Dongqi, the deputy head of the National Development and Reform Commission’s macroeconomic research institute, in an interview said[15], “One is to gradually release the steam and the other is to put on a sudden brake.”
To translate: the former is to hope for a benign landing, the latter is to expect a crash.
Either way, all bubbles will deflate. Interventions can only defer the day of reckoning but along with it magnify the extent of imbalances and its commensurate consequence—a bubble bust.
The Chinese government has resorted mostly towards the regulatory path, yet such have not been sufficient to deflate China’s inflating bubbles.
Vincent Lo, a billionaire businessman, chairman of Shui On Land Ltd., a Shanghai-based developer who also serves as member of the government’s advisory board said that the spate of regulations have failed to quash the property bubble[16]. Although he is hoping that the recently imposed measures may accomplish the desired effects.
Unfortunately, regulators don’t seem to understand the nature of people. Authorities mostly deal with symptoms of the disease rather than with the disease itself. The repercussions of having more regulations have been for people to explore loopholes to circumvent regulations: unintended consequences.
Here is an interesting account. Dissolving marriages via divorce could be the du jour technicality to circumvent property curbs[17],
Wang Ying and Du Bibo only married a fortnight ago but already they are lining up in the divorce registry office in Shanghai’s Xuhui district to dissolve their marriage.
With big smiles on their faces – a facial expression that marks them out as not your normal warring couple – they explain that the mortgage officer at their bank recommended divorce as the best way around a new property tax.
A capital gains tax on housing sales was intended to cool China’s sizzling property market, but since it was announced last Friday it has had the exact opposite effect: a panic has been unleashed.
The other aspect of China’s bubble is the politics behind it.
There has been increasing number of billionaires-delegates to China’s parliament this year. There are about 83 billionaires members of the Chinese political elite, up 17% from last year[18]. While it may be true that a reason for the wealthy to join politics has been to “protect” their wealth or interests, I’d say that given the mixed nature of China’s political economy, where the distribution of state owned enterprises (SoE) with private enterprises have reportedly been about split (some say SoEs are a third of the economy)[19], many have instead used politics to gain a moat against competitors via political route in order to acquire wealth.
In the past, globalization has led to the reduction of China’s SoEs both in numbers and role. But stimulus spending to shield her economy from 2008 US crisis has led to a slowdown in the decreasing trend of SoEs, if not a reversal—an increase of SoEs.
Nonetheless SoEs have been said to become more powerful supposedly due to efforts to create “national champions”[20].
I take a different perspective: SoEs have been key instruments used by China’s government to implement her non-transparent policies. The Chinese government has not made any explicit significant stimulus announcements, but we see signs of credit booms occurring through SoEs.
For instance, the recent bounce in China’s Shanghai index came amidst the latest credit expansion from trust companies (whom are exposed to property developers and to the local government) as well as from local government financing vehicles[21].
So in trying to preserve the status quo which benefits those in power or those connected with the powers that be, the recent policy direction has been to re-politicize China’s economy, hence reinvigorating the role of SoEs.
Current trends should also give us a clue on how policymakers are likely to react. Chinese politicians are likely to chatter about tightening, but like the Fed’s poker bluff, they are likely to do the opposite as any “tightening” would likely undermine their financial and political interests.
Regulations are likely to be “symbolical” meant to exhibit “do something politics” for media consumption or for propaganda mileage. Such will likely be shrouded by lax enforcement from venal bureaucrats which is why Mr. Lo cavils about failed regulations.
The buying spree of wealthy political class or the politically connected Chinese of international properties, some in the US, have purportedly been in anticipation of the “stamping out” of corruption from new Chinese leaders[22]. I would doubt such a premise, considering the re-politicization (reversal of economic freedom) of the Chinese economy which means more corruption.
Rather my thoughts lean to the view where China’s political class and cronies may have perhaps realized that their policies have been unsustainable and thus have taken to hedge their wealth on international properties[23].
A bubble bust in China is likely to have wretched political consequences that could risk a disorderly change in her political structure. So I expect Chinese policymakers like their counterparts to throw the kitchen sink to preserve the status quo.
Thus far, the impact from China’s perceived policy tightening has been counterbalanced by expectations of continued easing elsewhere.
The point is that China’s current volatility could serve as paradigm for the world, including the Philippines.
Phisix: Reluctant to Retrench
Rising instances of price inflation has not been limited to China or Indonesia (as discussed last week).
The Philippines seem as manifesting seminal stages of price inflation as symptom to the current ballooning asset bubble dynamics. (chart from tradingeconomics.com)
Price inflation eked higher to 3.4% according to the local central bank, the Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP)[24]. This falls to within their expectations of 2.8-3.7% for the month.
And aside from noticing higher food prices which they offered no explanation, they impute SIN taxes and higher prices of oil as contributing to the current increase. Meanwhile the Philippine government sees consumer price inflation in the range of 3-5%. Such wide range of projections represents the government playing safe on predictions.
Also, like all central banks, the BSP does not include asset bubbles in her computation of inflation. The BSP, despite their armies of economists along with the mainstream, fails to realize that competition for scarce resources and credit will place strains on input prices which may or may not filter to consumer price inflation.
It must be realized that aggregate prices cannot be relied on to depict on the inflation story. Input prices covering sectors experiencing a credit boom, particularly property-shopping mall-financials, will likely feel the relative price pressures more than the rest of the industries. So the lack of generalized price inflation will mask the boom-bust structure.
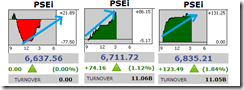
Meanwhile the manic phase in the Phisix continues to deepen.
In terms of intraday trade, except for Monday (left window) which looked like another occasion of “marking the close”, such ‘reluctant to correct’ attitude, has been extended through Tuesday (middle) and Wednesday (right) where sessions closed at the highs or near highs.
The Phisix moved in the opposite direction, Thursday, where markets closed at the session’s low; one rare day of what seems of normal profit taking.(charts from technistock)
But a day of correction wasn’t meant to last. Whatever losses endured by the Phisix last Thursday was essentially negated by Friday’s strong opening-to-closing day.
Thursday’s Phisix losses registered 110.08 points or 1.61%, while Friday’s 108.64 points or 1.62% gains offset Thursday’s losses. So the first 3 days made up for all of the week’s gains.
Again refusal to retrench. And again, back-to-back record highs.
Denigration of History: We’re Still Dancing
I have pointed out last week, that recent record highs have been accompanied by a surge in the number of trades.
This week’s daily number of trades (averaged weekly) again matched the previous highs. Again such could be due to increasing number of new accounts, or more participation from the public or aggressive churning of trades (overtrading) or a combination of. Nonetheless such are indications of swiftly growing overconfidence by the public.
And as anecdotal proof of deepening overconfidence, I was even surprised that during the last social gathering I attended, housewives talked the stock market! What used to be a boring, dull and ignored stuff has now become a social convention. I had to only watch and listen in amazement.
I recall that during the salad days of the China’s stock market mania housewives were among the group of retail investors, along with retirees, government officials, professionals, students[25] aside from farmers, cleaners, taxi drivers and house maids who jumped and piggybacked on the bandwagon[26]…and eventually were caught holding the empty bag.
Recent study covering China’s stock market suggests that 77% of retail investors lost money during the bubble bust. I don’t think this has been different with the last bubble bust even in the Philippine context.
And as perilous as it is, as the mania develops, the sweeping rationalizations and justifications from mainstream experts, such as “the Philippines is resilient to external forces”, “is not crisis prone”, “has low debt levels”, among the many others, has reinforced the view that the boom is a one way street.
As I wrote in 2010[27] contradicting the ridiculous idea that housemaids should invest in the stock market.
And the rising tide compels people to make various attributions to market actions, such as economic growth or earnings or mergers and acquisitions, no matter how loosely correlated they are or how little relevance they are with the genuine market drivers. Most of this account for as popular dogmatic fables or widely held superstitions as evidences does not support the causality nexus from such premises.
This Bloomberg article[28] which says that Philippine equities currently trades at “21.6 times reported earnings” has been seen by an analyst from a major domestic institution as not having been overvalued.
Such represents as “denigration of history” by which author Nassim Nicolas Taleb in Fooled by Randomness[29] defines as the concept were “gamblers, investors and decision-makers feel that the sorts of things that happen to others would not necessarily happen to them”
Here is “denigration of history” Thailand’s central bank version.
In a recent speech, Deputy Governor of the Bank of Thailand, Mr Pongpen Ruengvirayudh enumerated[30] the three challenges to Thailand, namely credit bubble, global uncertainty and capital flows.
The first key challenge is on the domestic side. Private sector credits, particularly those in the household sector, have been growing at a high pace, spurred by domestic demand momentum, fiscal stimulus as well as easy financial conditions. International evidence suggests that a prolonged period of rapid credit growth could lead to a build-up of financial imbalances, strain households’ debt servicing ability and loan quality, as well as sow a seed for asset price bubbles. While the more adverse scenarios currently remain a remote possibility in Thailand, the MPC is not complacent and has been monitoring risks to financial stability closely
The Thai deputy governor clearly understands the essence of asset bubbles when he said “rapid credit growth could lead to a build-up of financial imbalances”. However he opaquely admits that Thailand has been undergoing, “Private sector credits, particularly those in the household sector, have been growing at a high pace”. Then he makes a 180 degree turn through a categorical denial of the risks of a bubble with “remain a remote possibility in Thailand”.
In fit of cognitive dissonance, where two ideas seemingly contradict each other, the Thai governor displays “sorts of things that would happen to others would not necessarily happen to them” as he implies that they are ready to act on them when required.
The problem is when to draw the line on the sand.
This has been the same predicament which Former Federal Reserve Chairman Paul Volcker has expressed to challenge the incumbent leaders of the US Federal Reserve noting that the latter may find difficulty in withdrawing historic stimulus because “there is a lot of liquor out there now.”
The Bloomberg quotes Mr. Volker in a forum[31]
At some point when the worm turns and the party is getting under way, to use that old analogy, at what point do you begin retreating…You can make a mistake and go too quick, but the much more frequent mistake in my judgment is you go too slow, because it’s never popular to take the so-called punch bowl away or to weaken the liquor.
The Thai deputy governor’s speech reminded me of this hallmark remark[32] made by former Citibank President Charles Prince that accentuates the height of the US housing bubble:
When the music stops, in terms of liquidity, things will be complicated. But as long as the music is playing, you’ve got to get up and dance. We’re still dancing
When the music did stop, Citibank[33] eventually ousted Mr. Prince and the company, despite all of their highly paid experts, became a US government ward.
Well to give a snippet on Thailand’s periphery to the core transition of the bubble cycle which ultimately paved way for the Asian Crisis, this from the Columbia University[34]
Unfortunately, the golden years did not last long. Starting from the year 1995, Thailand’s economic growth became much slow down due to a number of factors such as the contraction in the real estate sector, the emergence of China as an intimidating competitor in international trade, the fall of world demand of semiconductor which was one of the Thai major exports in 1996, and an appreciation of the dollars after Spring 1995. As previously discussed, real estates were non-tradable; thus, there was a constraint in market demand of them. Too many houses and business buildings were built; by 1997, the commercial vacancy rate had gone up to 15%. The real estate business had become unprofitable., and the business owners, thus, had no capacity to pay back their debts to financial institutions when the maturity came. The percentage of non-performing loans had risen up to 13% in 1996. This soar of the non-performing loans began the era of banking crisis as banks’ balance sheet had been deteriorated.
Increasing incidences of oversupply led to cascading debt defaults that snowballed into a regional crisis.
Déjà vu, Asian crisis?
Monkey See, Monkey Do
Here is another noteworthy article depicting the evolving mania in the US as seen through the lens of leveraged loan funds via repricing…
From the Financial Times[35]
Private equity firms have lost no time taking advantage of record low yields in the global leveraged loan markets. And like a school of piranhas sensing blood, they have thrown themselves into the fray with gusto
And as I have been saying mania represents that yield chasing phenomenon that are essentially underpinned by voguish themes unquestioningly embraced by the public and most importantly enabled, facilitated and financed by credit expansion
It is important to realize that manias are not merely about human behavior, as “irrationality” as expressed through prices will always have to be underpinned by a transmission mechanism: credit expansion
Let me close this outlook with a quote from historian and author Charles P. Kindleberger on the role played by transmission of credit on asset bubbles[36].
Now, overtrading is by no means a clear concept. It may involve pure speculation for a price rise, an overestimate of prospective returns, or excessive “gearing.” Pure speculation, of course involves buying for resale rather than use in the case of comodities or for resale rather than income in the case of financial assets. Overestimation of profits comes from euphoria, affects firms engaged in the production and distributive processes, and requires no explanation. Excessive gearing arises from cash requirements that are low relative both to the prevailing price of a good or asset and to possible changes in its price. It means buying on margin, or by installments, under circumstances in which one can sell the asset and transfer with it the obligation to make future payments. As firms or households see others making profits from speculative purchases and resales, they tend to follow: “Monkey see, monkey do.”
And how people are influenced by the bandwagon effect; again Mr. Kindleberger
In my talks about financial crisis over the last decades, I have polished one line that always gets a nervous laugh: “There is nothing so disturbing to one’s well-being and judgment as to see a friend get rich. When the number of firms and households indulging in these practices grows large, bringing in segments of the population that are normally aloof from such ventures, speculation for profit leads away from normal, rational behavior to what has been described as “manias” or “bubbles.” The word mania emphasizes the irrationality; bubble foreshadows the bursting. In the technical language of some economists, a bubble is any deviation from “fundamentals,” whether up or down, leading to the possibility and even the reality of negative bubbles, which rather gets away from the thrust of the metaphor. More often small price variations about fundamental values (as prices) are called “noise.”
The bottom line is that manias signify as part of the process of the bubble cycle which takes time to unfold or evolve.
Current social policies, both domestic and international, have only been intensifying the yield chasing phenomenon that continues to evince signs of ballooning asset bubbles across the financial world.
As assets prices go higher, so does the attendant risks.
Unless some shocks would occur, for the Phisix and the world financial markets, I expect such manic phase to escalate or intensify. Although we are in the manic phase we are unlikely to be at the inflection point YET.
Again the Phisix at 10,000 in 2013 and in early 2014 should not be discounted. On the other hand, a “retracement” of 5-10% should be considered as salutary before another massive leg up. Everything now depends on the actions of monetary authorities domestic and international.
Nonetheless the apparent maturing bullmarket phase of the stock market will likely be accompanied by continuing inflation of credit which has already become evident on areas experiencing the boom: property-shopping mall-and financials.
When I was asked at the social gathering of what I thought about the market, my curt reply was “it’s a risky time”.
Trade with caution. Avoid from chasing prices.