It’s hard enough for politicians to face the music, to dispense bad news, to make hard choices, allocate pain to constituencies whether it’s spending cut or tax increase. But when the Fed destroys the bond market, which is the benchmark for the whole capital market, and tells the Congress that you can borrow money for two years at eighteen basis points, which is -- as far as Washington’s concerned -- that’s a rounding error. It’s the same as free. When you’re giving that kind of signal, then there is no incentive, there’s no motivation for people to walk the plank and face down this monster of a fiscal deficit and imbalance that we have. Washington thinks you can kick the can down the road, the debt is more or less free, and we’ll get around to solving the problem. But today, let’s not make any tough choices. That’s where we are. - David Stockman
It’s the Boom Bust Cycle, Stupid
Why would global markets fall in sync in September 22nd?

It would also seem myopic to suggest that this has been a byproduct of liquidity trap[1], where monetary stimulus—low interest rates and an increase in money supply—had been the cause of this.
The chart above of the ASEAN markets has been emblematic of what I have been repeatedly saying long ago—the message of which has been encapsulated from my earlier remarks[2] during the bear market embers of November 2008, (bold highlights original)
The other important matter is that of the understanding of the mutually reinforcing dynamics of inflation and deflation. Deflation and inflation is like assessing the virtues of right and wrong- an ex-post measure of a previous action taken. An action and an attendant reaction. Yet, you can’t have deflation when there have been no preceding inflation. At present times, the reason government has been massively inflating is because they have been attempting to combat perceived threats of equally intense debt deflation…
Thus, reading political tea leaves seem likely a better gauge in determining how to invest in the stock markets.
Since 2009, ASEAN markets had climbed on the back of the intensive inflationism employed by global central banks mostly led by the US Federal Reserve, through its zero bound rates and asset purchases or Quantitative Easing (see black arrow).
If this has been about a global liquidity trap then obviously there would have been no antecedent boom in ASEAN or global market equities during the stated period (2009-2010).
Yet during the past quarter where the Eurozone debt crisis has escalated, exacerbated by visible signs of an economic slowdown in the US and parts of the global economy, global financial markets has been strained.
Yet financial market expectations, whom have been deeply addicted towards bailout policies, have increasingly embedded expectations of another US Federal Reserve rescue.
Such expectation had not been realized.
The Liquidity Trap Canard
Before proceeding, it is important to point out that despite the current financial market turmoil, the Eurozone has not been suffering from ‘deflation’ as a result of lack of ‘aggregate demand’.
On the contrary, the EU has exhibited symptoms of stagflation[3].
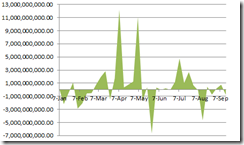
In the US, aside from exploding money supply, consumer and business loans have been materially improving.
5 year chart of Business Loans from St. Louis Federal Reserve
5 year chart of Consumer Loans from St. Louis Federal Reserve
Both charts depict that the current problem or market meltdown hasn’t been about liquidity traps.
Importantly consumer spending in the US has remained robust.
To quote Angel Martin [4]
real personal consumption expenditures have recovered from pre-recession levels. This recovery can be clearly seen in this graph, which shows quarterly data from the first quarter of 2006 to the second quarter of 2011.
So the recent downdraft seen in the financial markets has NOT been about liquidity traps, which has been fallaciously and deceptively peddled by some.
Politically Induced Monetary Paralysis
So what has been the market ruckus all about?
In a September speech prior to the Federal Open Meeting Committee[5] (FOMC) meeting, which decides on the setting of monetary policy, Federal Reserve chief Ben Bernanke hinted that he would consider the lengthening the duration of bond purchases and possibly include further Quantitative Easing as part of the measures to further ease credit conditions[6].
Apparently going into the FOMC meeting on September 22nd, opponents of Bernanke’s asset purchasing program mounted a publicity assault which included several Republican legislators[7], and most importantly, even Mr. Bernanke’s predecessor Mr. Paul Volker at the New York Times[8].
Even the outcome of the FOMC meeting, where Mr. Bernanke’s telegraphed policy of manipulating the yield curve via “Operation Twist” had been formalized or announced, the decision arrived at had not been unanimous and reflected internal political divisions.
Except for the inattentive or those blinded by bias, it has been obvious that only half of what had been impliedly promised by the Mr. Bernanke became a reality.
The net result has been a global financial market jilted by Mr. Bernanke[9].
Lately, even Federal Reserve of the Bank of Dallas President Richard Fisher acknowledged that their institution has been under siege “from both ends of the political spectrum”[10].
Such political impasse is not only seen in the US Federal Reserve, but also over fiscal policies in Washington, as well as, the schisms over prospective measures required to deal with debt crisis in the Eurozone. A good example has been the rebuff US Treasury Secretary Tim Geithner received from the German Finance Minister[11].
This has been coined by some as ‘political paralysis’ which continues to plague the markets[12].
As proof of politically driven markets, this week’s furious rally in global markets has been bolstered by renewed expectations of bailouts, as the German parliament overwhelmingly voted to beef up their contributions to the European Financial Stability Facility bailout fund. There are still 6 of the 17 euro zone countries[13] whom will need to pass the agreement reached in July 21st.
Rumors have also floated that IMF might expand her exposure towards Euro’s bailout to a whopping tune of $3.5 trillion[14], which means the world, including the Philippines, will be part of the rescue team to uphold and preserve the privileged status of Euro and US bankers as well as the Euro and US political class.
Yet all these seem to have helped market sentiment and partly reversed earlier losses.
The point of all of the above is to exhibit in essence, how global financial markets have been substantially dependent on policy steroids. In other words, markets have been mainly driven by politics than by economic forces or that the current state of financial markets has been highly politicized and whose price signals has been vastly distorted.
And most importantly, the latest financial market meltdown represents as convulsions over failed embedded expectations from the apparent withholding of the expansion of rescue programs from which the financial markets have been operating on.
To analogize, today’s jittery volatile markets are manifestations of what is usually called as ‘withdrawal syndromes’ or symptoms of distress or discomfort from a discontinuation of a frequented or regularized activity.
In addition, financial markets appear to be blasé on merely promises, and seem to be craving for concrete actions accompanied by “big package approach[15]” from global policymakers. In short, policymakers will have to positively surprise the markets with even larger dosages of bailouts.
Non-Recession Bear Markets
I would like to further point out that it is not a necessary condition where recessions presage bear markets.
While some global equity indices have broken into bear market territory[16], the US and ASEAN markets have not yet reached the 20% loss threshold levels enough to be classified as bear markets.
Bear markets occur mainly because of political actions that creates boom bust conditions. This has been the case of China and Bangladesh[17].
The US has also experienced TWO non-recession bear markets.
The first instance was in 1962 which was known as the Kennedy Slide[18] where the S&P fell 22.5%.
Ironically the Kennedy Slide coincided with the failed original experiment of Operation Twist in 1961, as Ben S. Bernanke, Vincent R. Reinhart, and Brian P. Sack wrote in a 2004 paper[19],
Operation Twist does not seem to provide strong evidence in either direction as to the possible effects of changes in the composition of the central bank’s balance sheet.
Except that the authors thought that the limits to the size had been responsible for this policy inadequacy, and Ben Bernanke today is conducting this experiment in a very large scale.
The Kennedy Slide’s boom phase appears to be triggered by the dramatic lowering of interest rates following the recession of 1960-61.
The bear market turned out to be short lived as the S & P 500 had fully recovered in a about a year later.
The second non-recession bear market is the notorious Black Monday Crash of October 1987.
The expansionary policies of the Plaza Accord[20] which represented coordinated moves by major developed economies to depreciate the US dollar, fuelled a boom bust cycle which eventually paved way for the lurid global one day crash.
As the great Murray N. Rothbard wrote[21],
To put it simply: the reason for the crash was the credit boom generated by the double-digit monetary expansion engineered by the Fed in the last several years. For a few years, as always happens in Phase I of an inflation, prices went up less than the monetary inflation. This, the typical euphoric phase of inflation, was the "Reagan miracle" of cheap and abundant money, accompanied by moderate price increases.
By 1986, the main factors that had offset the monetary inflation and kept prices relatively low (the unusually high dollar and the OPEC collapse) had worked their way through the price system and disappeared. The next inevitable step was the return and acceleration of price inflation; inflation rose from about 1% in 1986 to about 5 % in 1987.
As a result, with the market sensitive to and expecting eventual reacceleration of inflation, interest rates began to rise sharply in 1987. Once interest rates rose (which had little or nothing to do with the budget deficit), a stock market crash was inevitable. The previous stock market boom had been built on the shaky foundation of the low interest rates from 1982 on.
The crash had been a worldwide phenomenon according to the Wikipedia.org[22]
By the end of October, stock markets in Hong Kong had fallen 45.5%, Australia 41.8%, Spain 31%, the United Kingdom 26.45%, the United States 22.68%, and Canada 22.5%. New Zealand's market was hit especially hard, falling about 60% from its 1987 peak, and taking several years to recover. (The terms Black Monday and Black Tuesday are also applied to October 28 and 29, 1929, which occurred after Black Thursday on October 24, which started the Stock Market Crash of 1929. In Australia and New Zealand the 1987 crash is also referred to as Black Tuesday because of the timezone difference.) The Black Monday decline was the largest one-day percentage decline in the Dow Jones. (Saturday, December 12, 1914, is sometimes erroneously cited as the largest one-day percentage decline of the DJIA. In reality, the ostensible decline of 24.39% was created retroactively by a redefinition of the DJIA in 1916.)
Yet many experts had been misled by the false signal from the flash crash to predict a recession, again from the same Wikipedia article,
Following the stock market crash, a group of 33 eminent economists from various nations met in Washington, D.C. in December 1987, and collectively predicted that “the next few years could be the most troubled since the 1930s”. However, the DJIA was positive for the 1987 calendar year. It opened on January 2, 1987, at 1,897 points and would close on December 31, 1987, at 1,939 points. The DJIA did not regain its August 25, 1987 closing high of 2,722 points until almost two years later.
And in typical fashion, central banks intuitively reacted to crash by pumping mass amounts of liquidity into the system[23].
It took 2 years for the S&P to return to its pre-crash level.
The non-recession bear markets reveal that in the case of the US, such an occurrence would likely be shallow and the recovery could be swift.
But it would different story in China as the Chinese government continues to battle with the unintended effects of their policies which has spilled over to the real estate or property markets. Apparently, China’s tightening policy drove money away from the stock market, which continues to drift near at September 2009 lows, but shifted them into the real estate sector.
In short, like the crisis afflicted West, the current depressed state of China’s stock market signifies as an extension of the bubble bust saga which crested in October 2007, a year ahead of the Lehman episode. China’s cycle remains unresolved.
Should the US equity markets suffer from a technical bear market arising from the current stalemate in Federal Reserve policies, but for as long as a recession won’t transpire from the current market distress, then the downside may be mitigated.
So far, the risk for a US recession has not been that strong and convincing as shown by the above recovery in lending.
Conclusion: Navigating Turbulent Waters Prudently
And as I concluded two weeks ago[24],
I would certainly watch the US Federal Reserve’s announcement and the ensuing market response.
If team Bernake will commence on a third series of QE (dependent on the size) or a cut in the interest rate on excess reserves (IOER), I would be aggressively bullish with the equity markets, not because of conventional fundamentals, but because massive doses of money injections will have to flow somewhere. Equity markets—particulary in Asia and the commodity markets will likely be major beneficiaries.
As a caveat, with markets being sustained by policy steroids, expect sharp volatilities in both directions.
The point of the above was that my expectations had conditionally been aligned to the clues presented by Ben Bernanke of putting into action further bailouts which apparently did not occur.
And since Mr. Ben Bernanke appears to be politically constrained to institute his preferred policies, it is my impression that he would be holding the financial markets hostage until political opposition to his policies would diminish that should pave way for QE3.0. This means that the balance of risks, in my view, have now been tilted towards the downside unless proven otherwise.
Remember, it has been a dogma of his that the elixir to US economy emanates from asset value determined ‘wealth effect’ spending via the transmission mechanism which he calls the Financial Accelerator[25]
To quote the BCA Research[26],
But until QE3 is credibly articulated by Bernanke, there could be more downside for risky assets and further upside for the dollar.
And converse to my abovestated condition or premises, and because I practice what I preach, I materially decreased exposure in the local markets, as I await further guidance from the actions of policymakers.
Although I still maintain a bullish bias, in order to play safe, I would presume a worst case scenario—current global bear markets are signifying a recession—as the dominant forces in operation.
It’s easy to falsify the worst case scenario with incoming policy actions, data and unfolding market events.
Alternatively, this means that for as long as a non-recession scenario becomes evident then it would be easy to position incrementally, hopefully with limited downside risks.
In other words, for as long as there remains no clarity in the policy stance, I see heightened uncertainty as governing the markets. Thus I would need to see the blanc de l'oeil or the French idiom for seeing ‘the white of their eyes’ before taking my shots.
Bottom line: In the understanding that incumbent markets have been driven by politics, reading political tea leaves or the causal realist approach will remain as my principal fundamental analytical methodology in ascertaining my degree of market level risk-reward exposure.
[1] Wikipedia.org Liquidity trap
[2] See Stock Market Investing: Will Reading Political Tea Leaves Be A Better Gauge?, November 30, 2008
[3] See Stagflation, NOT DEFLATION, in the Eurozone, October 1, 2011
[4] Martin Angel The Stagnant U.S. Economy: A Graphical Complement to Higgs’s Contributions, Independent.org, September 23, 2011
[5] US Federal Reserve Federal Open Market Committee
[6] See US Mulls ‘official’ QE 3.0, Operation Twist AND Fiscal Stimulus, September 9, 2011
[7] Yahoo News Republican lawmakers warn Federal Reserve against action on economy, September 21, 2011
[8] See Paul Volker Swings at Ben Bernanke on Inflationism, September 20, 2011
[9] See Bernanke Jilts Markets on Steroids, Suffers Violent Withdrawal Symptoms, September 22, 2011
[10] Bloomberg.com Fisher Says Central Bank Is Under Attack From Ron Paul, Barney Frank, September 28, 2011
[11] See German Minister Calls Tim Geithner’s Bailout Plan ‘Stupid’, September 28, 2011
[12] New York Times, Stocks Decline a Day After Fed Sets Latest Stimulus Measure, September 23, 2011
[13] New York Times, Germany Approves Bailout Expansion, Leaving Slovakia as Main Hurdle, September 29, 2011
[14] See Will IMF’s bailout of Euro Reach $ 3.5 trillion? September 30, 2011
[15] Johnson Simon What Would It Take to Save Europe?, New York Times September 29, 2011
[16] Bloomberg.com Global Stocks Drop 20% Into Bear Market as Debt Crisis Outweighs Profits, September 23, 2011
[17] See Can Bear Markets happen outside a Recession? China’s Shanghai and Bangladesh’s Dhaka Indices October 1, 2011
[18] Wikipedia.org Kennedy Slide of 1962
[19]Bernanke Ben S., Reinhart Vincent R., and Sack Brian P. Monetary Policy Alternatives at the Zero Bound: An Empirical Assessment, 2004 US Federal Reserve
[20] Wikipedia.org Plaza Accord
[21] Rothbard, Murray N. Nine Myths About The Crash, Making Economic Sense Mises.org
[22] Wikipedia.org Black Monday (1987)
[23] Lyons Gerard, Discovering if we learnt the lessons of Black Monday, thetimesonline.co.uk, October 19, 2009
[24] See Definitely Not a Reprise of 2008, Phisix-ASEAN Equities Still in Consolidation, September 18, 2011
[25] Bernanke Ben S. The Financial Accelerator and the Credit Channel, June 15, 2007 US Federal Reserve
[26] BCA Research U.S. Dollar: Waiting For More Policy Action, September 27, 2011