The Philippine equity benchmark, the Phisix seems to be knocking on the gateway of another milestone high, as I noted two weeks back[1],
One must be reminded that bubbles come in stages. So far the Philippines seem to be at a benign phase of the bubble cycle.Again bubbles will principally be manifested on capital intensive sectors (like real estate, mining, manufacturing) and possibly, but not necessarily, through the stock markets.This means that for as long as the US does not fall into a recession or a crisis, ASEAN outperformance, fueled by a banking credit boom and foreign fund flows operating on a carry trade dynamic or interest rate and currency arbitrages (capital flight I might add), should be expected to continue.And again I will maintain that ASEAN’s record breaking streak may be sustained at least until the end of the year 2012.
Friday’s substantial decline in the US stock markets may put a start-of-the-week dampener on the current momentum. However this seems unlikely a hurdle to the Bernanke-Draghi inspired Christmas or year-end rally particularly for the record setting ASEAN bourses as shown above [Philippine Phisix PCOMP orange, Indonesia JCI green, Thailand SET yellow, Malaysia FMKLCI red].
Emerging Market Bonds Outperform Equities
The price actions of the bonds of emerging market should give us a clue.
The zooming pace of the JP Morgan USD Emerging Market Bond Fund (EMB) appears to be accelerating.
In the bond fund, the Philippines and Indonesia have been among the major components of with 6.81% and 6.56% share of the pie in the total portfolio[2]. This implies that the ASEAN bond markets have been outperforming their respective equity peers.
A further clue can be seen in what appears as emerging bond markets (EMB) eclipsing the gains of emerging equity (EEM)[3] counterparts.
As caveat, the country based distribution of weightings of the bond and equity indices have been different. This means that we can’t entirely depend on its accuracy when making a comparison.
Nevertheless, for local bond currency market, the huge jump in the share distribution of the real estate (18% in June vis-à-vis 13% December 2011) and infrastructure-based industries (from insignificant to 6%) gives further evidence of the business cycle in progress.
As per the largest issuers by sector, banks and financials remain the largest but have lost 3% of the share of the pie. This is followed by the rapidly growing real estate sector and holding companies.
And for the share of the ownership of investors by type, based on % of local currency denominated government bonds issued, banks and financial institutions have been the largest, albeit on a steady marginal decline in terms of trend over the past 7 years.
Other major investors, according to the Asian Development Bond includes[4]
1) BTr-managed funds which account for Bond Sinking Fund (BSF) Securities Stabilization Fund (SSF), and the Special Guaranty Fund (SGF),
2) contractual savings and tax-exempt institutions (TEIs) which represent government pension and insurance funds (e.g., Government Service Insurance System [GSIS], Social Security System [SSS], and Philippine Health Insurance Corp. [PHIC]), private insurance companies, and tax exempt funds and corporations
3) custodians which are BSP-accredited securities custodians for investor-clients and lastly
4) other government entities such as government-owned and -controlled corporations (GOCCs), and various corporate and individual investors.
The apparent boom in emerging market bond markets may have been partly reflected on the sectoral returns in the equity markets.
The financial sector, property and holding companies—which have been heavy on both—have returned a whopping 42.54%, 40.95% and 33.32% respectively; on a year-to-date basis (see light maroon bars).
Except for the service sector, the nearly broad based weekly gains (dark maroon bars) for the rest of industry compounded on the outsized year-to-date returns (see light maroon bars).
Bonds are Less Risky or a Bubble?
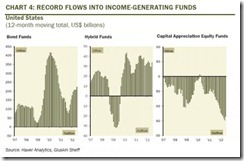
The positive flows into the bond markets have not been limited to Asia, this has apparently been true even in the US, where fund flows have mostly been concentrated on fixed income related investments such as ETFs and “hybrid” balance funds with income orientation as retail investor flee equity markets[5].
Yet the idea that bonds are relatively “less risky” represents charade bestowed upon by global central bank’s tsunami of monetary inflation and financial and banking regulations that have biased towards incentivizing financial and bank institutions to hold bonds[6].
For instance, Japan’s central bank, the Bank of Japan (BoJ) recently warned the banking and financial industry of their high sensitivity to interest rate risks; where for every 1% increase of interest rates, large banks and regional banks could suffer losses of ¥ 3.7 trillion and ¥3.0 trillion respectively[7]
But the supreme irony has been that the BoJ themselves have been responsible for putting at risks the domestic banking system through their pronounced policy of supposedly fighting deflation through inflationism via asset purchases. The BoJ’s balance sheet[8] now accounts for about 30% of the IMF’s estimated economic growth rate.
Reports also suggest that the BoJ may even add to their monetary easing efforts[9] on October 30th
Noticeably Japan’s outward investment flows, which are at near record levels[10], have supplanted China, despite the streak of failures where the batting average of outward FDIs have been unfavorable and the losses have been substantial.
About 26 trillion yen ($330 billion) have accounted for the lost market value from the 10 biggest overseas purchases by Japanese companies from 2000 to a year ago. Apparently the batting success average of Japan’s outward Foreign Direct Investments has been 1: 5 or 20%, where two posted gains while eight companies suffered losses during the said period.
And of the two winners, one is from Kirin Holdings whose acquisition of 48% of San Miguel Brewery [PSE:SMB] in 2009 has tripled in value[11].
I have been pointing out here that beyond the mainstream’s false notion of Japan’s deflation bogeyman, monetary policies, policy or regulatory (regime) uncertainties, interest rate risks and credit risks have all compounded to haunt Japan’s increasingly crony based political economy, prompting resident investors to take larger and unnecessary risks abroad for either survival or to seek out higher returns[12].
Going back to the fund flows in the US, ironically, despite the sustained outflows in the equity markets and last Friday’s slump, the US major bellwether the S&P 500 ended the week marginally on the positive note (dark violet bars).
Yet major global equity markets, led by the S&P 500, have mostly been significantly up on a year-to-date basis (light violet bars).
This fantastic but unsustainable run in the bond markets, which has exhibited symptoms of bubble dynamics, will unlikely persist.
We can either expect a shift out of bonds and into the stock markets or that the bond markets could be the trigger to the coming crisis.
In my view, the former is likely to happen first perhaps before the latter. To also add that triggers to crisis could come from exogenous forces.
Central Bank Actions Rule the Day
So far, steroids from central banks aimed at supporting the asset markets will continue to distort market price signals. And this time I am not alone saying this.
This recent commentary from Financial Times[13] seems highly relevant to the current state of affairs (bold emphasis mine)
Much of the blame for this tends to be attributed to the fact that markets now move to a drumbeat of statements from politicians and central bankers, such as the head of the US Federal Reserve. “All 500 S&P companies have the same chairman and his name is Ben Bernanke,” says Jurrien Timmer of the Fidelity Global Strategies Fund.It is also true that securities within markets, as well as far-flung debt and equity markets have been trading more “in sync” with each other: the willingness of investors to take on risk being a common factor behind price moves.
The conditions of a parallel universe—where markets have become seemingly detached to economic reality—which I have been pounding on the table since, has even been recognized by the chief executive Mohamed El-Erian of PIMCO one of the largest fixed income firms.
At the Financial Times Mr. El-Erian writes[14] (bold mine)
Essentially, the Fed is inserting a sizeable policy wedge between market values and underlying fundamentals. And investors in virtually every market segment – including bonds, commodities, equities, foreign exchange and volatility – have benefited handsomely. In the process, many asset prices have been taken close to what would normally be regarded as bubble territory, with some already there.Central bank action, both real and perceived, rules the investment day, and will continue to do so for now. This is also the case in Europe.
And if central bank actions have truly become the rule for the investment world, then to what degree of relevance does traditional or conventional knowledge apply on pricing and valuing stock markets in the current setting?
Another commentary from the Lex Column of the Financial Times nails it[15],
Perhaps the most horrifying thing about the current combination of sales deceleration, margin contraction and high valuations is that it might not even be a sell signal. The central banks of the US and Europe may well keep investors trapped in risky assets indefinitely. Those who look at the fundamentals and flee to cash had better be patient.
In reality market participants are being sucked into the vortex of speculative mania, which means another round of intensive build-up of misallocated resources or malinvestments and a future bust. We are in a boom phase of a bubble cycle.
FED policies have begun to diffuse into the US property markets which have shown significant broad based recovery[16]: particularly in existing home sales, housing starts, new home sales, building permits, builder confidence, to even a decline in shadow inventories, and signs of the inflection point of real estate loans at ALL commercial banks.
The assumption that FED policies have been successful would signify as presumptive or short sightedness or even blind belief of the capabilities of bureaucrats.
People forget that costs are not benefits. What seems as a boom today will ultimately end in tears. And bubbles, which have been growing in scale and frequency, once pricked will lead to massive capital destruction that would take years to recover especially when interventions delay them and or even make them worse.
General destruction of wealth and wealth generating activities can never be a benefit even from the Pareto optimal perspective.
The recovering US real estate industry is being buttressed by the improving state of credit as seen by the annual % change in consumer loans and commercial industrial loans at ALL commercial banks. (Source St. Louis Fed)
Yet once the colossal excess reserves by depositary institutions held at the US Federal Reserve flows into the system, the US and the rest of the world will be faced with the risks of price inflation.
And price inflation or the market’s recognition of the unsustainability of the fiscal positions of US will likely serve as the proverbial the pin that would perforate and end the inflating bubble.
For now, the US asset bubble will likely be sustained.
Miniature Stock Bubble: Alcorn Petroleum
At the local markets, as pointed out last week, inflationary booms titillates the gambling ticks and speculative adrenalin of many participants. Punters and tyros will be seduced to the allure of easy money based on dramatic price surges, and eventually, fall prey to gruesome price collapses.
And the imprudent and those bearing the entitlement mentality will pass the blame on ‘manipulation’ or ‘fraud’ to the markets and call for regulations without accounting for the incentives brought about by bubble policies on people’s behavior.
Let me quote anew the great libertarian economist, journalist Henry Hazlitt[17]
Inflation, to sum up, is the increase in the volume of money and bank credit in relation to the volume of goods. It is harmful because it depreciates the value of the monetary unit, raises everybody's cost of living, imposes what is in effect a tax on the poorest (without exemptions) at as high a rate as the tax on the richest, wipes out the value of past savings, discourages future savings, redistributes wealth and income wantonly, encourages and rewards speculation and gambling at the expense of thrift and work, undermines confidence in the justice of a free enterprise system, and corrupts public and private morals.
More regulations will not solve the behavioral imbalances caused and rewarded by antecedent immoral policies.
Over the past two weeks Alcorn Petroleum [PSE: APM] has skyrocketed to close on Friday by an eye-popping 600+%!
The company officially disclosed that they “cannot confirm” the rumored backdoor listing by allegedly the other “retailing” businesses owned by the same of owners, although the firm “appointed a financial adviser” to submit recommendations[18]. If the rumor involved different parties then such denial would seem sensible as negotiations involve the risks of transaction failure. But in this case, the parties supposedly are the same owners.
The company also referred the excessive price fluctuations or movements to a possible “oil exploration play”. Alcorn Petroleum has a 9.32% participating interests at the Service Contract 51- covering the East Visayas Basin.
Yet since the other partners in the same service contract[19] have had mixed performance this week, particularly, Trans Asia (+5.79%) [PSE: TA] and PetroEnergy [PSE: PERC] (-.84%) one can hardly impute an oil exploration play to the astronomical price surge of APM.
Whatever the reasons behind the price spike, prudence dictates that such huge series of price surges characterizes bubble dynamics which overtime typically ends up with huge frustrations for those left holding the proverbial bag.
Property giant Century Property Group [PSE: CPG], which got listed through the backdoor from the buyout of East Asia Power Resources in August[20] of last year, had seen a similar stratospheric surge as many jumped in on the rumored backdoor play.
However when the rumor became fact, CPG retrenched most of its accrued bottom-to-peak gains. As of Friday, CPG’s prices have been down about 62% from its zenith closing price.
Today’s bullmarket, and partly CPG’s financial heft, have essentially provided support to her current price levels.
CPG’s tale is unlike the sordid experience of another stock bubble in 2000, which again involved another backdoor listing play, particularly Philweb [PSE: WEB] through formerly listed South Seas Oil[21]. Not to mention the BW Resources scandal in 1999.
In the backdrop of a bear market and upon the realization of the deal, WEB virtually gave back all its 1,000++% gains or returned whence it came from. And many punters who took part in the play had about a decade or more to recoup part of their losses (that’s for those who can’t accept their mistakes).
WEB’s experience seems to parallel the Thailand episode during the Asian Crisis as previously discussed[22]. Bubbles take time to heal whether seen from a macro or micro level.
The bottom line is to apply the Duck Test[23] for suspected stock bubbles: if it walks like duck, swims like a duck and quacks like a duck, it must be a duck.
These are the issues to avoid and to ignore.
This wisdom quote from author C Joybell C should apply to stock picking as well
Choose your battles wisely. After all, life isn't measured by how many times you stood up to fight. It's not winning battles that makes you happy, but it's how many times you turned away and chose to look into a better direction. Life is too short to spend it on warring. Fight only the most, most, most important ones, let the rest go.
Today’s bullmarket should come with a lot of opportunities without having to expose oneself to enormous risk. And all it takes is emotional intelligence[24] and self-discipline[25]
[1] See Phisix-ASEAN Bellwethers at Fresh Record Highs, October 8, 2012
[2] iShares.com J.P. Morgan USD Emerging Markets Bond Fund us.iShares.com
[3] iShares.com MSCI Emerging Markets Index Fund us.iShares.com
[4] ADB, Asia Bond Monitor, Asianbondsonline.org September 2012
[5] Zero Hedge R(osenberg) & B(ernstein): Two Ex-Merrill Colleagues, Two Opposing Outlooks, One Permabull Rebuttal, October 19, 2012
[6] See How Capital Regulations Contributed to the Current Crisis December 5, 2011
[7] Wall Street Journal Japanese Banks Face Huge Rate Rise Risk, Warns BOJ, October 19, 2012
[8] Pedro Da Costa Central bank balance sheets: Battle of the bulge Reuters Blog April 12, 2012
[9] Asahi Shimbun BOJ mulls further monetary easing, October 18, 2012
[10] Zero Hedge Forget China; Japan Is 'Taking Over' The World Again October 15, 2012
[11] Bloomberg.com Softbank’s Son Seeks to Skirt Cross-Border Failure History, October 17, 2012
[12] See Will Japan’s Investments Drive the Phisix to the 10,000 levels? March 19, 2012
[13] Dan McCrum End to ‘alpha’ spells trouble for fund managers Financial Times September 10, 2012
[14] Mohamed El Erian Beware the ‘central bank put’ bubble Financial Times, October 10, 2012
[15] Dave Glen Markets Remain Bid Despite Weakish Fundamentals September 18, 2012
[16] See US Federal Reserve Policies Re-Inflate US Property Bubble October 20, 2012
[17] Henry Hazlitt What You Should Know About Inflation p.18 Mises.org
[18] Alcorn Petroleum Re: Comment on Inquirer.net News Article PSE.com.ph October 16, 2012
[19] Business Inquirer.net Drillers settle dispute on farm-in deal August 10, 2012
[20]Business Inquirer.net Century Properties sets backdoor listing on Philippine Stock Exchange, August 18, 2012
[21] Newsflash.org BOI OKAYS REGISTRATION OF PHILWEB AS NEW I.T. FIRM January 29, 2001
[22] See FED-ECB’s Nuclear Policies: Risk ON is Back! September 17, 2012
[24] See Applying Emotional Intelligence to the Boom Bust Cycle August 21, 2011
![clip_image001[4] clip_image001[4]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjlUq0pKsH-OLxTwRyMM04QfunLUXFFVnCohOJoSr-4oj0A12OcR2iWTLkJ3MIIw8zBj23uW3JRppg0HnVzjTncJnDoq8TAqtZjJt03ip5B7dFLQuP3opEZLb1iQYAMNvbKyQkk/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[4] clip_image002[4]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhSIn9H1Ddsh50FR96VyezfaPntqdWylvWy6bxvYLU1QepkkVi65DnvR-JcAnRBAytT_fB7A0IgWtoTLXlDJZG57wY-OlfoPNnKy7wKFTnymBFHlmfr_oBJZa9fXw8fPgoQiqqV/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image004[4] clip_image004[4]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEj6ynlFjyTZE6HsJfa9OBGJ1yia2UgcIIyidtjyAhZgLUT0__DgK-41yihe15x8tym9_dGUPmNKNg7TQENEpX4w44U9XO-iJvfXBiHXqwaK45lmdW0kirJXg4Xc7ipNGThVcv-G/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image005[4] clip_image005[4]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhg9hd6sD3j45zohi4T3F5AcTDxBqIoUAXMFgZRe4g2exF5iDG_uSHe2-rPZEkRe37Jh4XVoiX6Nx9QSC_BVZmDDmHnkw1dhPQkBvOlkcddCOFbABGQq436GGWOf8ce2dkyV7Gw/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image007[4] clip_image007[4]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhysAFt-O8ybC0qFt8W5oeRZwCHR_PiUVfZ1U2OSXgr3TsmGfhVfuMhvg59oKPIFMW0bVhebsfuU3NEA0WC-tBRtIvPHNHHVGcaS7yyjI4tJU8nj0Z5zu5FvCBW6FYXZigFSbXj/?imgmax=800)