Methodological Individualism Applied to Holiday Shortened Trading Sessions
Trading sessions will be limited to just three days in the coming week as two days have been declared as public holidays by the Philippine government in the tradition of paying homage to the dead.
Since not everyone practices the tradition, others have used such occasion for leisure and travel.
Yet such extended holidays are likely to divert the attention of market participants on how and what to do during the mandated respite from work.
When markets are on a vacation mode, I expect trading activities to slowdown which may be reflected on Peso volume (excluding block and special block sales).
But lethargic trading does not necessarily reduce volatility.
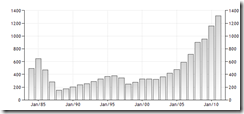
For the past two years, holiday abbreviated weeks with three day trading sessions have posted substantial over 1% moves
*Aug 29 and 30 in 2011, Eidul Fitr and National Heroes Day[1]
**August 20 2012 Ninoy Aquino Day (Replaced to Monday)[2]
The same goes with All Saint’s Day week celebrations since 2007.
The natural intuition for the mainstream would be to impute from the above facts statistical correlations and or to seek out patterns from which to project into the future.
For instance, it would be easy to deduce of the dominance of negative returns by simple observation and the employment of heuristics without examining the operating conditions which had led to such outcomes
Let’s say, the -1.43% from November of 2011 came amidst the oversold bounce from the flash September market meltdown, as most likely an offshoot to the US Federal Reserve chairman Ben Bernanke’s jilting of market’s expectations of QE 3.0[3]
The other instances have shown to be responses to what seems as short term overbought conditions (in April and August 2012 marked by blue arrows) following new highs.
Thus, losses from Holiday shortened week have most likely accounted for profit taking.
Nonetheless the losses from the above incidentally marked the interim bottoms which eventually led to milestone highs.
Or how about the negative output during November’s of 2007 and 2008? The unfolding bear market cycle during the said period can serve as convenient explanation.
Today, considering that the Phisix has just been marginally off the record highs, along with the ASEAN peers, this means that price volatility can go in either direction.
On the downside, profit taking, possibly to fund vacations, leisure or traditional activities, could partly explain why the proclivity for negative returns.
On the upside, aggressive participants may take advantage of any new information that could eclipse such profit taking activities that may push the market higher.
In essence, there are no linear and clear cut answers to such short term events
What this implies is that even if the week’s results should turn out negative, this may not be suggests of an inflection point as the general market trend remains on the upside. This is unless of course, exogenous tail risk events may rattle the highly interconnected and intercorrelated global markets and gets transmitted to the ASEAN equity markets and to the Phisix.
The bottom line is that it would signify a serious mistake to perceive history as mechanically repeating itself for the simple reason that history is a complex phenomenon.
History as factual episodes represents heterogeneously embedded unique circumstances as consequence to “multiple causes” where “none of the factors are in constant relationship with the others” [Rothbard 1976[4]].
This also means that historical facts, according to the great Austrian Professor Ludwig von Mises[5], “cannot be used as building material for the construction of theories and the prediction of future events. Every historical experience is open to various interpretations, and is in fact interpreted in different ways”.
This also implies that while history can give us some clues, it is the understanding of science of human actions which is most important.
Again Professor Mises from the same material[6]
The subject matter of all historical sciences is the past. They cannot teach us anything which would be valid for all human actions, that is, for the future too. The study of history makes a man wise and judicious. But it does not by itself provide any knowledge and skill which could be utilized for handling concrete tasks.
Author Samuel Langhorne Clemens popularly known as Mark Twain[7] nailed it when said ‘history does not repeat itself, but it does rhyme’.
Financial Markets Are Now About Bernanke Put
Some have expressed alarm over the recent downside volatility seen in the overseas markets.
It’s all about framing, I’d say.
This week’s retracements (blue bar) seem to be in response to last week’s gains (red bars). While the degree of price changes has been different from last week to the other week, the scale of volatility has been evident. Heightened volatility from market distortions brought about by interventionism has been the crux of the current market environment.
Yet for some, declining US markets serves as a reason for concern.
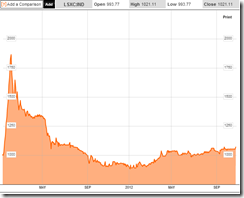
The S&P 500, which I use as a key benchmark for the US markets, have lost 1.48% this week. Add to such loss the current level of the S&P 500, which represents nearly 4% loss from the most recent or September peak, we have a short term bear market story.
But there is the other view; year-to-date the major US benchmark has still been robustly up 12.27%. This remarkable advance by the US markets as exemplified by the S&P 500 has lubricated the outperformance of the Philippine Phisix and Thai’s SET and an animated global equity markets.
There are also those who claim that declining earnings will drive US markets lower.
But this concern seems valid when markets operated on merely the platform of the barrage of promises by the FED.
Expectations of the FED’s coming steroids provided the shot in the arm that produced a risk ON environment despite material signs of disconnect with the real economy or in terms of declining earnings and of the weakening of the economy[8].
Since promises are subject to diminishing returns, they are unsustainable. Rising markets based on empty talks simply increased the sensitivity to enormous downside risks or that this represents a recipe for a market crash.
Either trapped by their own policy signalling measures, or in the realization that failed expectations could bring chaos and relive the September 2011 flash meltdown, the FED and the ECB HAD to deliver.
And they DID. Both will be flooding the world with money to the preliminary tune of $2 trillion.
Add to this that this fact that it will not just be the FED-ECB but other major central banks as well. The Bank of Japan (BoJ) just joined the bandwagon with additional stimulus[9] while the Bank of England (BoE) has once again signaled its intent to expand her balance sheet further[10].
And most importantly, the US Fed Chairman Ben Bernanke made explicit that QE Forever/QEternity has been meant to sustain asset prices[11].
Many seem to forget that it is central bank actions that really matters since the market’s price mechanism has been skewered by their repeated interventionism.
Today’s risk environment has dramatically shattered conventional thinking. In a recent “Bagehot” lecture at the Buttonwood in New York City, PIMCO’s chief Mohamed El-Erian poignantly remarked[12]
What we are ultimately talking about is an “unusually uncertain” distribution of potential baseline outcomes, as well as unusually shaped tails. This inevitably undermines the robustness of lots of conventional wisdom, as well as a range of historical contracts and entitlements. It also challenges the agility of institutions in both the public and private sectors.
If corporate earnings have hardly been a factor in driving up market prices, then why should corporate earnings become a factor in marking down prices?
Earnings have recently become a matter of concern only after central bank’s rescue mechanism has been put in place. What this really shows is of the market dynamic of “buy the rumor sell on news”.
And given the reality of the slated expansion of money supply from central banks via asset purchases, this will also mean that sales revenues of enterprises will rise faster than the costs of business, where the latter has been incurred during the time prior to additional money infusions.
This implies that inflation creates the illusion of greater ‘corporate profits or earnings’, where the more the inflation, the greater the profit margins.
As financial analyst Kel Kelly explains[13]
Another way of looking at it is that, with more money being created through time, the amount of revenues is always greater than the amount of costs, since most costs are incurred when there is less money existing. Thus, because of inflation, the total monetary value of business costs in a given time frame is smaller than the total monetary value of the corresponding business revenues. Were there no inflation, costs would more closely equal revenues, even if their recognition were delayed…Since business sales revenues increase before business costs, with every round of new money printed, business profit margins stay widened; they also increase in line with an increased rate of inflation. This is one reason why countries with high rates of inflation have such high rates of profit. During bad economic times, when the government has quit printing money at a high rate, profits shrink, and during times of deflation, sales revenues fall faster than do costs.
This profit mirage from monetary inflation represents the ephemeral boom phase of business cycle.
Also as previously noted, the seeming recovery in the US real estate sector[14] will likely to be used as pretext to boost stock prices.
So far, the Dow Jones US Real Estate ($DJUSRE) and the iShares Real estate (IYR) along with Regional Bank Index (KRE) and the Philadelphia Bank Index (BKX) have all backed off from the recent highs. Although there has been little signs of any material deterioration,
Finally given the explicit goal by the FED to support asset prices via the “Wealth Effect” or Portfolio Balance Channel[15], any adjustments to the newly instituted QE Forever policies will likely be in accordance to the conditions of the financial markets.
In short, the Bernanke Put is in motion: conditions of the financial markets will dictate on the FED’s actions.
This also implies of the policy of redistributing resources from main street into the financial sector.
And any attendant tail risks will likely come from rising consumer prices (inflation risk) or the escalation of political squabbles e.g. the risks of growing secession movements in Europe[16] (political risks) or the recognition of insolvency of crisis afflicted nations or the lack of capital (credit risks), all of which will be manifested through interest rate channel.
How Interest Rate Regimes Affect Asian Stock Markets
Current easing policies by developed economies have translated into a boom through most of Asia.
That’s because most of Asia has mimicked their developed economy counterparts but from a lesser aggressive stance.
In the region, interest rate regimes can be categorized as[17]
-rate cuts in 2012: These include China, South Korea, Singapore, Thailand, Philippines, India, Pakistan and Australia
-previous rate changes prior to 2012, but remains on hold through 2012: These includes New Zealand who cut in 2011, Taiwan increased in 2010 until July 2011, Vietnam raised rates in 2010 until early 2011, Indonesia cut rates from last quarter of 2011 until January 2012 and Malaysia increased rates in mid 2011.
-increased rates in 2012: Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Mongolia
The relationship between interest rates and equity market performance has been striking.
Countries who cut rates in 2012 mostly outperformed: Pakistan, India, Philippines and Thailand. For those whose rates were unchanged, e.g. Malaysia, Indonesia and Taiwan, the benchmark equity performance has largely been the median.
The losers or the laggards are economies that have been raising rates: Bangladesh, Sri Lanka and Mongolia.
The Philippine central bank, the Bangko Sentral ng Piliipinas (BSP) appears to have succumbed to pressures from the external agents during the recent IMF-World Bank annual gathering by raising interest rates for the fourth time this year last week[18].
The BSP announced through Mr. Amando Tetangco that such measures were meant to “help ward off risks associated with weaker external demand by encouraging investment and consumption.”[19]
Consumption does not emerge from a vacuum. Consumption would need to be satisfied through exchange via division of labor that arises out of production.
This means production has to come from capital good investments which are financed by capital or through savings, and not from printing of money or digital creation of money.
As a reminder all economic growth stems from savings. According to the great Professor von Mises[20],
At the outset of every step forward on the road to a more plentiful existence is saving--the provisionment of products that makes it possible to prolong the average period of time elapsing between the beginning of the production process and its turning out of a product ready for use and consumption. The products accumulated for this purpose are either intermediary stages in the technological process, i.e. tools and half-finished products, or goods ready for consumption that make it possible for man to substitute, without suffering want during the waiting period, a more time-absorbing process for another absorbing a shorter time. These goods are called capital goods. Thus, saving and the resulting accumulation of capital goods are at the beginning of every attempt to improve the material conditions of man; they are the foundation of human civilization. Without saving and capital accumulation there could not be any striving toward non-material end
Inflationism, thus, only dilutes the purchasing power (even Lenin and Keynes recognized this[21]), as well as, creates economic imbalances that promote bubbles and social instability.
The BSP further admits that there has been increasing risks of price inflation through “impending electricity rate increases and rising global prices for some grains could upset the inflation outlook” but recklessly assumes that “subdued global demand should temper the overall picture by easing price pressures on oil imports”
But price inflation has been creeping upward[22] in spite of “subdued global demand” and falling Philippine exports[23]. Perhaps local monetary officials have yet to discover that there exists an economic phenomenon called stagflation—high price inflation, high unemployment and economic stagnation[24]--which dominated the 1970-80s
Nonetheless with diminishing recession risks from the US despite the recent corrections in the equity markets, explicit policy support from global central bankers led by FED-ECB on the financial markets, the still “benign” domestic price inflation, the deepening domestic negative real rates regime and the recently established momentum from the breakout, we should expect domestic financial markets (the Phisix, the Peso) to outperform at least until the year end unless external shocks will derail the above dynamics
We should also expect that sluggish commodity prices in the environment of near coordinated monetary easing implemented by almost every major economy to make an eventual rally, not entirely because of ‘consumption demand recovery’ but because of reservation demand[25] or the “demand to hold stock” or “hoard” out of anticipation of higher prices or greater use of the good or more exchange opportunities of the good for other goods.
Applied to the local stock market, stocks will rise barely because of conventional wisdom of earnings or economic growth, but because of the growing urgency to chase for yields, to gamble and to punt which all represent as products of the policy regime of negative real rates. And proof of such progression has been the growing incidences of miniature bubbles[26].
[1] PublicHoliday.org Philippines 2011 Holidays Calendar
[2] PublicHoliday.org Philippines Holidays 2012 Calendar
[3] See Bernanke Jilts Markets on Steroids, Suffers Violent Withdrawal Symptoms, September 22, 2011
[4] Murray N. Rothbard Praxeology: The Methodology of Austrian Economics Mises.org
[5] Ludwig von Mises 1. Praxeology and History Chapter II. The Epistemological Problems of the Sciences of Human Action, Human Action Mises.org
[6]Mises, Ibid
[7] Wikipedia.org Mark Twain
[8] See ECB-China Stimulus: Has the Risk ON Environment Returned? September 10, 2012
[9] see Bank of Japan Adds More Stimulus October 27, 2012
[10] Bloomberg.com King Says BOE Is Ready to Add to QE If U.K. Recovery Fades October 24, 2012
[11] see FED-ECB’s Nuclear Policies: Risk ON is Back! September 17, 2012
[12] Mohamed El-Erian Mohamed El-Erian's Bagehot Lecture From Buttonwood Minyanville.com October 24, 2012
[13] Kel Kelly How the Stock Market and Economy Really Work September 1, 2012 Mises.org
[14] See US Federal Reserve Policies Re-Inflate US Property Bubble October 20, 2012
[15] See Phisix-ASEAN Bellwethers at Fresh Record Highs October 8, 2012
[16] Atlantic Sentinel Secessionist Movements Threaten Foundation of Europe, October 17, 2012
[17] Asian Bonds Online Asia Bond Monitor September 2012
[18] ABS-CBNNEWS.com BSP ready to ease policy rates anew – Tetangco October 14, 2012
[19] Inquirer.net Philippines trims key interest rates again October 25, 2012
[20] Ludwig von Mises 2. Capital Goods and Capital XV. THE MARKET Human Action
[21] See IMF’s Christine Lagarde Inflationist Delusions October 20, 2012
[22] Danske Bank Brighter global outlook but every rose has it thorns, Emerging Market Briefer October 15, 2012
[23] See I Told You So Moment: Philippine Exports Hit in August October 12, 2012
[24] Wikipedia.org Stagflation
[25] See Are Surging Oil Prices Symptoms of a Crack-up Boom? February 24, 2012
[26] See Will Frothy Bond Markets Drive the Phisix Higher? October 22, 2012