We are big fans of fear, and in investing, it is clearly better to be scared than sorry. -Seth Klarman
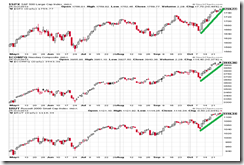
Stock markets of the US and select developed countries continue with its melt-UP record smashing breakout streak.
This week, the Dow Industrials (not in chart) climbed 1.1% approaching a record while her peers at historic highs also posted gains, particularly, S&P 500 +.88% and the Nasdaq +.74%. The Russell 2000 small cap closed nearly unchanged +.003%.
Outperforming US stocks, this week, relative to emerging markets and against many other developed peers imply that the share of US stocks in terms of market capitalization to the world should be expanding.
However, the flagging US dollar has essentially offset nominal currency gains made by US equities.
Net foreign selling in US equities during the 2nd quarter, which I cited two weeks back[1], represents the second largest in record since the 1990s.
Political bickering theatrics over government shutdown, debit ceiling and Obamacare reportedly prompted for net foreign selling of US assets in August. Net sales of U.S. equities by official holders abroad were a record $3.1 billion, according to a report from Bloomberg[2].
Rising stock markets amidst severe currency strains hardly represents signs of economic strength. Instead such dynamics are manifestations of an escalation of monetary ailment.
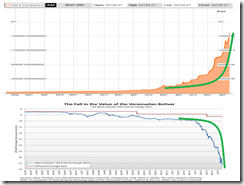
A good example of such extremes can be seen in the unfolding real time currency crisis in Venezuela. The Caracas Index or Venezuela’s stock market benchmark has been in a phenomenal vertiginous parabolic climb—up 347.5% (!!!) year-to-date, this adds to the 2012 gains at 302.81% for a total of 650.31% in one year and ten months (!!!)—as the collapse of the Venezuelan Bolivar[3] as shown via its black market rates steepen.
Ironically, in the face of massive goods shortages or an economic standstill, the increasingly desperate Venezuelan government decrees a Vice Ministry of Supreme Social Happiness[4]. Individual “happiness” will now be substituted for collective “happiness” as perceived and implemented by the political leaders[5].
I know the US is not Venezuela. Japan is not Venezuela too. But all three has exercised the same currency debasement programs, resulting to the same outcomes at varying degrees.
Venezuela which is at the advance stage of a currency crisis, serves as example of what may happen to the US or Japan if political leaders insist proceeding towards such trajectory.
And since the world still depends on the US dollar as main currency for foreign currency bank reserves and as the principal medium for payment and settlements for international financial transactions, despite actions by some nations to wean themselves from the US dollar via currency swaps, bilateral currency trade deals and barter[6], the fate of the US dollar will have significant influence on the direction of the global financial markets.
I would also add that aside from the US dollar, developments in the US financial markets—the largest in the world, for instance, the US stock markets, despite the fall of US market cap relative to the world, remains at 34.6% (as of October 13, 2013) according to Bespoke Invest[7]—will also have big sway on global markets. The meltdown from the perceived tapering by the Fed last May which intensified the actions of the bond vigilantes should be a noteworthy example.
In today’s globalization expect connectivity not just in the web, or telecoms but also in financial markets and economies.
Manipulating Earnings Guidance to Boost Share Prices
When market participants frenziedly bid up stock prices to astronomical levels, the unsustainability of such actions can be established by simple observations.
Again as I pointed out last week, zooming stocks has led to astonishing valuations. The small cap Russell[8] 2000’s PE ratio[9] has been valued at a fantastic 84.51 as of Friday’s close.
Given that the Forward PE has been estimated at 22.5, this means that earnings for the coming year have been expected to explode by a stunning 276%!
However if one were to weigh on the sentiment of small businesses to assess such potentials, a recent survey by small business (conservative lobbying[10]) organization the National Federation of Independent Business (NFIB)[11] seems barely sanguine to justify such valuations (bold mine)
Small-business owner optimism did not “crash “ in September, but it did fall, dropping 0.20 from August’s (corrected) reading of 94.1 and landing at 93.9. The largest contributing factor to the dip was the significant increase in pessimism about future business conditions, although this was somewhat offset by a notable increase in number of small-business owners expecting higher sales
So we have basically a neutral condition unsupportive of wild earnings growth expectations.
The same hold true with Dow Utility. With a trailing PE at 30.89 and forward PE at 16.15 this means that priced at Friday’s close, the drop in forward PE will mean that earnings must jump by 92%!
Aside from bond based share buybacks discussed last week, publicly listed companies “beat earnings estimates” by resorting to lowering guidance[12] has been a major pillar in driving up US stocks.
As one would note, 62.6% of corporations recently beat earnings estimates. Although the positive surprise trend has been on a decline since 2006.
On the other hand, the spread or the variance between positive and negative guidance by companies has been in a deficit since the 3rd quarter of 2011.
In other words, listed firms set easier profit goals which they eventually outperform via “beat estimates”. The positive surprise then spurs higher prices.
In my view this looks like accounting prestidigitation.
Yet negative guidance according to the Factset has been at record levels[13]
For Q3 2013, 89 companies have issued negative EPS guidance while 19 companies have issued positive EPS guidance. If 89 is the final number of companies issuing negative EPS guidance for the quarter, it will mark the highest number of companies issuing negative EPS guidance since FactSet began tracking guidance data in 2006.
Managing earnings expectations in order to “beat the estimates” has usually been a bear market technique used by the management.
According to Investopedia.com[14] “It is one of the analyst's jobs to evaluate management expectations and determine if these expectations are too optimistic or too low, which may be an attempt at setting an easier target. Unfortunately, this is something that many analysts forgot to do during the dotcom bubble.”
The Factset graph also shows that Utilities and Telecoms have had 100% negative guidance changes. In short, these two industries expect materially LOWER profits thus the widespread downscaling of their estimates.
So how on earth will Utility earnings jump by 92%?!
Except for the energy sector, positive guidance has been a scarcity.
Since corporate profits represent a component of the income side of the National Income and Product Account (NIPA) [15], the lowering of profit guidance hardly reflects on a robust economy. This hardly justifies a sustainable upside run of stock market prices.
But again over the interim, rational irrationality may rule.
The other way to look at these: Management of many publicly listed corporations may have purposely been guiding “earnings” expectations down in order to generate “surprises”. Such positive surprise should extrapolate to an increase in (earnings performance based) compensation.
Rewarding executives based on earnings performance has been loaded with agency (conflict of interest) problems
According to an academic paper written by Lan Sun of UNE Business School, Faculty of the Professions[16] (bold mine)
In theory, a link between a CEO's compensation and a firm performance will promote better incentive alignment and higher firm values (Jensen & Meckling, 1976). However, executive compensation contract is an incentive where opportunistic earnings management behaviour is likely to be detected since CEOs are expected to have incentives to manipulate earnings if executive compensation is strongly linked to performance. A substantial literature has emerged to test the relationship between executive compensation and earnings management and has documented that compensation contracts create strong incentives for earnings management…When earnings management is driven by opportunistic management incentives, firms will ultimately pay a price and its negative impact on shareholders is economically significant.
So far, total corporate profits based on y-o-y changes inclusive of Inventory Valuations Adjustments (IVA) and Capital Consumption Adjustment (CCAdj)[17] have chimed with the trend of lowering of profit expectations.
Yet curiously bad news (negative trends), which represents the underlying largely overlooked or ignored real factor of declining trend of profitability or eps growth rate and net income as shown last week, has been seen as good news (by mainly focusing on beat estimates or nominal growth figures or Fed easing)
It’s all about selective perception or picking of information to fit one’s biases or beliefs.
Let’s Keep Dancing: The Intensifying Credit Orgy
In a manic phase of the boom-bust cycle, zooming stocks equals ballooning credit.
Back to the future with exploding leveraged loans and covenant lite bonds, from the Financial Times[18] (bold mine)
Neiman Marcus, the upscale US department store chain, is no stranger to fashion trends. But in the autumn of 2005 the luxury retailer started a very different kind of fad – this time for an unusual new bond structure known as a “payment-in-kind toggle”.Pik-toggle notes, as they became known, gave Neiman Marcus the option to pay its lenders with more bonds instead of cash if the retailer ever ran into financial difficulty. For a company that was at the time being bought by private equity giants TPG and Warburg Pincus, in a leveraged buyout involving about $4.3bn worth of debt, that additional financial flexibility was considered a savvy move….The average amount of debt used to finance LBOs has jumped from a low of 3.69 times earnings in 2009 to an average 5.37 so far this year, according to data from S&P Capital IQ. At the height of the LBO boom, average leverage was 6.05.The $6bn sale of Neiman Marcus to Ares and a Canadian pension fund is expected to leave the retailer with a debt of about seven times earnings.At the same time, more than $200bn of “cov-lite” loans have been sold so far this year, eclipsing the $100bn issued in 2007. That means 56 per cent of new leveraged loans now come with fewer protections for lenders than normal loans.
Regulators have sounded the alarm bells on covenant light loans but the industry group has pushed back saying that loan warnings will hurt the “neediest borrowers”[19]. Such characterizes the rationalization of the mania phase. Echoing the infamous words of ex-Citibank chair Charles Prince during the height of the US housing boom, “For as long as the music is playing, you’ve got to get up and dance. We’re still dancing[20].”
Let’s keep dancing
And when it comes to yield chasing via increased leveraging, the absence of a stamp of approval by credit rating agencies has hardly become a factor to Wall Street’s peddling of Commercial Mortgage Bonds (CMBS). [note credit rating enthusiasts, credit rating warnings ignored by markets]
From the Bloomberg[21]: (bold mine)
Wall Street banks that package commercial mortgages into bonds are forgoing a ranking from Moody’s Investors Service on the riskier portions of the deals, a sign the credit grader isn’t willing to stamp the debt investment-grade amid deteriorating underwriting standards.Moody’s didn’t grade the lower-ranking debt in 9 of the 14 commercial-mortgage bond transactions it’s rated since mid-July, according to Jefferies Group LLC. Deutsche Bank AG (DBK), Cantor Fitzgerald LP and UBS AG (UBSN) are selling a $1 billion transaction this week that doesn’t carry a Moody’s designation for a $64.3 million portion that Fitch Ratings and Kroll Bond Rating Agency ranked the lowest level of investment grade, said two people with knowledge of the deal.Moody’s absence from the riskier securities in commercial-mortgage deals suggests the New York-based firm is taking a harsher view of the quality of some new loans as issuance surges in the $550 billion market, Jefferies analysts led by Lisa Pendergast said in a report last week. Credit Suisse Group AG’s forecast for $70 billion of offerings this year would be the most since issuance peaked at $232 billion in 2007.
Credit bacchanalia has gone global. Booming issuance of high yield (junk) bonds linked to M&A has reached 2007 highs.
From the Financial Times[22]:
A burst of investor “animal spirits” has boosted the value of mergers and acquisitions-related bonds to the highest raised since the financial crisis.Global acquisition-related bond issuance from non-investment grade, or high yield, companies has risen by 15 per cent to $62.9bn for the year to date compared with the same period in 2012.This is the highest amount since 2007, according to Dealogic, the data provider.The surge has been driven by purchases outside the US as non-US acquisition bond issuance nearly tripled to $14.1bn compared with last year, including deals such as Liberty Global ’s $2.7bn issue
High grade corporates likewise reveals of a debt issuance bonanza.
From the Wall Street Journal[23], (bold mine)
According to data provider Dealogic, the $884.3 billion of highly rated corporate bonds sold in the U.S. this year through Wednesday has been the most of any year at that point since 1995, when it began keeping records.October’s rush of supply has helped put 2013 back on track to exceed the record $1.01 trillion issuance seen in 2012.
The accounts above validate my view on the transition process of companies from hedge financing to Ponzi financing.
As I wrote last week[24], (bold original)
So while most publicly listed US companies have yet to immerse themselves into Ponzi financing, sustained easy money policies have been motivating them towards such direction.
The greater the dependence on debt, the more Ponzi like dynamics will take shape.
The Fallacy of Little Screwy People
Record or near record issuance of high yield bonds, commercial-mortgage bonds, covenant lite bonds leverage buyout loans and investment grade bonds constitute signs of liquidity trap? To the contrary it would seem like a tidal wave of money.
Yet most central bankers and the consensus see the former (as if the world exists in some vacuum) to justify direct intervention via QE.
And thus far all these credit easing has failed to accomplish its end.
And we don’t need to heed on the former Fed chief Alan Greenspan’s view[25] about forecasting.
We really can't forecast all that well. We pretend that we can but we can't. And markets do really weird things sometimes because they react to the way people behave, and sometimes people are a little screwy.
And if officials can’t forecast on the consequences of their policies using their econometric models, then why experiment?
Yet it is hardly about people being a “little screwy” but more about people responding to daft experiments imposed on societies as economic policies (US and their multiplier effects worldwide) by ivory tower bureaucrats who hardly knows about real economic relationships except to see them as mechanistic mathematical models, and at the same time, have the impudence to undertake grand trials because they barely have skin on the game.
Moreover policies which punish savings and simultaneously “nudge” the public to wantonly indulge in reckless risk activities leads people to become “screwy”. Bad ideas have bad consequences.
So the cost of their policies will be borne by the average citizenry via restrictions of economic opportunities, financial losses, assuming a bigger burden of financing pet projects of politicians and their bureaucracy, diminished purchasing power and many other non-pecuniary social costs (e.g. erosion of moral fiber, curtailment of civil liberties, social upheaval and etc...)
And these booming credit markets have largely undergirded the financing of the housing or the stock markets bubbles rather than channelled to the real economy for productive activities. The opportunity cost for monetary policy-induced speculation has been the productive sectors, thus the real economy’s growth remains muted or sluggish relative to asset markets.
Monetary inflation has essentially been absorbed by the asset markets. Monetary inflation has spurred massive risk taking, speculative splurge, blatant momentum yield chasing, having been financed by exponential credit growth that has resulted to severe misallocation of resources, blatant mispricing of assets and maladjusted economies.
And such asset bubbles have become international. Thus risks from any unhinging of the bubbles from the US or from any developed economies or even from big emerging markets may likely have a domino effect.
We don’t really need to forecast. All we need is to understand the real economic relationships applied to instituted policies to appreciate the risks.
As the great dean of Austrian economics Murray Rothbard explained[26]: (bold mine)
Economics provides us with true laws, of the type if A, then B, then C, etc. Some of these laws are true all the time, i.e., A always holds (the law of diminishing marginal utility, time preference, etc.). Others require A to be established as true before the consequents can be affirmed in practice. The person who identifies economic laws in practice and uses them to explain complex economic fact is, then, acting as an economic historian rather than as an economic theorist. He is an historian when he seeks the casual explanation of past facts; he is a forecaster when he attempts to predict future facts. In either case, he uses absolutely true laws, but must determine when any particular law applies to a given situation. Furthermore, the laws are necessarily qualitative rather than quantitative, and hence, when the forecaster attempts to make quantitative predictions, he is going beyond the knowledge provided by economic science
[1] See Phisix: Rising Systemic Debt Erodes the Margin of Safety October 14, 2013
[2] Bloomberg.com Foreigners Sold U.S. Assets as China Reduces Treasuries October 22, 2013
[3] Steve Hanke Venezuela The Troubled Currencies Project Cato Institute
[4] Telegraph Venezuela creates Social Happiness ministry October 26, 2013
[5] Happiness See Amidst Hyperinflation, Venezuelan Government Decrees a ‘Happiness’ Ministry, October 27, 2013
[6] See Has the Fed’s Taper Talk induced foreign selling, swap and bilateral currency deals? October 23, 2013
[7] Bespoke Invest US Loses Share to Rest of World October 14, 2013
[8] Russell Investments Russell 2000® Index The Russell 2000 is a subset of the Russell 3000® Index representing approximately 10% of the total market capitalization of that index. It includes approximately 2000 of the smallest securities based on a combination of their market cap and current index membership.
[9] Wall Street Journal P/Es & Yields on Major Indexes Market Data Center
[10] Wikipedia.org National Federation of Independent Business
[11] National Federation of Independent Business October Report Small Business Economic Trends
[12] Bespoke Invest Guidance Remains Weak October 24, 2013
[14] Investopedia.com Earnings Guidance: Can It Accurately Predict The Future?
[15] Bureau of Economic Analysis Corporate Profits: Profits Before Tax, Profits Tax Liability, and Dividends
[16] Lan Sun EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION AND CONTRACT-DRIVEN EARNINGS MANAGEMENT ASIAN ACADEMY of MANAGEMENT JOURNAL of ACCOUNTING and FINANCE 2012
[17] Yardeni.com US Economic Indicators: Corporate Profits in GDP, October 26, 2013
[18] Tracy Alloway and Vivianne Rodrigues Boom-era credit deals raise fears of overheating Financial Times October 22, 2013
[19] Bloomberg.com Fed Loan Warning May Hurt Riskiest Borrowers, Trade Group Says October 26, 2013
[20] Deal Book Citi Chief on Buyouts: ‘We’re Still Dancing’ July 10, 2007
[21] Bloomberg.com Wall Street Skips Moody’s as CMBS Standards Slip: Credit Markets October 25, 2013
[22] Financial Times M&A bonds surge to highest in six years October 21, 2013
[23] Wall Street Journal Latest Headlines Low Rates Bring Bond Bonanza October 25, 2012
[24] see Phisix: US Debt Ceiling Deal and UNTaper Spurs a Global Melt UP October 21, 2013
[25] BusinessInsider.com 'YOU JUST LEARNED THIS?!?' — Jon Stewart Struggles To Understand How Former Fed Head Greenspan Missed Wall Street 'Screwiness' October 22, 2013
[26] Murray N. Rothbard, 1. Economics: Its Nature and Its Uses CONCLUSION: ECONOMICS AND PUBLIC POLICY Man, Economy & State