Here is another example of the normative way of how politicians deal with problems: They treat the symptoms rather than the disease.
From the Wall Street Journal,
Prime Minister Mario Monti has issued a new "growth decree" to revive Italy's moribund economy. Among other initiatives, the 185-page plan proposes discount loans for corporate R&D, tax credits for businesses that hire employees with advanced degrees, and reduced headcount at select government ministries.
Will any of this solve Italy's economic problems? Only in the sense that one could theoretically drain Lake Como with a ladle and straw. Allow us, then, to illustrate why Italy's economy stagnates.
Imagine you're an ambitious Italian entrepreneur, trying to make a go of a new business. You know you will have to pay at least two-thirds of your employees' social security costs. You also know you're going to run into problems once you hire your 16th employee, since that will trigger provisions making it either impossible or very expensive to dismiss a staffer.
But there's so much more. Once you hire employee 11, you must submit an annual self-assessment to the national authorities outlining every possible health and safety hazard to which your employees might be subject. These include stress that is work-related or caused by age, gender and racial differences. You must also note all precautionary and individual measures to prevent risks, procedures to carry them out, the names of employees in charge of safety, as well as the physician whose presence is required for the assessment.
Now say you decide to scale up. Beware again: Once you hire your 16th employee, national unions can set up shop. As your company grows, so does the number of required employee representatives, each of whom is entitled to eight hours of paid leave monthly to fulfill union or works-council duties. Management must consult these worker reps on everything from gender equality to the introduction of new technology.
Hire No. 16 also means that your next recruit must qualify as disabled. By the time your firm hires its 51st worker, 7% of the payroll must be handicapped in some way, or else your company owes fees in-kind. During hard times, your company may apply for exemptions from these quotas—though as with everything in Italy, it's a toss-up whether it's worth it after the necessary paperwork.
Once you hire your 101st employee, you must submit a report every two years on the gender dynamics within the company. This must include a tabulation of the men and women employed in each production unit, their functions and level within the company, details of compensation and benefits, and dates and reasons for recruitments, promotions and transfers, as well as the estimated revenue impact.
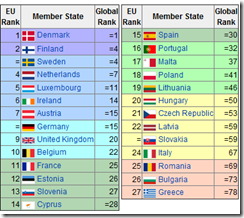
I earlier posted the labor markets of France and Germany compared to Spain.
Such astounding maze of regulations has been one of the major dynamics for today’s crisis. This has produced a huge bureaucracy that has been draining productive resources from entrepreneurs. This has also increased the costs of doing business. Reduced the incentives of entrepreneurs to expand. Shifted many activities to the informal or shadow economy.
Italy has one of the largest informal economies relative to the OECD nations
As well as encouraged corruption. Italy ranks as one of the most corrupt in Eurozone. Overall, such regulations has reduced Italy’s competitiveness.
So reduced competitiveness leads to diminshed output (income) – ballooning government (expense)= crisis (deficits)
And how does the Italian government intend to fix the problem?
Among other initiatives, the 185-page plan proposes discount loans for corporate R&D, tax credits for businesses that hire employees with advanced degrees, and reduced headcount at select government ministries
Gosh, 185 pages of more regulations and more bureaucracy.
Note: reduced headcount at “select” government ministries looks more symbolical and seems like a loophole.
Yet the mainstream advice of solving this problem by inflation will only worsen the situation, as this does not address the root: asphyxiation from big government.
Doing it over and over again and expecting different results only reinforces the worsening of this crisis.