The art of economics consists in looking not merely at the immediate hut at the longer effects of any act or policy; it consists in tracing the consequences of that policy not merely for one group but for all groups—Henry Hazlitt
Sunday, August 02, 2020
The Historic Gold and Bond Bull-Market Tango
Wednesday, March 07, 2012
ECB’s Record Balance Sheet Tops the US Federal Reserve
From the Bloomberg,
The European Central Bank’s balance sheet surged to a record 3.02 trillion euros ($3.96 trillion) last week, 31 percent bigger than the German economy, after a second tranche of three-year loans.
Lending to euro-area banks jumped 310.7 billion euros to 1.13 trillion euros in the week ended March 2, the Frankfurt- based ECB said in a statement today. The balance sheet gained 330.6 billion euros in the week. It is now more than a third bigger than the U.S. Federal Reserve’s $2.9 trillion and eclipses the 2.3 trillion-euro gross domestic product of Germany (EUANDE), the world’s fourth largest economy.
The ECB last week awarded banks 529.5 billion euros for three years in the biggest single refinancing operation in its history, adding to the 489 billion euros it lent in December. The flood of money, which aims to combat Europe’s sovereign debt crisis by unlocking credit for companies and households, has increased the risk exposure of the 17 euro-area central banks that together with the ECB comprise the Eurosystem.
Here are the accompanying charts also from Bloomberg
ECB’s € 3.0 (US $ 3.96) Trillion
US $2.9 Trillion
In seeing the above, we understand that underneath today’s veneer of tranquility, there has been a lingering disorder that has yet to be manifested on the marketplace and on the real economy. These can be analogized to rapidly spreading cancer cells at the earlier stages.
Yet the above does not include the balance sheets of the Bank of England, Bank of Japan and the Swiss National Bank whom have all been undertaking similar actions.
Despite occasional publicized opposition, these policy palliatives will be sustained by political authorities in the hope of rehabilitation and the preservation of the incorrigibly degenerate political system.
Policymakers of developed economies will likely push this or exploit the use of central banks to the limits until a blowback in the economy and the monetary system becomes apparent.
Because the public is hardly aware of the operations of central banks, central bankers have assumed the role of hatch men for politicians and their privileged cronies the banking class.
Yet to desist from the current actions will translate to a collapse of too big to fail banking institutions that should drag along the welfare-warfare state, a development which current political agents have fervently been trying to defer, thus the unprecedented experiment.
There is no way for any person who understands the fundamentals of money to be bearish on prices of precious metals given the prospective extension of these policies.
The recent surge in global stock markets has been symptomatic or signifies as the initial outcome of the the second wave of central banking money therapy that is being applied. I expect that equity markets particularly those from emerging markets to mainly benefit from these remedial measures for the time being. This will hardly be an issue of earnings or valuations, but of the evolving state of money.
Lastly with the Euro balance sheet surpassing that of the US Federal Reserve, it’s time to be temporarily bearish the Euro. I say temporary because I expect the US Federal Reserve to eventually ramp up on their balance sheet through another QE (or a variant of it) for many earlier stated reasons.
However, I wouldn’t short the Euro though, the political management of fiat currencies have already been evincing of their innate tendencies of returning to their intrinsic value—zero. I’d buy precious metals instead
We have to be reminded that the relative valuations of currencies is determined by the relative demand and supply of currency units.
As the great Ludwig von Mises wrote,
These observers do not understand that the valuation of a monetary unit depends not on the wealth of a country, but rather on the relationship between the quantity of, and demand for, money. Thus, even the richest country can have a bad currency and the poorest country a good one.
Thursday, July 29, 2010
$23.7 Trillion Worth Of Bailouts?
Nassim Taleb spoke of definancialization as the main cure to the system.
However, his suggestion would be revolutionary since we cited that financialization is the heart of the US political economic system (and globally) which has operated around the central banking platform, particularly in the US, the US Federal Reserves.
Proof? This from Bloomberg,
U.S. taxpayers may be on the hook for as much as $23.7 trillion to bolster the economy and bail out financial companies, said Neil Barofsky, special inspector general for the Treasury’s Troubled Asset Relief Program.
The Treasury’s $700 billion bank-investment program represents a fraction of all federal support to resuscitate the U.S. financial system, including $6.8 trillion in aid offered by the Federal Reserve, Barofsky said in a report released today.
“TARP has evolved into a program of unprecedented scope, scale and complexity,” Barofsky said in testimony prepared for a hearing tomorrow before the House Committee on Oversight and Government Reform.
Treasury spokesman Andrew Williams said the U.S. has spent less than $2 trillion so far and that Barofsky’s estimates are flawed because they don’t take into account assets that back those programs or fees charged to recoup some costs shouldered by taxpayers.
“These estimates of potential exposures do not provide a useful framework for evaluating the potential cost of these programs,” Williams said. “This estimate includes programs at their hypothetical maximum size, and it was never likely that the programs would be maxed out at the same time.”
Barofsky’s estimates include $2.3 trillion in programs offered by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corp., $7.4 trillion in TARP and other aid from the Treasury and $7.2 trillion in federal money for Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac, credit unions, Veterans Affairs and other federal programs.
We shouldn’t forget that the US banking system has been plagued by toxic securities mostly from mortgage lenders, such as Fannie and Freddie and other private labels, thus the encompassing system wide rescue package.
This can clearly be seen in the Federal Reserve’s Balance sheet, where the bulk (brown) of the assets held comprise Federal Agency Debt Mortgage Backed Securities
This reminds us of President Woodrow Wilson who once wrote,
“A great industrial nation is controlled by its system of credit. Our system of credit is privately concentrated. The growth of the nation, therefore, and all our activities are in the hands of a few men who, even if their action be honest and intended for the public interest, are necessarily concentrated upon the great undertakings in which their own money is involved and who necessarily, by very reason of their own limitations, chill and check and destroy genuine economic freedom.”
Sunday, July 05, 2009
Inflation Is The Global Political Choice
``Conventional wisdom contends that the current recession was caused by the free-market zealotry of recent economic policy and by excessively low interest rates. It is an absurd view, given that interest rates are not determined by market forces. Interest rates are manipulated by central banks with a government-mandated monopoly in the issuance of money. Some of those still defending free markets protest that, contrary to popular opinion, banks were heavily regulated before the financial crisis. So they were. But this is quibbling. The role of central banks means that, at its core, we did not have a free market financial system. We had a command economy. Command economies do not fail because the central planning agencies lack the powers required to bring about the best outcomes. They fail because, without market prices, nobody has the information required to adapt the allocation of scarce resources to the demand for them. They fail because central planners have an impossible job.” Jamie Whyte, banker and philosopher and the author of Bad Thoughts: A Guide to Clear Thinking, Strip the Bank of England of its power
I find it amusing when mainstream experts and officials argue about the risks of systemic deflation. That’s simply because we understand their mental or thought process and their latent intentions-they have been selling fear in order to justify the further expanded use of government inflationary programs.
As Ludwig von Mises predicted over half a century ago, ``In discussing the situation as it developed under the expansionist pressure on trade created by years of cheap interest rates policy, one must be fully aware of the fact that the termination of this policy will make visible the havoc it has spread. The incorrigible inflationists will cry out against alleged deflation and will advertise again their patent medicine, inflation, rebaptising it re-deflation. What generates the evils is the expansionist policy. Its termination only makes the evils visible.” (bold emphasis mine)
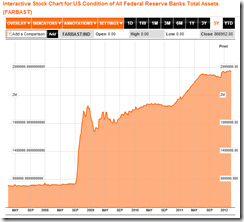
Recently there have been raging debates on whether the US Federal Reserve Balance sheet [see Figure1] will trigger inflation or not.
 Figure 1: Cumberland Advisors: Composition of Fed Balance Sheet
Figure 1: Cumberland Advisors: Composition of Fed Balance Sheet
For the inflationists, despite ballooning reserves, the fundamental argument boils down to a highly indebted consumer that couldn’t afford take up additional or more loads of debt and the banking systems’ vastly impaired balance sheets which have opted to rebuild capital by playing the yield curve or by receiving interest payments from the US Federal Reserve on their bank reserves than to operate on the normal credit lending process.
So bloated reserves, for them, won’t translate to “circulation credit” or a credit process-which is not supported by savings or by deposits-but from money “created from thin air”.
For the mainstream, this is called the “liquidity” trap where monetary policies have been rendered impotent and where the only solution lies in a cycle of government taking over the spending process.
Further, for some, it is even held with confidence that the Fed’s interest payment scheme on bank reserves will reduce the risks of an outbreak of inflation once the credit lending process starts improving.
It’s kindda bizarre that the polemic on inflation have been reduced to a technical dimension when the essence of the entire process has been apparently circumvented or shortcircuited.
To put on our Ivory Tower thinking cap, inflation is the process of expanding government’s liabilities over the economy’s goods and services. This can be done through different channels: the banking system via circulation credit (which has underpinned the debate) or by government deficit spending programs or central banking buying of private assets (Quantitative Easing).
The point is as Henry Hazlitt wrote, ``For inflation does not come without cause. It is the result of policy. It is the result of something that is always within the control of government—the supply of money and bank credit. An inflation is initiated or continued in the belief that it will benefit debtors at the expense of creditors, or exporters at the expense of importers, or workers at the expense of employers, or farmers at the expense of city dwellers, or the old at the expense of the young, or this generation at the expense of the next. But what is certain is that everybody cannot get rich at the expense of everybody else. There is no magic in paper money.” (bold highlight mine)
Inflation As Public Policy
And what is a public policy, if not a politically determined legal action?
It is derivative from a process where the government determines the redistribution of resources coercively acquired via taxation. It’s a mechanism where some vested interest individuals or groups in the society, who intends to benefit from other people’s money, utilize the welfare state to impose regulation, subsidies, protection and other forms redistribution programs to achieve such goals at the expense of the rest.
In addition, policy decisions are always determined by political influences, ideology, party affiliation, compromises, perceptions shaped by divergent knowledge or familiarity or biases or priorities or other forms of preferences ingrained in the policymakers.
Policies are never about “right” moral virtues. In the same plane, policymakers are merely human beings, whom are subject to moral frailties, cognitive biases, limited knowledge, and operates on a preferred set of network. In short, the officialdom does not possess God like omniscience.
Proof?
The recent cap and trade bill which sailed past the house of the US Congress by a slim margin is a fundamental example, this from the New York Times, ``As the most ambitious energy and climate-change legislation ever introduced in Congress made its way to a floor vote last Friday, it grew fat with compromises, carve-outs, concessions and out-and-out gifts intended to win the votes of wavering lawmakers and the support of powerful industries.”
So for those thriving under the illusions of morality in governance- our reply is-Get Real!
All these suggest that the preferred policy route by the present policymakers in the US, the Philippines, China or elsewhere has been inflation.
It is a direction borne out of the comfort zone by the present crops of political leaders, by their adopted economic ideology, and the emphasis on narrow time preferences to approach any social or economic ills.
It doesn’t really matter if “output gaps” or “Phillips curve” didn’t work in the stagflation era of the 70s or in the Hyperinflation episodes in Weimar Germany or in Zimbabwe, what matters is that these models have been convenient tools for adopting policy frameworks used by the governing politicians and their bureaucracy and advanced by their academic allies and adherents.
It’s almost been a forgotten principle that political leaders exists primarily for power and is hardly about plutonic salvation of their constituents- a prevarication continually peddled by media and politicians, and solemnly embraced by the gullible public.
Hence the preferred solutions have basically been short term fixes that would enable these officials to carry past any unintended effects after their tenure. And it is also why political leaders almost always fall for populism based policies.
Thereby, the risks of the unintended consequences from kneejerk reactions to the present financial market turmoil will breed and nurture the next crisis.
This has been a political, economic and social cycle.
And all these yammering about deflation risks is understandable, say from Janet Yellen, President of the Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco (WSJ), or from mainstream’s pop economic icon Nobel Prize awardee Paul Krugman who recently wrote policymakers to “stay the course” who incidentally wrote in 2002 advocating a bubble ``To fight this recession the Fed needs more than a snapback; it needs soaring household spending to offset moribund business investment. And to do that, as Paul McCulley of Pimco put it, Alan Greenspan needs to create a housing bubble to replace the Nasdaq bubble” or from hedge fund manager” (now you know his model depends on serial bubble blowing), or from Hedge fund manager Eclectica’s Hugh Hendry, ``I think this paranoia today that inflation is happening today I think it puts in place a motion for a decline in the economy. I think they're not printing enough money… with regards to the wealth destruction that has been happening over the past 18 months.”(CNBC/greenlightadvisor.com)
And this is why the obvious route is to inflate the system regardless of the impact of the puffed up FEDERAL RESERVE balance sheet, because the alternative recourse of policy actions could be to increase deficit spending (although this could encounter some difficulties due to the growing recognition of its attendant risks and burdens) or it may resort to the more abstract and less publicly understood central bank action known as the “printing press” or QE.
As Ludwig von Mises presciently warned over 60 years ago ``There is need to stress this point, because the public, always in search of a scapegoat, is as a rule ready to blame the monetary authorities and the banks for the outbreak of the crisis. They are guilty, it is asserted, because in stopping the further expansion of credit, they have produced a deflationary pressure on trade. Now, the monetary authorities and the banks were certainly responsible for the orgies of credit expansion and the resulting boom; although public opinion, which always approves such inflationary ventures whole heartedly, should not forget that the fault rests not alone with others. The crisis is not an outgrowth of the abandonment of the expansionist policy. It is the inextricable and unavoidable aftermath of this policy. The question is only whether one should continue expansionism until the final collapse of the whole monetary and credit system or whether one should stop at an earlier date. The sooner one stops, the less grievous are the damages inflicted and the losses suffered.”
So the US government will inflate because it deems such path as the most politically correct and justified for its interest. This implies that such policy actions would need keep asset prices afloat in order to “prevent a collapse” of the reverse debt pyramid foundation from which the US financial system has been built upon, and because the only other path of resolving the debt or overleverage problem other than inflation is to accept deflation or bankruptcy. And yielding to debt deflation essentially undermines the deified image from which has been used as rationale to undertake the vastly shifting structure of its political institutions.
Evidences Of Globalized Inflation
Moreover, in contrast to the one dimensional oversimplistic thinking that the world revolves around the US, the trend of inflationary policies has been global see figure 2.
 Figure 2: DollarDaze.org: Estimated Global Monetary Aggregates
Figure 2: DollarDaze.org: Estimated Global Monetary Aggregates
The world monetary base has been exploding.
Morgan Stanley’s Joachim Fels enumerates the inflationary actions of global central banks (all bold highlights mine),
``QE is alive and kicking... The sharp increase in US 10-year yields and mortgage rates, with 10-year yields reaching 4% in mid-June, led many investors to question the effectiveness of the QE programme. While a continued increase in yields would certainly create headwinds for economic recovery, it is important to keep in mind that keeping yields low was only one aspect of the programme. As important, if not more so, is the increase in money supply and excess liquidity. On this measure, the Fed has continued to run a successful campaign, as have a host of other countries that have implicitly or explicitly turned to QE.
``...globally: On our count, the Fed, the ECB, the BoE, the BoJ, the Swiss National Bank, the Swedish Riksbank, the Norges Bank and the Bank of Israel all adopted some form of QE around September 2008 (see "QE2", The Global Monetary Analyst, March 4, 2009). M1, the measure of narrow money supply, has been growing strongly in most of these countries since then. M1 growth in the G4 is ticking along at 12%, driven by M1 growth of nearly 20% in the US, around 8% in the euro area, and a move into positive territory for M1 growth in Japan. Outside the G4, money supply is moving up strongly in Switzerland and Israel, with the latest M1 growth numbers showing 42%Y and 54%Y growth, respectively. The Norges Bank's QE programme has kept the monetary base at highly elevated levels and M1 growth has begun to shrug off the effects of previous tightening and is now in positive territory. Finally, the increase in the monetary base allowed by the Riksbank has pushed up M1 growth to over 6%.
``While there has been no QE announcement from the Chinese monetary authorities, the efforts made to increase money supply and credit in China over the past few months have been highly successful. M1 growth has clocked in at 18.5%Y while loans are growing at 28%Y. India briefly flirted with QE-type policies by buying a sizeable chunk of government bonds since April. However, efforts to push up money supply don't seem to have been pursued vigorously since then. Both economies are expected to outperform the global economy. If anything, our economics team sees the dramatic rally in equities and property as a development that central banks will have to monitor closely.
``More to come: In the major economies, there is plenty more to come. The Fed is about halfway through its US$1.75 trillion purchase programme, while the Bank of England has about 18% (£23 billion) of its programme yet to go. Meanwhile, the ECB will start purchasing €60 billion of covered bonds this month. In short, there is plenty of firepower waiting to come out of the central banks' QE muzzles. If the impact on money supply so far is anything to go by, we can expect excess liquidity to continue to grow and support economic recovery and asset markets.”
So all these unfolding events have been happening exactly in accordance of the von Mises manual or guidebook.
Reconfigured Global Economy Heightens The Inflation Transmission
In addition, structural dynamics on a national scale applied globally are likely to influence the inflation transmission by central banks.
If inflationists argue that excess capacity amidst a slack in global demand will lead to a globalized “deflation”, we have countered that nations with less systemic leverage and high savings rate will respond positively to zero bound interest rates and see an expansion in circulation credit and most likely become breeding grounds of the next bubble.
And this is the reason why we have been witnessing a big jump in emerging markets and Asian stocks.
It isn’t mainly the issue of “excess capacity” but of the issue of accelerating speculative activities induced by easy money policies.
It’s because sustained elevation of asset prices fueled by central bank policies will likely absorb some of the “idled” resources. Inflationists tend to ignore the impact of money to demand and supply of goods and services.
But again, many of the redirected flow of speculations will account for temporal misallocations that will be subject to the business cycles or boom bust cycles. Whether it is the Japan bubble bust, the Tequila Crisis, the Asian Crisis, the dot.com bust or today’s US mortgage and banking crisis, the underlying forces that cultivate such bubbles remain the same and in operation. But only this time the degree involved is way bigger than the past and is likely going to get a lot bigger.
Moreover, the unfolding accounts of deglobalization amidst a reconfiguration of global trade, labor and capital flow dynamics, which used to be engineered around the US consumer, will likely be reinforced by an increasing trend of reregulations which may lead to creeping protectionism and reduced competition and where higher taxes may reduce productivity and effectively raise national cost structures, as discussed in Will Deglobalization Lead To Decoupling?
Proof?
The gradual escalation of protectionism in the form of policy induced programs to reduce migration flows. This from The Economist, ``Governments are reducing quotas for foreign workers and imposing tougher entry requirements on them in an effort to control the flow. Some are even paying existing migrants to go home”.
 Figure 3: OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook: CPI and Food Price Inflation in select Emerging Markets and select OECD economies.
Figure 3: OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook: CPI and Food Price Inflation in select Emerging Markets and select OECD economies.
More proof?
Amidst the culmination of the near systemic collapse of the US banking system that rippled across the globe in September-October of 2008, and where global “deflation” became the main cause of concern, the chart from OECD-FAO 2009 outlook shows how CPI rates have been mostly positive on a year to year basis in most OECD or even in Emerging markets!!!
So this Ivory Tower analyst operates in a world of real evidence compared to mainstream or conventional thinking, which operates in a world of models fitted to validate their biases or data mining.
Clash in Policies And Expectations A Source Of Confidence?
Another bizarre notion is the expressed confidence over global central banks ability to overturn present policies once the recovery in the global economy gains traction.
For countries unaffected by the deluge of debt in the past bubble, this could be true. But for economies scourged by overleverage hangover, this would seem highly questionable.
For instance, the ability by the US Federal Reserve to pay interest on bank reserves has been inferred to by some as a superior tool, which would function as a brake, against the risk of an outbreak of inflation.
Yet this wonkish article Federal Reserve of Atlanta shows how the US Federal Reserve has been in a bind-it has been struggling to close the gap between Fed Fund rates and Interest on paid bank reserves. If under a benign environment the Fed seems in a predicament on managing some of its tools under watch, how much more when the psychology tips towards inflation?
Be reminded that inflation, aside from being a political process, is importantly psychologically driven. As Nassim Taleb in a recent interview said, ``Because all you need is for people to think there’s gonna be inflation to start hoarding.”
And that’s why central bankers keep a close vigil to inflation expectations as signaling channel. It is also another reason why governments can and will manipulate gold (a major barometer of inflation) or other commodities as oil, as part of their array of tools to manage inflation expectations. Hence, the idea of free markets in a world of central banking is a delusion.
Moreover, even the objectives of government policies appear similarly in a fix, as actions and intent have been in a collision. Let’s call it the paradox of save and spend.
Where savings under the present economic ideology is an anathema to aggregate spending, government deficit spending which substitutes for lost private consumption requires financing from global savers, official forex surpluses or local savers.
Nonetheless, if the official surpluses from emerging central banks or global savers won’t suffice to fill in to fund US government spending programs, then it would require resident savings to do so.
Yet ironically, the policy thrusts have been directed against attaining these goals. So essentially, clashing goals and policies from the paradox of save and spend, don’t account for an optimistic outcome.
This means that without sufficient financing, the US government would have a Hobson’s choice which is to monetize these debts.
I’d like to further point out that it’s an apples-to-orange comparison when experts use the debt to gdp ratio to account for deficits.
For instance, the US economy at $14.265 trillion is about 24% of the global economy at $60.690 trillion in 2008 (IMF), second to the Euro zone. So even if Japan’s public debt is about 170% (2008-Flag counter) of its $4.924 trillion (IMF) economy which translates to around $7.3 trillion, the US debt which is 60% of the GDP (2007) translates to some $8.6 trillion. So nominal debt figures or debt to global GDP would be a better measure since funding options would likely be on a global scale.
The striking difference is Japan has huge surpluses ($1.02 trillion-chosun.com) and even more humongous savings ($14.9 trillion!!!-Bloomberg) that can finance most of its locally held debt.
Hence the crux of the matter is that the financing aspect of the deficits is more important than the deficit itself. And here savings rate, foreign exchange reserves, economic growth, tax revenues, financial intermediation, regulatory framework, economic freedom, cost of doing business, inflation rates, demographic trends and portfolio flows will all come into play. So any experts making projections based on the issue of deficits alone, without the context of scale and source of financing, is likely misreading the entire picture.
Finally, it is equally odd for experts to become confident on global governments exiting the remodeled structure of today’s financial markets when the underlying expectations appears to have been built around the sustained backstop of governments.
Consider this piece from Richard Barley at the Wall Street Journal (bold emphasis mine), ``As policy makers discuss how to exit from quantitative easing, investors need to position themselves for the government-bond-market turmoil that is likely to follow.
``The markets got a taste of what might be in store this week when the Bank of England decided to stop buying two bonds originally included in its £125 billion ($204.68 billion) quantitative-easing program. The prices of those bonds plummeted, suggesting there is big money to be made for investors who get their trading strategy right.
``The snag is that some government-bond markets are so potentially distorted by central-bank programs that it is hard to feel confident of where prices should be…
``But even if the bank decides to continue with quantitative easing, it may come under pressure to expand the basket of securities it is buying to avoid building up excessive holdings in other single issues…”
Three observations from this article:
One, take away the pillar of the present platform and renewed volatility follows.
Two, intervention begets even more intervention which is the basic premise of any inflationary cycles.
Three, markets are built around incentives and expectations. Short term policy based patchwork could result to a clash between policies and expectations.
Implications For The Financial Markets
What does these mean to the financial markets?
It means that global financial markets have been operating fundamentally on the expectations of sustained government interventions and persistent inflationary actions. And expectations have seemingly been geared towards the deepening of such activities.
Any expectations built on sound recovery will likely be a mirage. Any economic recovery will probably be temporary and predicated on bubble dynamics of malinvestments.
Because deflationary forces remain in several OECD economies, the policy thrust will likely be to further reinflate the system, most likely by QE, justified by low current CPI rates and the bogeyman of deflation. Nevertheless, recessionary forces and policy inflation will likely result to sharp volatilities.
Any major liquidity withdrawal, especially from the US Federal Reserve, will likely cause massive dislocations in the global markets.
Emerging markets and Asia are likely to be the center of the next bubble.
We seem to be approaching a threshold point where bubble afflicted governments will have to decide whether to embrace deflation or accelerate the inflation process to a greater level even at the risks of compromising the conditions of their currencies.
And those saying the US dollar will unlikely be replaced as the international currency reserve anytime soon should heed the lessons of inflation. Once the public recognizes that the sustained and accelerated erosion of money’s store of value, they will be replaced as history has shown. Hence, the fate of the US dollar will depend on the underlying policies taken.
As an old saw goes, nothing is certain in this world except death and taxes, and may I add, popular delusions and lies.