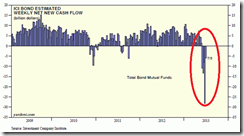
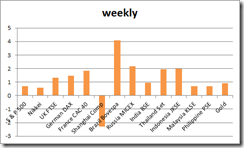
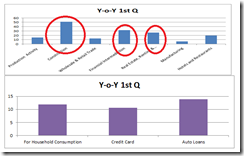
The real interest rate is not the difference between the nominal rate and the change in the CPI; it is actually the rate of exchange between present goods and future goods. Also, there is no such thing as the real interest rate — there are a multitude of real rates, which cannot be added to a total. -Frank Shostak
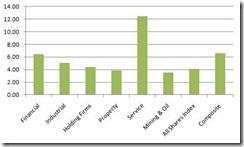
In sympathy with the actions in global markets, the Phisix declined 1.82% over the week which reduced year to date gains to .44%.
Negative Real Interest Rate and BSP’s Admission of External Influences
The Philippines and most of ASEAN have so far been less politically influenced relative to other markets.
But this doesn’t make us immune.
Proof?
From Bloomberg[1],
``Bangko Sentral will review inflation forecasts for this year and 2012 at the June 16 meeting, Tetangco said. An extension of the Federal Reserve’s so-called quantitative easing, “if it happens,” will tend to boost inflows to emerging- markets, bolster liquidity and strengthen currencies, he said.”
The good governor does not directly say it; but he implicitly acknowledges that there exists a strong transmission mechanism from US Federal Reserve policies, which have substantial effects on local assets, the local economy and inflation.
Governor Amando Tetangco thinks he has all the required tools to manage this.
I quote Governor Tetangco anew from the same article,
“If you look at the May figure, inflation pressures still exist,” Tetangco told reporters in Manila today. “We will look at the options available, the instruments included in the toolkit including the policy rate, reserve requirement and macro prudential measures.”
And I have been saying that local media and the BSP have not been forthright[2] and will miscalculate on estimating inflation trends.
This has been happening.
Nevertheless, the Philippines still operates on an accommodative monetary policy.
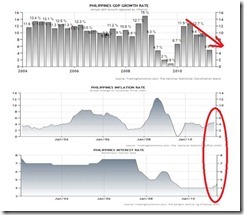
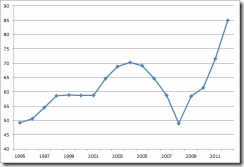
Previously, the Philippine (CPI) inflation rate, as shown in the chart from tradingeconomics.com[3], has been slightly above interest rates which make for a negative real interest rate environment[4], where inflation is greater than interest rates. In this article, I will be wearing on the mainstream’s thinking cap on interest rates.
So accounting gains from fixed income investments on a nominal basis could likely be overestimated unless adjusted for by inflation.
The Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP) increased its policy interest rates twice this year but so far, the level of rates are just about the level of BSP’s statistical inflation.
Yet given the public’s outcry over price hikes in energy and food, I think that the mathematical construct of the BSP’s CPI basket seems to underreport real CPI inflation.
This only means that the current operating conditions imply that negative interest rate environment could be alot greater than what can be gleaned seen using BSP computations.
The overall implication, according to Wikipedia.org[5], is that negative real interest rates leads
to commodity speculation and business cycles, as the borrower can profit from a negative real interest rate
Also, given the combination of the current level of economic growth rate, which remains far above the interest rate, coupled with the negative real interest rate outlook, suggests that the Philippines continues to operate on a loose monetary inflation stoking environment.
Easy money policies which favor debtors also mean favoring speculators. Thus, current environment remains supportive of an upbeat Phisix, despite a current slowdown elsewhere.
So both external and internal forces in fusion points towards higher inflation which will go beyond the expectations and the statistical estimates of the BSP.

The Peso yield curve seems to be indicating the same inflation outlook (chart from ADB’s Asian Bonds Online[6])
Our current yield curve (red) has further steepened from last year (yellow) implying higher future inflation.
To add, going back to the economic growth, inflation and interest rate chart, despite the slowing growth momentum (measured in quarterly changes upper window), which is signified by the red arrow, the above dynamics seems representative of symptoms known as stagflation—high inflation accompanied by high unemployment and slower economic growth[7].
So this could be a preview of what’s going to happen once inflation intensifies.
Stagflation and the EPIRA law
Aside from local and foreign monetary policies, part of the worsening of domestic inflation has recently been seeded.
The passage or the extension of the politically correct but economically unfeasible decree signified by the massive electricity subsidies based on the Electric Power Industry Reform Act [EPIRA] law[8] will be part of such force. In 2010[9], I have previously discussed on how this would contribute to today’s inflation. Apparently we see signs of price pressures[10] part of which has been due to this.
These subsidies would intensify demand for electricity consumption, where the benefits of political free lunches aimed at acquiring votes, will only be passed and added to the burdens of all productive enterprises.
The outcome will reminisce the past where increasing costs of energy will translate to higher cost of doing business, elevated risk premiums and high hurdle rates that would imply fewer investments, higher levels of unemployment, lower growth rate and importantly lower standards of living.
Moreover, this law impels for the growing risk of power supplies shortages.
Eventually socialist type of free lunches runs dry. As former UK Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher says[11], Socialism
always run out of other people's money. It's quite a characteristic of them
Proof?
Venezuelan President Hugo Chavez claims that energy is a “birthright” for Venezuelans[12]. The result has been a massive rolling blackout, a model we should look forward to especially in the face of the continued uptrend in commodity and energy prices.
In addition, like Venezuela[13], we can expect more smuggling or black market or illegal connections to take place.
Indonesia has learned from such unviable and absurd policies and has begun dismantling subsidies to all sectors.
As the Jakarta Post reports[14],
The government expects to remove the electricity subsidy completely by as early as 2014 so that it will have more funds available to fight poverty and improve healthcare directly for the poor, a minister has said..
Unfortunately we have taken the opposite route.
Yet this is an example of redistributive tax scheme, where publicly listed Meralco, a legally franchised monopoly, would serve as the conduit for such mandate. This validates only my observation about Meralco’s status as a pet company for politicians[15].
The good news is that stagflation does not automatically translate to wreckage for the stock markets. Not if we use Venezuela as a model.
Venezuela has had an amazing stock market run this year[16] despite inflation tipping towards hyperinflation earlier, along with high unemployment and a two year economic slump which she has reportedly emerged from[17].
This is not to say that stagflation is good for the stock market, instead the returns of Venezuela’s stock markets remains negative when computed for inflation.
Put differently Venezuela’s stock market could have functioned as a defensive store of value from her rapidly devaluing currency.
The other point is that Venezuela’s dynamic may or may not apply elsewhere because of every nation’s idiosyncrasy or structural uniqueness.
For most, the current state of boom bust cycles, which drives global stock markets evinces that meltdowns are a mostly result of liquidity contraction from a previous inflationary environment such as the recent cases of Bangladesh[18] and Vietnam[19] or the global 2008 crisis.
PSE: It’s a Correction Phase
Last week’s correction seem as broadmarket based.

All sectors endured losses. Even the mining sector which has sizzled for 10 consecutive weeks finally relented.
The good news is that despite the losses, market breadth hasn’t been as dire as declining issues led advancing issues moderately.
Even net foreign trade posted slightly negative.
The Peso declined along with the local benchmark market, albeit only marginally lower from php 43.205 to a US Dollar last week to php 43.28 at Friday’s close.
Market internals and the Peso’s actions have not yet been manifesting signs of sharp deterioration.
Thus, I’d read the actions in the Phisix as a consolidation phase awaiting a trigger for a next run.
One would further note that the last time the Phisix collapsed was in an environment of higher rate of inflation and higher level of interest rates than today. Of course the 2008 episode accounted for as contagion which whose origins were from external forces.
The point is I don’t see substantial signs of severe corrosion of financial and economic conditions yet.
Finally, we should expect the continuance of current global volatility until political issues abroad would get threshed out.
As for the timing of when this resolution will happen is beyond my capabilities as analyst, I can only speculate.
As Ludwig von Mises wrote[20], (bold emphasis mine)
In the real world acting man is faced with the fact that there are fellow men acting on their own behalf as he himself acts. The necessity to adjust his actions to other people's actions makes him a speculator for whom success and failure depend on his greater or lesser ability to understand the future. Every action is speculation. There is in the course of human events no stability and consequently no safety.
And since I expect the current market actions to represent more of a countercyclical reprieve than a major inflection point, then it should be considered as windows of opportunities to accumulate or for trade.
[1] Bloomberg.com Philippines’ Tetangco Says Inflation Pressures ‘Still Exist’ (1), June 10, 2012
[2] See The Code of Silence On Philippine Inflation, January 16, 2011
[3] Tradingeconomics.com Philippine Indicators
[4] Investorglossary.com Real Interest Rates
[5] Wikipedia.org Negative Real Interest Rates
[6] Asianbondsonline.adb.org Philippines
[7] Wikipedia.org, Stagflation
[8] Businessworldonline.com Legislators OK extension of lifeline subsidy scheme, June 7, 2011
[9] See Earth Hour In The Philippines: Rotational Brownouts! The Revenge Of Economics, April 09, 2010
[10] Philstar.com Power, fuel rates up, April 6, 2011
[11] Thatcher Margaret TV Interview for Thames TV This Week 1976 Feb 5 Th
[12] Yahoo.com Hugo Chávez challenges Venezuelan 'birthright' to cheap gas, March 4, 2011
[13] Reuters Africa, World's lowest gas prices fuel Andean smuggling, June 10, 2011
[14] Jakarta Post, Govt expects to remove electricity subsidy by 2014, March 23, 2010
[15] See Meralco’s Run Reflects On The Philippine Political Economy, July 12, 2009
[16] See Global Equity Markets: Signs of Exhaustion; What US Outperformance Means, May 17, 2011
[17] Wall Street Journal 2nd UPDATE: Venezuela 1Q GDP Up 4.5% Vs Previous Year, May 17, 2011
[18] See Bangladesh Stock Market Crash: Evidence of Inflation Driven Markets, January 11, 2011
[19] See Vietnam Stock Market Plunges on Monetary Tightening, May 24, 2011
[20] Mises, Ludwig von UNCERTAINTY: Case Probability, Chapter 6 Section 4 Human Action