``Genius is the act of solving a problem in a way no one has solved it before. It has nothing to do with winning a Nobel prize in physics or certain levels of schooling. It's about using human insight and initiative to find original solutions that matter. Genius is actually the eventual public recognition of dozens (or hundreds) of failed attempts at solving a problem. Sometimes we fail in public, often we fail in private, but people who are doing creative work are constantly failing. When the lizard brain kicks in and the resistance slows you down, the only correct response is to push back again and again and again with one failure after another. Sooner or later, the lizard will get bored and give up.” Seth Godin
After this week’s remarkable and historic breakout by the Philippine Phisix to a fresh all time nominal record highs, we should be having our victory lap.
Another Sweet Vindication
Sorry I can’t help but vent this pleasant and pleasurable feeling of total exoneration: I TOLD YOU SO!
That’s because it’s been years since my analysis and forecasts have been met by various incredulous expressions of scepticisms from almost all quarters.
And it’s not just the breakout that matters; it has been the operational process of the domestic and global financial markets which seems to have aligned in near precision with our analytical methodology predicated mostly upon a combination of non-mainstream theories: Austrian economics, Public choice theory, Hyman Minsky’s Financial Instability hypothesis, George Soro’s reflexivity theory, Alvin Toffler’s “Knowledge Economies”, behavioural finance (Nassim Taleb) and other theories on psychology (e.g. PTSD, Pavlov’s experiment).
Given the momentous force that had accompanied the recent breakout, wherein a whopping 9.44% of accrued gains had been established over the last two weeks, one should expect to see a reprieve over the coming week/s.
We don’t know of the scale of the pause, whether it should signify a substantial correction or a mere consolidation. But we know one thing: no trend goes in a straight line, and that the upcoming countertrend should signify as an opportunity to accumulate than for exit.
As we have previously pointed out, not all bullmarkets are like[1]. As the growing conviction phase of the bubble cycle deepens, as represented by the recent buyside calls of “Golden Era”[2], one should expect to see heightened volatility in market actions which means more frequent explosive moves.
Timing the markets, unless one is very lucky, could translate to lost opportunities, as sharp losses can equally translate to even swifter recoveries.
As a side note, attribution bias, or claiming skills as reasons for ‘trading’ successes, will predominate the coming atmosphere. This especially will be amplified for retail participants, but unknowingly for most, they would be just plain lucky, as the rising lifts most if not all boats.
In a bullmarket, as an old saw goes, everyone is a genius.
Peso Remains A Buy, Politicizing Market Success (Peso Bond Float)
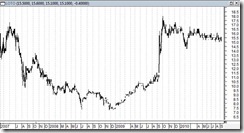
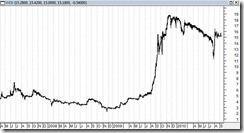
Figure 1: Yahoo/Bloomberg: Milestone Phisix, Lagging Peso
The difference in today’s secular bullmarket compared with the past (1986-1997) is that this time the Phisix (right window) will be accompanied by a rising Philippine Peso. Lately the Peso has apparently lagged (left window).
In late 2007 where the Phisix made a new high, the Peso likewise belatedly caught up and peaked in January of 2008 (Php 40 to a US dollar).
And perhaps we can expect the same trailing performance by the Peso as foreign fund flows (compounded by immigrant and OFWs) into local assets magnify the demand for the Peso.
Meanwhile, the monetary accommodation by the US government and other developed economies will enlarge relative supply scale of the money supplies in favour of ASEAN and Asian currencies.
Importantly, the sustainability of the relative outperformance between asset prices of developed economies and that of the ASEAN (or emerging Asia) powered by the divergences of monetary policies will prompt for more inflows into the region.
And one of the glaring example of the unfolding of such dynamics has been the recent success by the $1 billion Peso bond float.
Yet like always, unfortunately events like this will always be tainted with political colour, as political personalities speedily associate these events with populism.
As we have argued this administration has been so image conscious, such that it would seem that the elections have never ended. To impute the successful bond float to “landslide vote of confidence[3]” for the new administration is no less than PR work meant at propping up imagery of the administration, even if the relevance of the purported linkages were less than half true or constitutes a logical fallacy.
Figure 2: AsianBondsonline.adb.org[4]: Size and Composition of Emerging East Asian Local Currency Bond Markets
The alleged “vote of confidence” does not consider the larger spectrum which would show that the region’s local currency bonds markets have been vastly improving (see figure 2).
In fact, the Philippines have lagged our Asian neighbours and falls below the average performance of the total Emerging Asia, (perhaps even if we add the latest US $1 billion float).
So on a relative scale, the vote of confidence on the Philippines isn’t that impressive, because investors have voted with more confidence on the markets of Thailand (which ironically just experienced a nasty city-wide riot[5] last May), Indonesia and has only been at par with Malaysia.
Given the above picture, I would dare argue that even under the past unpopular regime, the bond issuance would have had a similar magnitude of “warm” reception.
That’s because in a world where prices have been distorted by government’s manipulation of the interest rate (price of time), people conjure up all sorts of excuses, valid or not, just to chase for yields. In short, as the reflexivity theory would say, prices shape opinions.
Yet politicians are quick to grab credit for any actions as their own doing even if these are unrelated, unsupported or has little correlations.
And evidence from the above exhibits that politics have had little effect on the supposed “vote of confidence” of the latest Philippine bond float (or even applied to Thailand).
Another reason why the Philippine Peso has lagged has been due to domestic politics[6]. Particularly that of the politics of OFWs, and secondarily, of the exporters.
So yes, the Peso remains a buy and should be expected to appreciate towards the 40-levels by the yearend, barring any unforeseen circumstances (e.g. war on Iran) and unless our central bank will match the US Federal Reserve in inflating the system (our tail risk).
Unlikely A US Double Dip Recession
These sanguine forecasts are likewise predicated on the conditions that there will be NO double dip recession in developed economies, as a recession will likely drain liquidity in the global financial system despite the proclivity of central banks to counteract such dynamics by flooding the system with money.
Unless we can see further proof where domestic liquidity can get insulated from a liquidity drain abroad, it would be imprudent to bet against “convergence”, which apparently have been the hallmark of globalization.
And a recession is NOT inevitable for earlier reasons cited[7] plus some additional inputs:
1. Global central banks have placed under their stringent sponsorship the banking industry.
Unlike the Great Depression where collapsing banks had a domino effect throughout the economy, today global central banks led by US has backstopped their banking system (specifically creditors) with trillions of taxpayer money. This signifies as a pyrrhic short term victory whose enormous costs would certainly emerge sometime in the future.
Yet it would be a folly for the mainstream to declare victory on what is clearly a short-term panacea. Paying the Piper will be different from what the mainstream expects.
2. Globalization continues to progress.
In contrast to the Great Depression, collapsing banks, protectionism and regime uncertainties via a slew of massive regulatory obstacles caused a standstill and a decline in trade and investments. This is hardly today’s picture.
During the height of the recent crisis, marked by the Lehman bankruptcy, the near seizure of the US banking system rippled throughout the global banking system. However, many entities persisted to trade and channelled them via barter[8] and local currency[9]. And this empirically disproved the mainstream notion that the crisis was one of the failures of aggregate demand. Thus, the mainstream had been caught unaware of the 2009 “recovery” which was likewise supported by the Fed’s (Quantitative Easing) printing press.
Importantly, while the banking system of crisis affected areas like the US have resulted to large scale deterioration in the credit conditions as the crisis culminated, there appears to be material improvement over some aspects of the credit markets as previously discussed[10]. It is likely that the credit markets in the US could finally be responding to the yield curve dynamics which cyclically has had a 2-3 year lag period[11].
Another feature of globalization has been the financing dynamics outside of the banking system, or in particular the explosive growth of the bond markets.
According to Bloomberg[12],
``Global high-yield bond sales are poised to exceed 2009’s record issuance as the riskiest companies take advantage of plunging borrowing costs and investor demand to refinance debt.”
So while the permabears continue to tunnel onto the credit growth as a reason to argue for another recession, the complexities brought about by globalization is certainly keeping them on the wrong side of the fence.
Finally, in contrast to conventional wisdom, credit isn’t the foundation growth, savings is.
As the great Professor Ludwig von Mises wrote[13],
The only source of the generation of additional capital goods is saving. If all the goods produced are consumed, no new capital comes into being.
Figure 3: Deutsche Bank[14]: The Rising Impact Of Asia On The Global Economy
Flushed with savings, emerging markets have not optimized the utility of savings into investments due to their underdeveloped state of the markets (see figure 3). However, globalization appears to be reconfiguring this role as markets are liberalized to accommodate on foreign investments.
Yet of course, artificially suppressed interest rates have been also been a major factor into generating policy “traction” or having to accelerate such dynamics.
And for as long as interest rates will remain at über-accommodative levels in developed economies, emerging markets, like the Philippines, should generally be expected to outperform compared to the debt hobbled counterparts in developed economies.
3. More signs of transition to the Information Age.
The transition to the information age is no more than an extension of the highly competitive and increasingly diversified markets brought about globalization that has spurred massive technological innovation.
Most experts still use industrial age metrics to measure economic activities, which has increasingly become obsolescent. To analogize, the mainstream still think in terms of analog instead of digital, even when many of them increasingly use digital instruments to transact or engage in commerce or conduct many activities in their lives.
In the US, since the adjustment process from a bubble economy to a rediscovery phase takes a longer period, especially in the light of a growing specialization of trade patterns, government intervention only delays these rediscovery phase.
Nevertheless, signs of such transitions have become manifest as seen in the growing mismatch between job availability (high skilled) and manpower supply (labor exposed to malinvestments) as we have pointed out earlier[15].
It isn’t necessarily that there has been a paucity of jobs, but in many instances, the skills required for specialized jobs have been inadequate or have been in a mismatch. And this has mainly been due to the distortive effects from previous inflationary policies that has caused massive misdirection of use in terms of labor and resources. And currently, interventionist policies (unemployment benefits, Obamacare, prospects of higher taxes et.al.) have proven to be an obstacle in the retooling process required for their labor force to adapt to the new reality.
Additionally the latest trade data shows that capital spending has led the economic growth of the US, which has mostly been seen in the industrial machinery and computer exports sectors.
As this Wall Street Journal article illustrate[16],
``While capital projects abroad, especially in emerging economies, are designed to expand production capacity, U.S. businesses are spending to modernize existing facilities and to boost productivity in their work force. Business spending on equipment accounted for one-third of gross domestic product growth in the first quarter and almost all of second-quarter GDP growth.
``The increased foreign demand, coupled with spending here in the U.S., is why business equipment is leading economic growth. U.S. output of business equipment jumped 11.7% in the year ended in July, compared with a 7.7% gain for all manufacturing production.
So specialization, division of labor and comparative advantages highlight substantial part of the economic conditions in the US.
In short, for the mainstream there is alot more for them to chew on, which apparently they refuse to do.
[1] See How To Go About The Different Phases of The Bullmarket Cycle, August 23, 2010
[2] See The Rationalization Phase Begins: ‘Golden Era’ Equals The ‘New Paradigm’?, September 8, 2010
[3] Inquirer.net Peso bond sale nets $1B, September 11, 2010
[4] AsianBondsonline.adb.org, Asian Bond Monitor: Summer Issue Bond Market Developments in the First Quarter of 2010
[5] See Politics And Markets: Bangkok Burns Edition, May 20, 2010
[6] See Global Policy Divergences Favors A Rising Peso, August 22, 2010
[7] See Why Deflationists Are Most Likely Wrong Again, August 15, 2010
[8] See What Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) Have To Do With Today’s Financial Crisis, February 1, 2009
[9] See Emerging Local Currencies In The US Disproves The 'Liquidity Trap’, February 16, 2010
[10] See The Road To Inflation, August 29, 2010
[11] See Influences Of The Yield Curve On The Equity And Commodity Markets, March 22, 2010
[12] Bloomberg.com, Treasury 10-Year Note Yields Climb to One-Month High on Economy, September 10, 2010
[13] Mises, Ludwig von The Anti-Capitalistic Mentality by Ludwig von Mises, Section 4
[14] Lanzeni Maria Laura Lanzeni The Rising Impact Of Asia On The Global Economy June 2010
[15] See US Unemployment: It’s Partly About Skills-Jobs Mismatch, August 10, 2010
[16] Madigan Kathleen, Trade Data Show Importance of Capital Goods Wall Street Journal Blog, September 10, 2010