Since the advent of 2011, the Philippine Phisix has been on a losing streak.
In four out of the five weeks into the year so far or a string 4 consecutive weeks in the red, the Philippine benchmark has accrued a year-to- date decline of 10.76%
Regional Event and Seasonality
Before jumping to conclude about what’s been ailing the Phisix, we should take note of the following:
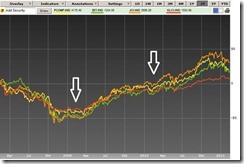
Figure 1: Bloomberg: Correcting ASEAN Bourses
One, this has been a regional phenomenon.
As the above chart reveals, our ASEAN contemporaries (Thailand-green, Indonesia-orange) have been synchronically on a downside path since November of 2010 (with the exception of Malaysia (red).
To extrapolate, there seems no internal dynamic that has been causing the current weakness—not the Rabusa expose nor the Angelo Reyes incident. And I don’t think that local or regional consumer price inflation has reached critical levels yet to incite political hysteria.
The Philippines just posted a record economic growth during the last quarter of 2010[1], and so with Indonesia[2], whose economic growth hit a 6 year high.
One may suggest that these events account for as past performances that does not serve as a good indicator of the future, from which the markets could be be pricing in. This could be true.
And that perhaps the market could be portending of a possible downshift following a turbocharged upside momentum. This could likely be a factor, too. But I would refrain from fixating on this premise as the main causation to the current market action.
The other thing is that the current correction could signify a cyclical motion.
The white arrows on figure 1 points to general market infirmities at the onset of 2009 and 2010.
The first quarter of 2009 marked the trough of the 2007-2008 bear market which culminated with the post Lehman bankruptcy global market collapse in October 2008.
In 2010, the first quarter weakness was then attributed to the Greece Debt Crisis, where the mainstream had insisted that deflation would return, the financial market would collapse and that the Euro dies along with this. All of which we had set out to debunk[3] and had been validated or proven correct.
So it appears that we have a normal countercyclical trend unfolding before our eyes.
No Egypt and Middle East Domino Contagion
Next, no this isn’t about Egypt nor is it about Tunisia’s Jasmine revolution or the falling dominos of autocratic regimes in the Middle East.

Figure 2: Bespoke Invest: Flight To Safety, Where?
As the excellent Bespoke Invest[4] charts shown in Figure 2, there hardly has been material signs of widespread anxiety as seen in the US dollar (left window) or Gold (right window). In short many of so-called market stress attributed to Egypt has been predicated on available bias.
Going back to the ASEAN equity markets, the interim bullmarket reversals began in November 2010, way before such Middle East “People Power” movements or political events that had long been predicted by French judge, political philosopher and anarchist, Étienne de la Boétie[5], during the 16th century who once wrote[6], (bold emphasis mine)
``Resolve to serve no more, and you are at once freed. I do not ask that you place hands upon the tyrant to topple him over, but simply that you support him no longer; then you will behold him, like a great Colossus whose pedestal has been pulled away, fall of his own weight and break in pieces.”
In addition, people always tend to fall prey to mainstream media’s soundbites, yet the media blitz over Egypt has eclipsed the Thailand-Cambodia border military skirmishes that has also accounted for as negative news[7] this week. The risk of military escalation between our neighbors has apparently been eluded mainstream analysts.
Yet, such bellicostic incident should have prompted for a collapse in Thailand’s stocks, if we go by the mainstream’s logic. But this has not been so. Thailand SET lost 3.6% over the week was even less than Korea’s Kospi 4.6% or even nearly at par with the declines registered by the Philippine Phisix 3.18%.
I’d also like to point out that the bloody street riots[8] in Bangkok, Thailand’s capital, in May of 2010, didn’t trigger a collapse in Thai stocks, in the same way as the latest political crisis in Egypt.
In other words, political events do not necessarily or automatically create volatility in stock market pricing.
Inflation Led Slowdown? Not So Fast....
Some may argue that rising inflation could be a factor.
Theoretically, inflation will not be good for equities in general because from the corporate earnings perspective—earnings get squeezed or crimped out of rising real cost of capital and losses on the net asset position that are fixed in nominal terms.
Most importantly, the biggest threat to shareholder value, writes McKinsey Quarterly[9], lies in the inability of most companies to pass on cost increases to their customers fully without losing sales volumes. When they don’t pass on all of their rising costs, they fail to maintain their cash flows in real terms.
But I would argue that the impact to equities from an inflationary environment greatly depends on the underlying state or conditions. That’s because equities have proven to be hedges during episodes of hyperinflations, such as in 1920 Weimar Germany hyperinflation[10] or most recently the Zimbabwe hyperinflation.
I quoted an All African article[11] in 2008
``The feat continued into 2008 with industrials posting a year-to-date growth of 960 quadrillion percent, which is 4,15 billion times as much as July's annual inflation of 231 million percent.
``The resource index is up 444 quadrillion percent since January. And so, from the look of things, ZSE investors may have indeed managed to hedge their assets against the effects of high inflation but some have been at a loss in US dollar terms."
A great living example of the stock market as an inflation “hedge” would be Venezuela (see Figure 3)

Figure 3 Tradingeconomics.com[12]: Venezuela Stock Market Driven By Rampant Inflation
Notice as the rate of annual change in consumer price inflation ramps up, the stock market, on a time lag, follows. As the inflation rate declines, the Venezuela’s stock market bellwether also, on a time lag, declines.
I’d like to further point out that Venezuela’s inflation rate has been at high double digits (25-35%) and appears to nearly tip over to the hyperinflation level or where inflation exceeds 50% a month[13].
The fundamental premise why stocks can function as a hedge doesn’t tag along the lines of earnings but rather on the public’s perception of the changes in the role of money—a deterioration in the “store of value” function.
As Adam Fergusson wrote about the disastrous Weimar Hyperinflation in When Money Dies[14],
October 1922, however, was the nadir for shareholders. From then on not only did money find its way back into shares, but people who could obtain cheap credit, or were unable to send their money abroad, began to realise the advantages of buying up their own country's industrial and other assets at a fraction of their true value. Although in real terms the stock market began to go up, the mark's purchasing power continued to go down.
Said differently under the state of high inflation, even if the values of shares go up, in real terms share values lose money because the money’s value erodes faster than the increase in share prices.
And those who argue on the premise where ‘company earnings determine share prices’ have found current movements in the global stock markets baffling and inexplicable. That’s because these experts have basically been focusing on the wrong aspects and has been ignoring the fast expanding role of monetary inflation’s impact on share prices[15].
Perhaps even Warren Buffett’s dramatic shift to political lobbying-crony capitalism[16] based investment approach could, in reality, be reflective of such changes.
To add, since inflation is basically a redistribution process, some industries are likely to benefit more than the others. Thus, a generalized or broadmarket decline is definitely not a characteristic of the supposed inflation based anxieties.
So all these point to an unsubstantiated premise where the decline in the values of ASEAN bourses has been imputed on the risks of inflation.
More On Growing Divergences
Here’s more: earlier we have pointed to several divergences[17] in the global market such as surging commodities, developed economy share prices and a firming Peso.
I’d like to add that one of the serious manifestations of a market meltdown/breakdown could be seen in the price actions of the local currency.

Figure 4: Bloomberg: JP Morgan Asia Dollar Index
That’s because market meltdowns tend to instigate a “flight to safety” dynamic where investors both local and foreign flee domestic capital markets and seek safehaven elsewhere abroad. In two words: capital flight.
This was demonstrably the case during the 2008 Lehman episode in 2008, (as shown by the white down arrow in the above chart) where the bellwether basket of Asian currencies represented by Bloomberg-JP Morgan Asia Dollar Index cratered.
Today, despite the quarter long weakness envisaged by the region’s stock market, Asian currencies values have remained buoyant.
Yet it is important to point out that Asian currencies tanked only during the latter half of 2008 or nearly at the pinnacle of the crisis. The Philippine Peso likewise began its descent 3 months after the peak in the local stock market.
This only means that as lagging indicators currency values can’t be used as a standalone metric to assess the state of the markets. It has to be combined with other indicators.
Finally here’s another important divergence as noted by Bespoke Invest (see figure 5)

Figure 5: Divergences in Global Markets (Bespoke Invest)
Figure 5 shows that the Exchange Traded Funds (ETF) of various emerging markets, the natural gas, various treasuries funds and gold mining issues have failed to live up to the animated performances by their contemporaries.
As Bespoke Invest[18] notes,
It's not the emerging markets in one region of the world that are struggling either. ETFs that track Brazil, Latin America, China, India, and Asia Pacific are all below their 50-days. Typically when the US market is rallying, emerging markets are rallying even more. Bulls looking to outperform the S&P 500 have been using emerging market securities to do so for multiple years now. Recently, however, this strategy has been a performance killer.
As duly noted by Bespoke, past performance can’t be expected to deliver similar results.
And it should apply opposite ways.
Although such divergences may be construed or seen by some as decoupling, it isn’t. Asian and most of emerging markets have vastly outperformed in 2010, thus given that no trend goes in a straight line, today’s relative underperformance signify as a pause or natural correction process and is likely a temporary event.
Bottom line: Current developments represent as buying opportunities.
[1] Inquirer.net, Philippines posts record economic growth at 7.3%, January 31, 2011
[2] Financial Times Asia, Indonesian growth hits six-year high, February 7, 2011
[3] See Why The Greece Episode Means More Inflationism, February 15, 2010
[4] Bespoke Invest Where's the Flight to Safety? February 11, 2011
[5] Wikipedia.org, Étienne de la Boétie
[6] de la Boétie, Étienne The Politics Of Obedience: The Discourse Of Voluntary Servitude, Mises.org, p.47
[7] Telegraph.co.uk Ancient temple damaged by shell fire in Cambodia, February 7, 2011
[8] See Politics And Markets: Bangkok Burns Edition, May 20, 2010
[9] McKinsey Quarterly How inflation can destroy shareholder value, Winter 2010
[10] Wikipedia.org Inflation in Weimar Germany
[11] See Black Swan Problem: Not All Markets Are Down! November 11, 2008
[12] Tradingeconomics.com, Venezuela Indicators
[13] Wikipedia.org, Hyperinflation
[14] Fergusson Adam, When Money Dies: The Nightmare of the Weimar Collapse, p.78
[15] See Stock Market Prices: Inflation versus Corporate Fundamentals, February 8, 2011
[16] See Warren Buffett: Embracing Crony Capitalism, February 12, 2011
[17] See Phisix: Panicking Retail Investors Equals Buying Opportunity, January 31, 2010
[18] Bespoke Invest Emerging Markets Not Participating in Global Rally, February 10, 2011