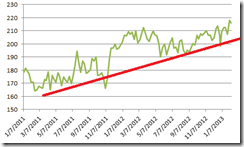
SIX consecutive weeks of gains backed by 11% in nominal local currency returns has simply been amazing!
The Phisix has now gone parabolic.
Deepening Mania Reflected on Market Internals
And equally incredible are claims that many have resorted to in defense of the current mania such as “many people are waiting for a correction to get in” and that “only Phisix heavyweights have been benefiting from the current run”. Sidestepping the issue will not help disprove the theory backed by evidences of the formative bubble which the Phisix seems to be transitioning into.
While “waiting for a correction” could be true for some people, and while indeed Phisix issues have been major beneficiaries from the current boom, how valid are these assertions from the general perspective?
The chart above accounts for the total or cumulative issues traded for the week divided by the number of trading days per week or the daily number of issues traded (averaged weekly).
This trend has been ascendant and could be at record levels. I have no comparative figures for the 1993 boom.
Yet such indicator suggests that the market have been looking and scouring for issues to bid up. This also means formerly illiquid issues are becoming tradeable. Today about 62% of the 344 issues[1] listed in the Philippine Stock Exchange are now being traded compared to about 50% in 2011.
How can we say that most of the growth in the number of issues traded has favored the bulls?
Well, the ratio of the advance-decline averaged on a weekly basis reveals of an increasing trend. The widening spread simply means that significantly more issues have been advancing than declining. Gains have been spreading.
The percentage share of listed companies within 10% of the 52-week highs could be a helpful indicator, but I don’t have a measure on this.
I may add that another sentiment indicator has been suggesting of the growing intensity of speculative activities: The number of trades.
The above represents the weekly cumulative trades divided by the number of trading days per week, which gives us the daily number of trades (averaged weekly).
The current boom has brought trading activities to the pedestal of the first quarter 2012.
The implication is that people have become more restive possibly signified by increasing frequency of account churning or short term trades.
Another is that retail investors have been jumping into the bandwagon.
It is simply naïve to believe that the prospects of easy money won’t lure the vulnerable.
People are social animals. Many fall for fads or faddish risk activities.
We have seen business fads in lechon manok, shawarma, pearl shakes and etc…, where at the end of the day either the more efficient ones become the major players at the expense of the marginal players or that the vogue theme fades (but not entirely). The difference is that business fashions have not translated to systemic issues. In short, they have not morphed into bubbles.
Fads are also why people have been drawn towards scams such as Ponzi schemes or pyramiding. The revelation of huge Ponzi scheme that hit the Southern Philippines late last year has been something I expected and had warned about[2].
People not only want to partake of newfound economic opportunities, importantly they see fads as opportunities to signal participation which translates to social acceptance channeled through talking points.
Anecdotal evidences suggests of a blossoming mania too.
A dear friend fortuitously dropped by an office which is proximate to an online trading office and told me that he saw about 200 people applying for online trading accounts. Of course, this may just be a coincidence or that it could be a symptom.
Additionally, I am asked by a close friend, who owns a manpower training agency to teach investing in the stock market to prospective retail participants. Lately, my friend says that they have been encountering increasing number of queries on this at their office. The last time I did so was about the same period in 2007. The rest is history.
Finally, the ongoing price level rotation dynamic has been prevailing. This has been validating my predictions consistently which also serves as concrete evidence to the inflationary boom.
While the property sector continues to dazzle, last year’s laggards led by the mining sector, as well as, the service sector seem to be reclaiming leadership. The domestic mining sector has been catapulted to the top anew, widening its lead relative the property sector.
On the other hand, the service industry, at third spot, appears to be closing in on the second ranked property sector.
Rotation also means relative price gains will spread from the core to the periphery. This is being confirmed by the number of issues traded and the advance decline ratio.
The bottom line is that market internals have been exhibiting broad based growth of risk appetite which has not been limited to Phisix issues.
Record levels of issues traded, the dominance of advancing issues, record high of number of trades, price level rotation among the industries, and the ongoing rotation from the core to periphery represent as symptoms of a flourishing manic phase in the Phisix.
While some may indeed be “waiting for correction to enter”, the bigger picture shows otherwise, retail participants have been piling onto the market’s ascent, churning of accounts seem to become more frequent and there appears to be increasing interests by the general public on the domestic stock market, all of which appears to reinforce general overconfidence.
A further help on this which I don’t have access to is the industry’s net margin to clients. Although I suspect that this has also been ballooning.
Mainstream Chorus: This Time is Different
Another set of incredulous claim has been that “local authorities have learned from their mistakes” and that “low interest rate policies are sound”
Let me put this in simple terms, business cycles exists not because of sheer patterns or mechanical responses or repetitious actions, but because social policies induce or shapes people incentives to commit errors in economic calculation that are ventilated on the markets and the economy.
Global financial crisis have become more frequent[3] (see grey bars) since the Nixon Shock[4] or when ex US President Nixon overhauled the world’s monetary system by closing the gold anchor of the Bretton Woods[5] or the “gold exchange standard” in August 15, 1971.
The intensification of international financial crisis reveals that contrary to the false notion that authorities have learned from their mistakes, policymakers have fallen for the curse of what philosopher, essayist and literary artist George Santayana said about the repetition of history[6]:
Progress, far from consisting in change, depends on retentiveness. When change is absolute there remains no being to improve and no direction is set for possible improvement: and when experience is not retained, as among savages, infancy is perpetual. Those who cannot remember the past are condemned to repeat it.
In short, policymakers hardly ever learn.
Additionally, if low interest rate policies are “sound” why stop at being low, why not simply abolish it altogether?
Unfortunately the war against interest rates has long been a political creed which has been masqueraded as an economic theory that has been embraced by interventionists.
As the great Professor Ludwig von Mises warned[7],
Public opinion is prone to see in interest nothing but a merely institutional obstacle to the expansion of production. It does not realize that the discount of future goods as against present goods is a necessary and eternal category of human action and cannot be abolished by bank manipulation. In the eyes of cranks and demagogues, interest is a product of the sinister machinations of rugged exploiters. The age-old disapprobation of interest has been fully revived by modern interventionism. It clings to the dogma that it is one of the foremost duties of good government to lower the rate of interest as far as possible or to abolish it altogether. All present-day governments are fanatically committed to an easy money policy.
Indeed today, such doctrine has been adapted as the standard operating tool used by political authorities in addressing economic or financial recessions or crises.
The policy of lowering of interest rates appears to have almost been concerted and synchronized. As I pointed out at the start of the year[8], more than half of the world’s central banks have cut rates in 2012. Developed economies have appended zero bound rates with radical balance sheet expansion measures.
In January of 2013, of the 41 central banks that made policy decisions, 9 central banks cut interest rates while 30 were unchanged[9].
Unfortunately, credit expansion from low interest rates meant to foster permanent quasi booms only results to either boom-bust cycles (financial crisis) or a currency collapse (hyperinflation).
Again the great Mises[10]
The wavelike movement affecting the economic system, the recurrence of periods of boom which are followed by periods of depression, is the unavoidable outcome of the attempts, repeated again and again, to lower the gross market rate of interest by means of credit expansion. There is no means of avoiding the final collapse of a boom brought about by credit expansion. The alternative is only whether the crisis should come sooner as the result of a voluntary abandonment of further credit expansion, or later as a final and total catastrophe of the currency system involved.
The basic reason why interest rates can’t be kept low forever is simply because of the changing balance of demand and supply for credit. There could be other factors too, such as inflation expectations, state of the quality of credit and availability and or access to savings.
In a credit driven boom, where demand for credit rises more relative to supply, the result would be to raise price levels of interest rates
As German banker, economist and professor L. Albert Hahn[11] explained[12],
Interest rates cannot be held down in the long run, for interest rates rise because higher prices demand greater amounts of credit.
If larger amounts of credit are created through the progressive increase of money, i.e., by the printing press, the process ends in a hopeless depreciation of the currency, in terms of both domestic goods and foreign exchange.
In other words, manipulation of interest rates means that inflationary booms are temporary and will translate to an eventual bust, which is hardly about “sound” economic theories.
So when people argue from the premise of extrapolating future outcomes solely based from past performances, they are essentially seduced by the “outcome bias” and similarly fall prey to “flawed perception” trap—based on the reflexivity theory. The latter means that many tend to create their own versions of reality by misreading price signals. Yet such arguments are in reality based on heuristics and cognitive biases rather than from economics.
Bubble cycles are not just about irrational pricing of securities, but rather bubble cycles represent the market process in response to social policies where irrationalities are fueled or shaped by credit expansion accompanied or supported by faddish themes.
While I don’t believe that we have reached the inflection point, manifestations of the transition towards a mania, not only in the Philippines but elsewhere, are being reinforced through various aspects as.
And one of the strongest signs hails from the four deadliest words of investing according to the late investing legend John Templeton “This Time is Different” as above.
Moreover, there are many ways to skin a cat as they say. One way to chase for yields by increasing access to credit has been to launder quality of collateral via collateral swaps.
This has been best captured from the recent speech by the speech of US Federal Reserve governor Dr. Jeremy C. Stein which he calls as collateral transformation[13].
Collateral transformation is best explained with an example. Imagine an insurance company that wants to engage in a derivatives transaction. To do so, it is required to post collateral with a clearinghouse, and, because the clearinghouse has high standards, the collateral must be "pristine"--that is, it has to be in the form of Treasury securities. However, the insurance company doesn't have any unencumbered Treasury securities available--all it has in unencumbered form are some junk bonds. Here is where the collateral swap comes in. The insurance company might approach a broker-dealer and engage in what is effectively a two-way repo transaction, whereby it gives the dealer its junk bonds as collateral, borrows the Treasury securities, and agrees to unwind the transaction at some point in the future. Now the insurance company can go ahead and pledge the borrowed Treasury securities as collateral for its derivatives trade.
Of course, the dealer may not have the spare Treasury securities on hand, and so, to obtain them, it may have to engage in the mirror-image transaction with a third party that does--say, a pension fund. Thus, the dealer would, in a second leg, use the junk bonds as collateral to borrow Treasury securities from the pension fund. And why would the pension fund see this transaction as beneficial? Tying back to the theme of reaching for yield, perhaps it is looking to goose its reported returns with the securities-lending income without changing the holdings it reports on its balance sheet.
So markets are looking at innovative ways to arbitrage on the incumbent regulations.
Also when celebrities such as 16 year old Desperate Housewives star Rachel Fox preaches about stock market investing by bragging about how she earned 64% last year[14], these again signify signs of overconfidence. This reminds me of the “basura queen” in 2007[15] who swaggered in a local TV news program how she made millions betting on third tier issues. Ironically that program was shown at the zenith of the pre-Lehman boom
Yet every blowoff phase simply posits that accelerating gains in asset prices will only whet on the public and financial institution’s enthusiasm to expand and absorb more credit or to increase leverage in the system. Such phase would also magnify systemic fragility and vulnerability to internal or external shocks that eventually will be transmitted through higher interest rates.
Emerging markets, like China and the ASEAN, cushioned the global economy and markets from the 2007-2008 US mortgage-housing-banking crisis; a crisis that eventually spread to the Eurozone that still lingers on today.
Yet the difference then and today is; as the crisis stricken nations have hardly recovered, as manifested by the accelerating bulge in the balance sheets of major central banks, emerging markets like the Philippines[16], Thailand[17], India, China[18] and many more have been blowing their respective domestic bubbles. For instance, reports say that bad debts in India are headed for a decade high[19]
And should another crisis resurface, which is likely to have a ripple effect across the world and equally prick homegrown bubbles, then it would be possible that even emerging markets will embark on similar frenetic balance sheet expansion programs. And this will run in combination with developed economies whose easing programs are even likely to intensify.
When most central banks run wild, the return to the current RISK ON environment will not be guaranteed. Instead I expect more of a cross between stagflation and volatilities from bursting bubbles.
Yet one thing seems clear; whatever tranquility we are seeing today looks fleeting.
Yellow Flag: Rising US Interest Rates May Impact the Phisix Mania
The Philippine Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas reported that price inflation rose by 3% in January from 2.9% last year[20].
Although my neighborhood sari-sari store’s beer which rose by 9.5% in November 2012 (from Php 21 to Php 23), has risen again this weekend from (Php 23 to Php 24) or by 4.34%. I believe that the current rise may have partly been due to the implementation of the “sin taxes”.
Yet I don’t see how statistical inflation has been reflecting on reality.
Bond markets of ASEAN majors looks placid. The yield of Thailand’s 10 year government bond (topmost) has risen from the lowest point in 2010 but remains rangebound. This seems in contrast to her contemporaries Indonesia (middle) and the Philippines (lower pane) whose yields have been trading at the lows. Chart from tradingeconomics.com
Nonetheless the level of bond yields so far resonates with how the market accepts statistical inflation. And such has been supportive of the ASEAN equity outperformance.
But events have been changing at the margins.
The firming boom in the stock markets and in the property sector in the US appears to be pressuring interest rates upwards.
The iShare Barclays 20+ Year Treasury Bond Fund (TLT) continues to flounder. The same goes with the iShares Barclays MBS Fixed-Rate Bond Fund (MBB), a benchmark for mortgage bond ETF, the SPDR Barclays High Yield Bond ETF (JNK), a benchmark for high yield high risks corporate bonds and even the iShares JPMorgan USD Emerging Market Bond Fund (EMB) have recently dropped[21].
Sinking bond funds only signify rising interest rates.
Reflation in the US property has become evident during the last quarter[22]. And considering that rents have accounted for as the biggest weight in the US CPI basket, it would not be a surprise if price inflation ticks higher if not makes a surprise jump[23]
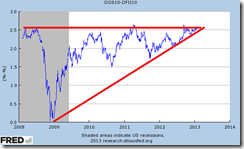
Part of this seems to have already been building up through resurgent inflation expectations as shown by the US 10 year constant maturity (DGS10) minus the 10 year inflation indexed security (DFII10).
As I have been pointing out, if inflation expectations continue to rise and breakout from the triangle, then the US Federal Reserve will be caught in a big predicament of their own making.
Many have begun to notice them too. The number of bond bears appears to be growing.
Investing savant George Soros predicts a spike in US interest rates this year[24]. Another investing guru Jim Rogers recently chimed with bond sage PIMCO’s Bill Gross[25] in warning of a possible bond market rout.
Pardon my appeal to authority but rising interest rates are unintended consequences or a backlash to the Fed’s policies which all of them recognizes.
And a sustained increase in interest rates will also pose as a threat to the overleveraged US political economy that will unmask many of the malinvestments, as well as, asset bubbles that may even force the FED to accelerate on her balance sheet expansion
Rising US interest rates could impact also Philippine asset prices.
As indicated by the above charts from Reuters[26], sensitivity of emerging markets to US treasuries has materially increased, as measured by the proportion of the yield of 10 year US Treasuries relative to her Emerging Market counterpart.
The risk is that the narrowing of spreads reduces the attractiveness of emerging market assets that may induce outflows. Of course not everything is about arbitraging spreads.
And as stated above, credit booms will alter the balance of demand and supply of credit which will be reflected on interest rates, which is what rising interest rates in the US has been about.
I still believe that unless there should be an abrupt move via a spike interest rates in the US markets, creeping rates will hardly be a factor yet for Philippine asset markets during the first quarter of 2013.
This means that I expect the Phisix to remain strong until at least the end of the first quarter. Although we should expect the much needed intermittent pullbacks.
Rising Rates In Crisis Europe: Credit Risks or ECB Balance Sheet Shrinkage?
Rising interest rates could also mean concerns over credit standings or credit quality.
Are increasing rates of 10 year government bonds of Portugal (GSPT10YR:IND ; orange), Italy (GBTPGR10:IND; red) and Spain (GSPG10YR:IND, green) evincing recovery? Or has the effects of the stimulus been receding, where markets are beginning to reappraise credit risks? I am inclined to see the latter.
Or could rising rates have been representative of the recent contraction of the balance sheet of the European Central Bank[27] (ECB) which recently shrank to an 11 month low? Could gold’s suppressed activities been also due to this?
A revival of the euro crisis will likely lead to the activation of the unused Outright Monetary Transaction (OMT[28]) and the reversal of the current balance sheet shrinkage.
Since markets have essentially been a feedback loop or a Ping-Pong between market responses and the subsequent reactions from political authorities, it is necessary to observe the evolution of events.
It’s hard to view the long term when markets operate within the palm of political authorities led by central bankers.
[21] Mike Larson Bond Forecasts Coming True — in Aces and Spades! Are You Protected?, MoneyandMarkets.com February 8, 2013