I can already smell QE3. Now we'll see if Mr. Bernanke is a true money printer or an amateur money printer. If he is a true money printer, he's going to start printing soon, markets will rally but not to new highs-Dr. Marc Faber
Important: The US has been downgraded by the major credit rating agency S&P after the market closed last Friday[1], so there could be an extended volatility on the global marketplace at the start of the week. This largely depends if such actions has already been discounted. The first thing on Monday is to watch Japan’s response.
Nevertheless given the actions of the US markets last Friday, where rumors of the downgrade had already circulated[2], there hardly has been any noteworthy action which presages more trouble ahead.
At the start of the week, the mainstream attributed the weakness in the US markets as a function of the risk of a debt default. This, according to them, should arise if a debt ceiling deal would not be reached.
I argued that this hasn’t been so[3], for the simple reason that market signals has been saying otherwise.
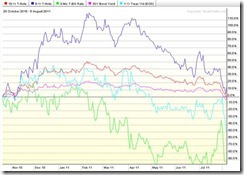
A credit rating downgrade means higher costs of financing or securing loans and a possible rebalancing of the balance sheets of the banking system to comply with capital adequacy regulations.
The chart above shows that short term yields initially spiked (1 year note light blue and 3 month bill-light green) during the 11th hour of the negotiations. But once the debt ceiling deal was reached and the bill was passed, interest rates across the yield curve converged as they fell along with prices of Credit Default Swap.
Instead I pointed to the deteriorating events in Europe as a possible aggravating factor on US markets.
Impact of Downgrades
There are two basic ways to measure credit risks. One is the interest rate, the other is through credit default swaps (CDS) which fundamentally acts as a form of insurance against a default.
It is misleading to think that downgrades drive the marketplace as some popular personalities as my former icon Warren Buffett recently asserted[4]
Financial markets create their own dynamics, but I don’t think we’re facing a double dip recession…Clearly what stock markets do have is an effect on confidence, and this selloff can create a lack of confidence.
Mr. Buffett has gotten the causality in reverse. Downgrades happen when market forces—popularly known as the bond vigilantes[5] or bond market investors protest current fiscal or monetary policies respond by selling bonds—has already been articulating them.
US CDS prices have steadily been creeping upwards[6], this has been indicative of marketplace’s perception of the festering credit conditions by the US. The problem isn’t that “selloff can create a lack of confidence”, but rather too much debt, which is the reason for the downgrade, has been fostering an atmosphere of heightened uncertainty.
Downgrades signify as a time lagged acknowledgement by social institutions of an extant underlying ailment being vented on the markets.
The fact is that 3 credit rating agencies have already downgraded the US[7].
Also downgrades as said above affect financial institutions more, not only because of higher costs of funds but also because of the compliance to capital adequacy regulations.
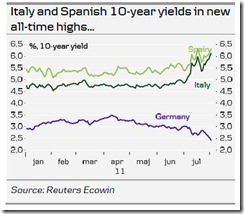
A fundamental picture of an ongoing market based downside rerating is the unraveling crisis in the Eurozone.
The escalating PIIGS crisis has been causing a panic on Spain and Italian bonds, whose interest yields have been spiking[8] and where European investors can be seen stampeding into Germany’s debt or the Swiss franc.
So how has Europe responded? In mechanical fashion, by inflationism.
Supposedly wrangling politicians/bureaucrats found a common cause or conciliatory ground to work on. The European Central Bank (ECB) commenced with its version of Quantitative Easing (asset purchases) initially buying Irish and Portuguese bonds[9], which the equity markets apparently ignored and continued to tumble.
The ECB now has promised to extend buying Italian and Spanish bonds, this coming week, in order to calm the markets[10].

The Swiss National Bank[11] has gotten into the act ahead of the ECB, by surprising the currency markets with an intervention allegedly meant to control a surging franc. I think that they were flooding liquidity for the benefit banks, with the currency as an excuse for such action.
The Swiss intervention, which has been estimated at CHF 30 billion ($39 billion) to CHF 80 billion[12], by expanding the monetary base, appears as having fallen short of achieving its declared currency goal (see right window). The franc trades at the levels where the SNB initiated the intervention. The result seems as $39 billion down the sink hole.
Japan has likewise followed the Central Bank money printing shindig by engaging in her own currency intervention, allegedly aimed at curbing the rise of the Yen. The Bank of Japan (BoJ) reportedly intervened with a record high amount in the range of $56.6 to $59.26 billion[13]

Total cumulative size of Japan’s QE has now reached 46 trillion yen[14] (US $627 billion)
Hence, the European debt crisis partly explains the recent global market crash.
And importantly the above dynamic demonstrates how central banks respond to a market distress or a mark down in credit standings.
As an aside, one would further note that since central banks of Japan, Eurozone and the Switzerland has now been funneling enormous liquidity into the system, all these funds will have to flow somewhere.
The same dynamics should be expected with the US, where a credit rerating would not only impair US government debt risk profile and the attendant higher costs of financing, but also debt of government sponsored agencies, municipal liabilities and corporate bonds who thrive on subsidies, guarantees, bailouts or other form of parasitical relationship to the US government.
Since many of these securities comprise asset holdings major financial institutions, a US downgrade also means downgrades for US banks, insurance companies and credit unions.

Martin Weiss of Weiss Ratings estimates that a staggering $6.3 trillion of securities constituting of government agency securities $2.2 trillion, $725 billion in municipal bonds and $2.9 trillion in corporate and foreign bonds are subject to immediate or future downgrades in the wake of a U.S. government debt downgrade[15]. This represents one-third of all the financial assets of all US financial institutions
So given the operating manual or basic procedure of central banks in treating downgrades, the S&P action essentially paves way for the next US Federal Reserve’s asset purchasing moves.
Thus, a downgrade on the US is essentially a downgrade on the US dollar.
[Funny how local investors continue to believe in the US dollar as safehaven, when the fundamental problem has been the US dollar!]
Current Environment Seems Ripe for QE 3.0
It’s been a long time theme for me in saying that part of the process to set up interventions has been through what central bankers call as the signaling channel[16].
The fundamental aim is to manipulate the public’s expectations in order to justify prospective policies, usually meant for inflation expectations management.
Over the May-June window, there had been extensive interventions in the commodity markets (raised credit restrictions sharply on various commodity markets, IEA’s release of strategic oil reserves[17] and the ban on OTC trades[18]) and in the debt and equity markets (via restrictions of short selling[19] and proscriptions on US asset sales by US residents through overseas markets[20]) which appears to have been designed as price controls.
This came amidst a spike in academic and research papers which tried to dissociate the Fed’s previous QEs with surges in commodity prices.
The process of interventions as I previously wrote[21],
First is to apply the necessary interventions on the market to create a scenario that would justify further interventions.
Second is to produce papers to help convince the public of the necessity of interventions.
Then lastly, when the 'dire' scenario happens, apply the next intervention tools.
As one can see, signaling channel has also been used to in the political context.
Similar to last week’s haggling for the US debt ceiling deal by two supposedly ‘opposing’ political parties, negotiations appears to have been leveraged or anchored on an Armageddon scenario from a debt default, if a deal had not been reached at the nick of time.
Channeling Mencken’s hobgoblins, fear had essentially been used as lever to reach an 11th hour deal which means ramming down the throats of the Americans. The debt ceiling bill was predicated on what I called as legal skulduggery or prestidigitation[22] as government spending cuts were all based on promises (baseline projections rather than actual cuts)
Now that the debt ceiling bill has been passed, such jawboning appears to have morphed into a self-fulfilling prophesy. Markets went into a spasm.
This brings us to the core of what I think has been the epicenter of last week’s crisis.

The US equity market, represented by the S&P has been mostly buttressed by the money printing by the US Federal Reserve as shown from the chart from Casey Research[23].
One would note that in the above chart, an almost comparable decline occurred during the five month window since the Fed completed its QE 1.0 on March 2010.
The timeline for QE 1.0 is officially from March 2009 to March 2010, and QE 2.0 from November 2010 to June 2011.[24]
The difference between the actions of the US equities in post-QE 1.0 and post-QE 2.0 has been one of scale and speed.

Global equities functioned in the same manner too.
The closure of QE 1.0 (blue horizontal lines) saw an across the board decline and consolidation phase by global equity markets represented by world (FTSE All World FAW), Europe (STOX50), Asia (P1DOW) and Emerging Markets (EEM)—all marked by red ellipses. These had been reversed once the QE 2.0 was announced and implemented.
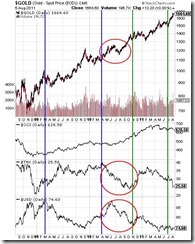
Importantly, during that post-QE 1.0 lull window (QE 1.0 blue horizontal lines; QE 2.0 green horizontal line) marked again by the red ellipses, the US dollar surged (USD), gold consolidated, US treasury yields (TNX) had been on a decline while commodities (CCI) likewise had been rangebound.
Today, post-QE 2.0, we see some important difference and similarities. Similar to the post-QE 1.0 environment, global-US equity markets have been under selling pressure as US treasury yields have been on a decline along with the commodity markets.
The difference is that the US dollar remains WEAK and has NOT generally functioned as the previous shock absorber during market stresses or during the post-QE 1.0.
Importantly gold continues to surge!
My point is: this episode of market turbulence seems like a contraption to the next asset purchasing measures by the US Federal Reserve or QE 3.0 (or in whatever name the Fed wishes to call it).
In other words, like the debt ceiling deal of last week, a crisis scenario has been put in place meant to justify the next round of interventions. And this reminds me of the shocking and revolting comment by Emmanuel Rahm, US President Obama’s former chief of staff which seem to resonate strongly today[25],
You never let a serious crisis go to waste. And what I mean by that it's an opportunity to do things you think you could not do before.
With the US debt ceiling bill in place, the unraveling debt crisis in the Eurozone, an “alleged” risk of a sharp world economic growth slowdown or recession (I say alleged because I am not a believer), global equity market in turmoil, plus coordinated interventions by the central banks of Swiss, Japan and the ECB, pieces of the puzzles have been falling into place, as I have previously argued[26], which seem to pave way for Ben Bernanke and the US Federal Reserve to reengage in the next asset purchasing program.
And coincidentally the US Federal Reserve’s FOMC (Federal Open Market Committee) has been slated to meet on August 9th Tuesday (Wednesday Philippine Time)[27]. And given the current turn of events, we should expect announcements that should reinforce a stronger policy response.
Public Choice and Possible Incentives Guiding Team Ben Bernanke
It’s fundamentally nonsensical to say that team Bernanke won’t engage in QE simply because of the futility or of the inefficacies of the previous QEs programs.
People who say this either fictionalize the role of individuals working for the governments or naively think that political operators operate on the basis of collective interests.
Public choice theory tells us that bureaucrats, like Ben Berrnanke, are equally self interested individuals. This means that since they are not driven by the incentives of profit and losses, the guiding principles of their actions are usually based on the need to preserve or expand their political careers (tenureship) by serving their political masters or by making populists decisions.
Besides, who would like to see a market crash with them on the helm, and not be seen as “doing something”? Today’s politics, embodied by the Emmanuel Rahm doctrine has mostly been about the need to be seen “doing something” even if such actions entail having adverse long term consequences. Actions by the ECB, SNB and BoJ have all revealed and exemplified such tendencies. Even the debt ceiling bill was forged from the need to do something to avert an Armageddon charade.
Moreover, political operators are also most likely to desire acquiring prestige and social clout by virtue of having expanded political control over the economy under the guise of social weal. That’s why more and more regulations are being imposed on the belief that a command and control economy would be more effective than one of free markets. Never mind the experience of Mao’s China and the USSR. Socialist champion billionaire and philanthropist George Soros got a taste of his own medicine when the Dodd Frank law compelled him to close his 40-year hedge fund[28].
Public choice also tells us that the political operators have beholden to vested interest groups such as the banking sector. The US Federal Reserve has thrown tens of trillions of dollars to save both US[29] and foreign[30] based banks. This accounts for as demonstrated preference or deciphering priorities from action over words.
Moreover, since their careers have been erected on the incumbent institutions, why should they enforce radical reforms that would only jeopardize their career or the institution’s existence, whom their allegiance have been impliedly sworn to?
To add, some policymakers operate on the ideological principles such as the theory of wealth effect, where increases in spending that accompanies an increase in perceived wealth[31]. From such pedagogical belief emanates the trend of ‘demand management’ based policy actions.
Take for instance, Ben Bernanke’s chief dogma “Crash course for central bankers” which he wrote as a Princeton Professor[32].
There’s no denying that a collapse in stock prices today would pose serious macroeconomic challenges for the United States. Consumer spending would slow, and the U.S. economy would become less of a magnet for foreign investors. Economic growth, which in any case has recently been at unsustainable levels, would decline somewhat. History proves, however, that a smart central bank can protect the economy and the financial sector from the nastier side effects of a stock market collapse.
Today, most of the central bankers seem to adhere to such principles.
So even if previous QEs didn’t work as planned, what will stop Mr. Bernanke from pursuing the same policies and expecting different results? All he has to do is to assume the academic stance of saying the past policies didn’t work because they have not been enough.
So while I don’t know what’s going on in Team Bernanke’s mind, personal incentives, path dependency and dogmatism all point to QE 3.0 pretty soon.
Political Actions over Economic Data and Technical Picture
Lastly the US economic picture can be seen positively or negatively depending on one’s bias, but in my view, I hardly see the imminence of recession.

In the US, ISM Manufacturing index[33] has fallen steeply but this has not yet gone beyond the 50 threshold which could be an indicator of a recession. Offsetting this view is that recession probability from the yield curve has been very low[34].
Of course looking at economic figures are based on the past (ex post) activities. Since today’s markets have been driven by political actions such as QEs, then past data wouldn’t weigh so much compared to the anticipatory (ex ante) policy directives by central bankers.
Yet the problem with today’s conventional mindset has been that of the chronic addiction to rising prices of anything, be it economic data or asset prices. Anything that falls translates to the necessity or call to action for government intervention.
So false signals can be used as basis to demand political actions.
Nevertheless I also think that technical factors did play a secondary role in last week’s US market crash.

The S&P has been on a bearish head and shoulder pattern.
Given the current market milieu, technically based market participants jumped into the bearish momentum from which this pattern became another self-fulfilled reality.
The pattern basically aggravated the current environment rather than having caused it.
Bottom line:
If the US Federal announces a major policy stimulus anytime soon, then this should be seen as a strong signal to buy both commodities or on ASEAN equity markets and the Phisix.
Otherwise, we should expect more downside market volatility and probably take some money off the table.
Again, profit from political folly.
[1] See NO Such Thing as Risk Free: S&P Downgrades US August 6, 2011
[2] Telegraph.co.uk Debt crisis: as it happened, August 5, 2011
[3] See Today’s Market Slump Has NOT Been About US Downgrades, August 3, 2011
[4] Bloomberg.com S&P Erred in Cutting U.S. Rating: Buffett, August 7, 2011
[5] Wikipedia.org Bond Vigilante
[6] See Graphic: US Default Risk—Short and Long Term, August 2, 2011
[7] See How the US Debt Ceiling Crisis Affects Global Financial Markets, July 31, 2011
[8] Danske Bank Mr. Trichet will ECB buy Italy? ECB Preview August 4, 2011
[9] See ECB Intervenes in Bond Markets, More to Follow, August 5, 2011
[10] See ECB Expands QE: Will Buy Italian and Spanish Bonds, August 6, 2011
[11] See Hot: Swiss National Bank Intervenes to Halt a Surging Franc August 3, 2011
[12] Marketwatch.com Swiss central bank battles to halt franc’s rise August 3, 2011
[13] CNBC.com Japan Sells Record $58 Billion in FX Intervention, August 5, 2011
[14] Danske Bank Japan: BoJ tries to draw a line in the sand, August 4, 2011
[15] Weiss Martin, Day of Reckoning! TOMORROW!, August 1, 2011, Moneyandmarkets.com
[16] See War on Precious Metals: The Rationalization Process For QE 3.0, May 7, 2011
[17] See War on Commodities: IEA Intervenes by Releasing Oil Reserves, June 24, 2011
[18] See War on Gold and Commodities: Ban of OTC Trades and ‘Conflict Gold’, June 18, 2011
[19] See War on Speculators: Restricting Short Sales on Sovereign Debt and Equities, May 18, 2011
[20] See US Government’s War on US Expats and American Investments Overseas, June 21, 2011
[21] See War on Precious Metals Continues: Silver Margins Raised 5 times in 2 weeks!, May 5, 2011
[22] See Debt Ceiling Bill: Where are the Spending Cuts?, August 2, 2011
[23] Casey Research Too Much of a Good Thing
[24] Ricketts Lowell R. Quantitative Easing Explained Liber 8 Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis, April 2011
[25] Wall Street Journal In Crisis, Opportunity for Obama, November 21, 2008
[26] See Poker Bluff: No Quantitative Easing 3.0?, June 5, 2011
[27] Mam.Econoday.com FOMC Meeting Announcement 2011 Economic Calendar
[28] See George Soros on Closing Hedge Fund: Do As I Say, Not What I Do, July 27, 2011
[29] See US Taxpayers Could Be On The Hook For $23.7 Trillion!, July 21, 2009
[30] See Fed Audit Reveals US Federal Reserves’ $16 Trillion Bailouts of Foreign Banks, July 26, 2011
[31] Wikipedia.org Wealth effect
[32] See The US Stock Markets As Target of US Federal Reserve Policies, May 11, 2011
[33] Harding Jeff, Destruction of Capital Resulting in Global Manufacturing Slowdown, Minyanville.com August 2, 2011
[34] Moneyshow.com A Red Flag for Emerging Markets... and the US, Minyanville.com August 4, 2011