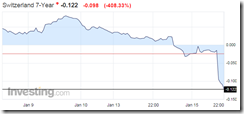
More on Swiss National Bank’s pulling the plug on the franc-euro cap which I posted Thursday.
Recently, divergences between the monetary policies of the major currency areas have increased significantly – a trend that is likely to become even more pronounced. The euro has depreciated substantially against the US dollar and this, in turn, has caused the Swiss franc to weaken against the US dollar. In these circumstances, the SNB has concluded that enforcing and maintaining the minimum exchange rate for the Swiss franc against the euro is no longer justified.
-FXCM Inc., the biggest retail foreign-exchange broker in the U.S. and Asia, said in a statement that because of unprecedented volatility in the euro against the Swiss franc, clients’ losses left them owing it about $225 million and that it was trying to shore up its capital.
-In the U.K., retail broker Alpari Ltd. entered insolvency after racking up losses amid the currency turmoil following the SNB’s decision.
-Global Brokers NZ Ltd., which is registered in New Zealand, said it would close its doors as it could no longer meet regulatory minimum-capitalization requirements of 1 million New Zealand dollars ($782,500). The firm is connected to online currency trading websites Cashback Forex, Forex Razor and Excel Markets and appears to be owned by entities in the British Virgin Islands.
-Japan’s Finance Ministry was checking on trading firms Friday after industry sources said the country’s army of mom-and-pop foreign exchange traders suffered big losses.

Oh by the way, Swiss stocks which collapsed 8.97% on Thursday, had a follow on 5.96% meltdown on Friday. For two days the SMI has lost 14.93%!
Stock market crashes and sharp financial volatility have become real time events!
The Swiss equity bellwether has apparently diverged from many other European stocks where the latter has rallied strongly. Last week’s stock market bids have largely been anchored on next week’s highly anticipated full scale QE from the ECB.
Nonetheless here are some interesting commentaries from various experts.
Austrian economist Patrick Barron at the Mises Canada Blog says that Switzerland has implicitly abandoned the European Monetary Union (bold mine)
Oh. You didn’t know that Switzerland was part of the European Monetary Union? You thought that the Swiss used their own currency, the Swiss franc? In a definitional sense only, you are correct. Within its monopolized currency area, the political boundaries of Switzerland, the Swiss franc is legal tender. But for approximately three years the Swiss National Bank has maintained a Swiss franc to euro ratio of 1.2 francs per euro. The usual suspects, exporters, were the driving political force behind the SNB’s policy. They feared fewer sales to eurozone countries should the franc cost more in euro terms. This policy made the European Central Bank (ECB) the determinant of monetary policy in Switzerland and relegated the Swiss National Bank to the mechanical role of currency board. When the Swiss franc started to appreciate against the euro, meaning that buyers were willing to accept fewer than 1.2 francs per euro, the Swiss National Bank printed francs and bought euros. Over the last three years as demand for Swiss francs from euro holders increased, the SNB’s balance sheet exploded with new euro reserves. However, as the world now knows, in a surprise move the SNB abandoned its currency peg policy. Today the franc exchanges approximately one for one with the euro, meaning that the franc has appreciated by approximately twenty percent against the euro.
As far as I know the SNB has made no official announcement of the reason for its surprise move. I suspect that the Swiss people had made themselves heard that they feared inflation from the ECB’s imminent quantitative easing policy. The Swiss gold referendum on November 30 would have required their central bank to hold a fixed percent of reserves in the form of gold. It was defeated only after the major political parties and the SNB amounted a concerted anti-referendum blitz. Still in control of their own currency, it was a relatively simple matter for Switzerland, in effect, to veto the ECB’s proposed policy by abandoning the currency peg. This shows the rest of Europe that at least one nation does not fear returning to full control of its currency nor does it fear the consequences of a temporary drop in exports. (The drop will be temporary, because Swiss import prices will fall and eurozone users will be awash with depreciated euros and willing to pay more for the Swiss franc.)
The lesson is clear. If Switzerland can retake control of its money, so can any eurozone nation. The process may take longer, as the country reissues is own currency and re-denominates its bank accounts in local currency terms, but it can be done. Already there are reports that the Danish central bank is contemplating abandoning its currency peg of approximately 7.5 krone per euro. If the sky does not fall on Switzerland and Denmark, other nations may follow. Does anyone know how to say deutsche mark?

Austrian economist Frank Hollenbeck at the Mises Institute notes that the surprise SNB action has been intended to shield Swiss political economy from ECB’s forthcoming irresponsible actions (emphasis added)
In theory, the Swiss could have held the floor. To keep your currency from appreciating, all you need to do is print, print print. Of course, this printing is not without consequences. With this bold move, the Swiss have crossed the Rubicon. They cannot go back. They have in dicated to speculators there is a pain threshold, or monetary expansion, that the Swiss are not willing to bear. Any attempt to set a new floor would set up a one way bet for speculators.
By pegging your currency to that of a bigger neighbor, you are essentially letting your neighbor determine your monetary policy. Dubai fixed its currency, the dirham, to the dollar and imported the US’s excessive monetary policy which led to the same real estate bubble in Dubai as the bubble in the US. In other words, by fixing your currency, you have to follow your bigger neighbor’s irresponsible monetary policy.
With the increasing likelihood that the European Central Bank would violate the Maastricht treaty and purchase sovereign debt, the Swiss finally decided they had had enough. The talk now is that the ECB will purchase over a trillion euros worth of bonds. To keep the peg, the Swiss would have had to increase the money supply by the same percentage, which would have been irresponsible monetary policy for such a small country.
By letting the peg go, Switzerland did the right thing. It should now concentrate on eliminating most EU debt from its balance sheet. There is an EU storm brewing, and Switzerland will no longer be one of the innocent bystanders.
In an interview, American entrepreneur and financial commentator Peter Schiff said that the SNB has been the first central bank to "surrender" or to back away from them global ‘currency war’.
“First of all, it’s not just the euro that collapsed. The US dollar collapsed almost as much. I think it was the right thing to do. I think it was a mistake for the Swiss to have adopted that peg in the first place. In fact, by abandoning the peg, they’re admitting it was a mistake, because now the Swiss franc has appreciated anyway, which was something the peg was designed to prevent. Now the Swiss National Bank has tens of billions of francs worth of losses on a 500 billion plus cash of euros and dollars that they’ve accumulated to defend that ridiculous peg. Of course, had they not ended it, the losses would have mounted. If Europe launches QE, they could have lost hundreds of billions of francs…
“Central bankers rarely admit their mistakes. What’s changed? It’s not necessary because it didn’t work. It was never necessary. They probably have a much greater supply now of euros and dollars on their balance sheet than they bargained for. The prospect of having to back up the toboggans and fill them full of euros was very daunting. So they abandoned this peg, thankfully for the Swiss… Swiss people are going to benefit. Look at the drop of oil prices in terms of Swiss francs. Prices are going to come down and the Swiss are going to be that much more prosperous because of a stronger franc…
“I think that is a mistake. I don’t think they need negative interest rates. I think that is taking some of the luster off of the franc. It would be even stronger had they not done that. But a strong currency is not a bad thing. A weak currency is a bad thing. Switzerland should take pride in the strength of its currency. Now they have to deal with the losses by trying to prevent it from rising. Of course, there have been some economic mistakes made in Switzerland and elsewhere, because of this monetary policy, that now have to be corrected. Unfortunately, these were needless mistakes that didn’t have to be made. I think a lot of people are now jumping to the conclusion that Europe is going to do a big QE program, and that’s why the Swiss are backing away. Without the Swiss, I think it makes it that much more difficult for Europe to do QE. So maybe they’re not going to be able to do it, because they no longer have the Swiss to support their currency. Maybe they’ll do some more substantive economic reforms instead. That would be a positive for Europe. I think that it could mean the US is the last central bank standing with QE, because I think we’re going to be doing QE4…
“I think that you’re going to see a complete breakdown in the confidence that people have for central banking over the next several years. The Swiss were saying, ‘Over my dead body. We will defend this peg to eternity.’ Then they went around and they didn’t do it. Of course, that’s generally what central banks do. They have to deny, deny, right up until the point where they do what they were denying they were going to do. I think you have a lot of confidence and trust and faith in central bankers. I think that bubble in central bank confidence is going to burst, is going to be shattered. Particularly when it comes to the confidence people have in the Federal Reserve and in Janet Yellen, because they’ve been talking about how great the US economy is. To anyone who has been payingattention to the statistics, this mirage of a recovery, this illusion is fading fast. I think instead of the promised recovery that Janet Yellen has been talking about, we’re going to have a relapse to recession. Instead of rate hikes, we’re going to have QE4. That’s going to be the end of their credibility…
We see the same concerns even in the mainstream.
The stock market bullish fund manager David R. Kotok chairman of Cumberland Advisors Chairman suddenly seems skittish: (bold mine)
Markets can handle good news, and they can handle bad news. Markets have trouble, however, with uncertainty. The pressure on stock markets and the volatility that has spiked due to the SNB’s move are the results of rising uncertainty about the foreign-currency-denominated debt and abrupt changes in central bank policy.
The Swiss have punched new holes in their cheese. They have boiled their chocolate so that it smells bad. They committed to a course, reversed themselves, and have now lost their credibility. This is the second governor of the Swiss central bank who has suffered a loss of credibility. The first one had to resign because a member of his household was allegedly trading a foreign currency position against the euro peg. The second governor has derailed billions in loans and pressured his citizens through his unexpected policy change.
When one central bank loses its credibility, all central banks suffer. The burdens on the Federal Reserve, the European Central Bank, the Bank of Japan, the Bank of England, and others have now intensified.
Finally, chief advisor to Allianz and economic commentator and author Mohamed El Erian, writing at the Financial Times says that the SNB’s actions looks like signs of widening cracks on the central bank induced low volatility environment: (bold added)
The implications of this historic policy turnround extend well beyond a period of bumpy economic and financial adjustment for Switzerland itself. They risk destabilising some other countries and decision-making in the neighbouring eurozone will become even more complicated and contentious.
Confirming the historical lesson that large currency moves tend to break things, they also highlight the extent to which central banks, operating in a world of growing economic and policy divergence, are struggling to maintain the paradigm of low market volatility that is central to their efforts to generate higher economic growth…
Following the abrupt removal of the currency peg, Switzerland is now looking at a period of bumpy economic and financial adjustment. Being a relatively “open economy”, in which trade and tourism play an important role, Swiss companies face a considerable competitiveness challenge ahead. The country will also have to deal with issues of currency mismatches, as well as having to battle larger, externally-induced deflationary forces.
But the implications extend far beyond Switzerland. Countries with Swiss franc denominated liabilities, such as Hungary, now have to deal with a major adverse valuation shock.
More importantly in terms of global systemic effects, politicians in the core economies within the eurozone — including Germany, Austria, Finland and the Netherlands — will see the SNB’s move as a reaffirmation of the dangers of substituting financial engineering for real economic reform. As such, they will be less willing to accommodate the hyperactivism of the ECB. And while this is unlikely to stop the ECB from doing more, it may increase the legal, reputational and unity risks it takes in doing so.
Then there are the consequences for a global economy which, in the absence of a comprehensive policy response in the advanced world, has ended up overly reliant on central bank interventions. Given that their tools cannot reach directly and sufficiently at what holds back growth and jobs, these central banks have been forced to use the partial channel of financial asset prices to influence real economic outcomes.
To this end, central banks have sought to repress market volatility as a means of encouraging risk taking that would then boost asset prices and thus encourage greater household consumption (via the wealth effect) and corporate investment (via animal spirits).
The SNB’s decision is further evidence that central banks are finding it harder to implement a policy of volatility repression that already was being challenged by the growing divergence in policy prospects between the eurozone and the US.
The ECB better deliver the highly expected "bazooka" next week because if not market volatility may return with a vengeance.
Yet has last week’s action by the SNB functioned as the causa proxima* for the return of global financial market volatility as the Swiss franc carry trade unravels that may lead to the breakdown of the euro and of bursting of the central banking confidence bubble?
*Causa Promixa is what historian Charles Kindleberger calls as "some incident that saps the confidence of the system" in Manias, Panics and Crashes p 104