Credit expansion not only brings about an inextricable tendency for commodity prices and wage rates to rise it also affects the market rate of interest. As it represents an additional quantity of money offered for loans, it generates a tendency for interest rates to drop below the height they would have reached on a loan market not manipulated by credit expansion. It owes its popularity with quacks and cranks not only to the inflationary rise in prices and wage rates which it engenders, but no less to its short-run effect of lowering interest rates. It is today the main tool of policies aiming at cheap or easy money. Ludwig von Mises
Global stock markets appear to be on a juggernaut!
Figure 1: Stockcharts.com: Where Is the Oil-Stockmarket Negative Correlation?
Figure 1 tells us that despite soaring oil prices, last traded at $113 per barrel as of Friday (WTIC), global equity markets have been exploding higher in near simultaneous fashion as demarcated by the blue horizontal line.
The Global Dow (GDOW)[1] an index created by Dow Jones Company that incorporates the world’s 150 largest corporations, the Emerging Markets (EEM) Index and the Dow Jones Asia Ex-Japan Index (P2DOW) have, like synchronized dancing, appear as acting in near unison.
We have been told earlier that rising oil prices extrapolated to falling stock markets (this happened during March—see red circles), now where is this supposed popular causal linkages peddled by mainstream media and contemporary establishment analysts-experts[2]?
Yet, the current actions in the global financial and commodity markets hardly represent evidence of economic growth or corporate fundamentals.
And any serious analyst will realize that nations have different socio-political and economic structures. And such distinction is even more amplified or pronounced by the uniqueness of the operating and financial structures of each corporation. So what then justifies such harmonized activities?
As we also pointed out last week[3], major ASEAN contemporaries along with the Phisix have shown similar ‘coordinated’ movements.
In addition, the massive broad based turnaround in major emerging markets bourses appear to vindicate my repeated assertions that the weakness experienced during the past five months had been temporary and signified only profit taking[4].
Yet if we are to interpret the price actions of local events as one of being an isolated circumstance, or seeing the Philippine Phisix as signify ‘superlative performance’ then this would account for a severe misjudgment.
Doing so means falling into the cognitive bias trap of focusing effect[5] —where one puts into emphasis select aspect/s or event/s at the expense of seeing the rest.
Ramifications of Rampant Inflationism
So how does one account for these concerted price increases? Or, what’s been driving all these?
We have been saying that there are two major factors affecting these trends:
One, artificially low interest rates that have driven an inflationary boom in credit.
That’s because simultaneous and general price increases would not be a reality if they have not been supplied by “money from thin air”.
As Austrian economist Fritz Machlup wrote[6],
If it were not for the elasticity of bank credit, which has often been regarded as such a good thing, a boom in security values could not last for any length of time. In the absence of inflationary credit the funds available for lending to the public for security purchases would soon be exhausted, since even a large supply is ultimately limited. The supply of funds derived solely from current new savings and amortization current amortization allowances is fairly inelastic, and optimism about the development of security prices, inelastic would promptly lead to a "tightening" on the credit market, and the cessation of speculation "for the rise." There would thus be no chains of speculative transactions and the limited amount of credit available would pass into production without delay.
Some good anecdotal examples:
Credit booms are being manifested in several segments of the finance sector across the world, such as the US Collateralized Mortage Obligations (CMO)
From Bloomberg[7], (bold emphasis mine)
The biggest year since 2003 for the packaging of U.S. government-backed mortgage bonds into new securities has extended into 2011, bolstered by banks seeking investments protecting against rising interest rates.
Issuance of so-called agency collateralized mortgage obligations, or CMOs, reached $99 billion last quarter, following $451 billion in 2010, according to data compiled by Bloomberg. The creation of non-agency bonds, which force investors to assume homeowner-default risks, is down more than 90 percent from a peak with parts of the market still frozen.
Facing limited loan demand and flush with deposits on which they pay close to zero percent, banks are turning to agency CMOs to earn more than Treasuries and gird for when the Federal Reserve boosts funding rates. Insurers, hedge funds and mutual- fund managers such as Los Angeles-based DoubleLine Capital LP are seeking different pieces of CMOs, which slice up mortgage debt, creating new bonds that pay off faster or turn fixed-rate notes into floating rates.
Or in Europe, the leveraged buyout markets...
Again from the Bloomberg[8], (bold emphasis mine)
ING Groep NV, the top arranger of buyout loans in Europe this year, sees a “liquidity bubble” building as lenders forego protection and accept lower fees.
“There is a liquidity bubble in the European leveraged loan market at the moment, driven by institutional fund liquidity,” said Gerrit Stoelinga, global head of structured acquisition finance at Amsterdam-based ING, which toppled Lloyds Banking Group Plc as no. 1 loan arranger to private-equity firms, underwriting 10 percent of deals in the first quarter.
Investors more than doubled loans to finance private-equity led takeovers in the first quarter to $6.7 billion as the economy shows signs of strengthening, reducing risk that the neediest borrowers will default. Inflows to funds dedicated to loans and floating-rate debt jumped to $8.5 billion this year, compared with $1.7 billion in the same period in 2010, data from Cambridge, Massachusetts-based EPFR Global show.
Second, it’s all about the dogmatic belief espoused by the mainstream and the bureaucracy where printing of money or the policy of inflationism is seen as an elixir to address social problems.
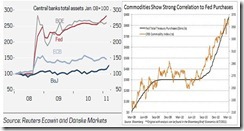
Figure 2: Swelling Central Bank Balance Sheets and Commodity Prices (Danske Bank[9] and Minyanville[10])
The balance sheets of developed economies central banks have massively been expanding (except the ECB, see figure 2 left window), as respective governments undertake domestic policies of money printing or Quantitative Easing (QE) programs, even as the global recession has passed.
Commodity prices have, thus, risen in conjunction with central banks QE programs (right window).
What this implies is that both inflationary credit and the ramifications of various QE programs appear to be mainly responsible for the rise in most commodity markets. This is a phenomenon known as reservation demand, which as I wrote in the past[11]
“commodities are not just meant to be consumed (real fundamentals) but also meant to be stored (reservation demand) if the public sees the need for a monetary safehaven.”
As the great Ludwig von Mises explained[12], (bold highlights mine)
with the progress of inflation more and more people become aware of the fall in purchasing power. For those not personally engaged in business and not familiar with the conditions of the stock market, the main vehicle of saving is the accumulation of savings deposits, the purchase of bonds and life insurance. All such savings are prejudiced by inflation. Thus saving is discouraged and extravagance seems to be indicated. The ultimate reaction of the public, the “flight into real values,” is a desperate attempt to salvage some debris from the ruinous breakdown. It is, viewed from the angle of capital preservation, not a remedy, but merely a poor emergency measure. It can, at best, rescue a fraction of the saver’s funds.
Ironically as I earlier pointed out, even the Bank of Japan (BoJ) has recognized the causal effects of money printing and high food prices[13], but they continue to ignore their own warnings by adding more to their own “lending” program using the recent disaster as a pretext [14]!
Yet despite increases of policy rates by some developed economy central banks as the European Central Bank (ECB) and the Denmark’s Nationalbank[15], not only as interest rates remain suppressed but the ECB pledged to continue with its large scale liquidity program[16].
To add, policy divergences will likely induce more incidences of leveraged carry trade or currency arbitrages.
Record Gold Prices and Poker Bluffing Exit Strategies
And it is of no doubt why gold hit new record nominal highs priced in US dollars last week (now above $1,470 per oz.)
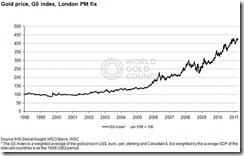
Figure 3: Surging Gold prices versus G-5 currencies (gold.org)
It wouldn’t be fair to say that gold has been going ballistic only against the US dollar because gold has been in near record or in record territory against almost all major developed and emerging market currencies.
Gold, as shown in Figure 3, has been drifting near nominal record highs against G-5 currencies[17] (US dollar, euro, Yen, sterling and Canadian dollar).
Figure 4: Gold Underrepresented as an Asset Class (US Global Investors[18])
Gold, despite record nominal prices, appears to be vastly underrepresented as a financial asset class compared to other assets held by global finance, banking, investment, insurance and pension companies.
Should the scale of inflationism persists, which I think central bankers will[19], considering the plight of the foundering “too big to fail” sectors or nations e.g. in the US the real estate markets (see figure 5), in Europe the PIIGS, this will likely attract more of mainstream agnostics (see figure 4) to gold and commodity as an investment class overtime.
This only implies of the immense upside potential of gold prices especially when mainstream finance and investment corporations decide to load up on it or capitulate.
Figure 5: Tenuous Position of US Real Estate, Bank Index and Mortgage Finance
This brings us back anew to “Exit” strategies that is said to upend gold’s potentials.
The Fed can talk about exit strategies for all they want, but they are likely to signify another poker bluff similar to 2010[20].
The Fed’s inflationist programs which had been mostly directed at the US banking system seem to stand on tenuous grounds despite all the trillions of dollars in rescue efforts.
US real estate appears to stagger again[21] (left window), while the S & P Bank Index (BIX) and the Dow Jones Mortgage Finance (DJUSMF) appears to have been left out of the bullish mode seen in the S&P 500 Financials (SPF) and the Dow Jones US Consumer Finance (DJUSSF), possibly reflecting on the renewed weakness of the US real estate.
In addition, there is also the problem of financing the enormous US budget deficits. And there is also the excess banking reserves dilemma.
So in my view, the US Federal Reserve seems faced with the proverbial devil and the deep blue sea. Other major economies are also faced with their predicaments.
Going back to the stock markets, as Austrian economist Fritz Machlup explained[22],
if all of these indices show an upward (or downward) movement, the presumption is very strong that inflation (or deflation) in the sense defined is taking place, even if the level of commodity prices does not show the least upward (or downward) tendency.
Well some commodity prices have paralleled the actions in the stock markets if not more.
Bottom line: Rampaging stock markets and commodity markets are symptomatic of rampant inflationism.
[1] Wikipedia.org The Global Dow
[2] See “I Told You So!” Moment: Being Right In Gold and Disproving False Causation, March 6, 2011
[3] See Phisix and ASEAN Equities: The Tide Has Turned To Favor The Bulls! April 3, 2011
[4] See I Told You So Moment: Emerging Markets Mounts A Broad Based Comeback! April, 8, 2011
[5] ChangingMinds.org, Focusing Effect
[6] Machlup, Fritz The Stock Market, Credit And Capital Formation Mises.org p.92
[7] Dailybusiness.com CMO sales at 7-year high as banks gird for Fed: credit markets, Bloomberg, April 5, 2011
[8] Bloomberg.com ING Sees ‘Liquidity Bubble’ in European LBO Financing Market, April 5, 2011
[9] Danske Bank Flash Comment Japan: BoJ upgrades its view on economy, April 7, 2011
[10] Minyanville.com When Will Fed-Created Melt-Up Turn Into a Meltdown?, April 8, 2011
[11] See Oil Markets: Inflation is Dead, Long Live Inflation November 4, 2010
[12] Mises, Ludwig von The Effects of Changes in the Money Relation Upon Originary Interest, Human Action, Chapter 20 Section 5 Mises.org
[13] See Correlation Isn't Causation: Food Prices and Global Riots, April 2, 2011
[14] Bloomberg, BOJ Offers Earthquake-Aid Loans, Downgrades Economic Assessment, April 7, 2011
[15] Reuters.com Danish c.bank raises lending rate by 25 bps, April 7, 2011
[16] See ECB Raises Rates, Global Monetary Policy Divergences Magnifies, April 8, 2011
[17] Gold.org, Daily gold price since 1998
[18] Holmes, Frank The Bedrock of the Gold Bull Rally, US Global Investors
[19] See The US Dollar’s Dependence On Quantitative Easing, March 20, 2011
[20] See Poker Bluff: The Exit Strategy Theme For 2010, January 11, 2010
[21] Economist.com Weather warning America's housing market is in the doldrums, March 30, 2011
[22] Machlup, Fritz Op.cit p.299