I love agitation and investigation and glory in defending unpopular truth against popular error.-- James A. Garfield (1831-1881) 20th President of the United States (1881)
In this issue
Phisix: PNOY’s 5th SONA: Desperately Seeking The Return of Boom Time Conditions
-How to Combat Decline in Popular Ratings? Appeal to the Public’s Emotions
-Self-Rated Poverty Increases on Mounting Stagflation
-Does Pork Barrel Scandals Translate to Good Fiscal Management?
-How Financial Repression Masks Debt-to-GDP Ratio: Blowing Bubbles
-How Financial Repression Masks Debt-to-GDP Ratio: Peso Loss of Purchasing Power
-The BSP’s Ambiguous and Non Transparent Signalling Channel
-How Financial Repression Masks Debt-to-GDP Ratio: The Other Factors
-Global Property Guide says Philippines has Ghost Cities!
-Tail Pieces: On the US Economy and Foundering Stocks….
-Tail Pieces: On China’s New Quasi QE
Phisix: PNOY’s 5th SONA: Desperately Seeking The Return of Boom Time Conditions
How to Combat Decline in Popular Ratings? Appeal to the Public’s Emotions
So the beleaguered Philippine President faced Congress in his State of the Nation Address (SONA) with a different but conventional political tack: appeal to emotions.
The President’s speech was supposedly more than conciliatory to the Supreme Court which he had recently censured for the latter’s ruling against the Disbursement Allocation Program (DAP); the President reportedly even shed tears in a segment of his speech!
This incredible excerpt from the speech[1]: “To my bosses: You gave me the chance to lead our country’s transformation. If I refused the challenge you laid before me, it is like saying I will help prolong your agony and my conscience cannot take that. If I turned my back on the chance given to me, it is like turning my back on my father and mother, and everything that they sacrificed for us. That will never happen,” the President said in Filipino. And then his voice cracked. Regaining his composure, the President continued: “As we tread on the straight path, you chose what is good and what is right; you remained true to me—and I remain true to you.” Some of the people in the audience stood up in one of the most loudly applauded parts of his 91-minute speech. “The transformation we are enjoying now can become permanent with the help of the Lord. As long as our faith and trust is complete, and as long as we become each other’s strengths, we will continue to prove that ‘the Filipino is worth dying for,” “the Filipino is worth living for,” and I will add: ‘The Filipino is worth fighting for,’” Aquino said.
Pardon my translation (or interpretation) of the speech: To my bosses (winks at the cronies and to political allies), the transformation we are enjoying now can become permanent, if the people won’t come into their senses to react adversely to our current (aggregate demand) policies which represents the “process of continuing inflation” as seen by the culminating 9 successive months of 30++% money supply growth rates that confiscates, secretly and unobserved, an important part of the wealth of the citizenry, whereby “while the process impoverishes many, it actually enriches some” (to borrow from John Maynard Keynes[2])
The Philippine President graduated with a Bachelor’s degree in economics at the Ateneo De Manila in 1981, so unless he was absent during the lecture sessions and on exams on the coverage of inflation or has been blinded by politics or by sheer vainglory, he or any economist worth one’s salt, should know what such money supply inflation “transformation” means.
And as for the maudlin speech, economic professor and blogger Don Boudreaux best describes this genre of political salesmanship[3]: Applause today, as loud as possible: that's pretty much all that matters to the thespians we call "government officials."
The article goes on to enumerate his accomplishments which can be summed up as basically populist politics of forcibly taking from Juan (via taxes) to give to Pedro with the rest spent by the government machinery through the following projects: cash transfers, weapons purchases, infrastructure projects and others.
The list adds “2.5 million Filipinos now above the poverty line” and “Good fiscal management has led to lower debt-to-GDP ratio” which I question below.
The President reportedly[4] also cited at six measures in his SONA, which included the uniformed personnel pension reform bill, supplemental budget for 2014, national budget bill and a joint resolution to clarify certain “definitions and concepts” in the Supreme Court decision against his Disbursement Acceleration Program.
Here is the litany of many other priority bills that haven’t included in the SONA: amend the build-operate-transfer law, cabotage law, Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas charter, Human Security Act, Ombudsman Act and the Anti-Enforced Disappearance Act, amendments to the law facilitating the “acquisition of right-of-way, site or location for national government infrastructure projects”, remove “investment restrictions in specific laws cited in the Foreign Investment Negative List”, freedom of information (FOI), Tax Incentives Management and Transparency Act, competition law, whistle-blowers act, revision of the criminal code, delineation of the Philippine maritime zone, act instituting reforms in land administration, national land use act, delineation of specific forest limits of public domain and the water sector reform act, likewise, civil service reform bill, a proposed magna carta of the poor, a proposed act protecting the rights of internally displaced persons and a strategic trade management bill.
I discussed the cabotage law—deregulation of the shipping industry—which was also raised in last year’s SONA as a welcome development[5]. Unfortunately seemingly good measures look only worth its intent. Given entrenched (politically connected) interests involved, such measures may hardly transform into reality.
The removal of restrictions in Foreign Investment Negative list seems also an economic plus, if this would be broadbased and not selective.
I have not parsed on the others enough to make additional comments. But some proposed legislation looks suspiciously protectionist like “competition law” and “strategic trade management bill”. Realize that all it takes for competition and trade to naturally emerge and flourish is to remove all legal barriers. Alternatively this means that to legislate or regulate competition and trade is to put barriers or prevent or limit its occurrence. And in doing so, such legal actions protect the interests of groups as so designated by political authorities. This similarly applies with “strategic trade management”.
Others like “magna carta of the poor” and a “proposed act protecting the rights of internally displaced persons” seems more like populist redistribution schemes which represents additional yoke to the productive sector of the economy and to the peso holders.
So like contemporary politics, the recourse to the “appeal to the emotion” has been intended only to defer on the ongoing erosion of political capital derived from the ramifications from invisible transfer policies.
And orthodox populist politics deals strictly with the symptoms and fixates on the short term rather than the disease—again the unintended consequences from incumbent policies. If you haven’t noticed populist politics has been all about (look good, feel good) Showbiz!
German’s Nazi chief Adolf Hitler gave a good account of how to manipulate public opinion through politics[6] (italics mine): “All propaganda must be so popular and on such an intellectual level, that even the most stupid of those towards whom it is directed will understand it. Therefore, the intellectual level of the propaganda must be lower the larger the number of people who are to be influenced by it…Through clever and constant application of propaganda, people can be made to see paradise as hell, and also the other way around, to consider the most wretched sort of life as paradise.”
Self-Rated Poverty Increases on Mounting Stagflation
As mentioned above, the SONA achievements included “2.5 million Filipinos now above the poverty line”.
Last week I noted[7] that during the past year, there has been a dramatic deterioration of perceptions of Philippine residents who rated themselves as becoming “poorer”. Such self-diagnosed poverty has sown the seeds or has paved way for the drastic shift in political sentiment against the once popular government. So aside from a dive in popularity ratings, three impeachment proceedings have been filed in just a week.
One of the major pollster who published surveys of self-proclaimed poor, the Social Weather Stations (SWS) has updated their findings during the SONA day[8]: “OVER HALF a million Filipino households have been added to the ranks of the poor, according to a new Social Weather Stations (SWS) report that estimated the number of families rating themselves as mahirap at 12.1 million. The SWS said a June 27-30 nationwide survey had 55% of the respondents claiming to be poor, up from the 53% (equivalent to an estimated 11.5 million families) recorded three months earlier.”
The self-rated poverty was up mostly in Mindanao, Visayas and Metro Manila but fell in Luzon. Paradoxically, the median poverty threshold in terms of household peso budget fell in Metro Manila by 20% to Php 12,000 while remaining unchanged for the rest of the nation.
The self-proclaimed poverty survey resembles the international measure called the Misery Index (developed by economist Arthur Okun) which combines unemployment rate and inflation rate to gauge society’s wellbeing.
The implication is that price inflation pressure may be down in Metro Manila but still elevated elsewhere. Importantly, the slackening of inflation in the Metropolis may have likely been accompanied by a dearth of jobs or sources of income, which have prompted more people see themselves as poorer.
The SWS chart has been revealingly insightful. Note: I superimpose my metrics.
First of all, please notice of the fantastic disconnect between the government or the NSCB’s “unrefined” and “refined” poverty data (blue line) with that of the SWS. Since 2009/10 both have been going in opposite directions. Government declared poverty rates has been trending down whereas SWS rates have been trending up!
And this looks like one superb example why one should rely less on empirical data, especially government statistics.
So the President’s claim runs contrary to the numbers shown by the SWS.
Let me clarify that I’m not endorsing the SWS but rather I am applying economic analysis from their data
This instead serves as a splendid demonstration of how statistics can produce different outcomes (deliberately or through errors). Therefore to obsess over empirical data without economic theory is to get lost in interpretation.
Another good example is the difference between how inflation is seen by the public and by “experts”. In a survey conducted by US economist Robert Shiller[9], the public generally sees inflation as purchasing power of money (what money can buy) as against experts who define them differently. Since experts has more influence on policymakers, then the public pays the price for the mistakes made by these “experts” whose prescriptions have been implemented by political authorities.
As the great Austrian economist Ludwig von Mises preached[10]: (bold mine)
There is economics and there is economic history. The two must never be confused. All theorems of economics are necessarily valid in every instance in which all the assumptions presupposed are given. Of course, they have no practical significance in situations where these conditions are not present
Unfortunately the mainstream confuses one with the other.
Second, which is relevant to the first, is that the SWS self-rated poverty has been on an UPTREND since the grand BSP’s PIROUETTE of 2009/10 or what I show above as the Tetangco PUT.
The shift from external trade to domestic growth dynamics via inflating a credit bubble is a wonderful depiction of the redistribution process by which inflation “confiscate arbitrarily; and, while the process impoverishes many, it actually enriches some”
The so-called “transformational boom” has been prompting for an UPWARD trending self-diagnosed poverty. The implication from the above chart is that a large segment of the Philippine society has been paying the price for the benefit of a few. It would be misguided to say these groups have been “excluded” from growth, because it is precisely their resources that have been funneled to subsidize industries from financial repression policies or facilitated through the “continuing process of inflation”.
Third the current uptrend in the poor self-perception has been the longest since 1992. The biggest rise came in from 1986-1992 which eventually paved way for the Asian Crisis in 1997. This is aside from the Marcos era 1983 period.
There were signs of some uptick in the pre-Lehman crisis boom, but apparently the global crisis nipped this in the bud.
Fourth, post bubble busts such as 1984 (recession) and post Asian Crisis 2000-2003 have shown a meaningful decline in self-perceived poverty. This implies that when the invisible political redistribution eases, the general public’s economic yoke diminishes. This represents the period where real productive growth surfaces!
Fifth, the survey suggests price inflation may be subsiding (perhaps confirming the decline in domestic liquidity growth rates), but this has been accompanied by signs of rising joblessness (declining investments). Such hardly provides for an optimistic view to the coming statistical economic growth which media and their apologists continue to tout.
So if there may be some degree of accuracy in the SWS survey, then the one sided trade or political outlook of 6-7% growth will be faced with more nasty surprises.
Does Pork Barrel Scandals Translate to Good Fiscal Management?
The President also averred “Good fiscal management has led to lower debt-to-GDP ratio” as one of his accomplishments
I call this the Talisman effect, where politicians and the consensus cherry pick on statistics to justify or promote a bias in the hope to “ward off evil spirits” or the negative aspects of the actions which they are defending.
If the claim of “Good fiscal management” is true, then the President’s popularity ratings won’t be in a sharp swoon and there won’t be two impeachment proceedings against him based on Pork Barrel. Remember Pork barrels are essentially about government spending which falls into the category of fiscal management. This exposes the post hoc fallacy from the said claim.
While the claim “lower debt-to-GDP ratio” is true for now, the escalating Philippine budget, which has been anchored on 7-8% growth rates IS bound for a magnificent reversal.
I am not going to tackle with the Pork Barrel aspect of the proposed budget. Nevertheless here is what media says on fiscal management circa 2015[11]: “The proposed budget is up 15 percent from last year’s budget of P2.265 trillion, reflecting the jump in the administration’s assumption of a 7- to 8-percent growth in gross domestic product next year.”
The Inquirer has a great graph on this. It shows of the accelerating rate of increases in the government budget particularly 10.4% in 2012, 10.5% in 2013, 12.9% in 2014 and 15.1% for 2015. In terms of year on year percent increases, 2013-2014 growth rate was at 22.8% while for 2014-2015 at 17.05%.
It doesn’t take us very far to deduce and ask, what happens if the one sided expectations of 7-8% statistical growth will not come into fruition? 1Q 2014 at 5.7% statistical growth rates has already been considerably below such estimates, and marks the third consecutive quarter of decline[12], what if this downtrend is sustained? What if the Philippine government due to external factors or even from internal imbalances suffers a recession down the road?
How will the government finance the gap between slowing tax revenues with the significant enlargement of the government spending? How will this impact the debt-to-GDP ratio and the government’s balance sheet?
Evidently politics abetted by media and vested interest groups have ensured that 7-8% growth has been set in the proverbial stone. This hallmarks a fantastic one way trade with hardly any leeway for errors. And this is why the one way political trade is destined to fail and may even give rise to a black swan due to overconfidence.
And blind hope hardly represents a good strategy whether for investments or for politics.
How Financial Repression Masks Debt-to-GDP Ratio: Blowing Bubbles
It is terribly misplaced to solely look at debt-to-GDP ratio and issue a self-vindication. Since debt is one of the three ways how government finances itself, aside from taxes and from inflation, we shouldn’t overlook on how tax revenues are currently being funded or even how 30% money supply growth rates has contributed to the current façade of fiscal serenity
The reason why debt-to-GDP has been low is PRIMARILY because of financial repression policies.
And as I said before, costs are not benefits. The social policy of negative real rates essentially serves as subsidies to government debt. All inflationism has been about access to resources via credit or simply access to cheap credit.
Such subsidies have been channeled through lower debt maintenance than would have been when priced in free markets. This allows governments to expand spending while keeping debt levels suppressed.
But such comes at what costs?
As I previously noted[13], The statistician cum economic analyst will see this as good news. Yehey, great debt management they say! But if we apply the great Bastiat’s methodology of looking at the “unseen” long term consequence from current policies that have brought about the current benign “visible” effects, we will see a vastly different picture.
Yet the PRINCIPAL cost to attain lower public debt has been to inflate a massive bubble. The current public debt levels have been low because the private sector debt levels, specifically the supply side, have been intensively building.
Zero bound rates (negative real rates) has impelled for a debt financed “buy high, sell higher” dynamic in the financial markets and in the ‘capital intensive’ segments of the real economy, specifically to the bubble sectors (real estate, construction, shopping mall, hotels and financial intermediaries) but certainly not limited to them as many other industries are connected with these bubble sectors.
Such price inflation arbitrages has inflated profits, earnings and incomes that have pillared the so-called ‘consumer demand’ which has spawned capital expansions (part of buy high activities) directed at consumers (sell high). The inflated profits, earnings and incomes have filtered into government coffers which imply that tax revenues have been inflated too. OFW and BPO remittances are only sideshows to the demand fueled by the massive balance sheet expansions. And such dynamic have, so far, provided the moorings for increased social spending from which political authorities see as a one way road.
But there is no such thing as a free lunch. Rising Non Performing Loans (NPLs) in the banking’s systems real estate consumer loans as well as auto loans in Q1 as noted[14] last week, are indications which not only reveals that debt levels have risen to hit their natural limits, but likewise herald increasing instability risks to the system.
How Financial Repression Masks Debt-to-GDP Ratio: Peso Loss of Purchasing Power
The SECONDARY major cost from inflating a bubble in order to keep debt levels low has been to diminish the purchasing power of citizenry. This has now become conspicuous whose signs have been converging via many angles, higher domestic bond yields (from a one year perspective), falling peso vis-à-vis the US dollar (one year frame) and BSP’s official inflation rates (which has become widespread[15] and now a major political issue[16]). Most important has been the BSP’s seemingly frantic responses to the current inflation environment.
Oh yes the dovish Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP) seems to have been pushed to wall for them to finally but reluctantly raise official rates last week.
From the BSP (bold mine)[17]: The Monetary Board’s decision is a preemptive response to signs of inflation pressures and elevated inflation expectations. Latest baseline forecasts indicate that the inflation target could be at risk, as the forecasts have shifted closer toward the higher end of the target range of 3±1 percent for 2015. At the same time, the balance of risks to the inflation outlook continues to be tilted toward the upside, with price pressures emanating from higher food prices, short-term volatility in international oil prices, and pending petitions for adjustments in power rates and transport fares. Moreover, while inflation expectations remain within target, they are seen to be settling toward the upper end of the inflation target range, particularly for 2015. The Monetary Board also sees the increase in policy rates as a preemptive measure in the context of the eventual normalization of monetary policy in some advanced economies. Given these considerations, the Monetary Board believes that an increase in the BSP’s policy rates will moderate inflation pressures and arrest potential second-round effects by helping anchor inflation expectations. The Monetary Board noted that the continued favorable outlook for domestic demand allows some scope for a measured adjustment in policy rates without adversely affecting the country’s economic growth prospects. Going forward, the BSP will remain vigilant against risks to price and financial stability and stands ready to undertake further policy actions as necessary.
Funny but, hasn’t it been for the longest period that the BSP has continually placed the burden of inflation on the supply-side constrains? So why the need to raise official rates at all?
Yet the BSP hardly even bothers to explain of the transmission mechanism of how adjusting interest rate channel impacts price inflation to the public. Why??? Do they expect the public to know this? Or do they expect the media and or their supporters to sanitize this for them? Or do they expect the public to be kept in the dark?
Essentially the above statement represents an indirect admission of the snowballing setback from credit fueled demand policies. It reveals of further signs that the phony boom has begun to hiss.
Moreover the BSP leadership claims that this has been a “preemptive response” at their risk of breaching their inflation targets. Really? Then why has BSP has launched FIVE actions (two reserve requirements[18], one banking stress test, and SDA interest rate[19]) including the July end official rates in a span of just 5 MONTHS which means one policy action per month???
If ‘inflation expectations remain within target”, then WHY the urgency??? And whatever happened to the alleged $2.7 billion siphoning from two reserve requirements? Why not give earlier actions a chance to gain ‘traction’? Again why the seeming desperation? Has the gap between the official inflation rates and real economy inflation been broadening? Have the reserve requirement been a rabbit out of the hat trick? Has all four measures miserably failed?
And who among the influential pressure groups has been compelling the BSP to act? I doubt that the BSP will solely heed on the warning by the Bank of International Settlements, if so who or which groups may be behind BSP’s actions? To what degree have they been affected?
The BSP’s series of actions has raised even more questions than it has answered.
The BSP’s Ambiguous and Non Transparent Signalling Channel
Yet I don’t see the need for the BSP to raise rates. That’s because I believe that the market has effectively already been doing the job. Proof? Growth rates of domestic liquidity have tumbled fast enough to have already reached my target, even before July!
From the Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (bold mine)[20]: Domestic liquidity (M3) grew by 23.0 percent year-on-year at end-June 2014 to reach P7.1 trillion. This increase was slower than the 28.4-percent expansion recorded in May. On a month-on-month basis, seasonally-adjusted M3 declined by 0.4 percent, following a zero growth in the previous month…Money supply continued to expand due largely to the sustained demand for credit in the domestic economy. Domestic claims rose at a stronger pace of 13.0 percent in June reflecting the steady uptrend in lending to the private sector. The bulk of bank loans during the month was channeled to real estate, renting, and business services, utilities, wholesale and retail trade, manufacturing, as well as the agriculture sector…As in previous months, the high—though decelerating—M3 growth reading in June continued to reflect in part the decline in the Special Deposit Account (SDA) placements of trust entities compared to their levels a year ago, in line with the BSP’s operational adjustments in the SDA facility.
As usual, the BSP resorts to smokescreens where they continue to blame “in part” SDA for money supply adjustments.
On the one hand, they raise interest rates supposedly to control price inflation, yet again they never explain how interest rates affect consumer prices. Yet on the other hand, they say that the decline in liquidity has partly been about SDA while admitting to domestic credit expansion as the larger component of changes in liquidity, as if to suggest that SDA and loans operate distinctly from each other.
They hardly ever explain on the connection, or more importantly, the casual linkages of how changes in interest rates affect demand for credit, how changes in liquidity and deposits are really symptoms of bank credit expansion, how spending power injected to the economy from credit expansion impacts prices both in the real economy and in the asset markets, how prices coordinates economic activities or how prices affects the flow of the production process, and lastly, how changes in interest rates affect SDA flows, as well as, the balance sheets of both lenders and creditors (from the banking and ex-banking sectors) or even the BSP.
The BSP signaling channel has been filled with opaque, non-transparent and most importantly self-contradictory messages. Such obfuscation represents added signs of concern that the monetary politburo may be concealing colossal risks from the gullible and vulnerable public whom has become dependent on BSP’s monetary wizardry.
The surge in 1Q NPL loans in the banking system’s real estate and auto loan portfolio combined with clues from the SWS self-rated poverty survey, the price inflation taking on the awareness of the political authorities, cascading liquidity and below expectations GDP in 1Q, reinforces my suspicion that the Philippine political economy “may already have reached a ‘saturation’ or ‘tipping’ point for debt absorption”[21]
This implies of the acceleration of the diminishing returns on debt for the domestic economy, particularly for the bubble industries which brings to fore greater risk of instability for a system that has become excessively reliant on debt.
To add evidence to this we see a marked slowdown in general banking loans, particularly in the supply side last June.
From the BSP[22] (bold mine): Loans for production activities—which comprised about four-fifths of banks’ aggregate loan portfolio—expanded by 17.7 percent in June from 19.0 percent in May…Loans for household consumption grew at a faster pace of 16.2 percent from 10.8 percent in the previous month, reflecting the expansion in auto loans and other types of loans (i.e. salary loans and personal loans).
As one would note, the decline in growth rates in loans to the real estate and the construction sector appears to have intensified. Although hotel loans continue to dazzle, loans to the financial intermediary may have inflected. Even the growth rates in the banking loan portfolio to the manufacturing sector have turned sharply lower.
The share of loans to the bubble sectors relative to overall banking loans have now fallen to 49.78% from above 50%.
As a side note the BSP will be overhauling its classification of industry loans based on the 2009 Philippine Standard Industrial Classification (PSIC) starting this month and will end original data in June 2015. The possible side effect is that there will be shortages of historical data if the old data will not be readjusted to conform with new accounting standards. If the latter holds true then this shows how government can erase “risk” via changes in accounting standards.
Meanwhile consumer loans, which is significantly less than supply side loans has picked up, despite rising 1Q NPLs. Consumer loans are less of a threat because of the limited penetration level by domestic households to the formal banking industry. But less does not mean immunity. Since current demand comes from supply side leveraged expansion, the reduction in supply side loans will eventually be reflected on consumer loans in terms of lower take up and higher NPLs as demand retrenches.
Nonetheless the falling growth rate of liquidity appears to have spread even to the banking loan portfolio which may most likely recoil to liquidity growth.
A further implication is that arbitraging through price inflation from the Tetangco PUT appears to be diminishing. This will put pressure on profits, income and earnings dependent on sustained money pumping.
My guess is that 2Q statistical GDP, which may fall to 5.5% or even below, will disappoint the consensus.
How Financial Repression Masks Debt-to-GDP Ratio: The Other Factors
These brings me back to “costs are not benefits” of the artificially low debt to GDP.
Aside from blowing bubbles and diminishing purchasing, the THIRD major cost is in the illicit and immoral transfer of resources not only to the government but also to politically connected firms who has and continues to benefit from the BSP sponsored redistribution.
A FOURTH major cost is that bubbles have effectively heightened “financial stability risks”. Contra to the BSP’s claim that they “remain vigilant against risks to price and financial stability and stands ready to undertake further policy actions as necessary”, by unleashing the inflation ‘Godzilla’ the major source of “financial stability risks” has been the BSP’s negative real rates policy which have been implemented by the leadership. Most of the BSP people are well meaning people and have been ignorant of the policy gambits which have been undertaken by the leadership that comes at the expense of the public.
The general public has also been unaware of the mischiefs employed by the BSP chieftains, otherwise as Henry Ford once admonished, “It is well enough that people of the nation do not understand our banking and monetary system, for if they did, I believe there would be a revolution before tomorrow morning.”
Fingerprints of financial instability can be seen not only in the escalating private sector debt levels, the previous absurd 30% money supply growth rates, but also in massively overvalued asset markets, as well as, the convergence trade.
A FIFTH major cost is that resources channeled to the bubble sectors have been malinvestments. Resources that should have been used by the market for real productive growth has instead been diverted to unproductive and speculative undertaking. This means that the massive misallocation of resources now awaits a potentially disorderly market clearing process which will underscore a shift in consumer’s preferences from which will bring to light consumed capital via financial losses.
A SIXTH major cost is that once the bubble implodes, government revenues will dramatically fall while government spending will soar as the government applies the so-called “automatic stabilizers” (euphemism for bailouts). This would also extrapolate to a phenomenal surge in debt levels. All these will unmask today’s Potemkin’s village seen in the fiscal and debt space. Such will likely be accompanied by tax increases, in particular the E-VAT which seems as the Philippine government’s seemingly most successful tax collection platform
A SEVENTH major cost is that not only will a bubble bust imply possible curtailment of civil liberties but the onslaught against economic freedom in particular the informal economy will likely intensify. This will come with more mandates, regulations and other restrictions. A government deprived or starved out of taxes for her insatiable spending appetite will desperate seek a larger tax base whose resources they intend to seize by taxation.
So never rule out a bank bail in or depositor’s haircut.
Global Property Guide says Philippines has Ghost Cities!
Warren Buffett once warned that “never ask a barber if you need a haircut”. Mr. Buffett’s word of caution has been predicated on the principal agent problem which underscores of the conflict of interest between interacting parties with different incentives.
Having read the recent report from the Global Property Guide reminded me of Warren Buffett’s warning. This is aside from the palpably desperate thoroughly confused state by property bulls to justify bubbles.
The article says that the rate of increase in Philippine land and rental prices has been cooling. Aside, vacancy rates have been inching higher. They believe that all these are temporary.
And because a major real estate investment and management firm declares that there is no bubble, the article accepts such ‘proof by assertion’ as a gospel of truth.
The reason given is that current oversupply comes from the completion of new projects. So the assumption is that demand will remain robust which means demand will eventually reduce excess supply. The company or the article does not explain how and where demand comes from except to assume its existence. Although ironically the article mostly focuses on demand from BPO and OFW.
Also another reason for their bullishness has been due to a statistical guidepost. While nominal prices of 3 Bedroom condo units has surpassed 1997 highs, because in inflation adjusted terms this represents 39% off the 1997 highs, prices thereby have been deemed as far from the dangers of 1997 levels and so the implied upside.
Here are my questions: What if official inflation rates have been calculated differently in the 90s or today? The BSP’s proposed changes in classification of bank loans seem as proof of continuing changes in accounting methodology. What if current inflation rates have been understated? Since inflation has recently become a key political issue which even hugged the headlines, how reliable are the official inflation numbers? Why has the BSP raised rates (or acted 5 times in a span of 5 months) if price inflation has been within their targets? How will inflation affect demand or disposable income?
As one can note, preoccupation with statistics can increase risks to one’s portfolio (if not one’s health too)
But here is the striking segment of the article’s commentary[23]
We believe that the middle tier is over-supplied. Many of these lower middle-class condominium developments are ghost cities.
Wow! Did you get that? Move over China, “Ghost cities” have landed in Philippine shores! Yet paradoxically there is NO bubble!
Yet I wonder how do the property bulls define bubbles: an ex post phenomenon?
Even more…[bold mine]
A visit to any ‘Barrio Fiesta’ in any city where Philippine OFWs work abroad is dominated by condominium offerings from developers like Megaworld, DMCI, Ayala Land, etc.. The Philippines is one of the world’s largest remittance recipients, with 10.5 million Philippine Overseas Foreign Workers (OFWs) living and working in 210 countries and territories worldwide, 47% of them permanent migrants, 40% temporary, and the rest "irregular migrants". Among the permanent overseas Filipinos, 65.2% live in the US, followed by Canada (13.1%), Europe (7.1%), Australia (6.8%), and Japan (3.4%), according to the Commission on Filipinos Overseas (CFO). In 2013, remittances from OFWs grew 7.4% to US$22.9 billion, or around 8.4% of GDP.It is estimated that 60% of these remittances go directly or indirectly to the real estate sector, according to the World Bank. These OFW remittances power the low-end to mid-range residential property market, housing projects and mid-scale subdivisions in regions near Metro Manila, such as Cavite, Batangas, and Laguna Provinces.According to the Philippine Housing and Land Use Regulatory Board, 452,198 condominium units were built in Metro Manila from January 2001 to March 2014. There are around 807,496 families or 27.5% of the NCR population who have a dispensable income greater than PHP 34,962 (US$ 783), which is the required monthly income to be able to afford the monthly amortization of PHP 10,500 (US$ 235). PHP 10,500 (US$ 235) is the minimum monthly amortization for a housing loan of PHP 2 million (US$ 44,801), with accommodating loan rates of 90% LTV, with an annual interest rate of 5.7%, and a loan tenor of 30 years.So for all these newly-built condominiums to be occupied by those who could afford to rent or buy (we calculate for the buying case, but given current interest rates it may be more expensive to rent), 56% of locals who have the financial capacity to occupy them would need to do so, i.e., 56% of the 807,496 families with the financial capacity to do so, should purchase or rent a unit, for the available supply of condominium units to be taken up.These are problematic numbers given that many of these families already have houses in the first place. The World Bank assumes only 10% of these capable end-users as prospective end-users, indicating a gross oversupply.In terms of affordability, property developers are building more mid-end condominium units than locally-based Filipinos can afford to occupy. Many of the buyers are OFWs, causing a mismatch between demand and supply.
Notice that the demand which the article focuses on, contributes only EIGHT Percent or specifically 8.4% of the GDP. My question why the focus on 8.4%, which has almost been the entire thrust of the article, when there is 91.6% to consider? Have developers and media been blind to the 90%? Or is it that 8.4% has been seen as quantifiable, therefore easy to write about?
Next look at the writer’s one tract fixation on statistics where numbers have been made to fit either “should purchase or rent a unit”.
Are people’s lives all about purchasing and renting condo or housing units? What if the qualified buyer instead decides to spend his/her money on helping the family or subsidizing education of relatives or indulge instead in shopping or traveling or to frequent gimmick outs with friends or even just to save? The writer doesn’t seem to give any consideration to this. The outlook has been tunneled to solely at buying or renting—a very fictitious sense of reality. Yet the World Bank’s data of capable end-users seem to have pushed back on the writer’s bias thus the generalization of “gross oversupply”. Even the World Bank’s model based data would be as good as a guess or basically unreliable numbers.
And as one would note, without economic theory, empirical based analysis would lead to grave reasoning lapses and heuristic fallacies.
Even bizarrely the writer castigates on the supposed miscalculation by OFW investors on their failure to match acquired properties with BPO renters.
By 2016, it is estimated that as many as 1.3 million people will be employed in the BPO sector. The sector is expected to generate as much as US$ 25 billion in annual revenue.BPO agents are likely to wish to rent residential spaces near their workplaces due to their night shift schedules. Since BPO agents have foreign countries as their clientele, their work hours follow suit. This means that most BPO employees work at the night time where commuting is risky while taxi cab fares are expensive.There is a puzzle here. The income of this rising demographic overlaps with the investments made by the OFWs. Many call-centre agents are in the targeted income-bracket. But anecdotal evidence suggests that many of condominiums bought by OFWs are in the wrong place for call-centre agents.In any case, the bottom line is that their spending-power is not yet strong enough to absorb supply. Many have family obligations and prefer to live at home or with relatives.
Another severe error here is to believe that OFW buying has all been about rental yields through matching with rental habits of BPOs workers.
OFWs have different reasons for buying properties, this could be for personal or family use, as vacation house, as inheritance, as speculative instrument, for rental income or more. I am quite sure that there are a handful of OFWs targeting BPOs for their property purchases but they are unlikely a significant force.
Yet the writer hopes that the demographic dividend or the demographic sweet spot will save the day. Well that really depends if people will be allowed to conduct commerce freely or if people will become all wards of the state and her private sector apparatus. The former will most likely reap a demographic dividend while the second will lead to standardized poverty.
Bubble blowing is a function of the second. This US homeownership chart should be a wonderful example.
Yet economics of demography is one of long term framework and not for short term or immediate response. Enterprises or financial institutions presently hooked on debt can’t wait for long term fixes.
Also while the article believes that there may be brewing oversupply of properties serving the mid tier markets, they believe that the high end and the low end segment will continue to be strong due to “economic growth”.
Apparently the writer has not considered how inflation harms the lower segment of the market by reducing disposable income. Well, here is what I wrote based on their article in October 2013[24]
Property bubbles will hurt both productive sectors and the consumers. Property bubbles increases input costs which reduces profits thereby rendering losses to marginal players but simultaneously rewarding the big players, thus property bubbles discourage small and medium scale entrepreneurship. Property bubbles can be seen as an insidious form of protectionism in favor of the politically privileged elites.Property bubbles also reduces the disposable income of marginal fixed income earners who will have to pay more for rent and likewise reduces the affordability of housing for the general populace.Outside the ethics of the property bubbles, the mania as shown by chronic overconfidence by industry participants, nominal prices of real estate at 1997 highs and signs of rising vacancy rates could be seen as a potential red flag especially if the bond vigilantes will reassert their presence.
So a reduction in disposable income due to a stagflationary environment will undermine demand for both low and mid-tier housing projects from which the article laboriously tries to conflate with deficiencies of OFW and BPOs where “spending-power is not yet strong enough”. The latter two may be contributing factors but hardly are they the primary cause.
Also stagflation will undermine both statistical and real economic growth.
The article also tries to rationalize the aggravating weakness in the property sector by spewing out selective statistics without the realization that the numbers and the participants they cite have been part of the mostly high and mid tier markets as well as some low end projects, for instance, “A visit to any ‘Barrio Fiesta’ in any city where Philippine OFWs work abroad is dominated by condominium offerings from developers like Megaworld, DMCI, Ayala Land, etc..”
This means that if the current ghost projects have been financed by debt, then the slack in demand for units implies a hit in both the income and balance sheet statements of property companies who cater to these markets.
Remarkably even spotty arguments of the property bulls contain bearish undertones.
And if the facts of the report are correct, then obviously cracks in the Philippine property bubble have been widening and has become palpable such that even the bulls can’t hide them anymore!
Tail Pieces: On the US Economy and Foundering Stocks….
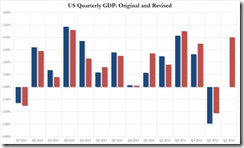
2Q US GDP beat expectations with a 4% growth rate[25]. A large segment or about 40% springs from real private inventories growth. Financial analyst Alasdair Macleod notes that the huge 14% increase in inventories and durable goods means that these will be subject to possibly big revisions[26]. Even perma bulls as the Canadian BCA Research thinks that the growth data seems “Good (If it is true”)[27].
Meanwhile the Fed continued to pare down on QE by reducing agency mortgage-backed securities at a pace of $10 billion (from $15 billion) per month and longer-term Treasury securities at a pace of $15 billion (from $20 billion) per month[28]. The growth data initially prompted for a spike in yields of 10 year US Treasuries but the selloff in stocks pushed yields back down.
US stocks have entered the month of August with sharp losses of more than 2.0% per major benchmark for the week. It is too early to call anything. But as I pointed out last week, the exodus in high yield bonds may have been instrumental in contributing to the loss. This week global investors yanked $4.4 out of high yield junk according to Reuters[29]. Adding to this has been a bigger selloff in US mortgage bonds[30], thus homebuilder index as seen by SPDR S&P Home builders Index have been hit hard.
Has the Fed’s tightening begun to impact financial markets?
Tail Pieces: On China’s New Quasi QE
The Chinese central bank the PBOC have launched a 1 trillion yuan ($171 billion) stimulus (or QE?) via the “Pledged Supplementary Lending"[31] (PSL) which has spurred the recent surge in China’s stocks [up 2.76% for the week and 6.04% in two weeks].[32] This fills in the gap I wrote last week—”this implies a Xi-Zhou PUT (from China’s President Xi Jin Ping and PBoC governor Zhou Xiaochuan) in motion”
What this implies is that the Chinese government can’t withstand pain from a withdrawal syndrome from debt addiction. And even more is that credit risks will likely balloon as banks assets continues to grow as debt levels grow.
Since 2009, the US has added $2.3 trillion in bank assets, exclusively thanks to the Fed's reserve creation, writes the Zero Hedge[33] (bold, italics and underline original), As for China... total bank assets more than doubled from $11.5 trillion to a record $25 trillion! This is a number that is nearly double that of the US, and represents a pace of $3.5 trillion per year - or nearly four concurrent QEs - a rate of "financial asset" addition five times greater than in the US!
Again, 2009 serves as the monumental pivot for global central banks.
As Credit Bubble Bulletin’s Doug Noland observed of China’s bubbles[34]: The Chinese Bubble is a government-dictated financial scheme of epic proportions.
Epic bubbles means epic collapse.
[1] Inquirer.net Aquino tears up in his 5th Sona July 25, 2014
[2] John Maynard Keynes, The Economic Consequences of the Peace, 1919. pp. 235-248 PBS.org
[3] Donald J. Boudreaux Sound & fury, signifying pandering August 10, 2011 Triblive.com
[4] Inquirer.net FOI measure No. 18 in Palace’s 26 priority bills July 31, 2014
[5] See 2013 PNOY’s SONA: A Political Economic Minefield July 29, 2013
[6] Adolf Hitler, Mein Kampf, Rense.com
[7] See Phisix: Stagflation Upends Boom Time Politics as BSP’s 1Q Property NPLs Surge! July 28, 2014
[8] Businessworld Online Self-rated poverty up among households July 27, 2014
[9] See Graphic of the Day: Inflation as seen by consumers and economists June 27, 2014
[10] Ludwig von Mises 10. The Procedure of Economics Chapter II. The Epistemological Problems of the Sciences of Human Action Human Action Mises.org
[11] Inquirer.net P2.6T national budget has P500B lump sum July 31, 2014
[13] See Phisix: In 2009, the BSP Engineered a Crucial Pivot to a Bubble Economy April 4, 2014
[14] Op. Cit July 28, 2014
[15] See Phisix: 30+% Money Supply Growth Rate Now Seen in Official CPI Data June 9, 2014
[16] See Phisix Breaks 6,900 as Inflation Risk Becomes a HOT Political Issue! July 6, 2014
[17] Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas Monetary Board Hikes Policy Rates by 25 Basis Points July 31, 2014
[18] See Phisix: BSP’s Response to Peso Meltdown: Raise Banking Reserve Requirements March 31, 2014; See Showbiz S&P Upgrade & BSP Actions Sends Phisix and the Peso into a Frenzied Blow off Top May 12, 2014
[19] See Phisix: BSP Under Pressure: Raises SDA Rates and Invokes Banking Stress Test June 23, 2014
[20] Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas Domestic Liquidity Growth Continues to Ease in June July 31, 2014
[21] See Phisix: Watch Out, Money Supply Growth Will Fall Sharply by July! May 25, 2014
[22] Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas Bank Lending Sustains Growth in June July 31, 2014
[23] Global Property Guide Slowdown in residential property price rises in Manila July 1, 2014
[24] See Cracks in the Philippine Property Bubble? October 7, 2013
[25] See US GDP Exceeds Forecasts, Grew by 4% in 2Q July 30, 2014
[26] Alasdair Macleod USD FMQ carries on growing despite tapering FinanceandEconomics.org August 1, 2014
[27] BCA Research U.S. Q2 GDP: Good (If It’s True) July 31, 2014
[28] Federal Open Market Committee Press Release July 30, 2014 FederalReserve.gov
[29] Reuters.com High-yield bond funds worldwide post $4.4 bln outflows –BofA August 1, 2014
[30] Zero Hedge Suddenly, Wall Street Is Bailing On Housing August 1, 2014
[31] The Australian China central bank gives CDB 1 trillion yuan July 22, 2014
[32] See Hong Kong Dollar-US Dollar Peg Under Pressure July 30, 2014
[33] Zero Hedge China's Credit Nightmare Explained In One Chart March 14, 2014
[34] Doug Noland Bubbles & Schemes Credit Bubble Bulletin July 25, 2014 PrudentBear.com