“…a long habit of not thinking a thing wrong, gives it a superficial appearance of being right, and raises at first a formidable outcry in defence of custom. But the tumult soon subsides. Time makes more converts than reason”—Thomas Paine, Common Sense, Introduction
In this issue
Phisix 7,050: The Peso in the Face of Crashing Emerging Market and ASEAN Currencies
-The Peso in the Face of Crashing Emerging Market and ASEAN Currencies
-Debunking More Weak Peso Myths
-Wilting Peso Signifies a Symptom of Diminishing Liquidity
-Diminishing Liquidity and the Pseudo Consumer Spending Recovery
-Philippine Bonds: Stealth Easing In Process, Yet More Easing Means Weaker Peso
-Phisix 7,050: Manipulations are Self Defeating Activities
Phisix 7,050: The Peso in the Face of Crashing Emerging Market and ASEAN Currencies
The Peso in the Face of Crashing Emerging Market and ASEAN Currencies
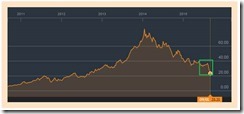
The USD-Peso (USD-PHP) officially closed the holiday abbreviated week at 46.73, nearly unchanged from last week’s 46.735.
But it was different story when viewed from the international forex market during the post Asia trading session. Four quotes from investing.com, yahoo, google finance and xe.com all showed that the USD-PHP ended the week at 46.93.
This only means that unless there will be material changes that may radically alter the sentiment, the USD-PHP will open this week’s trade at the Php 46.90s.
There will be many popular factors which will be attributed to this. August US jobs data which was below the consensus expectations, yet spruced up the probability of the Fed’s rate hike (from 72% Thursday to 81% Friday). Friday’s slump in US and Europe stock markets which virtually erased sharp midweek gains or even possibly the resumption of stock market trading activities in China, which is expected to remain visibly volatile, will likely get media’s attention.
Interestingly, all these have been happening as US Federal meeting is due in two weeks time (September 16 and 17). Here, the FOMC will decide whether to increase rates or if they will move its goalpost again. So given the popular fixation, the proximity towards the FED’s decision day should spur more weakness. But once the decision is made, this may ease some of domestic-Asian and Emerging Market currency pressures. Temporarily.
But hardly has there been a convincing opinion from the consensus in explaining the intensity and the rapidity of the strengthening of the US dollar against domestic-Asian and Emerging Markets.
To the contrary, they seem to ignore very important developments.
For instance, much of media seem to have overlooked that a global organization of financial institutions, the Institute of International Finance (IIF), just sounded off blaring sirens on the ongoing capital flight out of Emerging Markets. The IIF reported that this has reached crisis proportions! Measured based on historical perspective, this means that the current behavior of capital outflows on emerging market currencies have reached levels that previously had been followed by financial crises!
So why the heck would a potential hike by the FED, which would represent a smidgen of 25 basis points, trigger a frenzied stampede out of Asian-ASEAN-emerging markets??!!! The establishment never say. They just assume.
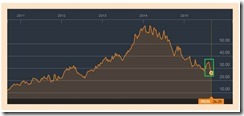
Based on Bloomberg’s end of the week quote, even currencies of developed Asian peers as Singapore, South Korea and Taiwan had been smacked down last week (see left).
Yet after a sharp recovery during early week, the tribulations of the ringgit-rupiah had been reignited at the week’s close. Year to date, the losses from the USD-ringgit-rupiah has already fit into the technical definition of a currency crash with a quarter to go!
Why the continuing crash? And what are the repercussions?
Economics don’t operate on a vacuum.
Debunking More Weak Peso Myths
In the domestic setting, the tumbling peso has repeatedly run roughshod over the establishment’s expectations. Given the current dynamics, the USD-Php 47 psychological threshold barrier will likely be overrun soon.
And fascinatingly media touts expert opinions, who continue to deny the ongoing reality show, to put on a copacetic mask over the falling peso.
For instance aside from the USD 47 target for the year, this article says the lower peso will boost consumption particularly from OFWs.
As foreseen last June[1]: I predict that there will be imbecilic rationalizations where the weak peso will associated with more purchasing power from USD based OFW and BPO remittances. The coming rationalizations will omit the insight of the transmission mechanism of import prices into the system. It’s the kind of same nonsensical popular imputations that says low oil prices equals stronger consumption spending.
I have previously dealt with this brazen misrepresentation. But I will debunk this ‘politically correct’ gibberish again.
A lower peso should not be seen in a very simplistic context.
Changes in the peso, which is a price or the exchange value of the domestic medium of exchange relative to the US dollar, will affect ALL commercial activities.
A lower peso, on the surface, may boost the consumption. But economics doesn’t stop here. Media skirts on the effect of the lower peso on imports, production, debt and the epiphenomenon or secondary causes from the latter factors.
Ceteris paribus (all things being equal), a lower peso means MORE peso required for any exchange transaction quoted in the US dollar. Simply said, any transactions related to USD will become MORE EXPENSIVE in peso terms.
Domestic prices of imported goods and services will RISE. So whatever alleged gains from a lower peso on OFW will be largely offset by the price increases on imported goods and services. And rising prices should REDUCE demand for imported goods.
For domestic production, prices of imported production inputs will also increase. Rising input costs should put a squeeze on the profits of producers. And profit margin strains will mean lesser investments, which subsequently should extrapolate to lesser outputs and diminished jobs and wage improvements.
And lesser production output means HIGHER domestic prices. In short, again whatever gains from the lower peso on OFW, exports, BPOs and or tourism will be mostly neutralized by rising domestic prices overtime.
And again, the ascendant domestic prices have been the effects of higher import prices.
Moreover, in the financial dimension, any USD based liabilities will require MORE peso to service. Once again this adds to the cost side of firms exposed on USD borrowings that will amplify debt servicing onus that may reduce access to credit, thereby, put strains on profits and magnify credit risks.
Some anecdotes from the current ordeals of Malaysia and Indonesia as examples.
From Nikkei Asia[2]: Indonesian and Malaysian companies are scrambling to protect their earnings against plunges in their local currencies, which are causing their U.S. dollar-denominated debt to balloon….In recent years, companies in countries that maintain high interest rates, such as Indonesia and Malaysia, have flocked to dollar-denominated debt because of the lower interest rates caused by the financial crisis in 2008. In Indonesia, foreign-denominated debt in the private sector reached an estimated $168 billion in May, twice as much as in 2010…This year, the rupiah and the Malaysian ringgit have been the two worst-performing currencies in Asia, both losing more than 10% of their value against the greenback. They are hovering at rates not seen since the Asian financial crisis in the late 1990s. Axiata has decided that borrowing in local currencies, which means higher interest payments, is safer than risking large fluctuations in foreign exchange rates.
How falling currency affects the balance sheet dependent on US Dollar based inputs, again from Nikkei: Malaysian budget carrier AirAsia saw its net profit tumble 34% to 243 million ringgit ($57.8 million) for the April-June period. The airline posted a foreign exchange loss of 43 million ringgit due to the ringgit's slide against the dollar. About 70% of the group's operating costs are in U.S. dollars, according to CIMB Research. Concerns over the ability of its Indonesian subsidiary to raise funds are mounting.
How financial losses and growing credit risks have been adversely impacting access to credit, thereby resulting to the tightening of liquidity conditions. From the same Nikkei Asian article: Suvir Varma at consultancy Bain & Co. said demand for short-term financing is growing among smaller companies trying to survive the turmoil. "We are already starting to see very keen interest" from risk-taking private funds, he said, noting that conventional banks have become wary of bad loans.
Yet soaring foreign debt burden has been Southeast Asian dynamic.
From Bloomberg[3]: Southeast Asia’s biggest companies have increased debt sixfold since the regional financial crisis, stoking concern over default risks as investors draw parallels with the 1998 meltdown. The region’s 100 largest listed companies by assets, including Thailand’s CP ALL Pcl, Petron Corp. of the Philippines and Singapore’s Wilmar International Ltd., had accumulated $392 billion by June 30, data compiled by Bloomberg show. That’s up six times from December 1998. Debt loads as a proportion of assets are climbing back near levels from the crisis at 31.7 percent, up from 29.5 percent in 2010…S&P said foreign-currency debts grew two to three times more rapidly than local debt for Malaysian, Philippine and Indonesian companies between 2010 and 2014, based on its own sample of the top 100 companies. The borrowings made up 30 to 50 percent of total debt there, it said.
I previously pointed out here that the foreign debt share of SMC is about 60% of the company’s overall Php 508 billion burden. And SMC is just one of the many others with big foreign debt exposures.
Finally, remember this?[4]
A falling peso isn’t legislated. A falling peso also doesn’t emerge out of metaphysical or supernatural causes. Instead, a falling peso is a product of human action. A basic explanation: demand for the USD is GREATER than the demand for the peso.
A greater demand for the USD means that there will be LESS incentive to HOLD onto Philippine peso assets (whether bonds, currency, stocks or property). There will also be LESS incentive to invest in peso.
This economic logic tells us why the falling peso will hardly boost consumption in the real economy. Not only will increasing domestic prices counterbalance any supposed gains from lower peso on OFW-BPO consumption, reduced investments will again lead to lesser jobs.
The principal foundation of consumption growth is INCOME growth, aside from supplementary factors of credit growth and depletion of savings which are ephemeral. This only means WITHOUT income growth, there will hardly be corresponding consumption growth. And any supposed growth from devaluation, which represents the foreign exchange effect or the “money illusion”, will be temporary.
The beneficial effects of spending from remittances will only occur during the narrow window from the lagging effects of higher import prices on trade and production relative to OFW-BPO spending.
Also, OFW remittances and BPOs account, which for about 20% of the GDP, are NOT static and inanimate numbers. They do not just jump out of the computer screens. They are products of human action.
Revenues of both OFWs and BPOs are SOURCED externally. This means OFW remittances depend on the INCOME of foreign employers. BPOs revenues depend on the INCOME of foreign based principals. This likewise means that the economic, social and political CONDITIONS of the nations serving as HOST to foreign employers and foreign principals essentially determine indirectly the REVENUES of OFWs and BPOs.
Consequently, this means that when the world enters a recession, OFW remittances and BPO activities will most likely get affected too. So OFWs and BPOs are not talismans. They are as vulnerable to any frailties from human action.
So even if the peso crashes similar to Venezuela or Argentina in scale, there will be NO consumption growth!
Wilting Peso Signifies a Symptom of Diminishing Liquidity
The mainstream does NOT say that mounting balance sheet constraints or impairments on an international system that has become chronically addicted to DEBT have spurred growing signs of illiquidity (in the Philippines or abroad).
So crashing EM-Asian-ASEAN currencies have been symptomatic of three convergent forces:
First, domestic debt overload dynamic.
Second, the resistance by domestic policymakers to remove free lunch subsidies or negative real rates policies that have supported such debt accumulation spree.
Finally, intertwined with the first two, the blind rampant crowding into assets or the yield chasing phenomenon from global arbitrage or carry trades. Carry trades has underpinned a considerable part of the economic and financial construct of the previous boom.
The latter cross border yield chasing activities have been encouraged by the mirage of a domestic credit boom which further amplified on such a boom. Think of all those credit upgrades that have become a magnet for yield chasing on Philippine stocks as an example.
Today, this dynamic appears to be transitioning into a reverse: BOOM will segue into a BUST.
The effects of shrinking liquidity have become more pronounced. This has been compounded or exacerbated by the previous ending by the FED of QE 3.0 and the current prospective rate hikes.
And shrinking liquidity paves way for market reversals. Thus, all those market crashes or violent market fluctuations have merely been manifestations of this boom bust process.
And shrinking liquidity signifies a substantial part of this time consuming reversal process.
There is another thing to remember.
Policies are NEVER neutral. Policies are designed to benefit one group at the expense of another.
Having said so, policies influence people’s incentives. This means policies influence not only markets and the economy, but institutions, politics and other social dynamics as well.
People’s actions are entwined, interrelated and interdependent.
Since policies help determine or influence market outcomes, then this also implies that policies influence earnings, valuations, and asset prices. So it would be naïve to simply look at historical raw financial or economic numbers without understanding the share of influence from prevailing policies on them. It would also be myopic to project historical numbers into the future without the comprehension of the action-reaction dynamics or basic laws of economics.
Importantly, markets are a process. With a very few exceptions (like natural disasters), they do NOT occur in random. This means Boom Bust cycles signify a process too.
Let us take the recent accounts of stock market crashes worldwide or even in the Philippines. Stock market crashes have hardly been anomalistic. They are not a product of people who woke up on the wrong side of the bed or had soured milk for breakfast or had a wrenching argument with a family member in the morning or watched the horror movie “Chucky” during the previous evening.
Instead, stock market crashes have accounted for as symptoms of hidden maladjustments (mostly caused by policies) that have found a relief valve to violently vent on the marketplace the accrued pressures from such imbalances.
And shrinking pool of liquidity which usually accompanies violent market fluctuations are, again, manifestations of mounting balance sheet imbalances.
Diminishing Liquidity and the Pseudo Consumer Spending Recovery
Last week, the Philippine central bank, the Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP) announced that Consumer Price Inflation (CPI) fell below the their inflation “target range of 3.0 percent ± 1.0 percentage point for 2015”, “mainly to slower price increases in both food and non-food items”.[5]
For the second month, the BSP’s own measure of CPI has fallen below their target. And the cascading CPI has been accompanied by sinking domestic liquidity.
The BSP admits that liquidity conditions have mainly been a function of bank credit activities. Bank credit growth remains at double digit rates. Last July, this was at 13.36% but down 14.52% from last June. Meanwhile, July M3 clocked in at 8.5% down from 9.3% in June. Banking loans account for 74% of M3.
This means that the 33% crash in the growth rate of bank loans to the industry—from the peak at 20.2% to 13.36% in July—caused money supply growth rate to collapse from its pinnacle of 38% in January 2014 to the July 2015’s 8.5%.
But still, bank credit growth remains at double digit rates! So where has all the money been going or flowing to? Debt servicing? Financial speculation?
What happens if bank credit expansion slows below the 10% threshold??? Will CPI be sucked into a DEFLATIONARY cesspool???!!! What more if bank credit stops growing at all????
The collapse in money supply growth rates has mirrored on the government’s CPI (with a time lag).
This only implies that the serial huge issuance of “money from thin air” by the banking system has not been circulating in the economy enough to combust inflationary pressures as in 2013!
Again what has been draining money supply?
Ironically, in the 2Q GDP, the public was told that 5.6% was a product of consumers spending growth!
Yet current bank credit, money supply and CPI conditions have signified a continuation from last midyear’s inflection point.
But seen in the context of the 2Q GDP, food supplies as represented by 2Q agriculture GDP has declined! As reminder, August signifies a continuing dynamic from the 1H of 2015.
Add to this the non-food perspective through the contraction (PSA) or miniscule growth (NSCB) in manufacturing and sluggish imports in 2Q.
In other words, declining CPI could not have been from a supply shock!
What does the “law of demand” tell us? If this had been from a supply shock, then given all things being equal, as the price of a product decreases quantity demanded increases. This means that if income continues to grow, then a sustained slump in CPI won’t be happening at all! An increase in demand will reverse the price slump.
Or there won’t be lethargic imports or manufacturing activities, if agriculture had been manacled by environmental conditions.
Economic logic just doesn’t square with the 2Q GDP numbers! [I have filtered out the peso in this discussion]
And again, the BSP’s personal savings data (right) suavely dovetails with the swooning CPI. Money saved isn’t money spent!
In short, 2Q and current conditions posits that there has hardly been a general consumer spending recovery.
Sustained signs of diminishing liquidity have been an obstacle to this. Hence, again, 2Q GDP was another statistical pump.
If there is anything that this administration has greatly excelled at, it is the showbiz performance of everything else.
And reduced liquidity are being manifested in real economic activities, the stock market and even the PESO!
So when experts or authorities claim that the pesos’ dilemma accounts for guilt by association or by the “herd mentality”, then such denial implies the failure to appreciate the essence of the market process.
Such obsession to statistics will extrapolate to blindness.
Now to bring back the peso into the equation. So far, the lower peso hasn’t percolated to domestic prices. But if the peso continues to fall, then eventually this dynamic will change. Markets are a process. These factors are still presently being incorporated into the real economy. And the effects of which we will see, perhaps as statistics, in the future.
Philippine Bonds: Stealth Easing In Process, Yet More Easing Means Weaker Peso
The BSP chief recently threatened to intervene to inject liquidity when required. He was quoted as saying that they are “ready to amend monetary policy if needed to ensure sufficient money supply.”[6]
But some entity/-ies has already been forcing a steep widening of the yield curve (see left) via the spread between 10 year and 3 month yields. This has been the case since April. But the spread has sharply steepened from end July through last week!
In other words, some unidentified entity/-ies has been orchestrating a monetary easing to “ensure sufficient money supply” via bank credit expansion channeled through the manipulation of bond yield spreads, particularly by forcing down short term rates.
While this hasn’t been publicly acknowledged by officials, it’s a start of the fight against deflation. Reality has begun to surface to take its yet subtle toll on the economy and financial markets.
Unfortunately, despite such manipulations, bank credit growth continues to founder. This means that the artificially widened spread has, so far, failed to do its wonders similar to 2009.
This is called time inconsistent policies. It seemed to have worked before, but have different consequences today. But authorities will likely adapt on the same path dependent (behavioral: anchoring) measures… even until everything blows up!
Perhaps, the Philippine banking system has reached a point of “pushing on a string” or that more easing won’t deliver more credit growth. That’s because balance sheets of borrowers have been burdened by so much debt that “you can lead a horse to the water, but you can’t make him drink”. In short, the ongoing slowdown in credit growth will translate to lower NGDP (nominal GDP).
Remember, only an estimated 12% of the population have access to the banking system’s credit facilities. This implies a massive concentration of credit to only a few number of people.
Of course, the high density of credit distributed to a small number of people creates the statistical façade of low credit levels in aggregate. This statistical charade has brought about the severe underrating of the credit risks! So fixation with statistics will lead the establishment to overlook on such micro dynamic.
Moreover, while the anonymous market manipulator/s has succeeded to steepen some parts of the largely illiquid bond markets, it appears that there has been so has many holes in it for manipulators to consistently and entirely control it. So while some spreads has sharply steepened, some has even flattened [2 year versus 10 and 20 year]! (see right)
The variegated dispersion of spread activities simply translates to lapses on the goal to silently ease the financial system!
And where government will officially ease, then this should spur deeper losses for the peso!
Because resources are fundamentally scarce, free lunches can’t last forever. The BSP’s free lunch invisible redistribution scheme has reached its twilight.
Finally, under conditions of extreme market sentiment, flashes of streaks or extended momentum will likely occur. This has been happening to the ringgit-rupiah.
But no trend ever goes in a straight line.
One should consider hedging against further market volatility or from more episodes of meltdowns or from a torturous bear market in stocks.
So here’s my recommendation, for Philippine residents I recommend to stay in cash, especially in US dollar. Use any USD-peso reprieve to buy the US dollar or sell the peso.
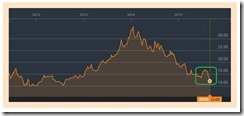
One can add gold (and or gold based assets) to such hedges. Gold may be down today (which makes it a value buy), but this may be a different story when the “real thing” arrives.
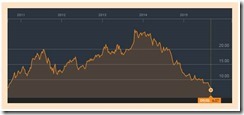
And by “real thing” I mean that if the current Emerging Market-Asian-ASEAN market selloffs morphs into a financial crisis, then the USD-PHP high in September 27, 2004 at 56.45 can easily be taken out.
And growing risks of confiscation from indirect means (inflationism) or from direct means (war on cash via negative nominal rates, wealth taxes, deposit haircuts) should spur a reversal in gold.
Phisix 7,050: Manipulations are Self Defeating Activities
Diminishing liquidity will serve as a critical headwind on the Phisix.
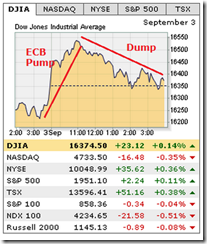
The Philippine equity benchmark, the Phisix (PSEi) lost only .66% over the week. Thanks to the massive push by index manipulators last Wednesday September 2nd, the PSEi rallied furiously from the depths of NEGATIVE 2.8% to close the session down by only .2%.
Fascinatingly the PSEi and China’s Shanghai Composite shared the same striking dynamics that day: A deep slump in the early morning (SCOMP was down by -4.4%), a ferocious rally going into the noon break and the late session push.
However, the Phisix delivered the icing on the cake: a “marking the close”. Bizarrely both closed down by .2%.
International media acknowledged the Chinese government’s heavy hand in the fantastic come from behind rally. But on Philippine markets, the silence was deafening.
Yet what has all these manipulations attained?
I noted of about only three rare accounts of index management in 1h 2013. Yet the 2013 record marked the original and authentic highs which had been supported by the broad markets.
This was not the case in 2014-2015. The second record high represented a manipulated pump.
Incidences of market manipulation only intensified during the 2h of 2014, particularly during the 4Q. It became an almost daily feature in 2015. The current decline has hardly changed the complexion of artificial props.
Yet again what has all these manipulations accomplished?
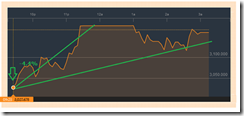
Manipulations has temporarily incited an upside breakout above 2013 high in January 2015. It set a string of records from the January breakout to early April or a three month honeymoon, based on a rotational pump on 10 of the top 15 issues.
But unfortunately the PSEi have regressed back to the levels where all manipulation has started!
The tryst, the headline fun, had been nothing but a short term ecstasy.
But this has generated so much imbalances as shown by the absurd valuations and the ridiculously skewed distribution of market weightings in favor to the top 10 issues.
Yet it’s sad to think about the ramifications from the losses used to artificially pump the index. Such maneuverings came at a heavy cost most likely from depositor-premium-taxpayer money.
For whose benefit? The egos and interests of politicians and their cronies. One can add the lining up of pockets of the supply and buy side industries, some of them related to the cronies.
This exploitation won’t stop until these vested interest groups can hoodwink the gullible public. Since these groups control media, media will play a big role in the deception. And abuse will continue until those losses surface on the balance sheets of entities that wantonly engaged in such unscrupulousness. And perhaps such losses or deficits may prompt for a public outcry.
And once losses become publicly acknowledged, people assigned to care for fiduciary resources will just resign and transfer elsewhere while leaving the public to hang out to dry with losses.
It’s a sad thing, but it is reality.
This only shows that education represents the best defense against political exploitations. And economics should be learned by everyone to exorcise economists and or statisticians masquerading as economists.
Well, index managers have been beaten black and blue. But they are still in the thick of the fight though. Sad to say, that their miseries will only compound. The mauling of their portfolios will continue.
The stock market’s liquidity conditions points at this eventuality.
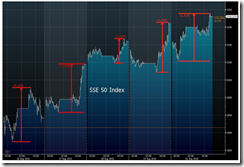
Last week’s daily peso volume dramatically shrunk going to the week’s close! (see left). Thursday and Friday’s volume was off by an eye-popping over 30% from Monday’s 10 billion peso.
While the index managers managed to save the index from another major slump Wednesday, it appears that they may be losing the bid to support the current price levels.
By Friday (Sept 4), the attempt to establish a beachhead at 7,100 simply corroded. So the day’s losses, which escalated in the afternoon session, was mitigated by a marking the close push which chipped off only .2% from the overall decline to close down by .66%.
So unlike Wednesday where bulls and index managers were able to make a dramatic ramp, Friday’s actions exposed their vulnerability: the vast erosion of firepower.
Add to this, the sharp retraction from last week’s spike in the daily Peso volume trade (weekly averaged) [see right]. Peso volume has now returned to the pre-crash levels.
And given that short selling has hardly been used due to bureaucratic encumbrances, the “silent” major sellers, whom are the marginal buyers, will likely ventilate their actions when it has become apparent that bids at present price levels can’t be sustained even at the presence of manipulators.
This will even escalate once manipulators join in the stampede to cut stock market exposure.
Again all it takes for another major downside move will be a headline event[7].
But when reality eventually filters into the headline; perhaps as in the form of economic numbers or a surprise missed interest payment by a major company, or the appearance of a major global event risk, then bids will evaporate.
Aside from a rapid decrease in volume, total daily traded issues have resumed its decline (see right). Again the reduction of stock market activities signifies as added sign of receding liquidity.
Additionally, market breadth in favor of sellers have widened again. It’s still a sign of the dominance of risk aversion.
I have also warned that the chasm of divergence between the headline index and broader market will eventually converge with violent tendencies…
Little has been appreciated that the headline index DEPENDS on the OVERALL health conditions of the entire population of listed stocks.
Thus divergences arising from manipulations only deepen the underlying imbalances impelled by financial repression policies.
Moreover, because manipulators are constrained by the availability of resources, the economics of manipulation ensures that divergent actions between headlines and the overall market activities are unsustainable.
And because they are economically unjustifiable, the accumulated structural disproportions would render market activities susceptible to violent reactions.
So aside from another bullseye, the same condition holds true today.
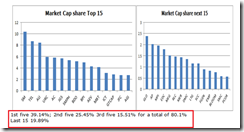
As of Friday, the PSEi has only been down by -2.47% year to date. However among 30 PSEi issues, losers edged out gainers with a slim majority 16 to 14.
But as shown on the left, the reason for the 7,050 or mitigated year to date -2.47% deficit have largely been because the bulk of gainers essentially populated the top 10 issues. Six of the top 10 issues posted returns of a stunning 6% and above. The top 10 issues account for 64.53% of the market cap weightings. And this shows where the pumps have been.
This also showcases the stark divergence between performances of the index and the broad markets. And the same divergence remains as a key source of imbalance that subjects the headline index to the risks of violent repricing.
Remember in 2013, the PSEi endured two accounts of 6% crashes. Both crashes eventually led to levels LOWER than the lows established from the crash.
And current conditions suggest that the PSEi will not be able to hold its present levels if volume does not improve and if risk aversion will remain the dominant sentiment.
I might add that headline events seem as getting less and less supportive of the delusional levels being propped up by index managers.
At the end of the day, markets eventually upend anti-market forces. Manipulations are exposed as self-defeating activities.
[1] See Record Phisix in Big Jeopardy! BSP 2Q Survey Reveals Bearish Consumers! More Cracks on Fundamental Headlines! June 14, 2015
[2] Nikkei Asian Review, Weak currencies sap Malaysian, Indonesian earnings September 3, 2015
[3] Bloomberg.com Southeast Asia's Biggest Companies Risk $392 Billion Debt Burden September 1, 2015
[4] See Phisix 7,700: Philippine Peso Tumbles, Why Manipulation Matters, The Philippine Competition Act: Same Dog Different Collar? July 26, 2015
[5] Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas August Inflation Lower at 0.6 Percent September 4, 2015
[6] Wall Street Journal Philippine Central Bank Ready to Amend Policy If Needed September 3, 2015
[7] See Phisix 7,600: 5.2% 1Q GDP Another Data Pump! DBP Accused of Market Manipulation; Scapegoating The US Dollar May 31, 2015