Everything we know “based on evidence” is actually based on evidence together with appropriate theory. Steven Landsburg
Prediction 2011: Largely on the Spot But Too Much Optimism
First, a recap on the analysis and the predictions I made during the end of December of 2010 in an article “What to Expect in 2011”[1]
I identified four predominant conditions that would function as drivers of global financial markets (including the Philippine Phisix) as follows:
1. Monetary authorities of developed economies will fight to sustain low interest rates.
2. More Inflationism: Bailouts and QEs To Continue
3. Effects of Divergent Monetary Policies
4. The Globalization Factor
How they fared.
1. Low Interest Rates Regime

I noted that the US Federal Reserve has the “penchant to artificially keep down interest rates until forced by hand by the markets”; this has apparently been validated last year even as most of the market’s focus has shifted to the Eurozone.
In fact, suppressing interest rates has not just been undertaken by the US Federal Reserve, whom has promised that current zero bound rates (ZIRP) would be extended to 2013[2] aside from manipulating the yield curve via ‘Operation Twist’, but by major developed and emerging central banks as shown above[3].
Apparently, the worsening debt crisis in Eurozone compounded by Japan’s triple whammy natural disaster and China’s slowing economy (or popping bubble?) has intuitively or mechanically prompted policymakers to respond concertedly, nearly in the same fashion as 2008. This has resulted to a decline of global interest rates levels to that of 2009[4].
2. Bailouts and QEs Did Escalate
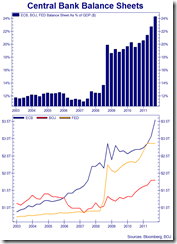
Except the US Federal Reserve, major global central banks have already been actively adapting credit easing or money printing policies.
The balance sheets of top 3 central banks has now accounted for almost 25% of world’s GDP[5]. Yet this doesn’t include the Swiss National Bank[6] (SNB) and the Bank of England[7] (BoE) whom has likewise scaled up on their respective asset purchasing programs.
The world is experiencing an unprecedented order of monetary inflation under today’s fiat standard based modern central banking.
3. Divergent Impacts of Monetary Policies on Financial Markets
I previously stated that
Divergent monetary policies will impact emerging markets and developed markets distinctly, with the former benefiting from the transmission effects from the latter’s policies.
While global equity markets have been down mostly on partial and sporadic signs of liquidity contraction arising from the unfolding Euro crisis and from indications of a global economic slowdown, monetary policy activism or strong responses by central banks did result to distinctive impacts on the marketplace.
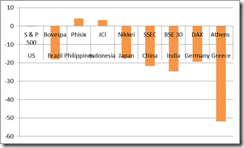
Emerging markets with the least inflationary pressures exhibited resiliency. ASEAN 4 bourses, going into the close of the New Year, were among the ten world’s best performers[8] and served as noteworthy examples of the above.
The relative performances of global bourses have likewise been reflected on the commodity markets[9].
4. Globalization Remained Strong which Partly Offset Weak Spots

While there had been signs of partial stagnation of global trade in terms of volume during the last semester of the 2011, trade volumes remained at near record highs and have hardly reflected on signs of severe downturn or a recession[10] despite the Euro crisis.

Since deepening trends of globalization (in finance and trade) has also been expanding the correlations of the financial markets[11], which has been largely characterized as ‘Risk On’ and ‘Risk Off’ environments, the aggressive actions by central banks and the non-recessionary global environment in the face of the Euro crisis and patchy signs of economic slowdown has partly neutralized such tight relationship which allowed for selective variances in asset performances.
Overall, almost every condition that I defined in December of 2010 had been validated.
5. Mostly Right Yet Too Optimistic
On how I expected the markets to perform, I wrote,
Unless inflation explodes to the upside and becomes totally unwieldy, overall, for ASEAN and for the Philippine Phisix we should see significant positive gains anywhere around 20-40% at the yearend of 2011 based on the close of 2010. Needless to say, the 5,000 level would seem like a highly achievable target. What the mainstream sees as an economic boom will signify a blossoming bubble cycle.
Of course my foremost barometer for the state of the global equity markets would be the price direction of gold, which I expect to continue to generate sustained gains and possibly clear out in a cinch the Roubini hurdle of $1,500.
To repeat, Gold hasn’t proven to be a deflation hedge as shown by its performance during the 2008 Lehman collapse. The performance of Gold during the Great Depression and today is different because gold served as a monetary anchor then. Today, gold prices act as a temperature that measures the conditions of the faith based paper money system.
2011 saw the Philippine Phisix and ASEAN bourses marginally up, which means that I have been too optimistic to suggest of a minimum 20% return that was way off the mark.

Nevertheless, it hasn’t been that bad since the long-time darling of mine, the Philippine mining index, overshot on my expectations.
And given that the mining sector’s extraordinary returns has alternated every year[12], it is unclear if mining index will remain to be the horse to beat. Yet, current global monetary dynamics may change all that.

Aside, another observation of mine has been validated.
Gold, allegedly a deflation hedge/refuge, has not turned out as many have said.
Except for the July-September frame, gold prices have largely moved along with the price direction of the S&P 500 (blue circles).
The July-September frame which marked a short-term deviation from the previously tight correlations seems to coincide with the end of the QE 3.0. This along with the unfolding Euro crisis put pressure on US equity markets first, which eventually culminated with FED chair Ben Bernanke’s jilting of the market’s expectations of QE 3.0.
The belated collapse of gold prices (red circle), in response to Mr. Bernanke’s frustrating of the market expectations for more asset purchasing measures, had been aggravated by other events such as the forced liquidations by MF Global[13] to resolve its bankruptcy and several trade ownership issues aside from other trade restrictions or market interventions[14] that has stymied on gold’s rally.
Nevertheless, the gold-S&P 500 linkage appears to have been revived, where both gold and the S&P has taken on an interim upside trend (green line).
The S&P 500 closed the year with microscopic losses while gold registered its 11th year of consecutive gains, up 10% in 2011.
Expect Volatile Markets in 2012
When asked to comment on the prospects of the stock market, JP Morgan’s once famous resounding reply was that “It [Markets] will fluctuate”.
1. Markets will Fluctuate—Wildly
2012 will essentially continue with whatever 2011 has left off.
Since 2011 has been dominated by the whack-a-mole policies on what has been an extension of the global crisis of 2008, which in reality represents the refusal of political authorities for markets to clear or to make the necessary adjustments on the accrued massive malinvestments or misdirection of resource allocation in order to protect the political welfare based system anchored on the triumvirate of the politically endowed banking sectors, the central banks and governments, then we should expect the same conditions in 2011 to apply particularly
1. Monetary authorities will continue to keep interest rates at record or near record low levels.
2. Money printing via QE and bailouts will continue and could accelerate.
3. There will be divergent impact from different monetary policies and
4. Globalization will remain a critical factor that could partly counterbalance the nasty effects of the collective inflationist policies (unless the ugly head of protectionism emerges).
I would add that since presidential election season in the US is fast approaching, most candidates or aspirants including the incumbent have been audibly beating the war drums on Iran[15], where an outbreak may exacerbate political interventions in the US and in the global economy and importantly justify more monetary inflationism.
One must realize that continued politicization of the marketplace via boom bust and bailout policies compounded by various market interventions and the risk of another war has immensely been distorting price signals which should lead markets to fluctuate wildly.
2. China and Japan’s Hedge—Steer Clear of the US Dollar
And where reports say that China and Japan have commenced on promoting direct transactions[16] by using their national currencies hardly represents acts to buttress the current system.
The Bank of Japan has also been underwriting their own Quantitative Easing (QE) which means the Japanese government are engaged in ‘competitive devaluation’ which is no more than a ‘beggar thy neighbour’ policy.
Instead, what this implies is that Japan and China, being the largest holders of US debt, seem to be veering away from their extensive dependence on the US economy as they reckon with, not only interest rate and credit risks, but also of currency, inflation, political and market risks. Even China and Japan appear to be taking measures to insure themselves from wild fluctuations.
On the other hand, China’s bilateral currency agreement with Japan plays into her strategy to use her currency as the region’s foreign exchange reserve[17].
3. Heightened Inflation Risks from Monetary Policies

QE 3.0 has not been an official policy yet by the US Federal Reserve but their balance sheet seem to be ballooning anew (chart from the Cleveland Federal Reserve[18]).
Yet this, along with surging money supply and recovering consumer and business credit growth, will have an impact on the US asset markets which should also be transmitted to global financial markets, as well as, to the commodity markets.
Yet given the large refinancing requirements for many governments (more than $7.6 trillion[19]) and for major financial institutions this year amidst the unresolved crisis, I expect major central banks to step up their role of lender of last resort.
Again the sustainability of the easy money environment from low interest rates and money printing by central banks will depend on the interest rates levels which will be influenced by any of the following factors: 1) inflation expectations 2) state of demand for credit relative to supply 3) perception of credit quality and or 4) of the scarcity/availability of capital.
Today’s bailout policies have been enabled and facilitated by an environment of suppressed consumer price inflation rates, partly because of globalization, partly because of the temporal effects from price manipulations or market interventions and partly because of the ongoing liquidations in some segments of the global marketplace such as from MF Global, the crisis affected banking and finance sectors of the Eurozone and also perhaps in sectors impacted by the economic slowdown or the real estate exposed industries in China, which may be suffering from a contraction.
However I don’t believe that the current low inflation landscape will be sustainable in the face of sustained credit easing operations by the central banks of major economies. Price inflation will eventually surface that could lead to restrictive policy actions (which subsequently could lead to a bust) or sustained inflationism (which risks hyperinflation). Signs from one of which may become evident probably by the second semester of this year.
Yet I think we could be seeing innate signs this: Given the current monetary stance and increasing geopolitical risks, oil (WTI) has the potential to spike above the 2011 high of $114 which may lead to a test of a 2008 high of $147.
4. Phisix: Interim Fulfilment of Expectations and Working Target
In the meantime, I expect the Philippine Phisix and ASEAN markets to continue to benefit from the current easy money landscape helped by seasonal strength, improvements in the market internals, and in the reversals of bearish chart patterns as forecasted last December[20]

The bearish indicators of head and shoulders (green curves) and the ‘death cross’ have now been replaced by bullish signals as anticipated[21]. The Phisix chart has now transitioned to the golden cross while ‘reverse head and shoulders’ (blue curves and trend line) has successfully broken out of the formation. It doesn’t require relying on charts to see this happen. Even the Dow Jones Industrials has affirmed on my prognosis[22].
The S&P 500, oil (WTI) and the Phisix seem to manifest a newfound correlation or has reflects on a synchronized move,whether this relationship will hold or not remains to be seen.
I believe that the Phisix at the 5,000 level should represent a practical working yearend target; where anything above should be a bonus.
Again all these are conditional to the very fluid external political-financial environment, which includes risks from not only from the Eurozone, but from China and the importantly US—whose debt level is just $25 million shy from the debt ceiling[23] (probably the debt ceiling political risk will become more evident during the last semester).
Moreover, I believe that gold prices will continue to recover from the recent low.
Gains will crescendo as global policymakers will most likely ramp up on the printing presses. Gold will likely reclaim the 1,900 level sometime this year and could even go higher and will end the year on a positive note.
But then again all these are extremely dependent or highly sensitive to the situational responses of global policymakers.
Predicting social events or the markets in the way of natural sciences is a mistake.
As the great Ludwig von Mises explained [24],
Nothing could be more mistaken than the now fashionable attempt to apply the methods and concepts of the natural sciences to the solution of social problems. In the realm of nature we cannot know anything about final causes, by reference to which events can be explained. But in the field of human actions there is the finality of acting men. Men make choices. They aim at certain ends and they apply means in order to attain the ends sought.
[1] See What To Expect In 2011, December 20, 2010
[2] See US Federal Reserve Goes For Subtle QE August 10, 2011
[3] Centralbanknews.info What Will 2012 Bring for Global Monetary Policy? December 27, 2011
[4] See Global Central Banks Ease the Most Since 2009, November 28, 2011
[5] Zero Hedge Top Three Central Banks Account For Up To 25% Of Developed World GDP, January 5, 2012
[6] See Hot: Swiss National Bank to Embrace Zimbabwe’s Gideon Gono model September 6, 2011
[7] See Bank of England Activates QE 2.0 October 6, 2011
[8] See Global Equity Market Performance Update: Philippine Phisix Ranks 6th among the Best, December 17, 2011
[9] See How Global Financial Markets Performed in 2011 December 31, 2011
[10] Key Trends in Globalization, New world trade data indicates slowdown but not recession in the global economy, November 25, 2011 ablog.typad.com
[11] Allstarcharts.com BCA Research: High Equity Correlations Are Here To Stay, January 4, 2011
[12] See Graphic of the PSE’s Sectoral Performance: Mining Sector and the Rotational Process, July 10, 2011
[13] See MF Global Fallout Haunts the Metal Markets, December 12, 2011
[14] See War On Gold: China Applies Selective Ban December 28, 2011
[15] See Could the US be using the Euro crisis to extract support for a possible war against Iran? January 8, 2012
[16] Bloomberg.com China, Japan to Back Direct Trade of Currencies, December 26, 2011
[17] See The Nonsense About Current Account Imbalances And Super-Sovereign Reserve Currency, April 20, 2011
[18] Cleveland Federal Reserve Credit Easing Policy Tools
[19] See World’s Biggest Economies Face $7.6 Trillion Bond Tab as Rally Seen Fading January 4, 2012
[20] See Phisix: Primed for an Upside Surprise December 11, 2011
[21] See How Reliable is the S&P’s ‘Death Cross’ Pattern?, August 14, 2011
[22] See US Equity Markets: From Death Cross to the Golden Cross, December 31, 2011
[23] Zerohedge.com Here We Go Again: US $25 Million Away From Debt Ceiling Breach, January 5, 2012
[24] von Mises Ludwig Misapprehended Darwinism, Refutation of Fallacies, Omnipotent Government p.120












