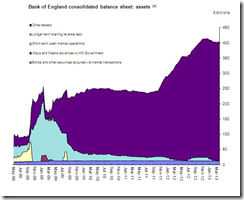
The Bank of England (BoE) says what I have been saying all along: markets have functioned in departure from reality or what I call as "parallel universe".
From the Bloomberg
The Bank of England said rising equity markets don’t reflect the underlying economic situation and warned that investors may be underestimating risks in the financial system.Gains by equities since mid-2012 “in part reflected exceptionally accommodative monetary policies by many central banks,” the BOE’s Financial Policy Committee said today in London in the minutes of its March 19 meeting. “It was also consistent with a perception among some contacts that the most significant downside risks had attenuated. But market sentiment may be taking too rosy a view of the underlying stresses.”
UK’s highly fragile banking system has been amplified by current yield chasing parallel universe. More from the same article:
At the meeting, the FPC recommended that U.K. lenders raise 25 billion pounds ($38 billion) of additional capital to cover bigger potential losses, possible fines for mis-selling and stricter risk models. While banks have strengthened their resilience in recent years, the FPC said today that not all of them may be able to withstand unexpected shocks and maintain lending to companies and households.The FPC discussed potential threats from the crisis in Cyprus, which agreed on an international bailout last month. While at the time of the March 19 meeting there were “minimal signs” of spillovers to other financial systems, there was “a risk that this situation could change,” the committee said….In their discussion, the FPC members noted the potential threats to the financial system from increased risk appetite among investors.“This was evident in the re-emergence of some elements of behavior in financial markets not seen since before the financial crisis, including a relaxation in some U.S. credit markets of non-price terms and increased issuance of synthetic products,” the committee said. “At this stage, they did not appear indicative of widespread exuberance in markets. But developments would need to be monitored closely.”The FPC also said that banks’ leverage ratios, a measure of their debt to equity level, would remain “very high” even after the new recommendations were met. It said there would be “little margin for error against a backdrop of low growth in the advanced economies.”
As noted in the above, central bank authorities either fail to comprehend on the distortive consequences of their inflationist policies or that they are in deep denial.
Because money is never neutral, central bank’s monetary expansion means “money from thin air” flows into the financial and economic system asymmetrically.
Such polices trigger what is called as the “business cycle”.
As the great dean of Austrian economics explained
The fundamental insight of the "Austrian," or Misesian, theory of the business cycle is that monetary inflation via loans to business causes over-investment in capital goods, especially in such areas as construction, long-term investments, machine tools, and industrial commodities. On the other hand, there is a relative underinvestment in consumer goods industries. And since stock prices and real-estate prices are titles to capital goods, there tends as well to be an excessive boom in the stock and real-estate markets.
(bold mine)
So England’s property bubble and elevated equity prices signify as a classic example of the business cycle in motion.
And given the increasingly hostile environment where productive (commercial) activities are being punished via higher taxes, financial repression and by increased regulations and mandates, such string of political actions compounds on the skewing of people’s incentives towards yield chasing activities.
Add to this the distorting effects of inflationism on economic calculation, again professor Rothbard: (bold mine)
By creating illusory profits and distorting economic calculation, inflation will suspend the free market's penalizing of inefficient, and rewarding of efficient, firms. Almost all firms will seemingly prosper. The general atmosphere of a "sellers' market" will lead to a decline in the quality of goods and of service to consumers, since consumers often resist price increases less when they occur in the form of downgrading of quality. The quality of work will decline in an inflation for a more subtle reason: people become enamored of "get-rich-quick" schemes, seemingly within their grasp in an era of ever-rising prices, and often scorn sober effort. Inflation also penalizes thrift and encourages debt, for any sum of money loaned will be repaid in dollars of lower purchasing power than when originally received. The incentive, then, is to borrow and repay later rather than save and lend. Inflation, therefore, lowers the general standard of living in the very course of creating a tinsel atmosphere of "prosperity."
Besides, like Spain, central banks have supported asset markets in order to finance unwieldy government spending or their highly tenuous welfare state via Ponzi financing.
In short, lofty equity prices are symptoms of monetary disorder. Another reality is that such policies have been designed to preserve on the unsustainable incumbent political economic cartel of the debt and inflation based crony banking-welfare/warfare state-central banking system through asset bubbles.
Yet if central banks desist from pursuing further monetary expansion that blows today's asset bubbles, the system falls asunder.
Eventually when a critical state have been reached from these cumulative unsustainable political actions, markets will also unravel.
Central bankers, in essence, have been caught between the proverbial devil and the deep blue sea.
The above also shows why conventional treatment of financial markets will be highly sensitive to significant analytical errors and losses. As hedge fund manager Kyle Bass recently noted, today's markets are largely Potemkin Villages.