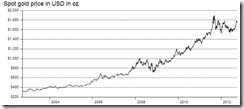
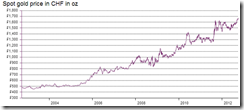
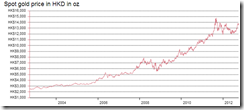
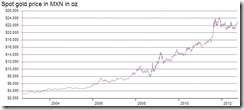
Congratulations, Mr. Bernanke. I'm happy. My asset values go up but as a responsible citizen I have to say the monetary policies of the U.S. will destroy the world.-Dr. Marc Faber
We have practically reached a virtual denouement phase for central bank communication “inflation expectations” management strategies as well as the penultimate stage for central bank asset-purchasing programs.
“Whatever it takes” to support the incumbent political financial order has been discharged into actual policies.
Last week, the ECB launched its Quantitative Easing (QE) version of unlimited bond buying[1] program. This week, it was the US Federal Reserve’s turn to validate my predictions[2].
Political Desperation Leads to the Nuclear Option
Doing things over and over and expecting different results appears to have reached a culmination point too.
The mainstream has repeatedly argued that central bank policies have not attained the targeted goals because of the supposed insufficiency of the degree of measures undertaken to attain the desired traction. In short, for the interventionists throwing money at the problem has never been enough.

For instance, putting into the limelight the fragility or the resiliency of the current statistical economic recovery of US, the trend of non-participants in the US labor markets has been steadily increasing (upper window blue bar trend). This could mean many factors such as many people may have given up on the search for jobs or that many may have gone into the informal economy or that many could have become dependent on government welfare (lower window exhibits the recent surge in food stamps and disability participants) or a combination of the above. (chart from dshort.com[3])
In addition to this, jobs that have been created has been on a sustained decline even amidst the gamut of credit easing policies, particularly QE 1.0, QE 2.0, Operation Twist and Operation Twist Extension of the US Federal Reserve.
Thus, given the latest policies announced by the FED, as well as the ECB, the efficacies of open ended and unlimited measures will be put under the proverbial microscope.
There will hardly be any further excuses for any subsequent policy mistakes. Proponents of the inflationism appear to have been boxed into a corner.
RISK ON is Back, For Now
The reactivation of the RISK ON environment essentially comes with the German constitutional court’s clearing of the legal hurdle for the European Stability Mechanism (ESM)[4], but with some conditional[5] stipulations* and the US Federal Reserve’s announcement of the nuclear “open ended” MBS buying program.
*The ever changing rules to accommodate these bailouts, I think, will unlikely become a barrier. Central bankers have gradually been assuming the role of politicians. FT columnist Gideon Rachman captures the zeitgeist best[6]
As a result of the ECB’s actions, voters from Germany to Spain will increasingly find that crucial decisions about national economic policy can no longer be changed at the ballot box.
In the Q & A portion of the post-FOMC announcement, US Federal Reserve chief Ben Bernanke unreservedly expressed that these policies had been intended to boost prices of financial assets in order to stimulate the “wealth effect” demand-driven spending[7] or Mr. Bernanke’s financial accelerator.
The tools we have involve affecting financial asset prices. Those are the tools of monetary policy. There are a number of different channels. Mortgage rates, other rates, I mentioned corporate bond rates. Also the prices of various assets. For example, the prices of homes. To the extent that the prices of homes begin to rise, consumers will feel wealthier, they’ll begin to feel more disposed to spend. If home prices are rising they may feel more may be more willing to buy home because they think they’ll make a better return on that purchase. So house prices is one vehicle. Stock prices – many people own stocks directly or indirectly. The issue here is whether improving asset prices will make people more willing to spend. One of the main concerns that firms have is that there is not enough demand…if people feel their financial position is better they’ll be more likely to spend….
Despite the economic justification which have been premised on popular economic fallacy, from where stones can be turned into bread through inflationism, Mr. Bernanke’s decision to trigger the nuclear option which validated my prediction, has been mainly about
1) funding the US budget deficits (what I called in the past as “poker bluff” or the propaganda that FED won’t do a QE[8]),
2) the fulfillment of the perpetual promises to stimulate (where a failed expectation would have meant a violent backlash), and
I wrote[9],
Mounting expectations and deepening dependence from central banking opiate, which has been clashing with the unfolding economic reality, will prompt for more price volatility on both directions. The Bank of America posits that QE 3.0 has been substantially priced in.
Eventually stock markets will either reflect on economic reality or that central bankers will have to relent to the market’s expectations. Otherwise fat tail risks may also become a harsh reality.
3) Importantly, Mr. Bernanke’s implied support for the re-election of the President Obama, which ensures his tenure as Chairman of the US Federal Reserve[10].
Yet while it has been true that a huge amount of stimulus have been priced into the markets, the Fed’s extension of the zero bound rates through 2015 and the open ended $40 billion monthly purchases of mortgage bonds combined with the existing $267 Operation Twist have been aggressively beyond expectations of the marketplace.
So the initial impact of the FED-ECB policies to subsidize financial assets represents attained its short term goal, they succeeded to inflate asset prices first.

Steroid dependent global equity markets were in revelry as the FED-ECB programs were made public.
Most of the global markets surged. Among the major benchmarks, the BRICS (except for China) posted the biggest gains while the rest of the developed economies, along with, the ASEAN majors scored substantial weekly advances of over 1%.

In the US market breadth turned substantially positive 84% of stocks soared above the 50-day moving averages[11] while Advance Decline ratio decidely went for the bulls[12]

The unveiling of the joint central bank nuclear policies also resulted to a huge rally in the bonds of distressed nations as Spain and Italy. Yields fell hard as bond vigilantes were beaten back by the ECB’s actions (chart from Dankse Research[13])
And as expected, rallying bond prices have reduced pressures on politicians of the criss stricken nations as Spain, to underake required reforms.
Spain’s prime minister, Mariano Rajoy, according to a news report[14], said last week that “he won’t allow the European Union or the ECB to stipulate how the nation narrows its budget deficit as a condition for buying the country’s bonds”.
So the ECB’s asset purchases have only increased the moral hazard aspects in the behavior of politicians. Efforts to redress such the imbalances that caused the crisis will likely be delayed. Instead of the ECB buying time for politicians to commence on reforms, the ECB has become THE tool for EU’s politicians to do the latter’s bidding.
The risk on rally has also diffused into global corporate bond markets.
In the US, a surge in corporate bond issuance has prompted yields on speculative-grade debt to drop to an unprecedented low, which according to Bloomberg, breaks the previous record set more than 15 months ago[15].
Unintended Consequences of the FED-ECB policies

In spite of all the euphoria, the FED’s operations may likely be reaching a tipping point.
The combined monthly $40 billion MBS purchases by US Federal Reserve, as well as, the $45 billion long term (10-30 year) US treasury bond buying from Operation Twist means that the Fed’s balance sheet is likely to expand to about $4 trillion by the end of 2013 from $ 2.8 trillion or an increase of about $1.17 trillion, according to Zero Hedge[16].
Yet the sterilization measures by Operation Twist of selling $45 in short term bonds to offset the long end buying will likely end by this year as the Fed runs out of short term securities to sell.
Essentially, roughly half of the US budget deficit will be monetized by the FED. Also the FED’s buying operations will accrue to about 24% of the GDP (see chart above)
Moreover, since the FED holds about $843 billion of Agency MBS[17], the open ended MBS purchases will extrapolate to expansion of the FED’s share of ownership of the entire mortgage market to about 33%, again according to the estimates of Bank of America BofA cited by Zero Hedge[18].
In addition the bond purchasing program means that ownership share of the FED “across the 6y-30y portion Treasury curve is likely to reach about 50% by end of 2013 and an average of 65% by end of 2014”, where “in just over two years the Federal Reserve will hold two thirds of the entire bond market with a maturity over 5 years” again according to the calculation of the BofA.
The FIRST point being that FED’s buying program may end up with FED owning a very large segment, if not all, of both the Agency MBS and the US Treasuries and may run out of bonds to buy to pursue their asset purchases.
Of course they can always resort to buying equities (similar to Bank of Japan[19]) and corporate bonds. But as appropriately pointed out by the only dissenting voice at the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) Jeffrey Lacker of the Richmond Federal Reserve, this would be unethical[20].
Channeling the flow of credit to particular economic sectors is an inappropriate role for the Federal Reserve.
In the world of politics, moral relativism belongs to those in power.
Also the NEXT point is that these combined policies will usher in a high period of Price inflation. Aggressive expansion of money through QE will eventually filter into the economic system.
Even from the monetarist perspective, particularly the Philip Cagan model which according to Professor Garrett Jones[21] states that “Today's price level depends mostly on the future supply of money”, the communication to the public of the FED and the ECB’s combined programs should imply for higher price levels than today.
Yet the huge amount of coming infusions from the FED-ECB will likely be complimented by the Bank of England, and Bank of Japan, as well as the Swiss National Bank whom has been the quasi-pioneer implementer of the unlimited option via the Swiss-Franc Euro price cap[22]
Seminal Signs of a Crack-UP Boom?

The recent strong performance of commodities may have altered balance between the recently outperforming stock market (S&P 500) and commodity prices (CCI or the CRB Reuters Index).
Commodities could be in a major inflection point relative to the stock market.
The same dynamics seems are being channeled into the currency markets.
It would be a mistake to see a rallying euro as a sign of “progress”. The rallying euro has been a manifestation of the obvious shift to a RISK ON environment through massive central bank manipulations.
As Doug Noland of the Credit Bubble Bulletin rightly points out[23]
I’ll state what others hesitate to admit: this week our central bank took a giant leap from radical to virtual rogue central banking. If Bernanke’s plan was to leapfrog the audacious Draghi ECB, our sinking currency – even against the euro – is confirmation of his success. If his goal was to provide markets a Benjamin Strong-like “coup de whiskey” – he should instead fear the dangerous instability central bankers have wrought on global markets and economies.
It would also be oversimplistic and misguided to see strengthening currencies as tempering “price inflation”.
In a world of fiat currencies and globalization, strengthening currencies could be a sign of a bubble in progress rather than of a structural advancement
The chart above shows that the race to devalue through unlimited or open ended QEs between Fed’s Bernanke and ECB’s Draghi have been transmitted through a rally in commodities priced in the US dollar (CCI:USD) and the Euro (CCI:XEU).
Put differently, both currencies, the US dollar and the Euro, have now been devaluing against the broad based benchmark of commodities. In the Austrian school of economics, these could signify as seminal signs of a crack-up boom
And contra mainstream empirical analysts, we must be reminded that the valuation of a monetary unit, according to the great Ludwig von Mises[24], depends not on the wealth of a country, but rather on the relationship between the quantity of, and demand for, money. Thus, even the richest country can have a bad currency and the poorest country a good one
A good example seems to be Brazil’s real. The real has firmed against the US dollar since 2008 post Lehman debacle (yahoo chart left window).

The supposed leakage from the sterilzation process from Brazil’s huge foreign reserve accumulation—where government bonds issued by Brazil’s central bank to sterilize foreign exchange purchases, has been used as collateral by banks to issue debt thereby expanding their balance sheets—has fueled a credit boom in Brazil’s economy. Claims on government have skyrocketed in 2011 as the real soared (right window).
The Brazilian government recently tried to curb through a series of tightening via interest rate hikes which may have prompted for the recent economic weakening.
The recent economic boom which could have been orchestrated through a covert quantitative easing scheme by Brazil’s central bank has been questioned by Jonathan Wheatley at the Financial Times blog[25] as a possible product of a central bank fueled boom-bust cycle.
Have inflows, then, been driving Brazil’s credit boom – and has the government been guilty of quantitative easing? It is hard to explain the expansion of credit from about R$500bn in 2005 to about R$2.2tn today on the basis of economic growth alone. Over that period, GDP growth has averaged 4 per cent a year – hardly a Chinese performance.
If quantitative easing really is the answer, it doesn’t just put the Brazilian government’s account of its monetary policies in question. It questions the basis of the whole Brazilian growth story.
By the way, Brazil’s government has recently joined the stimulus bandwagon with a $66 billion infrastructure stimulus[26].
The point being: In a world where central banks compete to destroy their currencies through devaluation, rising currencies may signify as symptoms of relative devaluation and they could also mask the bubble policies that underpins the statistical economic growth.

It would also be an error to likewise view rallying commodities signs of economic recovery, China who plays a major role in the commodity business, seems to be struggling from a bubble bust.
Despite the recent announcement of what seems as a reluctant and limited bailout program through infrastructure spending and through extension of bank loans to state owned enterprises, the deteriorating conditions of China’s shadow banking system[27] seems to be worsening. In addition, China’s oil imports continue to plummet[28] which is most likely a manifestation of a rapidly slowing economy.
Where commodities rise against a broad spectrum of fiat currencies, then this should be a cause of concern as they could be symptoms of the transition to a crack-up boom.
Again the from great Professor von Mises[29]:
But the boom cannot continue indefinitely. There are two alternatives. Either the banks continue the credit expansion without restriction and thus cause constantly mounting price increases and an ever-growing orgy of speculation, which, as in all other cases of unlimited inflation, ends in a “crack-up boom” and in a collapse of the money and credit system. Or the banks stop before this point is reached, voluntarily renounce further credit expansion and thus bring about the crisis. The depression follows in both instances.
FED-ECB Policy Impact on Asia, Philippine Peso and the Phisix
Asian currencies have rallied strongly in response to the FED-ECB easing programs.

While Asian currencies have been on an upswing from previous pledges to inflate since June, as shown by the JP Morgan Bloomberg ADXY[30] Asian basket of currency index (upper window), the biggest of the advances came from last week (lower window).
The Philippine Peso has been slightly up by .6% to 41.42 a US dollar from 41.68 last week but has strong year to date gains of 5.5%--in harmony with the scintillating gains of the local equity market.
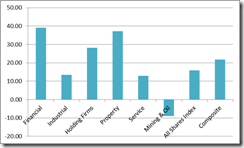
I believe that the interim response from the FED-ECB policies, designed to prop up financial assets, will likely provide strong support to the global stock markets including the Philippine Phisix perhaps until the yearend, at least.
The mining index, which has underperformed all sectors, will likely expunge its year to date losses at least by the yearend.
The mining index will likely retake command of the leadership in 2013 as it has outperformed biyearly since 2007[31].
In a world where central bank policies become the dominant factor in establishing price levels, the new normal is to expect dramatic price swings in both directions and of the amplification of risks
Former Federal Reserve Governor Kevin Warsh in a recent CNBC interview nails it[32].
If you continue to look at the markets right now, where asset prices continue to melt up where asset prices are driven less by fundamentals in particular companies and more by speeches and policies come out of Washington you are taking this risks. Risk are highest in the economy when measures of risk ARE lowest, when I look at the VIX at this level and you compare that to the headlines you guys read every morning they certainly do not seem in sync that’s when shocks happen
But given the projected substantial infusion of steroids, the current environment strongly favors an upswing. That’s until real problems will resurface such as concerns over the quality of credit, and or price inflation becomes more pronounced and or if politics becomes an obstacle to the central banks inflationism and or a combination of the above.
And since no trend goes in a straight line where I expect some interim reprieve from the bullish momentum, I would use any interim corrections as opportunity to position on resource issues.
No Justification for Bubbles
As a final note the FED-ECB policies will affect Asian economies and markets immensely as I have discussed before[33].
These policies will likely incentivize strong capital flows into the region, as investors “search for yields” or seek refuge to protect their savings from deliberate and sustained currency debasement—in reality these accounts for as the capital flight dynamic.
Capital inflows coupled with domestic negative real rates regime will likely translate into serial bubble blowing dynamics.
So yes, the risks of bubbles in Asia will become more enhanced. Even the local central bank or the Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP) has recently acknowledged of such risks[34] which they arrogantly claim they can control.
In addition, domestic and global bubbles will increase the risks of a global stagflation which is likely slam emerging markets harder.
The risks of ballooning bubble or stagflation will likely become evident in 2013-2014.
Yet the idea that bubbles are good for Asia emanates from a warped, demented and disoriented understanding of economic reality and theories.
Costs are not benefits. What seem as the illusion of progress through asset price inflation has in reality been transfers of resources from the rest of society to the owners of financial assets (stocks bonds and property).
The benefits which accrue to these politically privileged sectors do not take into account the social and economic costs of these transfers[35].
Bailouts benefit the rich at the expense of the poor. Rampant speculations fueled by inflationism are not productive undertaking which adds to products and services to the society. Addiction to debt for speculation or for consumption leads to bankruptcy. The shrinkage of purchasing power of the currency through price inflation hurts the middle class and the poor most.

Misallocated capital cannot be seen as “benefits” since at the end of the cycle, misdirected capital will be exposed as wasted or consumed capital through a bubble bust or a financial crisis. In short, boom bust cycles destroy capital, lowers society’s standard of living or impoverishes people.
The Asian crisis of 1997 as a consequence of the prior inflation boom reveals of how Thailand’s GDP per capita[36] fell by 66% and only recovered when imbalances were allowed to clear. It took roughly 10 years for Thailand’s per capita GDP to recover the high of 1996.
Myopic thinking that mistakes symptoms as causes and that promotes short term ‘benefits’ at the expense of long term ‘costs’ is very unhelpful and will not help produce better returns.
[1] See ECB’s Mario Draghi Unleashes “Unlimited Bond Buying” Bazooka, Fed’s Ben Bernanke Next? September 7, 2012
[2] See I Told You So Moment: US Fed’s Bernanke Unveils Open Ended QE 3.0 Bazooka September 14, 2012
[3] Lance Roberts QE3 And Bernanke's Folly - Part I Advisor Perspectives dshort.com September 14,2012
[4] See German Court Clears Way for ESM Fund, September 12, 2012
[5] OpenEurope.org.uk What will the German Constitutional Court ruling mean for the eurozone? September 12, 2012
[6] Gideon Rachman Democracy loses in struggle to save euro Financial Times September 10, 2012
[7] Cullen Roche A Disturbing Look Inside the Mind of Ben Bernanke, Pragmatic Capitalism, September 13, 2012
[8] See Poker Bluff: No Quantitative Easing 3.0? June 5, 2011
[9] See Phisix: Why The Correction Cycle Is Not Over Yet September 2, 2012
[10] See Phisix: The Correction Cycle is in Motion August 27, 2012
[11] Bespokeinvest.com Breadth Breakout? September 14, 2012
[12] Bespokeinvest.com Breadth Finally Makes a Higher High September 13, 2012
[13] Danske Research The Fed takes a major step forward, September 14, 2012
[14] San Francisco Chronicle European Stocks Fall on Concern Spain, German May Harm ECB Plan September 11, 2012
[15] Bloomberg.com Corporate Bond Sales in U.S. Busiest in Six Months as Fed Acts September 14, 2012
[16] Zero Hedge The Fed's Balance At The End Of 2013: $4 Trillion September 3, 2012
[17] Zero Hedge Rosenberg: "If The US Is Truly Japan, The Fed Will End Up Owning The Entire Market" September 14, 2012
[18] Zero Hedge, BofA Sees Fed Assets Surpassing $5 Trillion By End Of 2014... Leading To $3350 Gold And $190 Crude September 14, 2012
[19] See Bank of Japan Hearts the Stock Market May 08, 2012
[20] See Quote of the Day: Dissenting Opinion on Open Ended QE at the FOMC September 16, 2012
[21] Garett Jones Future money and today's NGDP Econolog September 14, 2012
[22] See Swiss National Bank’s Currency Interventions Spawns Property Bubble August 14, 2012
[23] Doug Noland QE Forever Credit Bubble Bulletin Prudentbear.com September 14, 2012
[24] Ludwig von Mises CHAPTER 1—STABILIZATION OF THE MONETARY UNIT —FROM THE VIEWPOINT OF THEORY (1923) The Causes of Economic Crisis p.18 Mises.org
[25] Jonathan Weathley Quantitative easing, Brazilian style Beyond BRICs September 10, 2012 Financial Times Blog
[26] See Brazil’s Government Unveils $66 Billion Stimulus August 16, 2012
[27] See More Signs that China’s $2.4 Trillion Shadow Banking System is in Big Trouble September 14, 2012
[28] Zero Hedge Chinese Crude Imports Plunge To Mid-2010 Levels September 11, 2012
[29] Ludwig von Mises, III. INFLATION AND CREDIT EXPANSION, Interventionism An Economic Analysis
[30] Bloomberg.com JP Morgan Bloomberg Asian Dollar Index ADXY
[31] See Graphic of the PSE’s Sectoral Performance: Mining Sector and the Rotational Process July 10, 2011
[32] See Video: Former Fed Governor on Bernanke’s QE: Unproven Experiment , Risks of Exit have to be Higher September 15, 2012
[33] See The Impact of Open Ended QEs on Asia: Bubbles or Stagflation September 15, 2012
[34] See Fatal Conceit: Philippine Authorities to Avert Asset Bubbles September 10, 2012
[35] See Inflationism Promotes Inequality, Immorality and Economic Hardship September 15, 2012
[36] KNOEMA.com GDP per Capita by Country Thailand