Highly volatile markets will be the outcome of today’s treacherous geopolitical conditions. That’s what I have been saying all along.
Volatility in Both Directions but with a Downside Bias
So far my perspective has been continually confirmed: volatility on both directions with a downside bias, especially for the Phisix.
A week ago, the Phisix got slammed early but the bulls worked their way to cover on the lost ground, and by the end of the week, losses had been trimmed to less than half[1].
The opposite scenario occurred this week: the Phisix had a strong opening carried mostly by the initial torrent from Spain’s bailout, but bulls eventually succumbed to the bears by the week’s close.
Technically speaking, in spite of all the volatility, the Phisix has been rangebound.
Volatility has been global.
In seeming defiance of gravity where bad news conventionally extrapolates to lower markets, today, bad news IS good news.
It is ironic to see central bankers scream for blood[2], yet global equity markets trekked higher. That’s because market participants have been conditioned to the Bernanke Put or expectations that central bankers, led by the US Federal Reserve, will like a knight in shining armor, ride to the rescue.
News of the $125 billion Spanish bailout prompted for a one day euphoria which quickly faded. It was evident that markets saw through the flaws of the proposed bailout[3]. However as the week progressed, the spate of bad news gave way to intensifying speculations, which has been further fuelled by promises[4] of renewed interventions by central bankers.
Except for ASEAN bourses which posted mixed showing, major global indices registered modest to significant gains over the week.
China’s Loan Growth and Chart Patterns
China’s loans unexpectedly jumped in May, according to news reports[5]. This has prompted the Shanghai index to post a modest advance of 1.13% over the week.
Most of the growth in China’s credit markets seems to have been driven by State Owned Enterprises (SOE). This means that China may have embarked on a furtive state based stimulus rather than a nationwide program.
Unfortunately SOE’s which have played a prominent role in the expansion of China’s highly fragile shadow banking system and which has already been encumbered by questionable loans, may have limited actions for further expansion. But of course, given that SOEs are government owned firms, restrictions may be circumvented to advance political goals.
Yet given the moderate gains exhibited by China’s equity markets on such development, investors must have remained cynical to the sustainability of China’s bailout policies.
Nevertheless surging bond yields have not posed as a burden to global stock markets in heavy anticipation of central bank steroids. In spite of Spain’s bailout, Spain and Italy’s bond yields soared[6].
A week’s action cannot be read as a sustainable trend, thus we must continue to observe how prices in various markets will react to China, as well as to the developments in Europe, particularly the Greece moment and in the US.
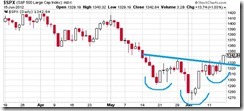
Many have crowed about the bullish potentials of the US stock market through the reverse head and shoulder pattern, which they think may have a spillover on the Philippines.
As I pointed out in the past, patterns don’t make prices, people’s actions do.
It will be actions of central bankers that will determine the directions of the marketplace rather than chart patterns. I pointed out last year that the death cross in the US S&P 500 in August of 2011 signified a false alarm[7] (false positive error) and was eventually validated four months after[8].
So far, US money supply M2 seem not supportive of a sustained rise by the S&P 500 owing possibly to the US Federal Reserve’s offsetting of the “flight to safety” inflows coming from the EU and from the closure or winding up operations of Operation Twist as discussed last week[9].
It would likely take the FED another ramping up of their balance sheet expansion to rekindle the monetary accommodation.
So the bullish chart pattern may play out its trend if the Fed will ease further, otherwise, the chart pattern will likely fail.
Buy the Rumor, Sell the News
Global financial markets have relied heavily on the “buy the rumor” from central banking rescues.
These are likely to have two short to medium term outcomes.
One, if central bankers FAIL to deliver in accordance to market’s expectations, then we will likely see another huge bout of downside volatility in global equity markets.
The Phisix, whom has not been immune to contagion, may breakdown its recent support level at 4,863, a level which represents nearly 10% from the peak. But a breakdown may not necessary lead to a bear market.
Yet such market turmoil may likely serve as fulcrum for the next batch of intensive interventions. Nevertheless, under such conditions, it would be best to wait and see until volatilities in the financial markets (stocks, commodities, bonds) subside, before considering to reposition.
On the other hand, if markets may be temporarily satisfied with REAL actions of central banks (e.g. $1 trillion bailout) then we should see a minor or a slight “sell on news”. But this should be seen as opportunities to RE-ENTER the markets incrementally.
Of course, the direction of gold prices, as well as, prices of general commodities, will serve as crucial indicators in determining the strength of the trend.
While gold’s price trend has significantly improved, there have been little signs of progress in the oil market (WTIC) and the general commodities (CRB).
Finally as caveat, I would like to reiterate that should markets continue to rise in ABSENCE of REAL actions from central bankers, we cannot rule out that the markets could fall like a house of cards (fat tail risks) or what I would call a Dr. Marc Faber event[10].
The market’s deep addiction to stimulus will eventually seek REAL stimulus more than just promises or in central bank lingo, signalling channel. Reversal of expectations can become violent.
As a side note, I find it ridiculous for people especially so-called experts to assert that today’s problems have been caused by lack of confidence, as if confidence has been randomly determined, and not in reaction to changes in the environment or in response to interactions with people. People have been not confident with the markets because of the persistent problem of insolvency and price artificiality and price distortions from political meddling. It’s a severe mistake to interpret effects as THE cause.
Bottom line: Global financial markets, including the Phisix, remains in a state of limbo. Uncertainty still governs. Under current conditions, the best guiding principle would be; patience is the better part of valor.
[1] See Expect a Continuation of the Risk ON-Risk OFF Environment, June 11, 2012
[2] See Central Bankers Talk Doom, Markets Surge, June 16, 2012
[3] See Why Spain’s Bailout may NOT Work June 12, 2012
[4] See Talk Therapy boost US Markets, June 15, 2012
[5] See China’s New Loans Unexpectedly Surged in May, June 12, 2012
[6] Danske Bank, All eyes on Greek election June 15, 2012 Weekly Focus
[7] See How Reliable is the S&P’s ‘Death Cross’ Pattern?, August 14, 2011
[8] See US Equity Markets: From Death Cross to the Golden Cross, December 31, 2011
[9] See Expect a Continuation of the Risk ON-Risk OFF Environment, June 11, 2012
[10] See Dr. Marc Faber Warns of 1987 Crash if No QE 3.0, May 11, 2012