Deficits are always a
spending problem, because receipts are, by nature, cyclical and volatile, while
spending becomes untouchable and increased every year—Daniel Lacalle
In this issue
Debt-Financed Stimulus
Forever? The Philippine Government’s Relentless Pursuit of "Upper Middle-Income" Status
I. Changes in Tax
Collection Schedules Distort Philippine Treasury Data and Highlight Fiscal Cycles;
Spending’s Legal Constraints
II. Stimulus Forever?
The Quest for "Upper Middle-Income" Status and Credit "A" Rating,
Rising Risks of a Fiscal Blowout
III. 10-Month Public Revenue
Growth Deviates from PSEi 30’s Activities
IV. Q3 2024: 2nd Highest
Revenue to NGDP, Headline GDP Weakens—The Crowding Out Effect?
V. Record 10-Month Expenditure:
The Push for "Big Government"
VI. 10-Month Debt Servicing
Costs Zoom to All-Time Highs!
VII. Rising Foreign Denominated
Debt Payments!
VIII. Despite Slower
Increases in Public Debt, Little Sign of the Government Weaning Off Stimulus
IX. Q3 2024: Public Debt
to GDP rises to 61.3%
X. Conclusion: The Relentless
Pursuit Of "Upper Middle Income" Status Resembles a Futile Obsession
Debt-Financed Stimulus
Forever? The Philippine Government’s Relentless Pursuit of "Upper Middle-Income"
Status
Improvements in the 10-month fiscal balance
have fueled the Philippine government’s unrealistic fixation on achieving
'Upper Middle Income' status—here's why.
I. Changes in Tax
Collection Schedules Distort Philippine Treasury Data and Highlight Fiscal Cycles;
Spending’s Legal Constraints
Inquirer.net, November 28: A
double-digit revenue growth helped swing the government’s budget position back
to a surplus in October, keeping the 10-month fiscal deficit below the 2024
ceiling set by the Marcos administration. The government ran a budget surplus
of P6.3 billion in October, a reversal from the P34.4- billion deficit recorded
a year ago, figures from the latest cash operations report of the Bureau of the
Treasury (BTr) showed.
Most media outlets barely mention that recent
changes in tax collection schedules have distorted the Bureau of the Treasury’s
reporting data.
As noted in September, these adjustments
significantly impact the perception of fiscal performance.
That is to say, since
VAT payments are made at the end of each quarter but recorded in the first
month of the following quarter, this quarterly revenue cycle inflates reported
revenues for January, April, July and October, often resulting in a narrowed deficit
or even a surplus for these months.
Therefore, we
should anticipate either a surplus or a narrower deficit this October.
(Prudent Investor, October 2024)
Figure 1
For instance, October’s surplus of Php 6.34
billion underscores how the quarterly revenue cycle boosts collections at the
start of every quarter, often leading to either a surplus or a narrowed
deficit. Surpluses were observed in January, April, and October this year. (Figure
1, topmost chart)
However, as the government pushes to meet its
year-end 'budget execution' targets in December, a significant spike in the
year-end deficit could emerge from the remaining spending balance.
Based on the budget allocation for 2024 amounting
to Php 5.768 trillion, the unspent difference from the ten-month spending
of Php 4.73 trillion is Php 1.038 trillion.
Notably, in contrast to previous years, 2024
has already experienced three months of public spending exceeding Php 500
billion, with December still underway. (Figure 1, middle image)
On the other hand, this could indicate a
potential frontloading of funds to meet year-end targets.
While spending excesses are constrained by
law, the government has consistently exceeded enacted budget allocations since
2019. (Figure 1, lowest diagram)
Consequently, this trend, shaped by political
path dependency, suggests that the remaining Php 1.038 trillion could likely be
surpassed.
According to the Department of Budget and
Management (DBM), budget adjustments are permissible under specific conditions:
(DBM, 2012)
1. Enactment of new
laws,
2. Adjustments to
macroeconomic parameters, and
3. Changes in resource
availability.
These provisions may provide political
rationales to justify increases in the allocated budget.
Figure 2
Expenditures, while down from last month,
remain within their growth trajectory, while revenues have so far outperformed
expectations. (Figure 2, topmost graph)
Despite October’s 22.6% revenue growth
contributing to a lower ten-month deficit—down from Php 1.018 trillion in 2023
to Php 963.9 billion—it remains the fourth largest on record.
II. Stimulus Forever?
The Quest for "Upper Middle-Income" Status and Credit "A" Rating,
Rising Risks of a Fiscal Blowout
What is seldom mentioned by mainstream media
is that such deficits serve as "fiscal or automatic stabilizers,"
ostensibly for contingent or emergency (recession) purposes.
While authorities repeatedly propagate their
intent to elevate the economy to "upper middle-income"
status
and attain a credit "A"
rating
soon, they fail to disclose that current political-economic conditions are
still functioning under or reflect continued reliance on a "stimulus"
framework.
In fact, as we keep pointing out, the Bangko
Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP)’s reserve requirement ratio (RRR) and interest rate
cuts represent monetary measures, while authorities have ramped up fiscal
measures or "Marcos-nomics stimulus" for their political
agenda—namely, pre-election spending and a subtle shift toward a war economy,
alongside centralization through increased public spending and an enlarged
bureaucracy or "Big Government."
Finally, while expenditures adhere to
programmed allocations and revenues fluctuate based on economic and financial
conditions as well as administrative efforts, they remain inherently
volatile.
Any steep economic slowdown or
recession would likely compel the government to increase spending, potentially
driving the deficit to record levels or beyond.
Unless deliberate efforts are made to
curb spending growth, the government’s ongoing centralization of the economy
will continue to escalate the risk of a fiscal blowout.
Despite the mainstream's Pollyannaish
narrative, the current trajectory presents significant challenges to
long-term fiscal stability.
III. 10-Month Public Revenue
Growth Deviates from PSEi 30’s Activities
Let us now examine the details.
In October, public
revenue surged by 22.6%, driven primarily by a 16.94% growth in tax
revenues, with the Bureau of Internal Revenue (BIR) contributing 16.19% and the
Bureau of Customs (BOC) 11.5%. Meanwhile, non-tax revenues soared by 87.7%,
largely due to revenues from other offices, including "privatization proceeds, fees and
charges, and grants."
These activities boosted the 10-month revenue
growth from 9.4% in 2023 to 16.8% this year, largely driven by a broad-based
increase, largely powered by non-tax revenues.
It is worth noting that, despite reaching a
record high in pesos, the BIR’s net income and profit growth significantly
softened to 8.3%, the lowest since 2021, remaining consistent with the 9-month
growth rate. This segment accounted for
50% of the BIR’s total intake. (Figure 2, middle pane)
In contrast, sales taxes jumped by 30.6% over
the first 10 months, marking the highest growth rate since at least 2017, and represents
30% of the BIR’s total revenues. Sales taxes vaulted by 31.6% in the first 9
months. (Figure 2, lowest chart)
The reason for focusing on the 9-month
performance is to compare its growth rate with that of the PSEi 30, allowing
for a closer understanding or providing a closer approximation of the BIR's
topline performance.
Figure 3
Unfortunately, when using same-year data, the
PSEi 30 reported a 9-month revenue growth of 8.1%, the slowest since 2021. This
pattern is echoed in its net income growth of 6.8%, which is also the most
sluggish rate since 2021. (Figure 3 upper window)
To put this in perspective, as previously
discussed, the 9-month aggregate revenues of the PSEi 30 represent
approximately 27.9% of the nominal gross domestic product (NGDP) for the same
period.
IV. Q3 2024: 2nd Highest
Revenue to NGDP, Headline GDP Weakens—The Crowding Out Effect?
In its September disclosure, the Bureau of
the Treasury cited changes in the VAT schedule as a key factor boosting tax
collections: " The
increase in VAT collections in 2024 is partly due to the impact of the
change in payment schedule introduced by the TRAIN law provision which
allows the tax filers to shift from monthly to quarterly filing of VAT return"
(Bureau of Treasury, October 2024) [bold added]
Once again, the adjustment in VAT
schedules played a pivotal role in increasing revenues, helping to reduce the
deficit and debt—a topic we discussed in September 2024 (Prudent Investor,
September 2024).
Or, whether by design or as an
unintended consequence, a critical factor in the slower deficit has been a
shift in government tax collection and accounting procedures.
But what will happen if, under the same
economic conditions or with only slight improvements, the effects of such
transient changes wear off? Will the deficit soar again?
Moreover, it is important to note that all
this is occurring while bank credit expansion and public debt are at record
highs.
What will happen to credit and
liquidity-fueled demand once household and corporate balance sheets become
saturated with leverage?
It’s also noteworthy that, even as the share
of revenue to nominal GDP (NGDP) reached its highest level in Q2 and Q3 of
2024, real GDP continues its downward trend—a dynamic that has persisted since
2016 and reemerged in 2021. (Figure 3, below graph)
Are these not symptoms of the "crowding-out
effect," where the increasing share of government interventions, measured
by expenditures, debt, and deficits, translates into diminished savings and
capital available for private sector investments?
V. Record 10-Month Expenditure:
The Push for "Big Government"
But what about expenditures?
Local Government Unit (LGU) spending surged
by 11.97%, and national disbursement growth reached 14.3%, powering an overall
increase in October expenditures of 11.1%. Interest payments, on the other
hand, fell by 6.1%. The former and the latter two accounted for shares of
18.1%, 66.64%, and 11.9% of the total, respectively.
For the first 10 months of the year,
expenditures grew by 11.5%, reaching a record-high Php 4.73 trillion, driven by
LGU spending, National disbursements, and interest payments, which posted
growth rates of 9.1%, 11.9%, and 23.03%, respectively.
As noted above, these record expenditures
are primarily focused on promoting political agendas: pre-elections, a
subtle shift towards a war economy, and an emphasis on centralization through
infrastructure, welfare, and bureaucratic outlays.
Figure 4
One notable item has played a considerable
role: 10-month interest payments not only outperformed other components in
terms of growth but also reached a record high in peso terms. (Figure 4,
topmost graph)
Additionally, their share of total
expenditures rose to levels last seen in 2009.
That said, the ratio of expenditures to NGDP
remains at 23.98% in Q2 and Q3 and has stayed within the range of 22% to 26%—except
for two occasions—since Q2 2020. (Figure 4, middle chart)
Over the past 18 quarters, this ratio
has averaged 23.4%.
As mentioned above, despite all the hype
about achieving "upper middle income" status and attaining a
"Class A" credit rating, the Philippines continues to operate
under a fiscal stimulus framework, which has only intensified with recent
policies which I dubbed as "Marcos-nomics stimulus."
In the timeless words of the distinguished
economist Milton Friedman, "Nothing is so permanent as a temporary
government program."
Current conditions also validate the
"Big Government" theory articulated by the economist Robert Higgs,
particularly regarding what he termed "The Ratchet Effect." This
concept refers to the "tendency of governments to respond to crises by
implementing new policies, regulations, and laws that significantly enhance
their powers. These measures are typically presented as temporary solutions to
address specific problems. However, in history, these measures often outlast
their intended purpose and become a permanent part of the legal landscape."
(Matulef, 2023)
The push towards "Big Government"
is evident, with approximately a quarter of the statistical economy deriving
from direct government expenditures.
This figure does not include the indirect
contributions from private sector participation in government activities, such
as public-private partnerships (PPPs), suppliers, outsourcing and etc.
As a caveat, the revenue and
expenditure-to-NGDP ratio is derived from public revenue and spending data and
nominal GDP—an aggregate measure where government spending is calculated
differently—potentially leading to skewed interpretations of its relative size.
In any case, as the government grows,
so too does its demand for resources and finances—all at the expense of the
private sector, particularly micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs),
as well as the purchasing power of the average Filipinos, represented here as
Pedros and Marias.
While government fiscal health may provide
some insights into its size, there are numerous hidden or immeasurable costs
associated with its expansion: compliance costs, public sector
inefficiencies, regulatory and administrative burdens, policy uncertainty,
moral hazard, opportunity costs, reduced incentives for innovation, deadweight
losses, productivity costs, economic distortions, social and psychological
costs, and more.
VI. 10-Month Debt Servicing
Costs Zoom to All-Time Highs!
Rising interest payments represent some of
the symptoms of "Big Government."
What’s remarkable is that, in just the first
10 months of 2024, the cost of servicing debt (amortization plus interest)
soared to an all-time high of Php 1.86 trillion—16% higher than the previous
annual record of Php 1.603 trillion set in 2023. And there are still two months
to go! (Figure 4, lowest visual)
Amortization and interest payments exceeded
their 2023 annual figures by 25.3% and 1.65%, respectively.
Notably, amortization payments surged by a
staggering 760% in October alone, reaching Php 161.5 billion.
As a result, amortization and interest
payments have already surpassed their full-year 2023 totals. However, because
the government categorizes
amortizations (or principal payments) as financing rather than
expenditures, they are not included in the budget.
VII. Rising Foreign Denominated
Debt Payments!
There's more to consider.
Figure 5Payments (amortization + interest) on
foreign-denominated debt in the first 10 months of 2024 increased by 52%,
reaching a record high. This brought their share of total payments to 21.9%,
the highest since 2021. (Figure 5, topmost chart)
Unsurprisingly, the government borrowed USD 2.5 billion
in the end of August, likely to refinance existing obligations. Adding to this,
authorities reportedly secured another $500 million loan from the Asian
Development Bank last week in the name of "climate financing."
Nonetheless, these serve as circumstantial
evidence of increased borrowing to fund gaps, reflecting the "synthetic
dollar short" position discussed
last week.
VIII. Despite Slower
Increases in Public Debt, Little Sign of the Government Weaning Off Stimulus
Here’s where mainstream narratives often
place emphasis: a slower deficit translates into slower growth in public debt. (Figure
5, middle graph)
In other words, a decrease in financing
requirements or a reduction in the rate of increase in public debt decreases
the debt/GDP ratio.
Authorities are scheduled to announce public
debt data next week.
The apparent gaslighting of fiscal
health suggests that authorities are employing tactical measures to improve
macroeconomic indicators temporarily. These efforts seem aimed at buying time,
likely in the hope that the economy will gain sufficient traction to mask
structural weaknesses.
Still, while public debt continues to
rise—albeit at a slower pace—bank
financing of public debt through net claims on the central government
(NCoCG), which began in 2015, appears to have temporarily plateaued. At the
same time, the BSP's
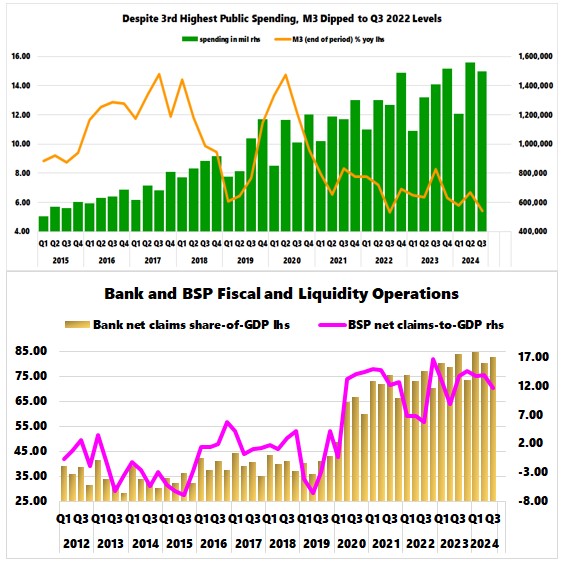
direct financing of the national government seems to have stalled. (Figure
5, lowest image)
However, none of these emergency measures
have reverted to pre-pandemic levels.
The government shows no indication of weaning
itself off the stimulus teats.
IX. Q3 2024: Public Debt
to GDP rises to 61.3%
Unfortunately, the record savings-investment
gap underscores a troubling reality: the GDP is increasingly propped up by
debt.
While mainstream narratives highlight the
prospect of a lower public debt-to-GDP ratio, they often fail to mention
that public debt does not exist in isolation.
In the aftermath of the Asian Financial
Crisis, the Philippine economy underwent a cleansing of its balance sheet,
which had been marred by years of malinvestment. When the Great Financial
Crisis struck in 2007-2008, the Philippine economy rebounded, aided by the
national government’s automatic stabilizers and the BSP's easing measures.
However, during that period, the BSP mirrored
the Federal Reserve's policy playbook, prompting the private sector to absorb
much of the increased borrowing. This reduced the economy’s reliance on
deficit-financed government spending and shifted the debt burden from the
public to the private sector, enabling a decline in the public debt-to-GDP
ratio.
Today, however, this is no longer the case.
Figure 6Following the pandemic-induced recession,
where bank credit expansion slowed, the government stepped in to take the
reins, driving public debt-to-GDP to surge. As of Q3, it remained at 61.3%—the
second highest level since 2021’s peak of 62.6% and the highest since 2004.
Currently, despite high-interest rate levels,
both public
borrowing and universal
commercial bank lending have been in full swing—resulting in a systemic
leverage ratio (public debt plus universal commercial bank credit) reaching
108.5% of nominal GDP in 2023.
This means that the government, large
corporations, and many households with access to the banking system are
increasingly buried in debt.
In any case, debt is perceived by consensus
as a "free lunch," so you hardly ever hear them talk about it.
X. Conclusion: The Relentless
Pursuit Of "Upper Middle Income" Status Resembles a Futile Obsession
In conclusion, while current fiscal metrics
may appear to show surface-level improvements, the government remains
addicted to various free-lunch policies characterized by easy money stimulus.
The government and elites will likely continue
to push for a credit-driven savings-investment gap to propel GDP growth,
leading to further increases in debt levels and necessitating
constant liquidity infusions that heighten inflation risks.
The establishment tend to overlook the
crowding-out effects stemming from government spending (and centralization
of the economy), which contribute to embedding of the "twin
deficits" that require more foreign financing—ultimately
resulting in a structurally weaker economy.
The relentless pursuit of "upper
middle income" status resembles a futile obsession—a "wet
dream" driven more by the establishment’s obsession with benchmarks
manifesting social signaling than substantive progress.
For distributional reasons (among many others),
the GDP growth narrative does not reflect the true state of the economy.
Persistent self-rated poverty and
hunger, widening inequality, elevated vacancies in the real estate sector, low
savings rates, and stagnating productivity are clear indicators that GDP number
benefits a select few at the expense of many. This, despite debt levels soaring
to historic highs with no signs of slowing.
Even the Philippine Statistics Authority’s
(PSA) per
capita consumer and headline GDP trendlines
contradict the notion of an imminent economic or credit rating upgrade.
While having the U.S. as a geopolitical ally
could offer some support in the pursuit of cheaper credit through a potential
credit upgrade, it is important to acknowledge that actions have
consequences—meaning the era of political 'free lunches' are numbered.
And do authorities genuinely believe they can
attain an economic upgrade through mere technical adjustments of tax schedules
and dubious accounting practices, akin to the "afternoon delight" and
5-minute "pre-closing pumps" at the PSEi 30?
Yet because the political elites
benefit from it, trends in motion tend to stay in motion, until…
___
References
Prudent Investor, September 2024 Fiscal
Deficit Highlights the "Marcos-nomics Stimulus"; How Deficit Spending
Drives a WEAKER Philippine Peso October 28, 2024
Department of Budget and Management, THE BUDGETING PROCESS, March 2012,
dbm.gov.ph
Bureau of Treasury, September 2024 Budget Deficit at P273.3
Billion Nine-Month Deficit Narrowed to P970.2 Billion, October 24, 2024,
treasury.gov.ph
Prudent Investor, Philippine
Government’s July Deficit "Narrowed" from Changes in VAT Reporting
Schedule, Raised USD 2.5 Billion Plus $500 Million Climate Financing, September 1, 2024
Michael Matulef Beyond Crisis: The
Ratchet Effect and the Erosion of Liberty, August 18, 2023, Mises.org