History will not be kind
to central bankers fixated on financial economy and who created serial
speculative booms to sustain the illusion of prosperity. It will also be
critical of governments unwilling to address weaknesses, who deflected shifting
hard policymaking to independent, unelected and largely unaccountable central
banks—Satyajit Das
In this issue
PSE Craters as
Financials’ Share of the PSEi 30 Hits All-Time Highs; A Growing Mismatch
Between Financial Index Performance and Bank Fundamentals
I. PSEi 30 Craters on
Signs of Re-Tightening Amid Rising Dollar and Higher UST Yields
II. Despite the Market
Carnage: Financials Share of the PSEi 30 Zoom to All-time High!
III. Financialization:
The Expanding Role of Banks in Achieving Political Goals
IV. "National Team?"
In Q2, Other Financials Corporations Sold, the PSEi 30 Plunged
V. In Q3, Mismatch Between
Financial Index-Bank Fundamentals Reached a Blow-off Phase!
VI. Worsening Bank
Liquidity Conditions as Cash-to-Deposits Hit Milestone Low
VII. Liquidity and
Collateral Crunch? Bank Borrowings, Focused on Bills, Zoomed to Record Highs in
September, as Repos also Hit All-time Highs!
VIII. Despite Lower
Rates Held to Maturity Assets Near All-time Highs, Record Bank QE
IX. A Snapshot of Q3 and
9-Month Performance of PSE Listed Banks
X. Highlights, Summary
and Conclusion
PSE Craters as
Financials’ Share of the PSEi 30 Hits All-Time Highs; A Growing Mismatch
Between Financial Index Performance and Bank Fundamentals
Even as the PSEi plummeted due to signs of
global and local re-tightening, the Financials outperformed, widening the
mismatch between share prices and fundamentals. Will a reckoning come soon?
I. PSEi 30 Craters on
Signs of Re-Tightening Amid Rising Dollar and Higher UST Yields"
Figure 1The Sage of Omaha, Warren Buffett, once said,
"Only when the tide goes out do you discover who's been swimming
naked."
Have the signs of tightening upended the
dream of easy money’s "goldilocks" economy, or have they exposed
those who have been "swimming naked?"
The surging US dollar index, coupled with
rising 10-year Treasury yields—both largely attributed to Trump's policies— has
sent global risk assets tumbling. Yet, these developments took shape two months
before the US elections. (Figure 1, topmost graph)
This includes the Philippine PSEi 30, which
plunged by 4.31%, marking its largest weekly decline in 2024 and the steepest
drop since the week of September 30, 2022, when it fell by 8.3%.
As of Thursday, November 14, the headline
index broke below the 6,600 level, closing at 6,557.09.
A notable oversold rebound in industrials,
led by Meralco (up by 7.78%) and Monde (up by 7.52%), along with financials
from BPI (up by 3.7%) and CBC (up by 4.58%), contributed to a low-volume rally
of 1.82% on Friday.
Year-to-date, the PSEi 30 is struggling to
maintain its narrowing return of 3.5%.
II. Despite the Market
Carnage: Financials Share of the PSEi 30 Zoom to All-time High!
The Financial Index, down by only 1.86%, was
the least affected in this week’s market carnage. BPI was the only member of
the PSEi 30 component to withstand the foreign-driven selloff, while Jollibee
ended the week unchanged. (Figure 1, middle pane)
Interestingly, this outperformance has
propelled the aggregate free-float market capitalization weighting of the three
major banks of the headline index to an all-time high. (Figure 1, lowest chart)
Figure 2
Furthermore, financials accounted for 41.7%
of the mainboard's volume on Friday—the third-highest share since October. (Figure
2, topmost diagram)
Meanwhile, October’s cumulative 29.92% accounts
for the sector’s highest share since July 2023, which also translates to a 2017
high.
In a related note, the Bangko Sentral ng
Pilipinas (BSP) has suspended
its free publication of non-BSP-generated data, including PSE data on
monthly price-earnings ratios (PER), market capitalization by sector, index
data, and volume distribution by sector. This suspension hampers our ability to
track critical developments in market internals. (Yes, I wrote them)
The point being, the increasing share of
mainboard volume by the financial sector has pillared the rising share of the
sector’s market cap share of the PSEi 30.
However, this dynamic also implies growing
concentration risk in the stock market.
III. Financialization:
The Expanding Role of Banks in Achieving Political Goals
Businessworld, November 13: THE
PHILIPPINE banking system’s net profit jumped by 6.4% at end-September as both
net interest and non-interest income grew, data from the Bangko Sentral ng
Pilipinas (BSP) showed. The combined net income of the banking industry rose to
P290 billion in the first nine months of 2024 from P272.6 billion in the same
period a year ago.
The PHP 290 billion profit and a 6.4% growth
rate represent the Q3 figures year-over-year (YoY).
Continuing from last week’s discussion, the
diverging dynamics in the Philippine Stock Exchange (PSE) have also been
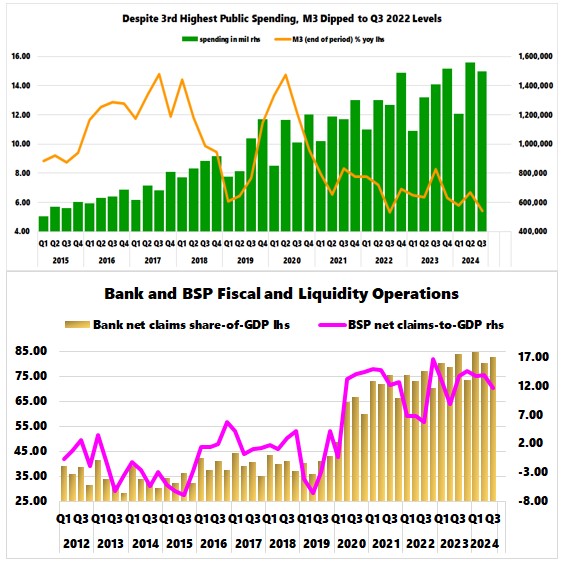
reflected in the GDP figures.
Although the financial sector has been on an
upward trajectory since the new millennium, its share of the real GDP has
rapidly deepened during the BSP’s historic rescue of the sector.
This was notably influenced by the BSP
historic intervention to rescue the sector, which included an unprecedented PHP
2.3 trillion quantitative easing package, historic cuts in official and reserve
ratios, as well as unparalleled subsidies and relief measures.
In line with the rising share of money supply-to-GDP,
the financial sector's share of GDP reached its third highest level at 10.8% in
Q3. (Figure 2, middle image)
It even hit an all-time high of 10.9% when
considering the 9-month real GDP data.
While this evolution may be labeled as
"financialization," the essential message is clear: BSP policies
have led to an economy increasingly immersed (or heavily reliant) in credit and
liquidity, primarily channeled through an elite-owned and controlled banking
system.
This deepening dependence comes at the
expense of the development of other competing financial conduits, such as
capital markets.
The underlying reason for this is
political: the bank-led financial sector serves as the primary non-BSP
financier of the government’s deficit spending.
As a result, the government's calls
for improvements in the capital markets appear to be mere lip service.
However, judging by their "demonstrated
preference" in policy choices, it appears that inflating bank shares
may serve to camouflage the adverse consequences of this deepening and complex
political-economic arrangement.
IV. "National Team?"
In Q2, Other Financials Corporations Sold, the PSEi 30 Plunged
The developments in Other Financial
Corporations (OFCs) provide valuable insights.
In Q2, OFCs eased their holdings of equities.
According to the BSP,
"The other financial corporations’ claims on the other sectors dropped as
their holdings of equity shares issued by other nonfinancial corporations
fell."
The Non-bank financial institutions and OFCs "includes
the private and public insurance companies, other financial institutions that
are either affiliates or subsidiaries of the banks that are supervised by the
BSP (i.e., investment houses, financing companies, credit card companies,
securities dealer/broker and trust institutions), pawnshops, government
financial institutions and the rest of private other financial institutions
(not regulated by the BSP) that are supervised by the Securities and Exchange
Commission (SEC)" (Armas, 2014)
In the same quarter, OFC
claims on the private sector decreased by 0.5% quarter-over-quarter (QoQ),
while the PSEi 30 index plunged by 7.1%. (Figure 2, lowest visual)
My guess is that some of these OFCs are part
of what could be considered the Philippine version of the "national
team."
V. In Q3, Mismatch Between
Financial Index-Bank Fundamentals Reached a Blow-off Phase!
Nevertheless, the deviation between the
fundamentals of banks and their share prices has reached "blow-off"
proportions!
Figure 3
In Q3, the banking system reported a modest
growth of 6.4%, slightly higher than Q2’s 4.1%. However, the financial index
skyrocketed by 19.4% quarter-over-quarter (QoQ).
From another angle, 9-month profit growth was
up by 5.07%, even as the financial index surged by a stunning 23.4%
year-on-year in Q3.
Worst of all, profit trends and the financial
index have moved in opposite directions.
Since profit growth peaked in Q3 2022 and
subsequently eased, shares of the seven-member bank stocks (excluding the
eighth member: PSE) within the financial index have continued to accelerate. (Figure
3, topmost window)
Meanwhile, given that universal and
commercial banks account for 93.9% of total bank assets, their profit growth
largely mirrors the entire banking system. In Q3, profit growth was 7.03%, and
on a 9-month basis, it stood at 6%.
These figures underscore the increasing
monopolization of the financial industry by banks validated by the BSP’s Total
Financial Resources (TFR) data.
Total
financial resources grew by 10.07% to a record PHP 33.08 trillion.
The banking sector’s share surged to an
all-time high of 83.3%, driven mainly by universal and commercial banks, whose
contribution reached a record 78.1%. (Figure 3, middle image)
So let us get this straight: banks have
increased their share of trading activities in the PSE, as well as their slice
of both the PSEi 30 and the GDP pie. They now command 83.3% of total
financial resources and are continuing to rise.
This dominance doesn’t even account for their
substantial role in the local bond markets, where they act as issuers,
intermediaries, and holders.
Even without the BSP acknowledging
this, what we are witnessing is the intensifying risks within the Philippine
financial-economic system.
VI. Worsening Bank
Liquidity Conditions as Cash-to-Deposits Hit Milestone Low
Have you ever seen any experts or
establishment analysts address the developing contradiction between the banks'
reported profits and their liquidity conditions?
Cash
and due from banks, or bank cash reserves, plummeted by 13.6% in September
2024, following a brief 4% rebound in August. This decline brought cash
reserves to their lowest level since 2019. (Figure 3, lowest graph)
To address the emerging liquidity shortfall,
the BSP previously reduced the bank
reserve requirement ratio (RRR) from 19% to 14%, implemented
in seven installments from March 2018 to December 2019.
Cash reserves saw a temporary spike in 2020
when the BSP injected Php 2.3 trillion into the system, accompanied by an RRR
cut from 14% to 12% in April 2020.
However, facing diminishing returns, cash
reserves resumed their downward trend.
Once again, doing the same thing and
expecting different results, the BSP reduced the RRR by a larger margin
than in 2020, lowering it from 12% to 9.5% in June 2023.
Despite these efforts, the challenges within
the banking system's cash reserve position have persisted.
Figure 4Moreover, while the growth in peso deposit
rates increased from 6.9% in August to 7.07% in September—the slowest growth
rate since July 2023—the BSP’s cash-to-deposit
ratio plummeted to 12.44%, its lowest ratio since at least 2013! (Figure 4, topmost
and second to the highest graphs)
Yet, with the record bank credit
expansion, why the sluggish growth in deposits? Where did the money flow into?
Even with the recent decline in inflation
rates, have a minority of "banked" households continue to draw from
their savings?
Furthermore, the banks' liquid
asset-to-deposit ratio, which includes both cash reserves and financial assets,
fell to 50.34%, reverting to levels seen during the BSP's rescue efforts in
July 2020.
Incredible.
And this is just one facet of the mounting
liquidity challenges that banks seem to be facing.
VII. Liquidity and
Collateral Crunch? Bank Borrowings, Focused on Bills, Zoomed to Record Highs in
September, as Repos also Hit All-time Highs!
More eye-catching data emerged last
September.
Bank borrowings—primarily in
short-term bills—skyrocketed to an all-time high! Borrowings surged by
49.7%, reaching a record PHP 1.7 trillion, with their share of total
liabilities climbing to 7.3%, the highest since 2021. (Figure 4, second to the
lowest and lowest charts)
The liquidity shortfall is most pronounced
over the short-term, this is why bank’s bills payable zoomed to unscaled
heights.
Figure 5
Not only that, bank short-term repo
(repurchase agreements) or RRP (reverse repurchase) operations with the BSP and
other banks have also launched into the stratosphere!
With record repo operations, the RRP’s 3.72%
share of the bank’s total assets surged to the highest level since at least
2015! (Figure 5, upper image)
Could this rampant use of repurchase
agreements (repos) be underlying growing collateral issues in the financial
system? As banks increasingly depend on repos for short-term liquidity, are
we witnessing a decline in the quality of collateral or a shortage of
high-quality assets available for these transactions?
These developments likely explain the BSP's
abrupt announcement of the latest series of RRR cuts, which took
effect last October.
However, such actions resemble a Hail Mary
pass, with RRR ratios now headed toward zero.
VIII. Despite Lower
Rates Held to Maturity Assets Near All-time Highs, Record Bank QE
Another paradox: banks reported that credit
delinquencies—across the board—marginally declined in September. (Figure 5,
lower diagram)
If this is true, then higher profits
combined with lower non-performing loans (NPLs) should result in more,
not less liquidity
Figure 6Additionally, the easing of interest rates,
as indicated by declining treasury yields, should have reduced banks'
held-to-maturity (HTM) assets. As noted repeatedly, HTM assets drain liquidity
because they lock up funds. (Figure 6, topmost graph)
Yet, there hasn’t been significant
improvement in this area.
Moreover, since authorities aim to meet
year-end spending targets, boost GDP, and finance the upcoming elections, it is
expected that the government will ramp up its deficit spending in Q4.
This increase in public spending will
likely lead to a rise in banks' and the financial sector’s net
claims on central government (NCoCG), which may translate to higher
HTM assets. (Figure 6, middle chart)
Furthermore, if the current trend of
declining inflation reverses, or we experience a third wave of rising
inflation, banks might resort to accounting maneuvers to shield themselves from
potential mark-to-market losses by shifting these assets into HTMs.
That is to say, increases in
debt-financed government spending and rising inflation rates could therefore
result in higher levels of HTM assets.
Above all, banks are not standalone
institutions; they have deep exposure to counterparties. As noted last week,
Led by banks, the
financial sector is the most interconnected with the local economy. Its health
is contingent or dependent upon the activities of its non-
financial
counterparties.
Alternatively, the
sector’s outgrowth relies on political subsidies and is
subject to diminishing returns.
Yet ultimately,
this should reflect on its core operational fundamentals of lending and
investing. (Prudent Investor, October 2024)
The transformational shift in the banking
system’s business model—from production and consumption—could be ominous.
Part of this shift has been motivated by pandemic-era subsidies and relief
measures, as well as a move away from unproductive industry loans.
As a result, the consumer share of total bank
loans (excluding real estate) reached an all-time high of 14.9% in September
2024, while the share of production loans declined to 82.7%. The remaining 2.4%
comes from non-resident loans. (Figure 6, lowest image)
Banks have embraced the government’s
belief that spending drives the economy, neglecting the balance sheet health of
individuals, as well as the potential misallocations as a result of
artificially low rates.
But what happens to the consumer
economy once their balance sheets have been tapped out?
This should not surprise to our readers,
given that the "inverted belly" of the Treasury yield curve has
already been signaling these concerns.
IX. A Snapshot of Q3 and
9-Month Performance of PSE Listed Banks
Finally, here is a snapshot of the micro
aspects of the financials.
Table 7The performance of PSE-listed banks indicates
that while all-bank profits grew by 14% to Php 226 billion in the first nine
months of 2024, bills payable jumped by 79%, or Php 579 billion, reaching Php
1.31 trillion. This increase in bills payable signifies more than double the
net profits generated over the same period. The data excludes the small-scale
Citystate Savings Bank [PSE: CSB]. [Table 7]
PSEi banks accounted for 84% of the
nine-month increase in bills, relative to their 73% share of net income growth.
Metrobank [PSE: MBT] represented the most aggressive borrower, with a 61%
share.
We have yet to reconcile the stark divergence
between the reported BSP bank performance and the aggregate activities of
listed firms.
Nonetheless, through aggressive lending,
banks boosted their top and bottom lines in Q3, positively impacting the
nine-month performance.
Fueled by a 29.7% growth in non-PSEi banks,
the net income growth of all banks soared by 22%.
X. Highlights, Summary
and Conclusion
In the end, we can summarize the banking sector
as having the following attributes: (as of September or Q3)
1. all-time highs in:
-Financial Index
-market cap share of the PSEi 30 (3 biggest
banks)
-turnover of financial sector to mainboard volume
(near)
-nominal or Philippine peso and % share of
total financial resources
-nominal net claims on central government
-nominal Held-to-Maturity assets
-total bank lending in Philippine pesos
-percentage share of consumer bank lending
-nominal bank borrowing (mainly Bills)
-nominal repo operations
- nominal net financial assets
2. Historical lows in:
-cash-to-deposits
-production pie of total bank lending
-reserve requirement ratio
3. Declining trend in:
-cash reserves
-profit growth
-deposit growth
-liquid asset-to-deposit ratio
How is it that the supposedly
"profitable" financial institutions, supported by the recent slowdown
in non-performing loans, have been accompanied by sustained declines in
deposit and savings rates, as well as a massive hemorrhage in liquidity
that compelled them to rapidly access short-term financing via bills and repos?
Have profits been overstated? Have
NPLs been understated?
To what extent have the BSP’s relief
measures and subsidies caused distortions in banks’ reporting of their health
conditions?
Why the flagrant disconnect between
stock prices and the actual conditions of the banks?
Could the "national team" have been
tasked with camouflaging recent developments through a panicked pumping of the
sector’s shares?
Does the ongoing shortfall in
liquidity portend higher rates ahead?
Given all these factors, what could possibly
go wrong?
As we recently pointed out,
To be clear, we
aren’t suggesting that CBC and other record-setting bank shares, such as BPI,
are a simulacrum of Lehman; rather, we are pointing to the distortive
behavior of speculative derbies that may hide impending problems in the sector.
(Prudent Investor, October 2024)
____
References
Satyajit Das, Central
banks: The legacy of monetary mandarins, New
Indian Express, November 15, 2024
Jean Christine A. Armas, Other
Financial Corporations Survey (OFCS): Framework, Policy Implications and
Preliminary Groundwork, BSP-Economic Newsletter, July-August 2014, bsp.gov.ph
Prudent Investor, Q3
2024 5.2% GDP: Consumers Struggle Amid Financial Loosening, PSEi 30 Deviates
from the GDP’s Trajectory, November 10, 2024
Prudent Investor, Important
Insights from the Philippine PSEi 30’s Melt-Up! October 7, 2024